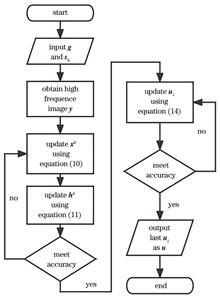
The resolution of a ground-based large-scale aperture telescope can be severely deteriorated by atmospheric turbulence. Adaptive optics (AO) systems have been widely used thus far to solve this problem. However, correction using AO is a partial solution. Degraded images generated by residual wavefronts can be restored via post-reconstruction. In this paper, a blind deconvolution algorithm to improve the quality of Poisson noise astronomical images acquired after AO correction is proposed. The algorithm uses an adaptive L1 norm term in the gradient domain for an accurate estimation of the point spread function (PSF) as well as the Richardson-Lucy algorithm followed by a low pass denoising filter to solve Poisson deconvolution. Experimental results for simulated and real astronomical images demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can obtain better PSF and reconstruction images than other algorithms and significantly improves the quality of post-AO astronomical images without further information.
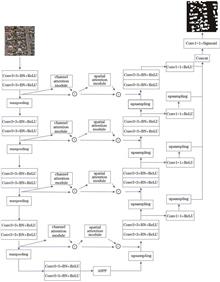
Building extraction from remote sensing images is of great significance to the construction of smart cities. Aiming to improve the low accuracy of traditional methods in extracting remote sensing images with a complex background, a remote sensing image building extraction method (MA-Unet) based on U-Net is proposed. This method mainly uses an encoder and a decoder. A convolutional block attention module is introduced into the encoder, in which a channel attention module is used to screen more important features and suppress invalid features, and a spatial attention module is used to screen deeper semantic features. An atrous spatial pyramid pooling module is introduced to extract features with different scales. In the decoder, to fuse object features with different scales, feature maps in the decoder are upsampled and connected in series. This information aggregation solves the difficulty of detecting objects with different scales to some extent. The experimental results show that MA-Unet method is superior to the U-Net method in terms of accuracy, precision, and intersection over union (IoU) by 1.7 percentage points, 2.1 percentage points, and 1.6 percentage points on the Massachusetts building dataset and by 1.1 percentage points, 1.4 percentage points, and 2.3 percentage points on the WHU building dataset, respectively. It is a more effective and practical target extraction method.
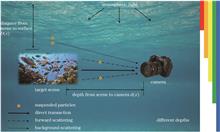
To address the issue of picture blur and color distortion in underwater images of complex water bodies, an underwater image restoration algorithm based on HSV classification, CIELAB equalization, and minimum convolution region dark channel prior (DCP) is proposed. By the thresholds of H and S, the underwater photos are separated into high saturation distortion, low saturation distortion, and shallow water images. Then, the underwater image is recovered using CIELAB equilibrium and adaptive image enhancement, where the system parameters of the categorized underwater image are estimated by minimum convolutional area DCP. The experimental findings demonstrate that the suggested solution is superior to the comparison algorithms in image restoration effect, evaluation quality, and real-time performance indicators. The average peak signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity values are increased by 26.88% and 17.3% on average, respectively, and the underwater image quality measurement value is increased by 4.3%.
Aiming at the low detection accuracy of existing object detection algorithms in a low-light environment, a dual-channel low-light image object detection algorithm called YOLOv5_DC according to an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm is suggested. First, we synthesize low-light images using Gamma transformation and superimposing Gaussian noise to expand the dataset and promote the network's generalization. Second, a feature enhancement module is proposed. The channel attention method is used to integrate the low-level characteristics of the improved image and the original image to decrease the effect of noisy features and increase the network's feature extraction capabilities. Finally, a feature location module is added to the neck network to boost the response value of the feature map in the target area, allowing the network to focus more on the target area and improve the network detection capabilities. The experimental results show that the proposed YOLOv5_DC algorithm achieves higher detection accuracy. On the low-light object detection dataset known as ExDark*, the mean average precision (mAP) @0.5 of the proposed algorithm reaches 71.85%, which is 1.28 percentage points higher than the original YOLOv5 algorithm.
The local contrast method is difficult to improve the significance of the target and suppress the background in infrared target detection, thus an enhanced local contrast method based on ring special preprocessing is proposed to detect targets. The high-frequency noise is removed by fast median filtering, the background is suppressed by improved morphological gradient, the significance of the target is improved by enhanced local contrast, and finally the real target to be detected is obtained by self-adaptive threshold. The results show that compared with the classical detection methods of human visual system, the proposed method has advantages in detecting infrared weak and small targets, and the effect is more significant in high brightness background.
The variation in pixel values between different objects during semantic segmentation of images leads to the loss of local image details in existing network models. An image semantic segmentation method (DECANet) is proposed to solve this problem. First, a channel attention network module is introduced to improve network clarity by modeling the dependencies of all channels, selectively learning and reinforcing channel features, and extracting useful information to suppress useless data. Second, using an improved atrous space pyramidal pooling (ASPP) structure, the extracted image convolutional features are multiscale fused to reduce the loss of image detail information, and the semantic pixel location information is extracted without increasing the weight parameters to speed up the model's convergence. Finally, the mean intersection over union of the proposed method reaches 81.08% and 76% on PASCAL VOC2012 and Cityscapes datasets, respectively. The detection performance of the DECANet is superior to the existing state-of-the-art network models, which can effectively capture local detail information and reduce image semantic pixel classification errors.
Based on block compressed sensing theory and random convolution theory, a new optical image block encryption method based on chaotic convolution is proposed. First, blocks of the same size are created from the plain image. A chaotic phase mask and a chaotic amplitude mask are generated for each block by a cascaded chaotic system, which is then used to convolute the block with the chaotic phase mask, and chaotic subsampling is followed using a chaotic amplitude mask to obtain the encrypted and compressed block image. Finally, all encrypted blocks are restored to the final encrypted image. Note that each block has a different key to increase the security, and fractional Fourier transform is used instead of Fourier transform in the process of chaotic convolution to increase the key space. Simulation is conducted on statistical analysis, noise attack resistance test, cropping attack resistance test, and key sensitivity test. The viability and security of the suggested encryption system are shown by numerical results.
Identifying the species of wild mushrooms is important to prevent mistaking the toxic type of mushrooms for non-toxic ones. Therefore, to improve the accuracy of the fine-grained classification of wild mushrooms, a parallel addition convolutional block attention module (PA_CBAM), which is improved from the convolutional block attention module (CBAM), is proposed. PA_CBAM changes the connections of the channel and spatial attention modules from serial to parallel and adds their results together. Consequently, the interference caused by cascading these attention modules is solved. In addition, the proposed method improves the performance of ResNet50 by referring to the concept of a feature pyramid, whose accuracies of the Top-1 and Top-5 are 86.03% and 97.19%, which are 0.86 and 0.73 percentage points higher than those of the original method, respectively. Furthermore, the Top-1 and Top-5 reach 88.52% and 97.58% using PA_CBAM, which are 3.03 and 0.69 percentage points higher, respectively. Moreover, to adapt the model for mobile terminals, combined with migration learning, the MobileNet_v2+PA_CBAM recognition method is proposed, obtaining an accuracy of 94.87%, which is 0.66 percentage points higher than that previously obtained. The results show that PA_CBAM has a better recognition and generalization effect in the fine-grained classification of wild mushrooms. Meanwhile, the size of MobileNet_v2+PA_CBAM is only 27.8 MB, and the recognition time required for a picture is only 1.3 ms, which is an ideal model for deploying wild mushrooms classification on mobile devices.
In order to solve the problem that the traditional defogging method based on the dark channel priori is easy to cause artifact and color distortion in the edge region and the sky region, a dark channel image defogging method based on regional transmittance fusion is proposed. First, the fog image is divided into three regions: non sky, sky, and transition edge. Then, the non-sky region and transition-edge region are fused in the dark channel combined with block transmittance estimation and point transmittance estimation, and the fused dark channel transmittance is obtained using gradient domain guided filtering. Next, the luminance transmittance of the sky region and the dark channel fusion transmittance are synthesized to obtain the final transmittance. Finally, the image is restored using the obtained transmittance and the improved atmospheric light value to obtain the defogging result image. Experimental results show that the proposed method is significantly better than the traditional dark channel method. It can effectively suppress edge artifacts and preserve the color features of foggy images. Compared with the traditional methods, the defogged images obtained by the proposed method can achieve better results in both subjective and objective evaluation.
Sketch person re-identification aims to identify images with identities similar to those of sketched person images located in an RGB image gallery. Although several cross-modal retrieval algorithms can be adopted for this purpose, the background settings of such algorithms are relatively simple and fail to consider that certain identities have only one modal sample in the training set, that is, the cross-modal identity is inconsistent. This significantly limits the application of such algorithms in practical scenarios. In this paper, a sketch re-identification network based on cross-classification is proposed. The network consists of two parts: cross-classification and identity information alignment based on distance. Among these, cross-classification guides the encoder to extract modal-invariant information from one modal using constraints of the classifier trained using other modal data. The alignment of identity information based on distance can reduce the feature distance between different modals of the same identity, suppress the influence of cross-modal identity inconsistencies, and strengthen the discrimination and robustness of features. To verify the performance of the re-identification network when the cross-modal identity is inconsistent, a new sketch re-identification dataset is generated based on Market-1501. The Rank-1 is improved by 11.0 percentage points on this dataset. Simultaneously, the model also achieves a Rank-1 of 60% on the public dataset Sketch Re-ID. The dataset used in this study is an open-source dataset available on “https://github.com/huangdaichui/Sketch_dataset”.
With the rapid development and wide application of artificial intelligence, intelligent investigation is becoming a new research hotspot in forensic science, and the realization of automatic recognition and classification of crime scene photographs is an essential aspect of intelligent investigations. We present an algorithm that automatically classifies crime scene photographs based on a convolution neural network. First, based on the data from criminal cases, a crime scene photograph dataset was constructed comprising 13164 scene photographs and 4008 negative photographs. Second, crime scene photograph net (CriSNet) was designed based on the data characteristics to accurately classify crime scene photographs by adding normalization processing to the convolution layer and improving the bottleneck module. The experimental results show that the accuracy of CriSNet is 1 percentage point better than that of the benchmark with good robustness, and CriSNet can still maintain excellent performance under low resolution and poor-quality conditions.
To address the problems of low contrasts and fuzzy details in foggy images, an adaptive dynamic range contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) algorithm for foggy image enhancement is proposed in this paper. Two adaptive parameters T1 and T2 are introduced to automatically adjust the range of image redistribution to improve the traditional CLAHE, and homomorphic filtering is further combined to improve the over-light and over-dark regions in the image. The original image is enhanced using a multi-scale detail enhancement algorithm. The processed detail image is combined with the result of homomorphic filtering to enhance the image contrast and details. The image results are compared and analyzed based on four objective evaluation indexes including information entropy, local contrast, average gradient, and running time. The subjective and objective test results reveal that the proposed algorithm can effectively enhance the image contrast and highlight the relevant details, which is convenient for image information extraction on foggy days.
The current mainstream weakly supervised object detection methods based on image-level annotation often occur local localization problem, tend to overfit the most discriminative regions, and ignore object integrity. To solve these existing problems, an end-to-end weakly supervised object detection network based on feature self-distillation (FSD-Net), in which the detachable feature self-distillation module fully uses the semantic and detailed information in the representation of different hierarchical features, is proposed. Additionally, through feature self-distillation loss constraint network training, the comprehensive performance of the detector is enhanced without increasing the calculation cost during the test period. Moreover, the regression branches are constructed to simply extract and effectively utilize the implicit location information in the features, improves the original supervision information generation algorithm, and balances optimization loss and other strategies to further improve the local localization problem of the weakly supervised object detector. Experiments on large-scale public datasets, such as Pascal VOC 2007, VOC 2012, and MS-COCO, show that FSD-Net has a better detection performance than the Baseline and other existing mainstream methods, effectively alleviating the local localization problem in weakly supervised object detection.
In the detection of moving objects in complex dynamic background, there are many problems, such as incomplete extraction of foreground objects and false detection of dynamic background as foreground. To solve the above issues, a moving object detection model that combines a nonconvex rank approximation function and a three-dimensional total variation (3D-TV) regularization term is proposed. Based on the original robust principal component analysis model, the proposed model introduces a nonconvex rank approximation function to describe the low rank of the video background part and uses the 3D-TV regularization term to constrain the foreground part in time and space. Finally, the alternating direction multiplier method is used to solve the proposed model. Furthermore, the experimental results show that the model can effectively improve the accuracy of moving target detection when dealing with complex scenes, such as dynamic background and bad weather, and has a better visual effect than existing methods.
Bronze inscriptions are rarely different from one another, deep learning network training is susceptible to overfitting, and the deeper the convolutional layer, the more intricate elements of the inscription are lost, leading to a low level of classification accuracy. A small sample bronze inscription classification approach that incorporates morphological aspects is offered in light of this issue. To preprocess the hole filling of inscriptions and lessen the impact of noise on the morphological structure of inscriptions, morphological algorithms must first be introduced. Second, modify the structure of the AlexNet network, and in each convolution layer to introduce batch normalization, control each batch of random input values, so that it conforms to the normal distribution standards, and avoid overlearning the network in a single direction to suppress overfitting. Last but not least, the speeded-up robust features (SURF) operator is used to extract the finer morphological details of the inscriptions. This merging of finer morphological details with abstract features from convolutional neural networks improves classifier expression. The classification accuracy in the bronze inscription dataset experiment is 98.86%, which is higher than traditional algorithms such as LeNet5, Vgg13, Vgg16, ResNet, and AlexNet and effectively addresses the issue of low classification accuracy.
The accuracy of moving target detection will be significantly impacted by environmental conditions including rain, snow, and continually changing lake surfaces. Therefore, the main task of moving target identification in complicated scenarios is precisely identifying foreground targets from dynamic backgrounds. A moving target identification approach combining the visual background extractor (Vibe) algorithm with the improved local binary mode (LBP) feature operator is suggested in order to address the issue that the current Vibe algorithm has poor detection performance under complicated backdrops and is easily affected by changes in illumination. First, the LBP value image of each frame is calculated and saved, and the adjacent frame compensation strategy is used to stabilize the image to reduce the influence of illumination on the gray value. The background model is then created using the Vibe algorithm, and the foreground target is then obtained by performing morphological operations after replacing the gray value with an improved LBP value for foreground detection. The experimental results show that, compared with other traditional algorithms, the proposed method has a good suppression effect on the dynamic background. The recall rate has increased by an average of 25.6%, the accuracy rate has been increased by an average of 12.5%, and the false detection rate has been reduced by an average of 22.6% when compared to the original Vibe algorithm.
To improve the diagnosis and treatment level of pneumonia in children in primary medical institutions and doctors' efficiency and quality in analyzing clinical medical images, an auxiliary diagnosis model of pneumonia in children, based on the Vision Transformer (ViT), is proposed. First, ResUNet is used to segment the lung region in the chest film of children, and the left and right lung regions are separated from the chest film to mitigate the interference of other tissues during pneumonia diagnosis. Further, the segmented image is input into the improved hybrid ViT model for diagnosis. This model uses the feature map of the traditional convolutional neural network (CNN) as the input of the Transformer and introduces the self-attention mechanism into the CNN to improve convolution to enhance its ability to obtain global correlation. Finally, the backbone network of the CNN and Transformer model are trained end-to-end so that the proposed model can achieve good image classification results. Experiments were conducted on the Chest X-Ray Images pneumonia standard dataset. The experimental results show that the accuracy, precision, and recall of the proposed model for pneumonia recognition reach 97.27%, 97.69%, and 98.60% respectively. In other words, the model has good feasibility and can significantly improve the clinical diagnosis accuracy of pneumonia in children at the grass-root level.
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) has various application scenarios but is limited due to computational cost. Therefore, a SLAM algorithm (FAST-SAM) based on adaptive features and closed-loop optimization is proposed. The proposed algorithm uses the adaptive feature extraction method Better Feature to ensure the accuracy of the feature extraction at different distances. Then, it uses the ground feature filtering method based on random sample consensus to remove unreliable features and keep the number of features stable. In the scan matching and loop-closure detection modules, we use a matching algorithm combining the normal distribution transformation, nearest point iteration algorithm, and the proposed two-stage loop-closure detection algorithm to output the laser inertial odometry and establish a global point cloud map. The experimental results on the LIO-SAM, KITTI open source datasets, and the measured datasets of Guangxi University show that compared with the mainstream SLAM algorithms, the proposed algorithm improves the accuracy and the computational efficiency of each link by more than 25.6%.
The problem of finding pathological features artificially from medical images over time, which ultimately leads to deterioration, has increased significantly. Thus, it has become a crucial area of interest for researchers. This study introduced a secondary feature extraction method (ω-net) with the ability to segment lung, liver, nucleus, and brain tumors. First, we used the full-size Unet as the primary feature extraction path. Similarly, we used the third layer on the upsampling path as the starting layer to expand the secondary feature extraction path to enhance the feature extraction capability. Second, we introduced two new-attention mechanisms at various stages for targeted optimization to establish long-term channel dependence and enhance feature location information. Finally, the study reproduced 10 classic networks. With the application of Unet in the medical imaging field, the commonly used indicators, including mean intersection of union, sensitiveness, precision, and accuracy of the proposed network, increase by 0.0787, 0.1287, 0.1216, and 0.0201, respectively, compared with the benchmark network. The study evaluated the effectiveness and superiority of the introduced network and compared the index values and visualization results on four types of datasets. The results showed that the introduced network outperformed the other existing networks.
Image deraining is the process of reconstructing a high-definition background image by removing rain marks. The deep convolutional neural network is now the most widely used to eliminate rain streaks. The core of the convolution operation is parameters globally sharing, which remarkably reduces the amount of calculation and improves the generalization ability of the algorithm. However, this also makes the convolution operation unable to effectively consider the connections between local parts and the influence of the distant pixels on the operated region. This will result in an over-smoothing phenomenon in single image deraining. Inspired by the great success that graph network has achieved in recent years, we hope to improve the convolution method by combining the kernel idea of graph network. First, all pixels are treated as graph nodes, the similarity between neighboring pixels is estimated, and the threshold value determines whether or not an edge connection exists. After the graph structure construction is completed, the obtained adjacent matrix and the similarity matrix will be used during the convolution operation, the parameters of the convolution kernel are adjusted, and the connection between the pixels and the extraction of topological information are fully considered. The intensive comparison experiments of several states-of-the-arts on several benchmark datasets show the effectiveness of the proposed enhanced convolution, which can effectively promote the performance of various latest algorithms without increasing a lot of computing resources.
Creating cartoon is a challenging and time-consuming task for artists. However, automated technology that converts real photos into high-quality cartoon-style images is significantly valued. Therefore, based on a generative adversarial network, this study proposes a lightweight image cartoon stylization method. By observing the cartoon drawing behavior, the cartoon image style is decoupled into three representations, including smooth surface, sparse color block, and high frequency texture. A generative adversarial network framework is used to learn the extracted representation and the style of cartoon images. Furthermore, deep detachable convolution and reverse residual blocks are used in generative networks to reduce number of network parameters and computational costs. Qualitative comparison and quantitative analysis are conducted in this study to evaluate the proposed method's effectiveness. The results show that the proposed method can quickly convert real-world photos into high-quality cartoon images and is superior to the existing methods.
To ensure the stability and accuracy of a large-scale optical module in the installation process, it is necessary to monitor and track the guide module. An adaptive scale target tracking algorithm based on dynamic template matching is proposed to address the problems of traditional template matching tracking algorithms in industrial applications, such as their inability to cope with target scale change and lack of a template adaptive update mechanism. First, the moving target area is identified from the first frame image, the center point of the target template is extracted, and the template image pyramid is generated. The template is updated using a dynamic template update strategy, and then the Kalman filtering algorithm is used to predict the potential target range in each subsequent frame. The similarity between the template image and the target image at each scale is calculated, and the scale factor with the highest similarity is taken as the scale change. In comparison to conventional algorithms, experiments on the OTB dataset demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can meet real-time requirements while increasing the coincidence rate by about 21 percentage points.
When obtaining the point cloud of an object to be measured by three-dimensional scanning, noise points and outliers will inevitably appear, which will significantly affect the accuracy of point cloud plane parameter estimation and plane fitting. An algorithm that combines random sampling consensus (RANSAC) and principal component analysis (PCA) can effectively estimate point cloud plane parameters and fit the plane, with some degree of robustness. However, the RANSAC algorithm needs to judge in each iteration process to distinguish between inner and outer points, which introduces redundancy and affects operation efficiency. Furthermore, its estimation results will be affected by the number of iterations. To solve the above problems, an algorithm that combines least square median (LMedS) and PCA is proposed to fit the point cloud plane, and three point cloud models are selected for experiments: Semantic3D outdoor scene point cloud database, part surface point cloud obtained using a line laser sensor, and indoor dataset of Princeton University. The experimental results show that, in the 100000 order of magnitude point cloud, the LMedS algorithm can effectively estimate the plane parameters of point clouds. Compared with the RANSAC algorithm, the LMedS algorithm can effectively estimate a plane model, with increased running speed, in less time, and with the same accuracy. The proposed method is a point cloud plane fitting method with strong robustness and advantages.
To address the problem of local features in point clouds being prone to mismatch between classes during multi-target pose estimation, a robust multi-target pose estimation algorithm based on point-cloud instance segmentation is proposed. First, point-cloud clusters are obtained by segmenting the scene point clouds based on density clustering, and the local feature of the point-cloud clusters are extracted using fast point feature histogram (FPFH) descriptor to describe the local geometry of the point clouds. Then, the random forest classifier is used to classify the aggregated local features of the point-cloud cluster, obtain the category to which the point-cloud cluster belongs, and completes the point-cloud instance segmentation. For each instance in the scene, the features of the scene instance and model are matched using the fast library for approximate nearest neighbors (FLANN) matching algorithm, and the matching points of the points after instance segmentation are obtained on the corresponding category model. Robust initial pose estimation is obtained using random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm and the least squares algorithm. Finally, the accurate pose estimation result is obtained using the point-to-plane iterative closet point (ICP) algorithm. The evaluation results in the CV-Lab 3D synthesis and UWA real-scene datasets show that the proposed algorithm significantly improves the interior point probability in the local feature matching stage, thereby improving the robustness and efficiency of pose estimation, particularly in applications with multiple instances in the scene, compared with the direct matching model and local features of all scenes for multi-target pose estimation.
In nanoparticle imaging, particle clusters and large impurity particles in the defocused position cause bright spots, thus hindering the existing focusing algorithms in realizing the autofocus function. This study used binarization segmentation based on the Otsu algorithm, as well as morphological opening and closing methods, to aggregate the dispersed diffuse spots into one area. Furthermore, the connected domain labeling method was used to filter out large regions of the spot area. A four-neighborhood level-diagonal square function and threshold-four-neighborhood level-diagonal square root function were constructed and used as the evaluation indicators for the coarse and fine focus, respectively, thereby improving the accuracy and reliability of autofocus search. The defocus sequence diagram was obtained and the proposed algorithm was compared to the five commonly used evaluation algorithms. The results demonstrate that the proposed autofocus evaluation algorithm is highly robust, unbiased, and unimodal.
This paper proposes a no-reference image quality evaluation algorithm based on semi-supervised learning and dual-branch network training to realize self-supervised learning in image quality evaluation. Specifically, it is a training process with two branches in which a small number of hand-labeled data samples are used for supervised learning in one branch. Self-supervised learning is performed in the other branch to assist the former in training the same feature extractor; the self-supervised learning part adopts several traditional full-reference methods to jointly label the training samples with soft labels. Extensive experiments are conducted on six public image databases. The results show that the proposed algorithm outperforms most current methods on the synthetic distorted image datasets and has a good generalization performance on the real distorted image datasets. The predicted results of the proposed algorithm are consistent with human subjective perception performance.
To address the problem of low target detection accuracy in lightweight networks, a lightweight target detection network MobileNet-RFB-ECA based on MobileNet is proposed. To consider the multi-scale characteristics of the target, this study proposes a feature pyramid network structure based on the lightweight extended receptive field block (RFB), which enhances the adaptability of the network to the multi-scale characteristics of the target. Moreover, owing to the large computation caused by the complex attention module, an efficient channel attention (ECA) module is added to the backbone feature extraction network to improve the performance of the convolutional neural network. Experiments reveal that compared with conventional MobileNet, the proposed method improves the detection accuracy by 4.2 percentage points and 15.4 percentage points on the PASCAL VOC and KITTI datasets, respectively. In addition, the model sizes of the proposed method are 50.3 and 48.5 MB for the aforementioned datasets, respectively, and the average detection speed achieved is 34 frame/s.
In order to reduce the radiation dose of X-rays, we present a total generalized variation constrained weighted least-squares approach for low-dose computed tomography (CT) reconstruction. Incorporating the total generalized variation regularization, a total generalized variation constrained weighted least-squares (TGV-WLS) approach is presented to reduce the noise in the projection (sinogram) domain, and the image is then reconstructed using the conventional filtered back-projection (FBP) algorithm. The root mean square errors (RMSEs) of the Shepp-Logan image reconstructed by the TGV-WLS method are reduced by 25.06%, 1.497%, and 15.21%, and the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) values increased by 10.29%, 0.53%, and 5.68%, respectively, as compared with those of the Gibbs constrained weighted least-squares (Gibbs-WLS), dictionary learning constrained weighted least-squares (DL-WLS), and total variation constrained weighted least-squares (TV-WLS) methods. In addition, for the Clock images reconstructed by the TGV-WLS method, the RMSEs are reduced by 42.72%, 23.45%, and 34.63%, and SNR values increased by 27.04%, 11.42%, and 15.49%, respectively, as compared with those of the Gibbs-, DL-, and TV-WLS methods. The experimental results show that the TGV-WLS method can achieve noticeable gains in terms of noise-induced artifact suppression and edge information and structural details preservation.
Most existing image super-resolution reconstruction algorithms have an extremely deep network structure, which leads to excessive parameters and an inability to fully extract features. To solve these problems, this study proposes an image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm based on an enhanced multi-scale residual network (EMSRN). The network consists of serial enhanced multi-scale residual blocks (EMSRB), and the backbone structure of the EMSRB is constructed using a residual block and parallel multi-dilation rate dilated convolution group, which effectively reduce the network parameters while obtaining the local and global multi-scale features of the image. The channel attention mechanism is used at the end of the block to adaptively weight extracted features, which enables the network to pay more attention to high-frequency information. Experiments show that, compared with the basic multi-scale residual network, the proposed algorithm improves the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) by 0.53 dB, and the structural similarity (SSIM) reaches 0.9782. Compared with the enhanced deep super-resolution network, the proposed algorithm achieves similar reconstruction performance with only 31.7% of its parameters.
This study proposes a static/dynamic automatic focusing method of microscopes based on image clarity evaluation to address the autofocus requirements of microscopes for observing dynamic planar targets. First, following the analysis of the focus-defocus image characteristics, the weighted Tenengrad function evaluation method and image sub-block selection focus window mode are established. Second, the focus search model is established using the simulated annealing theory to target the local maximum problem in the search. Finally, to evaluate the dynamic image, the image blur method is used to determine the dynamic no-reference image defocus level. Based on these, a static focusing model, a dynamic defocus detection and real-time focusing model are established. The experimental verification shows that the static focusing model can make the microscope automatically focus quickly and accurately, whereas the dynamic defocus detection and real-time focusing model can make the microscope meet the requirements of defocus detection and real-time focusing under dynamic observation.
Considering the problem of low fusion accuracy of multi-sensor pipeline defect detection data, a data fusion method of multi-instrument pipeline defect detection is proposed, which combines the improved bird swarm algorithm (IBSA) with the weighted regularized extreme learning machine (WRELM). First, pipeline defect data are collected using electromagnetic ultrasonic guided wave testing equipment, magnetic flux leakage testing equipment, and eddy current testing equipment. The Gaussian kernel function sample weight matrix and the regularization parameter are subsequently introduced into the extreme learning machine, and the WRELM data fusion model is established. The bird swarm algorithm is then optimized by introducing chaotic variables and Gaussian perturbations, which optimizes vigilance behavior and changes the step factor in the flight behavior. The IBSA is used to optimize the connection weight between the input layer and the hidden layer and the bias of the hidden layer of WRELM. Finally, the data fusion platform for multi-instrument pipeline defect detection is utilized for experimental analysis. The experimental results show that the error of the multi-instrument pipeline defect data fusion model using the IBSA to optimize the WRELM is the smallest at just 2.33%. The fusion accuracy of multi-instrument pipeline defect data is effectively improved.
This study proposed a dual-tree complex wavelet threshold denoising method with edge enhancement to address the poor edge preservation and low contrast of denoising image in existing Gaussian noise removal methods. The proposed method employed the exceptional dual-tree complex wavelet properties such as translation invariance and multi-directional selectivity. Thus, an adaptive threshold denoising model of dual-tree complex wavelet was presented based on the mathematical model of Gaussian noise and assumption. Furthermore, a multi-directional gradient operator was proposed to obtain an edge image from the denoising image using the threshold denoising model. The edge image was linearly parametrically superimposed on the denoising image to achieve the final denoising image with edge enhancement. The experimental results verify that the proposed method performs well in noise reduction and edge preservation. It also demonstrates that the proposed method has a higher computational efficiency.
The disparity accuracy issue still exists in weak texture and depth discontinuity areas, although the conventional stereo matching model has demonstrated good performance in accuracy and robustness. To address the above issues, a minimum generating cube matching algorithm based on enhanced matching cost and mean segmentation is proposed. First, in the matching cost computation stage, the initial matching cost is computed by the Census to transform, and the input image's edge information is extracted by the Sobel operator. The extracted image edge information is merged with the matching cost value after Census transform, and the nonlinear fusion is conducted with the cost value based on image brightness information to enhance the matching cost's accuracy. Then, the minimum spanning tree cost aggregation model is employed for aggregation operation and the winner-take-all technique is employed to estimate the image's initial parallax. Finally, in the disparity optimization stage, the MeanShift algorithm is employed to segment the image, and the mismatching points are corrected along with the image's contour information to further enhance the disparity accuracy in weak texture and edge areas. Experimental findings demonstrate that compared with some conventional algorithms, the proposed approach has higher disparity accuracy, and the disparity map's edges and textures are smoother and more robust than other algorithms.
Monitoring and measurement systems for railway subgrade settlement using a chain of cameras can realize high-precision, non-contact railway subgrade settlement monitoring with the image measurement method. The precision and sensitivity of image measurement requires accurate and rapid evaluation of system performance, and regular maintenance should be changed to dynamic maintenance. Herein we propose a strategy for determining system performance using the spot-image quality and introduce four parameters, viz. edge definition, relative brightness, image information entropy, and light vertical degree, to evaluate the quality of light spots. The weight of each parameter can be constructed using the analytic hierarchy process and the entropy method. A comprehensive evaluation model for spot quality is constructed. Simulation and field experiments are conducted. The simulation shows that the proposed model can track changes in the spot-image quality score with good sensitivity. The field experiment shows that this model can be used to accurately evaluate spot quality. In addition, when the quality score is set at 0.95, the positioning error exceeds 1 mm (the allowable error range in subsidence for settlement measurement). The system requires maintenance when the light spot-image quality score continuously misses the threshold and exceeds the resting time. This method realizes system-state real-time monitoring and dynamic maintenance.
This paper proposes a method based on cross-domain learning to address the problem of small sample sizes in one-shot object detection. The proposed method begins with the aim of data enhancement and progresses with the addition of datasets in other domains as auxiliaries to enhance the network learning capabilities, simultaneously a cross-domain learning algorithm based on image and instance scales is proposed to solve the problem of differences between domains. A domain classifier model is added to the input image features and candidate features of the detection network to enhance the background of the network to cross-domain data and the target domain adaptability. Experiments for two different cross-domain scenarios are conducted, the PASCAL VOC dataset is compared with current mainstream one-shot object detection algorithms, and it presents an improvement of 2.8 percentage points on the current best algorithm. This proves that the proposed method can effectively improve the performance of one-shot object detection algorithm.
An improved YOLOv5 network model is proposed to resolve high overlap, heavy occlusion, and complex background interference in X-ray luggage image security detection by introducing the convolutional block attention module, data enhancement strategy, and the weighted boxes fusion algorithm for X-ray prohibited item detection. The convolutional block attention module is introduced in the Neck to enhance the extraction of deep important features and suppress background interference of X-ray prohibited items features. The Mixup data augmentation strategy is employed during the training process to simulate the detection scene with high overlap and heavy occlusion items to strengthen the learning ability of the model for complex samples. During the testing process, the weighted boxes fusion algorithm is used to optimize the redundant prediction boxes to enhance its prediction accuracy. The proposed model is tested on three large-size complex datasets (SIXray, HiXray, and OPIXray), resulting in mean average precision values of 89.6%, 83.1%, and 91.6%, respectively. The results show that the proposed model can effectively improve the ability of YOLOv5 in detecting complex contrabands. The proposed model performs better than many current advanced algorithms, indicating its high accuracy and robustness.
To solve the problem of traditional surface defect detection's inadaptability to a complex industrial background, a surface-defect detection algorithm based on feature pyramid matching and self-supervision is proposed. First, the features extracted from two ResNet networks based on channel attention are structured into a pyramid, which enables defect detection using the output differences of each layer of the network. Second, bootstrap your own latent (BYOL) self-supervised learning is used in the training mode of the pretrained network; the network with self-supervised learning can extract general features and improve the generalization of the defect detection method. Finally, for fuzzy images, distillation training based on different resolutions is used to let a student network fully learn to extract the depth features of images. The proposed algorithm is tested on three datasets. Experiments show that the proposed method is better than the control group and has a higher defect detection accuracy.
Typically, networks are sensitive to targets being blocked or interference around the target when tracking moving targets, resulting in unreliable response positions and incorrect tracking frame. Thus, an anchor-free Siamese network-tracking approach based on deep learning is proposed. First, the feature weight of the target guidance is derived through the nonlocal perceptual network, which is then applied to refine the depth features of the target template branch and search branch, and to improve the remote dependence of the two branch features in a supervised manner to effectively suppress noise interference. Second, to correlate the multidimensional regression features with the tracking quality, a bounding box perception block is developed. This module strengthens the interaction between the target template branch and the search branch and enhances the accuracy of network positioning. Furthermore, the proposed method can track the target in real time and enhance accuracy, according to the experimental findings on standard data sets.
A lightweight YOLOv4s based on an attention mechanism is proposed to address the low accuracy and slow speed issue of the general target detection algorithm in multi-target life scenes. First, CSPDarknet53-s was used as the backbone network to extract image features, and these features were selected using the attention block. Subsequently, the feature pyramid network was adopted to fuse the features. Finally, the YOLOv4s head was used to process the two outputs after the feature fusion to improve the multi-target detection ability in living scenes. According to the experiment results, the YOLOv4s algorithm outperforms the prior algorithm in the PASCAL VOC and MS COCO datasets, exhibiting improvement in the mean average precision and average precision. Compared with the lightweight algorithm Efficientdet, the YOLOv4s algorithm also has a certain improvement in the AP on the MS COCO dataset, and achieves effective significant target detection.
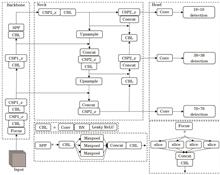
To solve the problem of the low accuracy and slow speed of traditional methods for detecting surface defects in steel plates, we propose an improved YOLOv5s algorithm. First, the steel datasets were re-clustered using K-means algorithm based on the intersection-over-union (IoU) metric distance, to obtain multiple groups of anchor boxes; a genetic algorithm was used to perform mutation operations and obtain multiple groups of anchor boxes that match the entire ground truth box better. Second, MixUp was fused with the Mosaic data enhancement to avoid over-fitting and improve the generalizability of the model. Then, the network structure was improved, and an attention module was incorporated to improve feature extraction capability of the network further. Finally, Focal loss was incorporated into the loss function to improve the convergence speed and detection accuracy of the network for hard-to-identify samples. Our experimental results show that the mean average precision (mAP) of the improved YOLOv5s algorithm on a test set is 78.4%, which is 3.0 percentage points higher than that of the original algorithm, and the speed is same as the original YOLOv5s. The detection performance of the improved YOLOv5s algorithm is better than that of DDN, Faster R-CNN, and YOLOv3, and it maintains a high detection speed.
Because CT lung nodules vary in size, shape, and texture, it is extremely difficult to diagnose benign and malignant lung nodules. Based on three-dimensional convolutional neural network, a network based on multi-depth residual attention mechanism (MDRA-net) is proposed to classify benign and malignant pulmonary nodules. The MDRA-net improves the network's perception of nodule location and global features using feature fusion and iterative hierarchical fusion on residual differential branches. Furthermore, combined with the attention mechanism, the projection and excitation block module is introduced to calibrate with spatial and channel information, which can further improve the ability of the network to extract features. Experimental results on the LUNA16 dataset show that the accuracy of the MDRA-net classification model is 96.52%, and the sensitivity and specificity are 93.01% and 97.77%, respectively, which are greatly improved compared with those of the existing classification methods of lung nodules, based on deep learning.
As a real-time, non-invasive, and high-resolution imaging method, optical coherence tomography (OCT) provides rich image information using feature extraction algorithms and provides basis for the objective diagnosis of diseases. This study imaged 17 normal thyroid tissues and papillary carcinoma tissues using the OCT system. According to the characteristics of thyroid tissue images, a gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM), gray level histogram (GH), center-symmetric autocorrelation (CSAC), and Laws' texture measure (LM) were used to extract the image eigenvalues. Similarly, we quantitatively evaluated the identification performance of the different feature combinations using a support vector machine (SVM) algorithm. The results indicate that GLCM-GH-LM model has the best performance, with a sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of 96.3%, 92.2%, and 94.3%, respectively. Moreover, it can obtain texture and gray feature information from multiple aspects. This study illustrates that the algorithm based on feature extraction and machine learning can not only provide real-time monitoring images, but also have important reference value for clinical diagnosis of thyroid malignant tumors when performing quantitative analysis and recognition for OCT images of papillary carcinoma of thyroid.
Recently, remote sensing image scenes have been increasingly widely used in monitoring the environment, exploring earth resources, and predicting natural disasters. Numerous data requirements aid in the rapid development of remote sensing image scene classification. Although the deep learning-based method has achieved decent performance in scene classification, how to effectively classify remote sensing scenes with complex backgrounds and drastic scale changes remains a great challenge in the classification task. To address this issue, this paper proposes a fine-grained approach to detect the salient region, uses the global and local branches to combine the global and local parts, and extracts the global features and local key information from the whole image and key region, respectively. To verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, comparative experiments are conducted using ResNet18 on three public remote sensing image scene classification datasets, and the experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed method is better than that of most advanced methods.
To accurately segment ground objects from a high-resolution remote sensing image, we propose a remote sensing image segmentation network based on multi-level feature optimization fusion that focuses on the fusion of feature maps at different levels in the feature extraction skeleton network, performs reasonable and effective extractions, and analyzes output feature map information by fusing different types of information in the network feature map. Simultaneously, layer-by-layer multi-scale coding and decoding modules are used to refine the shallow feature map that merges with the high-level feature map, and the different types of information are optimized to the high-level feature map. The hollow convolution pyramid is then used to extract the information of different receptive fields on the high-level feature map, and the output feature map of semantic segmentation is optimized. When conducting experiments on the ISPRS Vaihingen dataset, the overall accuracy of the proposed network reaches 90.34%, which effectively improves the accuracy of remote sensing image target detection when compared with the classical semantic segmentation network. Moreover, to prove the generalization of the proposed algorithm, a generalization experiment on the ISPRS Potsdam dataset is conducted; the overall accuracy of this algorithm reaches 91.47%, proving its effectiveness.
A blind deblurring method of remote sensing images based on local maximum and minimum intensity priors is proposed to solve the motion blur problem. The sparsity of local pixel intensity of remote sensing image is used as a prior condition in this method, and a simple iterative threshold shrinkage method is applied to solve the latent image and blur kernel, then we obtain the deblurred image using by non-blind deconvolution algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed method can improve the computational efficiency. For both optical and near-infrared remote sensing images, it can availably restore the texture details of the images, suppress artifacts, and improve the subjective effect and objective evaluation index for the restored images.
An image shadow removal algorithm based on minimum noise fraction (MNF) and a generative adversarial network (GAN) is proposed to improve the shadow removal effect. The algorithm takes GAN as its basic framework, introduces condition information into the generator and discriminator respectively, and adopts the multitask mode of end-to-end joint learning. The generative network adopts the encoding-decoding structure, and the discriminant network adopts the Markov discriminator structure. Additionally, the proposed algorithm uses MNF to restore the shade-free image after graying the noise-eliminating image with the shadowed image. Therefore, our network can focus on single feature embedding after the change in MNF instead of the traditional cross-task shared embedding. Experimental results indicate that the proposed algorithm can increase the mean structural similarity (SSIM) to 0.9780 and decrease the mean root mean square error (RMSE) to 9.8717 on the specified dataset. Both visual and statistic comparisons confirm that the proposed algorithm is better than other algorithms.
Optical waves as information carriers can process two-dimensional information in parallel with high speed and have many degrees of freedom (e.g., wavelength, amplitude, phase, and polarization). Therefore, optical encryption technologies and optical cryptosystems demonstrate great potential for applications. With the rapid growth of encrypted data transmission volume, it becomes increasingly important to realize information compression while encrypting because it shortens the time required to process these data and substantially saves storage space. In this paper, we propose the concept of generalized optical image compression-encryption and categorize its compression strategies into three types, including plaintext, ciphertext, and synchronous compressions. On this basis, the specific compression methods suitable for each strategy are specified, and the research progress of optical image compression-encryption is introduced by describing the applications of these compression methods at some instances. Moreover, the potential future research directions of optical image compression-encryption are also presented.
Currently, resources to improve the metrology and traceability of fluorescence flow cytometer are relatively limited. To study the technical development of flow cytometer based on fluorescence detection and accelerate progress toward standardization, this paper integrates domestic and foreign literatures. Furthermore, detailed information regarding types of fluorescence flow cytometers, their applications, standardization research progresses, and critical parameters including instrument resolution, scattered light and fluorescence sensitivity, fluorescence linear correlation coefficient, detection limit, accuracy, repeatability, and stability are summarized. Foreign and domestic conventional standards are available for several widely used metrology methods to evaluate fluorescence flow cytometer performance. Various research organizations and application areas have different requirements for flow cytometer performance. A complete and traceable set of metrology standards for characterizing flow cytometry, and corresponding evaluation methods enable reproducible and comparable research communications and discussions between laboratories.
Accurately controlling the end point temperature of converter steelmaking can considerably enhance the quality of final tapping. Modified colorimetric thermometry was used to determine the temperature of the furnace mouth flame to enhance the molten steel temperature prediction accuracy at the end point; furthermore, the improved competitive adaptive reweighted algorithm was used to extract the characteristic wavelength of the flame spectrum. Finally, the image and spectral features were fused and analyzed. Subsequently, a steelmaking end point temperature prediction model was established. The root mean square error of the proposed model' prediction is 15.8556 K, the accuracy within the prediction error of ±20 K is 87.50%, and the accuracy within the prediction error of ±30 K is 95.00%. Compared with the model established solely using the image feature or spectral feature, the prediction error of the proposed model is the lowest, and the accuracy is the highest. This confirms that the model established in this experiment has a good end point temperature prediction and can successfully meet the field requirements of steelmaking production.
Slimming medicines containing illegal additives, often distributed through mail and other delivery channels, are primary targets for public security organizations to curb food, drug, and environmental crimes. To enable rapid identification of such drugs, this study adopted molecular spectral analysis technology to examine slimming medication containing estazolam, sildenafil, sibutramine, flurazepam, and zolpidem; 145 groups of spectral data were obtained. Principal component analysis was utilized to extract the principal component factors and reduce data dimension. Based on the extracted 20-dimensional data, the Fisher discriminant analysis (FDA), K-nearest neighbor (KNN), and support vector machine models were established for comparison. In model 1, three Fisher discriminant functions were constructed to discriminate five types of samples, and the accuracy reached 100%. In model 2, the change of K value will affect the accuracy of the classifier. Through the adjustment of K value, 5 kinds of samples can be classified quickly, with an accuracy rate of 100%. In model 3, RBF kernel function was used to compare the classification effect of zolpidem and other four kinds of slimming drugs, and the accuracy rate reached 100%. Through the dataset in the experiment, the samples of different brands of zolpidem are identified and the actual cases are analyzed, which has a certain reference for the public security organs to investigate such cases.