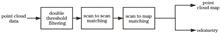
For the current inspection mode of high-voltage transmission lines in power grid of China, it is mainly through manual hand-held instruments or naked eyes to inspect facility defects,which is not only difficult and intense, but also inefficient, and cannot adapt to the safe operation and development of modern power grid. In recent years, with the rapid development of unmanned aerial vehicle technology and related sensor technology, unmanned aerial vehicle has been widely used in electric inspection. Therefore, a real-time localization and map construction (SLAM) scheme based on lidar and unmanned aerial vehicle near high voltage tower is proposed. In this scheme, lidar is used as the sensor to sense the environment, different matching algorithms are used to match the secondary point cloud, and loopback detection technology is used to achieve the precise positioning of unmanned aerial vehicle and the map construction around the tower. Experimental results show that this scheme can greatly improve the positioning accuracy of unmanned aerial vehicle around the pylons, thus improving the efficiency and flight safety of unmanned aerial vehicle.
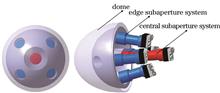
Because of its special visual mechanism, eagle eye has several advantages, such as a wide field of view, remote detection, and high-resolution imaging. In this paper, based on the eagle-eye vision, an innovative and intelligent detection method is presented that can automatically search for specific targets in key areas and create high-resolution images aimed at being part of a missile-borne optical-electric detection platform. In the long-wave infrared spectrum, a high-resolution imaging system is designed with five apertures. Based on the Agent intelligent control theory, a multisensor collaborative control scheme is established to realize automatic target positioning in a wide field of view. The multi-aperture image mosaic and variable resolution image fusion methods are studied to achieve the overall acquisition of large field of view background and high-resolution target images. Results show that our multi-aperture detection system can effectively solve the contradiction between large field of view and high-resolution in the far-field detection under an optical dome environment.
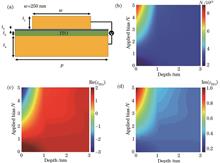
Transparent conductive oxides have been widely used in optoelectronic devices owing to their special optical property. In near-infrared wavelength region, the real part of the dielectric constant will decrease from positive to negative. Within epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) region, strong interaction will occur between light and matter, and wide phase modulation will be achieved. Herein, using a bias voltage of 0-5 V, the carrier concentration within a region (thickness: 1 nm) near the interface of an ITO-based MOS structure was adjusted, and a phase modulation close to 265° in a 1470-nm wavelength was achieved. Based on this modulation, the practical applications of the proposed structure in the fields of beam deflection and focusing have been explored. Furthermore, a dual-gated MOS structure, which further expanded the phase coverage region, was designed.
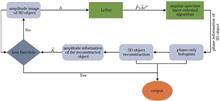
Traditional phase-only holographic imaging methods rely on high-intensity iteration, which is time-consuming, and the imaging quality is not high. To address this issue, a phase-only hologram generation algorithm based on depth learning and angular-spectrum layer-oriented, which can generate holograms quickly and improve the quality of hologram reconstruction, is proposed. The LeNet network structure predicts the complex amplitude information of three-dimensional objects, which reduces the amount of calculation. The accurate angular-spectrum algorithm creates a high-quality phase-only hologram of a three-dimensional object. The simulation results show that the algorithm is feasible and the quality of the reconstructed image is effectively improved.
Underwater imaging is one of the most commonly used methods for ocean exploration, and a growing number of studies have shown that polarization is the key to the underwater creatures having vision in low illumination. In this paper, a multi-turbidity underwater image recovery method based on deep learning and polarization imaging is proposed. Multiple turbidity underwater polarization data sets are obtained by capturing images of clean water and underwater polarization images with different turbidity. A small size neural network is proposed to better learn the mapping relation between underwater polarization information under different turbidity and clear underwater images. A sliding window superposition method with different steps is proposed for different circumstances. The results show that the polarization method proposed in this paper can effectively recover the underwater image, and the peak signal to noise ratio recovered under different turbidity is 47.39% higher than that of the original image on average. The proposed method combining deep learning and polarization imaging technology can restore underwater images in multi-turbidity environment and overcome the problem of poor restoration effect of ordinary underwater images.
Aiming at the problem that it is difficult for monocular mobile devices to capture background blurring images, this paper proposes an automatic background blurring algorithm based on the image perception and segmentation algorithm of deep learning. We use the image perception and segmentation algorithm of deep learning to obtain three auxiliary images, i.e., the focus map, depth map, and mask map, of the captured image. We use the auxiliary images to automatically determine the subject or specify the subject by the user, and the depth of each area of the background is calculated. Then, the multi-scale Gaussian filter is used to blur each area of the background in different degrees. Finally, the blurred background areas are merged with the subject, and the edges are optimized to finally generate a background blurred image. Experimental results show that this algorithm can realize more accurate and flexible image virtual processing by using perceptual map based on deep learning, and can automatically focus the image subject or refocus the designated area in a variety of scenes. The virtual effect is natural and hierarchical, and can better highlight the image theme.
Aiming at the problem that small masses and occluded masses are easy to be missed in breast cancer diagnosis based on deep learning, an improved YOLOv3 algorithm for breast mass detection is proposed. First, a bottom-up path is added into the feature fusion module, and the cascading and cross-layer connections are adopted to make full use of the underlying feature information to improve the recognition accuracy of small masses. Second, to filter out more accurate prediction bounding boxes and avoid missed detection of masses that occlude each other, the distance intersection over union (DIoU) is introduced in soft non-maximum suppression (Soft-NMS) algorithm to suppress the redundant prediction bounding boxes. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed breast mass detection algorithm has high accuracy and speed in detecting small masses and occluded masses, mean average precision (mAP@0.5) reaches 96.1%, which is 1.8 percentage point higher than that of YOLOv3, and the detection time of each mammogram target image is only 28 ms.
In order to realize automatic water level monitoring based on video images and solve the problems of poor environmental adaptability and low robustness of traditional video monitoring algorithms, a video water level monitoring method based on semantic segmentation is proposed. The improved DeepLabv3+ algorithm, combined with spatial attention mechanism, channel attention mechanism and edge refinement module, is used to segment the water level scale image to extract horizontal coordinate, and the actual water level value is calculated according to the linear interpolation of camera calibration results. The experimental results show that the average intersection ratio of the proposed algorithm on the water level scale dataset reaches 97.18%, which is better than DeepLabv3+ and BiSeNet (Bilateral Segmentation Network) semantic segmentation algorithms. The average pixel error rate of the proposed algorithm is 0.76%, and the error of water level reading is less than 1 cm in the measured environment. Compared with the existing traditional image processing water level monitoring algorithm and water level monitoring algorithm based on deep learning, the proposed algorithm has stronger environmental adaptability, higher robustness, more accurate reading, and can achieve more accurate automatic water level monitoring.
Because of the demand for intelligent detection of solid waste-based concrete three-dimensional (3D)-printed components in complex environments, this paper introduces the machine vision theory and proposes a target fine-segmentation algorithm based on the interlayer information entropy to realize the feature analysis and intelligent detection of 3D-printed components. First, considering the complex environment of concrete 3D printing, a preprocessing method for visual feature enhancement was constructed, the contrast was adjusted, and the image feature details were enhanced using Gamma grayscale transformation and histogram equalization algorithm. It was combined with adaptive median filtering to remove the random noise in images. Then, considering the layered superposition characteristics of the components, the interlayer information entropy index was defined, and a fine-segmentation method of printing components based on the interlayer information entropy and double threshold optimization was designed to realize the complex environment hierarchical detection and fine segmentation of 3D components. Finally, the target images of real concrete 3D-printed components were collected to verify the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm increases the accuracy by 12.44% and the F1 value by 30.79% on average, considerably improving target segmentation accuracy. It lays the foundation for further realizing accurate measurement and path optimization of 3D-printed components.
Current segmentation methods do not account for the segmentation accuracy and efficiency of visible and near-infrared heterogeneous noisy iris images; thus, in this study, we propose a codec network based on the fusion of attention mechanism and dense multiscale features. First, an improved residual bottleneck element based on deep separable convolution was introduced to reduce the number of parameters and computation while preventing information loss and gradient confusion. Second, the dense void space pyramid module's void rate combination was improved and placed behind the encoder to improve multiscale feature fusion. Finally, to improve the resolution of noise targets and iris pixels, an efficient parallel space-channel attention module was designed and integrated into each down sampling layer and decoder. The experiments conducted on three open iris data sets show that both the average F1-score and mean intersection over union (mIoU) of the proposed network are superior to the existing algorithms. Compared with the benchmark network, the occupied space, number of parameters, and amount of computation are reduced by 41%, 41.77%, and 65.35%, respectively. It can effectively improve the segmentation performance of the network for multispectral noise iris and is easier to be deployed on mobile devices, which can more efficiently and accurately distinguish noise and iris targets.
To obtain a seamless remote sensing image with wide field-of-view and high resolution, this study proposes a remote sensing image mosaic algorithm based on distribution measure and saliency information. Outlier removal, optimal seamline detection, and smooth transition during image mosaic are the main areas of improvement. To improve image alignment, the optimal inliers are first chosen based on the distribution quality of inliers in the overlapping area. Secondly, the saliency information of images is determined by line segments and guided filter to avoid the seamline crossing obvious features. Lastly, a two-scale image fusion is performed using a guided filter, and spatial consistency is used to achieve a smooth transition between the images on both sides of the seamline. The simulation results demonstrate that, when compared with the RANSAC algorithm, the proposed algorithm enhances the mutual information by 1.93% and the stability by 46.55% in outlier removal. In comparison to the QESE algorithm, the proposed algorithm improves structural similarity (SSIM) by 3.21% and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) by 2.55% in optimal seamline detection and smooth transition. A high-quality, wide field-of-view, and high-resolution remote sensing image is produced with uniform brightness and no ghosting.
In image segmentation based on DeepLabV3+, the different importance of features in different levels of feature images are ignored in the feature extraction stage, and a large amount of details are lost, resulting in poor segmentation effect. To solve this problem, an image semantic segmentation algorithm based on the combination of DeepLabV3+ and attention mechanism is proposed. Two low-level features are extracted in the backbone network Xception model as input features of the decoder to improve the accuracy of feature extraction. The channel attention module is used to effectively integrate high-level features and obtain rich context information. The spatial attention module is used to extract low-level features and filter background information to reduce the loss of details. The depthwise separable convolution is substituted for void convolution to effectively reduce the amount of parameters and improve the calculation speed. At the same time, the focus loss is used as the loss function to improve the final segmentation effect by reducing the internal weighting. Experimental results show that the mean intersection over union (mIoU) value of the proposed algorithm on PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset reaches 84.44%. Compared with the traditional algorithm and the improved algorithm based on DeepLabV3+, the proposed algorithm effectively improves the accuracy of feature extraction, reduces the loss of feature details, and improves the final segmentation effect.
In order to improve the difficulty of locating small-scale components such as contact network pipe cap in the process of fault detection, a contact network pipe cap target location algorithm based on improved Faster R-CNN is proposed. The proportion and area of anchor boxes generated in the region proposal network (RPN) layer are improved by K-means clustering algorithm (K-means), the proposed algorithm has good performance in locating small components such as contact network pipe caps. The optimal feature extraction network is selected by comparing the accuracy, recall, accuracy, harmonic average of accuracy and recall F1, and single sheet detection time of VGG16, resnet50, resnet101, and resnet152 feature extraction networks on the original and improved Faster R-CNN. The experimental results show that the improved Faster R-CNN deep network model based on resnet50 has obvious advantages in contact network pipe cap locating, the recall rate is 89.78%, the locating accuracy can reach 83.16%, the F1 value is 86.34%, and the single detection time is 0.283 s.
Convolutional neural network (CNN) is gradually applied to the field of image fusion because of its excellent performance. For the fusion task of infrared image and visible image, because there is no label data, unsupervised learning modeling is of great significance. To solve this problem, an unsupervised end-to-end depth fusion algorithm is proposed. The algorithm can directly predict the fused image containing significant information of the source image from the input infrared source image and visible light source image. The proposed algorithm constructs an auto-encoder network and uses real datasets for training. The loss function used in the network is the image structure similarity index measure (SSIM), which is widely used in image fusion tasks. Specifically, an improved non reference image evaluation index is designed to calculate the loss function, so as to achieve the purpose of unsupervised training of the network. In addition, the attention mechanism is introduced into the model to further improve the fusion results. The proposed algorithm is compared with many fusion algorithms, experimental results show that the fusion results of the proposed algorithm are very competitive in both subjective evaluation and objective index evaluation.
Aiming at the problem that the existing target tracking algorithms have poor effect on fast moving weak targets, a spatio-temporal continuous multi-feature fusion siamese network algorithm is proposed. First, the full convolution siamese network is used as the basic framework; second, a robust feature combining spatial information and semantic information from coarse to fine is designed to express fast-moving weak targets, and feature attention is added; Finally, the spatio-temporal information continuity model is used to effectively update the overall information, so as to select the best tracking target.In the fast moving weak target tracking sequence, compared with five different feature selection and update algorithms, the proposed algorithm shows good real-time tracking effect; the proposed algorithm is compared with 9 different algorithms and 5 similar twin network algorithms, and the comprehensive performance of the proposed algorithm is excellent. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has good robustness and real-time performance, and can effectively track fast moving weak objects.
Aiming at the problems of poor positioning accuracy, bad real-time performance, and potential safety hazards of shell positioning method in the range, a flame detection algorithm based on salient object detection is proposed. First, in view of missing datasets, a shell flame dataset is constructed for network model training and reasoning. Second, the parallel and crossed two-branch ResNet is used as the feature extraction module to learn foreground and background semantic information respectively. Furthermore, dilated convolution and attention mechanism are introduced to improve the receptive filed and synchronously enables the network to learn the ability of focusing on useful channels and spatial locations. Finally, the Bi-directional feature pyramid network (Bi-FPN) is introduced to fuse shallow texture information and deep semantic information to realize multi-scale and multi-stage prediction. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm significantly outperforms the existing algorithms in terms of the accuracy, the regional integrity, and anti-interference, which is able to meet the needs of daily projectile positioning training in the shooting range.
Aiming at the problem of difficult registration of feature points under the influence of modal and scale differences in the process of infrared image and visible image registration, an infrared image and visible image registration algorithm based on modal transformation and robust features is proposed. First, the generation adversarial network is used to generate the corresponding pseudo infrared image from the visible image; second, the position information of feature points in infrared image is extracted by accelerated robust feature (SURF) algorithm, and the feature description is realized by improved robust feature descriptor (PIIFD); then, based on the kernel method of Hilbert space reconstruction, a single Gaussian robust point matching model is established to estimate the mapping in the presence of outliers; finally, the weighted least square method is used to estimate the transformation type to realize image registration. The experimental results show that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm can improve the registration accuracy in the case of large scale difference between infrared image and visible image, the effective registration rate is 96% and has strong robustness.
This paper proposes a character pose transfer generative model fused with the self-attention mechanism to address the issues of loss of texture details and unreasonable pose transfer in images generated by character pose transfer. First, based on the two-stage pose transfer generative model, the improved self-attention module is introduced into the generative adversarial network to reduce the interaction between similar features,which improves the ability to learn texture details and capture information, enhances saliency modeling of posture features. Then, the Markov discriminative model is used to enhance the ability to discriminate the details of the generated image. Finally, the optimized content loss function is used to constrain the image feature information loss of the entire model, promote semantic consistency between the generated and the real images,and strengthen the rationality of pose transfer. The experimental results demonstrate that, compared with the PG2 method on the DeepFashion and Market-1501 datasets, the IS and SSIM values of our model has increased in 0.388 and 0.032, 0.036 and 0.065, respectively.
Due to the large number of semantic segmentation model parameters and time-consuming algorithm in deep learning, it is not suitable for deployment to mobile terminal. To solve this problem, a lightweight semantic segmentation algorithm based on improved DeepLabv3+ network is proposed. First, MobileNetv3 is used to replace the original DeepLabv3+ semantic segmentation model backbone network for feature extraction to reduce the complexity of the model and speed up the running speed of the model; second, the standard convolution in atrous spatial pyramid pooling module is replaced by depthwise separable convolution to improve the efficiency of model training; finally, the attention mechanism module and group normalization method are introduced to improve the segmentation accuracy. The proposed segmentation algorithm achieves a mean intersection over union (mIoU) of 72.94% on the Cityscapes validation set of semantic segmentation dataset. Experimental results show that compared with common segmentation algorithms such as SegNet, Fast-SCNN, and ENet, the proposed algorithm can improve the segmentation effect while reducing the number of model parameters.
With the maturity of three-dimensional (3D) measurement technology, a non-contact 3D palmprint acquisition system provides a new way for palmprint recognition. In order to improve the accuracy of 3D palmprint information acquisition, a non-contact portable 3D palmprint acquisition system based on binocular stereo vision and structured light is proposed. Firstly, the coding pattern is projected onto the surface of the palm of the target, and the binocular camera is used to obtain the left and right views. The Gray code-phase shift method is used to obtain the absolute phase information of the target. Then the Boyle Moore voting algorithm is introduced for maximum probability correction to reduce the jump noise in the disparity map. After sub-pixel stereo matching and stereo calibration of the binocular camera, the 3D palmprint information is obtained. Finally, experiments are carried out on a set of self-built portable 3D palmprint acquisition systems. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional 3D palmprint acquisition system based on binocular stereo vision, this method can improve the palmprint acquisition accuracy and obtain better 3D palmprint reconstruction effect.
The scale of contraband in security X-ray image is changeable and its posture is different, which brings great difficulties to automatic identification. To address this problem, an X-ray target detection algorithm based on pyramid convolution and strip pooling is proposed. First, pyramid convolution is introduced based on CenterNet, a one-stage anchor free frame target detection framework. Then, a pyramid hourglass network is proposed to enrich the receptive field of the hourglass-104 feature extraction network and enhance the ability of multi-scale feature extraction. Second, the introduction of strip pooling can capture the global information of the image context. It can also prevent information interference of irrelevant areas and consider local detail information. Finally, to enhance the performance of the scale prediction branch in the training process, the training loss of the prediction target scale branch is replaced by the intersection over union (loU) loss function. The ablation experiment results show that the average accuracy (mAP50) of the enhanced network is improved from 86.6% to 88.3%, and the accuracy is significantly improved.
Extracting the effective features of bronze inscription image is the key step of inscription recognition. Aiming at the problem of low recognition accuracy of inscription feature extraction method with image as information carrier due to high feature dimension and complex feature vector, an integrated learning and recognition method of inscription graphics based on the dual features of topology and mesh is proposed. Taking graphics as the representation of inscriptions, the proposed method extracts topological features and 7-dimensional text structure graphic features, which effectively describes the structure information of inscription text. On this basis, the proposed method uses the 8-dimensional and 4-direction elastic mesh features of the global and local structure information of the inscription after dimensionality reduction to solve the problem of high dimension of the feature vector caused by the extraction of the image features of the inscription. Finally, taking topological features and elastic mesh features as the feature vectors of integrated learning samples, Bagging method is used to integrate machine learning classifiers with different sensitivity of feature vectors, so as to improve the model training efficiency and recognition accuracy. The experimental results show that compared with the image feature extraction method, the proposed method improves the accuracy of inscription recognition by 15.54 percent, and the dimension of inscription feature vector and running time are greatly reduced.
When taking images in foggy environment, fog, haze, and other media lead to image blur, low contrast, and dim color. In this paper, the atmospheric scattering model and the principle of polarized light are combined to obtain the dual angle polarized image with the maximum brightness and the minimum brightness by using the Stokes parameters. The atmospheric light intensity at infinity in the scene is accurately estimated by the new method of comparing the mean value of the dark channel of the quartered image, and finally the foggy image is restored to the image without fog. The experimental results show that the image NRSS (no reference structural similarity) and mean gradient are greatly improved in both mist and dense haze environments.
Aiming at the requirements of high precision, small stroke, and compact structure of X-Y direction adjustment mechanism of moving mirror in lithography projection objective, an X-Y direction integrated adjustment mechanism is proposed. Based on the four-bar adjustment principle, the proposed mechanism uses X-Y flexure hinges with independent inner and outer rings to realize high-precision adjustment in X/Y direction without decoupling. First, the structure design of the proposed mechanism is completed according to the adjustment accuracy and stroke of the moving mirror in the projection objective; then, the performance of the proposed X-Y flexible adjusting mechanism is simulated and analyzed by using the finite element analysis method. The analysis results show that the adjustment stroke of the mechanism is greater than ±20 μm. The stiffness values in X direction and Y direction are 0.542 μm/N, 0.671 μm/N, respectively; the ratio of the vertical coupling error to the displacement in the main direction is 6.86% and 4%, respectively; the mode is greater than 100 Hz. Finally, the performance test of the proposed adjustment mechanism is carried out, the repeated positioning accuracy in X direction and Y direction is 36.3 nm and 41.7 nm,respectively. During the adjustment process, the angle offset is less than 0.5". The experimental results show that the proposed flexible adjustment mechanism can meet the high-precision adjustment requirements of X-Y direction for image quality compensation of lithographic projection objective.
The single-photon compression imaging method, which combines photon counting technology and single-pixel imaging technology, has the characteristics of low cost and ultra-high sensitivity, however it takes a long time to reconstruct images using the traditional compression reconstruction algorithms. Additionally, the compression reconstruction network based on deep learning not only realizes rapid reconstruction, but yields better reconstruction quality. The recent compression reconstruction network used for single-pixel imaging is primarily based on the optical detector working in an analog mode, using the system simulation data without noise or additive white Gaussian noise for neural network training. In this study, a noise model of the single-photon compression imaging system is established, and an anti-noise reconstruction network (RN) training method for single-photon compression imaging is proposed. Simulation data of the measured values with Poisson noise is used to train the neural network, and a single-photon compression imaging system is built for verification. The results show that the RN can significantly improve the image reconstruction quality of the various existing compression reconstruction networks. On this basis, this study proposes an anti-noise reconstruction network (RPN-net) dedicated to single-photon compression imaging. RPN-net adopts a leaping connection structure and progressive training method, and the results show that the reconstruction performance of the RPN-net is better than that of the existing compression reconstruction networks.
Camera calibration is an essential part of 3D sensing technology based on structured light, which links the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the measurement system with the 3D coordinates. The camera calibration approach based on feature points retrieved from gray information can be easily affected by image noise, contrast, and other factors. Thus, this study proposes an active camera calibration approach based on absolute phase target (APT), in which absolute phase is determined using the temporal phase unwrapping algorithm. The point where phase value is the integer multiples of 4π is selected as the feature point. The local window least-square linear-fitting approach is used to determine the precise subpixel coordinates of every feature point, then the one-to-one correspondence between the image and world coordinates of feature points is established. In simulation experiments, according to the absolute error change of the camera parameters under different degrees of Gaussian noise and blur, we concluded that the proposed APT calibration method is more robust to noise and blur than the traditional checkerboard calibration and dot calibration approach, and calibration accuracy is relatively high. The validity and feasibility of the proposed APT approach are further demonstrated by the real comparison experiment, which reveal that the calibration accuracy of the APT approach is higher and the reprojection error can be reduced by 58.68% under out-of-focus conditions (the target is outside the working distance of the camera).
An anisotropic multi-scale edge detection algorithm is proposed. First, the edge strength maps of the input image are obtained by using a set of anisotropic Gaussian filters at given multiple scales. Then, the obtained edge strength maps are jointly used to produce one fused edge strength map that has higher edge resolution and lower edge diffusion effect. Finally, the fused edge strength map is incorporated into the framework of the Canny edge detection algorithm to generate the final result of edge detection. A new multi-scale fusion strategy based on "signal average" is proposed creatively, and the advantages of the new strategy compared with the existing "geometric average" fusion strategy are explained from the perspective of theoretical analysis and numerical experiments. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm effectively solves the edge spreading problem of anisotropic filter in a single scale by using multi-scale fusion strategy, and can obtain better edge detection effect than the existing algorithms while maintaining robust noise robustness.
In order to promote the degree of autonomy and intelligence of garbage classification, the garbage bin need be equipped with visual sensor and intelligent hardware carrying effective garbage detection and classification algorithm. To meet this demand, an improved garbage identification and classification algorithm based on YOLOv3 is proposed. First, MobileNetv3 network is introduced to replace Darknet53, the backbone network of YOLOv3, and spatial pyramid pooling structure is added to reduce the computational complexity of the network model and ensure the accuracy of the model. Second, four different scales are used to enhance the detection ability of the model to small targets. Then, the loss function of the original YOLOv3 model is replaced by the complete intersection over union (CIOU) loss function to improve the accuracy of the network model. Finally, a household trash can test platform is built, and the proposed algorithm is transplanted to the edge computing module NVIDIA Xavier NX. The experimental results show that the average accuracy of the proposed optimization algorithm is consistent on the server and NVIDIA Xavier NX platform in the self-made garbage dataset,reaches 72.1%, which is 4.9 percentage point higher than that of YOLOv3 and 1.6 percentage point lower than that of YOLOv4; detection speed is 74,19 frame/s, which is much higher than 43,8 frame/s of YOLOv3 algorithm and 50,11 frame/s of YOLOv4 algorithm, indicating that proposed algorithm meets the requirements of edge computing equipment and has potential application value.
Precise positioning and accurate identification of personnel entering, exiting, and conducting important production activities in the mining area are important foundations for achieving intelligent and safe production in the mining area. This study proposes an unlabeled video retrieval method for personnel in the mining area using MK-YOLOV4 in the complex mining area production environment, which can realize multiperson target detection and reidentification of an individual's identity on unlabeled video of important gateway monitoring in the mining area. First, this study proposes the MK-YOLOV4 algorithm to achieve multiperson detection of unlabeled videos by building multiscale predictions on YOLOV4, and the K-means++ algorithm is combined to generate an anchor box that meets the characteristics of the samples, which can improve the representation learning of the convolutional neural network for small targets. Second, we propose a channel attention feature extraction network based on appearance invariance to achieve accurate reidentification of personnel in mining areas. Aiming at solving the problem of uniform work clothes for personnel in mining areas, this study proposes a weight-constrained difficult sample sampling loss function with two data enhancement strategies, where Color jitter and random erasure are combined to improve the accuracy and robustness of the identification network. Finally, according to the characteristics of the existing training dataset with few categories and single scene samples, a Miner-Market mining personnel reidentification dataset is constructed with the characteristics of the mining scenes, and the proposed method is verified on the standard dataset and Miner-Market dataset. The verification confirmed that the proposed method has high retrieval performance and recognition accuracy.
Aiming at the problems of complex network structure, difficult training and difficult deployment in mobile , and embedded devices of single-stage target detection in deep learning, a lightweight target detection algorithm based on adaptive spatial feature fusion is proposed. The proposed algorithm takes YOLOv4 as the basic framework of the network and uses lightweight MobileNet as the feature extraction network to reduce the network depth and training difficulty and improve the detection speed; an adaptive spatial feature fusion (ASFF) method is used to improve the poor effect of PANet on multi-scale feature fusion; by adding the output dimension of the network, the Gaussian algorithm is used to model the new dimension and output the uncertainty of the position of the prediction box; finally, the position loss function is redefined to improve the accuracy of position regression. The proposed algorithm takes the mask wearing detection robot during the epidemic as the deployment carrier to test the face mask wearing. The experimental results show that the detection accuracy of the proposed algorithm reaches 95.92% and the detection speed reaches 19 frame/s. Compared with the original algorithm and other mainstream detection algorithms, the proposed algorithm is more suitable for deployment in mobile and embedded devices to realize real-time detection.
Marine oil spills cause great harm to the marine ecological environment; thus, an accurate detection of the oil-spill area is of great essential for a rapid emergency treatment. At this stage, synthetic aperture radar (SAR) provides an important data basis for marine oil-spill detection, but the widespread marine biological oil film, the presence of low wind areas, and the considerable speckle noise of SAR images are very likely to be oil spills, limiting the accuracy of marine oil-spill detection. Therefore, the present research proposes an improved fully-convolutional network (FCN)-based marine oil-spill intelligent detection framework in multi-polarized SAR image. The first step is to perform Pauli decomposition and Refined-Lee filtering preprocessing on the polarized SAR image to ensure the polarization characteristic information while reducing the effect of the suspected oil-spill noise on the detection accuracy. Secondly, considering the lack of consideration of the spatial information in the FCN model, the fusion mechanism of convolutional layers with different levels is used to realize the fusion of high-level semantic features and low-level spatial details, thereby improving the accuracy of marine oil-spill area detection. Experimental comparison and analysis show that the marine oil-spill intelligent detection framework, based on an improved FCN, can effectively reduce the effect of suspected oil-spill areas on detection accuracy, while considering multi-polarization and edge feature information to achieve pixel-based oil-spill area detection. The excellent detection accuracy can reach 95.7%.
The damaged faces of statues are prone to getting redamaged during the restoration process, and the historical image data of statues are insufficient. To solve these problems, we propose a digital restoration method based on a deep learning network, which can use a single statue face image to restore the damaged face of the statue. First, the deep learning network is used to process the single image data of the undamaged statue to generate a point cloud. Second, the damaged statue point cloud is obtained through a laser scanner. Finally, the two data are registered and fused to generate a complete statue model to realize the digital restoration of the statue face. In this study, the artificially damaged point cloud of undamaged facial statues is used to simulate the damaged facial statues, and the proposed method is used for restoration. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively realize the digital restoration of facial damaged statues, and the generated statue model has correct facial details and high restoration accuracy.
Recently, deep learning-based algorithms have emerged in the image defogging field. A cyclic generative adversarial network (CycleGAN) was used to create an image defogging algorithm in this study. Further, the desired processing effect was achieved by optimizing the generator in the CycleGAN. In the encoding and decoding networks of the generator, Leaky ReLU and Tanh activation functions were used, and the residual blocks of the conversion network were optimized by reducing the number and weighting optimization. The use of fog in the design of a single image can result in improved clarity and detail. Peak signal-to-noise ratio, structural similarity, and information entropy are some of the objective evaluation indexes that were enhanced.
In this study, we detect and locate the disinfection objects and determine the scope of the disinfection in public places. Firstly, a depth camera was used to capture RGB images and a three-dimensional (3D) point cloud of the public disinfection objects. Secondly, using trained Mask R-CNN, the classification, detection, and instance segmentation of disinfection targets are carried out, yielding a 3D point cloud of the objects. The 3D point clouds from different perspectives were then stitched together to create a complete 3D point cloud of the disinfection object using the sample consensus initial alignment (SAC-IA) and iterative closest point (ICP) fine registration methods. Finally, the 3D point cloud's bounding box was optimized using principal component analysis (PCA). The experimental results show that the mean average precision(mAP) of object detection based on Mask R-CNN reaches 0.968, and the average intersection over union (IoU) of instance segmentation reaches 0.879. The optimization rates of surface area and volume of the bounding box are 29.2% and 28.8%, respectively. The effectiveness of this method in detecting and locating disinfection objects was demonstrated in this study. It lays a foundation for providing different disinfection methods suited for different objects, narrows the disinfection scope while simultaneously improving disinfection efficiency.
Yam is a kind of traditional Chinese medicine which contains many substances. It is of great significance to ensure the safe use of yam. In this article, the Raman peaks of the three pesticides, i.e., fenthion, triazophos, and thiram, were calculated by Gaussview/Gaussian09w. By combining with the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) of the standard pesticide solutions, the Raman characteristic peaks of these three pesticides are determined. The pesticide residues of fenthion, triazophos, and thiram in yam were studied by using the self-assembled confocal Raman microscope as the detection device, and the gold nanosol was used as the enhanced substrate of SERS. The volume ratio of pesticides, hydrochloric acid, and gold sol particles was optimized experimentally. The experimental results show that the Raman peak bands of fenthion pesticide are around 717, 1050, and 1221 cm-1, the lowest detection limit is 1 mg?L-1, and the linearity R between the intensity of Raman peak and fenthion pesticide concentration is 0.9762 within the fenthion concentration range of 5?15 mg?L-1. The Raman peak bands of triazophos are around 611, 978, 1001, 1321, 1408, and 1597 cm-1, the minimum detection limit is 1 mg?L-1, and the linearity is 0.9087 within the concentration range of 5?9 mg?L-1.The Raman peak bands of thiram are around 556, 865, 1146, and 1506 cm-1, the minimum detection limit is 0.1 mg?L-1, and the linearity is 0.9905 within the concentration of 0?20 mg?L-1. It is expected that the rapid on-site detection of pesticide residues in traditional Chinese medicines can be realized by using gold as the enhanced substrate for SERS.
Radiotherapy is a common treatment for tumors. To accurately control the radiation dose distribution and reduce the damage caused by radiation to normal tissues and organs in radiotherapy, organs at risk must be delineated precisely. In this study, a novel automatic segmentation method for organs in head and neck, named SAU-Net, was proposed, the architecture of which is based on the three-dimensional (3D) U-Net with residual connections. Nonlocal spatial attention implemented using the squeeze and attention (SA) module was introduced to solve the problem of unbalanced segmentation accuracy caused by massive differences in organs' volumes. This introduction increased the ability to aggregate multiscale contextual information by encoding global features. To avoid the stacking of excess local information by extra convolution operations and reduce the number of parameters, the model reduced the number of convolution kernels. The performance of the model was evaluated using the dice score, and SAU-Net achieved 13.7% and 8.2% higher segmentation accuracy than 3D U-Net and 3D residual U-Net (ResU-Net), respectively. Moreover, the proposed model achieved of an inference time 73% faster than that achieved by FocusNetv2. Thus, SAU-Net delineates organs at risk in the head and neck faster than AnatomyNet and more accurately than FocusNetv2.
When the traditional focus evaluation function is used to automatically focus the micro-nano structure, the diversity of the edge direction of the micro-nano structure will lead to poor focus stability and low sensitivity. In view of the above problem, the traditional focus evaluation functions are compared and analyzed,and a new focus evaluation function, i.e., Brenner2d_Roberts function is proposed by combining the Brenner function and Roberts function. Three groups of microstructure images with different edge directions are obtained through experiments, and the focus evaluation curves and related evaluation indexes are compared and analyzed. The results show that, compared with the traditional focus evaluation functions such as SMD, Brenner and Roberts, the proposed focus evaluation function shows better focus performance in multiple edge directions of microscopic images, and has better stability and higher sensitivity.
Infrared thermography is an effective method for the detection of metal fatigue damage conditions. However, it does not consider the effect of surface microstructure on spontaneous emission in the fatigue damage process; thus, interpreting the infrared thermal image characteristics from a microcosmic perspective is difficult. Metal fatigue is a complex energy dissipation process, and spontaneous emission has polarization properties. By incorporating polarization detection into infrared thermography, besides temperature field information, surface texture information including emissivity change can also be obtained. Based on the foregoing, this paper obtained the thermal infrared polarization images of the metal material surface under cyclic load using Q235 low carbon steel as the research object by constructing a tensile fatigue test platform and a polarization thermal image acquisition platform. We investigated the evolution processes of surface morphology of metal materials during metal fatigue damage by using the gray level co-occurrence matrix (GLCM) to extract the thermal image texture information, such as polarization azimuth, polarization degree, and Stokes parameters. The results of the experiments show that the texture features of polarized thermal images of metal components change with fatigue damage cycles, and the co-occurrence matrix statistics exhibit some regularity with cycles.
To solve the problem of insufficient detail processing in the existing image super-resolution reconstruction algorithm, a super-resolution reconstruction algorithm of images based on improved enhanced super-resolution generative adversarial network (ESRGAN) is proposed. Firstly, the deep information extraction module of the improved ESRGAN generation network is improved using multiscale dense block (MDB) instead of dense block (DB), and by adding channel attention mechanism after MDB to adjust the characteristic response values of different channels. Secondly, the shallow feature extraction module of the improved ESRGAN model is used to extract the original features of the low resolution images, and the deep information extraction module is used to extract the depth residual features of the low resolution images. The original features and the depth residual features are fused by adding the corresponding elements. Finally, the reconstruction module is used to complete the image super-resolution reconstruction. The proposed algorithm's two and four times super-resolution reconstructions are tested on Set5, Set14, and BSD100 datasets and compared to Bicubic, FSRCNN, and ESRGAN methods. The results show that the proposed algorithm's reconstructed image has a clearer edge, and it can provide more details, which greatly improves the image's visual effect. Compared to ESRGAN, the proposed algorithm improves the average peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity (SSIM) of 2-fold super-resolution reconstruction images by 0. 467 dB and 0. 005, respectively; At the same time, the proposed algorithm improves the average PSNR and SSIM of 4-fold super-resolution reconstruction images by 0.438 dB and 0.015, respectively.
Aiming at the problem of large extrinsic calibration error of micro electro mechanical system (MEMS) Lidar and camera, an extrinsic calibration method based on key points of calibration board is proposed. First, the multi-frame point clouds are superimposed for preprocessing, and then the edge line of the calibration board is fitted based on Hough transform to determine the key points. Finally, the constraints corresponding to the key points and normal vectors are set up, and the optimized calibration external parameters are obtained by using the point and plane correspondence algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed method can accurately extract the key points, make the average error of calibrated external parameters lower than the existing external parameter calibration methods, and improve the accuracy of calibrated external parameters.
Aiming at the parks and other similar environments application scenarios where the scene feature is unique and the global navigation satellite system (GNSS) signal is unstable, as well as the problem that the lack of semantic understanding in Lidar simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) results in a localization error of unmanned vehicle, a building method of three-dimensional semantic map with the data fusion of monocular camera and Lidar is proposed. This method is based on the characteristics of strong structural park environment and high dynamic variation of pedestrian in vehicles. The improved panoramic feature pyramid network (PFPN) is used for scene visual semantic segmentation, and then the pixel level fusion method is used to provide semantic information for the laser point cloud, so as to effectively remove the interference of dynamic targets in the process of normal distribution transformation (NDT) mapping, and then improve the robustness and accuracy of unmanned vehicle SLAM technology in the dynamic environment. Experimental validation is carried out on the cyclone intelligent self-driving platform and compared with the original NDT method, the experimental results show that the proposed method is able to improve the construction accuracy comprehensively, with the most significant improvement of 34.34% in positional accuracy; besides that, the number of point clouds for building the diagram is also reduced by 39.78%, which greatly improves the construction speed.
How to select a combination of bands with a good classification effect from an image is a key issue in the task of hyperspectral image classification. Aiming at the above problems, a band selection algorithm based on the separability of single-band image categories and the correlation between bands is proposed. According to the principle of inter-class separability, the mean and standard deviation of all kinds of sample point matrices in single-band images are used to measure the inter-class separability of single-band images. Combined with the correlation coefficient between bands, the band combinations with good inter-class separability and low inter-band correlation are selected. Finally, the images before and after band selection of the proposed algorithm and the images after band selection of the adaptive band selection algorithm are classified by support vector machine. The classification results on Indian Pines and Salinas datasets show that when the number of spectral bands selected is 20 and the classification training set is randomly selected 20 sample points for each type of ground objects, the overall classification accuracy of the proposed algorithm is improved by 7.34 percentage points and 2.96 percentage points respectively compared with the adaptive band selection algorithm.
Point cloud filtering is a necessary step in the application of airborne LiDAR point cloud post-processing. Most existing point cloud filtering methods have a better filtering effect in areas with flat terrain but a poor filtering effect in areas with high terrain fluctuation. To improve the accuracy of point cloud filtering methods and their adaptability to complex environments, this paper proposes a filtering method based on multiconstrained connected graph segmentation. In this paper, three constraint conditions, verticality, height difference, and distance, were set to construct the point cloud connectivity graph to achieve point cloud segmentation, and the ground seed point set was acquired and screened based on the ground coverage rate and the grid elevation. Finally, the ground point set optimization was realized based on the distance between the points and the adjacent ground seed point set. To test the filtering effect, 15 sets of point cloud data published on the website of the International Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS) were used. The experiment results show that the proposed method can produce good filtering results in various terrain environments. Compared with the other four filtering methods, the proposed method has the lowest average total error (5.44% ). In addition, the average type Ⅰ error and the average type Ⅱ error of the proposed method are relatively small, indicating that the proposed method can effectively protect terrain details while removing ground object points.
The extraction method of urban trees based on multisource remote sensing data is of great significance for urban resource investigation, health status evaluation, and scientific management. To further improve the accuracy of tree extraction, this paper combined the advantages of LiDAR and orthophoto data and proposed a tree extraction algorithm based on automatic feature segmentation. This algorithm is used to identify and extract the shadowed regions; the correlation between normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and digital surface models (DSM) local entropy features is used to reduce the background extraction threshold by combining with histogram subtraction. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm, which has been verified using the ISPRS Vaihingen dataset, has a high precision of tree extraction on multiple datasets and is robust to a certain degree, thus being suitable to be used in complex environments.
With the development of optical microscopy, people have been able to observe the microcosm on sub-micron scale, which has played a key role in deciphering the code of life activities. Among them, coherent Raman scattering (CRS) microscopy provides imaging contrast based on molecular specific vibration and enhances the spontaneous Raman scattering signal by several orders through a nonlinear optical process, improving the imaging rate and detection sensitivity. According to different nonlinear optical processes, coherent Raman scattering can be divided into coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS) and stimulated Raman scattering (SRS). Compared with CARS, SRS has the advantages of no non-resonant background interference, quantitative analysis, etc. This article will introduce the basic principles of coherent Raman scattering, and focus on the development and application of stimulated Raman scattering.
Aiming at the effect of multiple scattering under low visibility weather conditions, an improved method is proposed for inverting slant-range visibility based on the multiple scattering lidar equation. First, the semi-analytical Monte Carlo method is used to calculate the ratio m of multiple scattering to single scattering based on the backscattering peak fitting the scattering phase function. Second, using the Collis method, the visibility level value is obtained, and the corresponding m value is substituted into the multiple scattering lidar equation. Then, the Fernald method is used to invert the extinction coefficient and solve the slant-range visibility. Experiments were performed on the echo signals of haze and heavy rain with different visibility levels detected by lidar, and the slant-range visibility results obtained using the fitting method in this paper and the commonly used Henyey-Greenstein (HG) function method were compared. The results show that the slant-range visibility difference is 10.9% under haze conditions and 5.6% under heavy rain conditions. The proposed method improves slant-range visibility accuracy inverted by the backscattering lidar.
To conduct the discriminant analysis of apple origin, red Fuji apples from Aksu, Jingning, Lingbao and Yantai were used as research objects, and the hyperspectral data of apples were collected in the range of 800-1700 nm. First derivative, second derivative, standard normal transform, multivariate scattering correction (MSC), wavelet transform, smoothing transform, and Fourier transform were used to pretreat the original spectral data. The partial least squares discriminant analysis of the linear model and extreme learning machine (ELM) and the support vector basis (SVM) of the nonlinear model were established. The results showed that the MSC pretreatment method was preferable, and the nonlinear model outperformed the linear model. For the spectral data pretreated by MSC, principal component analysis, continuous projection algorithm, and competitive adaptive weighted sampling (CARS) were used to extract the characteristic bands. Thereafter, the ELM and the SVM discriminant analysis models of the apple-producing area were established based on the characteristic bands. The results show that the CARS method performs the best in the terms of extracting characteristic bands. The accuracy rates of the two machine learning algorithms were 98.75% and 100%, respectively, which can serve as a theoretical reference and experimental basis for apple-producing areas discriminant analysis.
Aiming at the problems of slow response speed and high cost faced by linear pipe jacking machine in tunneling guidance, a real-time pose measurement method based on dual camera targets is proposed. The measurement target is composed of two opposite industrial cameras and two photosensitive imaging screens installed in the opposite direction, supplemented by an indicator laser with known spatial orientation information. By using the techniques of spot image analysis and processing, calibration grid retrieval and Euler angle calculation, the proposed method can complete the measurement of horizontal/vertical deviation of machine relative to the planning line in the engineering coordinate system, so as to realize the guidance. The experimental results show that the azimuth repeatability measurement accuracy of the proposed dual camera target is better than 0.03°, the absolute measurement error is less than 0.05° and the horizontal/vertical deviation measurement error is less than 3 mm, which can fully meet the real-time accurate guidance requirements of the linear pipe jacking machine.
To quickly classify and identify common food packaging paper at the scene of the case, a visual inspection method of food packaging paper based on X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (XRF) and deep learning algorithm is proposed. First, the inorganic elements in 44 samples of food packaging paper from different sources were detected via XRF, and artificial classification and cluster analysis were performed based on the content of the main constituent elements. Second, to test the clustering effect and visualize data classification, two-dimensionality reduction algorithms, principal component analysis, and t-distribution random neighborhood embedding are used. Finally, 80% of the samples are randomly selected as the training set to construct the artificial neural network , and relevant experiments are carried out. The experimental results show that classification accuracy of the proposed method on the test set is 88.9%, which can be used as a reference for future practical applications of public security business.