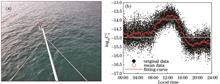
We used a microtemperature sensor to measure the atmospheric refractive index structure constant Cn2 of near sea-surface and combined ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) to obtain the intrinsic mode function (IMF) component with different time scales. Furthermore, the analysis of the IMFs’ periods indicates that their mean periods have a high correlation of natural exponential function. Thus, we can derive the space characters based on the ergodicity property of atmospheric turbulence. The result of the Hilbert transform for the IMF component shows the different scale fluctuations near the center frequency of each IMF. Additionally, we can obtain the Hilbert-Huang transform marginal spectrum of conventional meteorological elements and Cn2, and the results indicate that it is superior to the traditional fast-Fourier transform (FFT) in reflecting spectral distribution characteristics of optical turbulence. Further, we analyze the relationship between the Cn2 and conventional meteorological elements under different atmospheric stratification. From above, we can learn more about the space-time characters of near sea-surface optical turbulence, and the study results will provide some references for laser propagation in the marine atmosphere.
In this paper, a multilayer holographic flat waveguide display system has been proposed to realize the full-color display function of the augmented reality head-mounted display system. Furthermore, the diffraction principle, grating constant, and corresponding diffraction wavelength are investigated. First, the grating equation and total reflection theory were used to introduce the limiting relationship between the coupling grating constant and the transmitted light wavelength of the holographic planar waveguide. Second, to realize pupil expansion, the restrictive relationship between turning, out-coupling, and in-coupling gratings were applied. Third, the single-layer holographic flat waveguide display structure for 550-nm green light was simulated and designed. Next, based on the single-layer holographic planar waveguide, a three-layer holographic planar waveguide display system with 685 nm, 550 nm, and 437 nm as the three primary colors was established. Finally, the light output effect of three-layer holographic planar waveguide processing samples was examined using digital light processing projection system as a light source. The experimental results show that the three-layer holographic planar waveguide realized pupil expansion and panchromatic display. Moreover, multilayer holographic planar waveguide realized a full-color display of an augmented reality head-mounted display system.
Aiming at the problems that the edges of the targets object are blurred and the details are lost in the fusion process of infrared and visible images, an infrared and visible image fusion method based on rolling guidance filter (RGF) and convolution sparse representation (CSR) is proposed. First, RGF and Gaussian filter are used to decompose the matched source images. Second, aiming at the base layers, the comparison saliency map and weight matrix are constructed to fuse. Thereafter, aiming at the detail layers, the alternating direction multiplier method (ADMM) is used to solve the convolution sparse coefficients and the feature response coefficients are fused using CSR fusion rule. Finally, the graph of the fusion result is rebuilt. The experimental results show that the proposed method can avoid losing the details caused by blurring at the edge of the objects, preserve the contrast and the edge texture information of the source images, and improve the objective evaluation indexes.
It has been theoretically proven that dehazing models can effectively solve image exposure correction. To solve the abnormal exposure in a single image, we improved the transmittance in the dehazing model and proposed an image exposure correction method using the inversion fusion framework. First, we performed haze modeling for the overexposed high-intensity light source in the local area. Thereafter, we used the improved dehazing model to complete the overexposure correction task. For the underexposure correction problem, we obtained the pseudo-haze image using the inversion operation. The underexposure correction result image was obtained by combining the dehazing model and duality formula between the Retinex theory and dehazing method. Finally, we generated a new pyramid weight map using multiscale image fusion technology, and the final correction result was obtained via Laplacian pyramid reconstruction. Furthermore, we compared the proposed method with four mainstream image correction methods. The experimental results show that the proposed method corrects the abnormal exposure areas of a single image and minimizes the interference image distortion and halo artifacts.
Accurate and stable image feature extraction is of great significance to computer vision applications such as image stitching, 3D reconstruction, and feature-based visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM). In the nuclear radiation environment, the captured images have the problems such as many noise points, large noise blocks and the noises are easy to identify as features through the traditional feature extraction methods. An against nuclear feature (ANF) extraction algorithm is proposed based on the noise distribution characteristics of the γ rays affected images which is collected by the source blockage failure of an irradiation factory. Firstly, the red, green, blue (RGB) characteristics and grayscale characteristics of each pixel in the image under nuclear radiation are analyzed to obtain the pixels which are suspected as noise points. Then, the features are extracted by the traditional feature extraction algorithm. Finally, the Euclidean distances between the features and the suspected noise points are used to sort and filter the features, and the features which are suspected as noises with high probability are eliminated. The experiments based on the standard image data set combined noises and collected images in the real nuclear radiation environment show that the ANF method is more stable than the traditional features from accelerated segment test (FAST) method and binary robust invariant scalable keypoints (BRISK) method in extracting features, and can improve the effect of feature extraction and reduce the matching error rate.
There is a type of weak and imperceptible adversarial perturbation, which can change the output of a deep neural network in computer vision tasks such as image classification. A defense algorithm against adversarial attacks based on low-rank dimensionality reduction and sparse reconstruction is proposed to target adversarial perturbation in image classification. Because digital images are low-rank and sparse, the proposed algorithm uses low-rank decomposition to reduce adversarial perturbation. The low-rank approximated image is then subjected to multiscale sparse coding to remove residual perturbation and restore the original image’s rich textural details. Three attack algorithms are used to compare the proposed algorithm’s defense effect against the other four defense algorithms under black-box and gray-box attacks. The results show that the proposed algorithm processes adversarial images with the highest Top-1 accuracy of image classification compared to comparative algorithms and that the proposed algorithm is more robust.
The pixel-level sea-land segmentation of remote sensing images is a basic work for coastline extraction. Owing to the dynamic changes in the coastline, obtaining accurate coastline marker datasets is difficult. In this study, Google Aerial Photo-Maps-paired samples were used to construct a paired dataset after the sea-land binarization processing of Google Maps. Thus, we proposed the dual attention mechanism-cycle generative adversarial network (CycleGAN) based on the CycleGAN model to solve the problem of fewer samples in the new dataset. The new model fully considers the structural similarity between remote sensing images and sea-land binarized images, improves cycle consistency loss, and designs both channel and spatial attention modules to highlight salient features and regions to enhance the model’s performance in small feature learning ability under sample training. Furthermore, we applied three evaluation indicators, i.e., mean square error, mean pixel accuracy, and mean intersection over union (MIoU), and compared our experimental results to those of the full convolutional neural network and DeepLab models under multiple-scale dataset training. Results show that the improved model conversion of the sea-land binarized images is more consistent with the true value images and the MIoU values are increased by at least 7% and 6%, respectively, verifying the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method.
Aiming at the difficulties and challenges caused by the irregularity, disorder and sparsity to point cloud analysis, a point cloud analysis method that combines local information extraction and global feature reasoning is proposed. First, in order to group local points more effectively, the structure-aware K nearest neighbor (KNN) is used to search for local neighborhood points. Secondly, a feature negative feedback convolution module is improved based on edge convolution to extract more accurate local features in the mapped high-dimensional space. In addition, a global semantic reasoning module based on the attention mechanism is designed to avoid potential information redundancy by emphasizing the grouping point of different regions, so as to obtain point cloud features more comprehensively. Through tested on the public point cloud data sets ModelNet40 and ShapeNet, the overall classification accuracy and overall mean intersection over union (mIou) of the proposed method reach 93.8% and 86.4%, respectively. Quantitative evaluation indicators and qualitative visualization experiments prove the accuracy and robustness of the proposed method.
Excessive noise point cloud in photon-counting lidar data severely restricts the practical application of photon radar. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a denoising method for the detection system of push-broom photon radar and the characteristics of photon point cloud data distribution. First, we set the density threshold based on the spatial distribution of the point cloud dataset for rough denoising. Then, we calculated the slope of the detection laser beam to classify the remaining data into different intervals. Next, we combined the maximum density point to set the distance threshold for further denoising each interval. Finally, we used statistical filtering for the final denoising of some intervals. The experimental results show that the target point cloud recognition rate of the proposed method reaches 98.2% in the test area and the denoising rate reaches 93.8%. Thus, the proposed method can remove the noise point cloud in the photon data effectively and retain the signal point cloud relatively completely.
Current printed circuit board (PCB) image-denoising algorithms can easily produce excessive edge smoothing and detail loss in the denoising process. To improve the effect of PCB image denoising, this paper proposes a PCB image-denoising algorithm based on residual learning and image difference. First, an image downsampling method is used to expand the receptive field of the image based on the idea of residual learning. Thereafter, a residual block is designed to extract the noise characteristics of the PCB image. Meanwhile, batch normalization and ReLU activation function are added to the residual convolutional neural network element to improve the denoising efficiency. Finally, the noise is removed through the image difference process. The experimental denoising performance of various algorithms is compared under different noise levels and the results show that the algorithm proposed in this paper has better performance than other algorithms in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR) and structural similarity (SSIM).
Large-scale hyperspectral image clustering algorithms are widely used in the field of remote sensing, including K-means clustering and spectral clustering algorithms. However, the spectral clustering algorithm still has its limitations. Because of its high computational complexity, it is not suitable for large-scale problems. The spectral clustering algorithm based on the anchor graph can reduce the computational cost to a certain extent. However, in the large-scale hyperspectral image data processsing, the anchor points need to be dense enough, otherwise reasonable accuracy cannot be obtained. This makes the computing cost of the clustering algorithm increase sharply. In order to overcome these problems, a new fast spectral clustering algorithm based on multi-layer bipartite graph is proposed. Firstly, the anchor points are selected by the binary tree,and the multi-layer anchor points are selected to construct the multi-layer anchor point graph. Then a multi-layer bipartite graph is constructed, and finally the spectrum of the graph is analyzed. The high efficiency of the proposed algorithm is proved by experiments.
Aiming at the problems of difficult registration and long registration time of existing power equipment infrared and visible images, a registration method for power equipment infrared and visible images based on improved curvature scale space (CSS) algorithm is proposed. Firstly, the Freeman chain code difference is introduced to improve the feature point extraction accuracy of the CSS algorithm; Secondly, each feature point is assigned the main direction of the vertical distance from the point to the string, and the feature description operator is obtained using the speed up robust features (SURF) algorithm; Finally, the two-sided fast library for approximate nearest neighbors (FLANN) search matching and random sample consensus (RANSAC) method are used to obtain the correct matching point pair, and the affine transformation model parameters are obtained. The experimental results show that compared with the SURF, scale invariant feature transform (SIFT), and CSS registration methods, the improved CSS image registration method has significantly improved performance indicators and its average root mean square error (RMSE) is reduced by 77.73%, 80.32% and 7.63% and its average matching time is reduced by 30.82%, 40.12% and 10.57%, respectively. It improves the registration efficiency of the power equipment infrared and visible images.
In order to solve the problem of complex background in remote sensing images and the large variation of aircraft target size, a new algorithm for remote sensing aircraft detection based on the smooth label and multipath aggregation network is proposed. Considering the difficulty of aircraft target identification in remote sensing images, an associative attention mechanism is used to capture the target area and narrow the search range. Then, the improved path aggregation network is used to extract the four feature layers in the backbone network, so as to effectively extract the shallow feature information. When the features of each layer are normalized, they are fused to predict the position of the target. In order to avoid the training model relying too much on the prediction labels, resulting in over fitting, technology for the smooth label is used in the network to reduce the inter-class distance, which effectively improves the generalization ability of the training model. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified by a large number of experiments on two public data sets RSOD and HRRSD. The experimental results show that the average accuracy in the RSOD data set and the HRRSD data set is 0.967 and 0.993 respectively. Compared with the related algorithms, the detection accuracy of the proposed algorithm has been significantly improved.
An image feature point matching algorithm based on the oriented fast and rotated brief (ORB) algorithm and hue, saturation and value (HSV) is proposed and the experimental research is carried out. Firstly, the image is preprocessed by the combination of bilateral filtering and mean filtering. Secondly, the ORB algorithm is used to extract feature points. Thirdly, the K-D Tree algorithm and Hamming distance are used for matching of feature points roughly, and then the HSV information of the image are used for the secondary screening of matched feature point pairs. The experimental results show that, in the image preprocessing stage, the weighted average of variance, vollath and information entropy is used as the evaluation index, and compared with the original image, histogram equalization and bilateral filtering results, the evaluation index value obtained by the combination of bilateral filtering and mean filtering is the best. In the stage of feature point matching and image mosaic, the average matching correct rate of feature points is improved by 12.60 percentage points after using HSV information, and the quality of image mosaic result is better, as its natural image quality evaluation (NIQE) index value is smaller.
The existing tracking algorithms for network modulation ignore high order feature information, so they are prone to drift when dealing with large scale changes and object deformations. An object tracking algorithm that combines the attention mechanism and feature fusion network modulation is proposed. First, an efficient selective kernel attention module is embedded in the feature extraction backbone network, so that the network pays more attention to the extraction of target feature information; second, a multiscale interactive network is used for the extracted features to fully mine the multiscale information in the layer, and high order feature information is fused to improve the ability of target representation, to adapt to the complex and changeable environment in the tracking process; finally, the pyramid modulation network is used to guide the test branch to learn the optimal intersection over union prediction to achieve an accurate estimation of the targets. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves more competitive results than other algorithms in tracking accuracy and success rate on VOT2018, OTB100, GOT10k, TrackingNet, and LaSOT visual tracking benchmarks.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has outstanding soft-tissue contrast and provides unparalleled benefits in various diagnoses. It is an important way of observation in current clinical practice. The scanning period of an MRI, however, is long, which greatly limits the diagnostic efficiency. Obtaining undersampled K-space data through partial scanning at a specific acceleration magnification is a critical approach to save scanning time. Existing approaches only rebuild the K-domain or the image domain alone or alternately process the two domains through serially coupled image domain and K-domain convolution, resulting in poor reconstruction performance. A dual-domain parallel codec structure that processes image domain and K-domain data simultaneously is presented to provide high-quality reconstruction of undersampled K-space data at high acceleration rates. The proposed technique reconstructs the undersampled image domain and K-domain data using two parallel codec networks, respectively, then combines the features of the K-domain branch into the image domain using the inverse Fourier transform, considerably enhancing reconstruction quality. For presampling data with varying acceleration magnifications, experimental results reveal that the proposed method outperforms other U-Net-based image reconstruction methods. This proposed method is projected to develop into a high-performance, high-acceleration-magnification MRI undersampling data reconstruction method that can be used in clinical MRI reconstruction.
The image segmentation method using division-combination mitigates the limitations of the traditional pixel-based remote sensing image segmentation algorithm, such as noise interference, low segmentation efficiency, and poor segmentation effect. Thus, this paper proposes a new split-merge-based remote sensing image segmentation method using the super-pixel and dot product representation of graphs. First, the image is divided into super-pixels using the simple linear iterative clustering (SLIC) algorithm. Second, the texture feature of each super-pixel area is measured and distance between any two areas is calculated with respect to spatial proximity. Third, each super-pixel area is mapped as a vertex of the graph. Therefore, the dot product representation of graphs is modified and used to construct a similarity matrix; thereafter, all vertices (i.e., super-pixel areas) are mapped as new vectors clustered by angular-based k-means algorithm to get the final segmentation results. The experimental results show that the proposed method has stable segmentation results, improves the accuracy of the segmentation, and achieves a better visual segmentation effect.
Deep learning technology is proposed to solve the social problem of the frequent occurrences of wild mushroom poisoning in China. However, due to the small difference between classes and complex image backgrounds, fine-grained recognition accuracy is low. To solve this problem, this paper proposes an improved ResNeXt50 network. First, a multiscale feature guide (MSFG) module is designed, which guides the network to learn and use low and high-level features fully through short connections. Then, the improved attention mechanism module is used to reduce the network’s learning for complex backgrounds. Finally, the different hierarchical features in the model are fused, and the obtained joint features are used for recognition. Experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed network on the test set can reach 96.47%, which is 2.64 percentage points higher than the unimproved ResNeXt50 network. Comparison results show that the accuracy of the improved network model is 8.10 percentage points, 5.13 percentage points, 3.24 percentage points, 3.30 percentage points, and 4.25 percentage points better than VGG19, DenseNet121, Inception_v3, ResNet50, and ShuffleNet_v2, respectively.
Point clouds, unlike images represented by dense grids, are characterized by irregularity and disorder, making it difficult to precisely reason out the shape features in point cloud data. The internal-external shape son volution for point sets (IE-Conv) is proposed to address the limitations of current research. The local shape inside the point set is treated separately from the global shape outside the point set using an efficient bilateral design. Rich inter-point relationships are selectively studied in a gate-based manner within the point set, while point-by-point and local features are optimized by self-calibration functions; outside the point set, global shapes are constructed using graph convolution and focus on long-range dependencies between point sets. Finally, the organic fusion of the bilateral outputs is performed. This paper performs classification and segmentation experiments on the standard ModelNet40 and ShapeNet datasets by hierarchically embedding IE-Conv into the shape-reasoning convolutional network (SR-Net). The experimental results show that the classification task achieves an accuracy of 93.9% and the segmentation task achieves the mean intersection over the union of 86.4%, which verifies the good performance of SR-Net in point cloud analysis.
Some fundamental problems such as weak stability of feature points, uneven distribution, and poor matching quality arise in the matching process of heterogeneous images owing to the difference in the field of view of the image to be matched and the nonlinear difference in pixel gray. To mitigate these issues, an image feature point matching algorithm based on scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm is proposed herein. First, in the feature point detection, the weight coefficient was set in the scale space and the grid was set for each layer of images. Combined with the phase response intensity map of the image, the evenly distributed and stable feature points were selected using the quadtree method. Second, the descriptor was reconstructed and the normalized Euclidean distance was used to measure the feature descriptor instead of Euclidean distance. Furthermore, a two-way matching strategy was used for rough matching. Finally, the random sample consensus (RANSAC) algorithm was used for purification. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can extract reliable and stable features between heterogeneous images and improve the accuracy of feature point matching.
When stitching images with weak contrast, there will be a few matching feature points distributed on the images to be stitched because of poor contrast and other factors and the image registration error will be high. To address this problem and improve the quality of image stitching, this study proposes an image stitching algorithm based on contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) and improved zero-mean normalized cross-correlation (ZNCC). Before feature point extraction, we use the CLAHE algorithm to preprocess the weak contrast image for enhancing the image contrast, which increases number of matching points. Thereafter, the improved ZNCC algorithm combined with the main direction of the gradient of feature points is used to filter feature points, which improves the correct matching rate of feature points. Finally, we use the filtered feature points to calculate the transformation matrix and complete the image stitching. The experimental results indicate that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm increases number of correct matching points by approximately 25% in the weak contrast image and reduces the false matching rate by 0.5 percentage points?3 percentage points compared with the SIFT algorithm, effectively improving the image registration accuracy, reducing the registration ghosting, and optimizing the image mosaic results.
The study and the protection of movable cultural relics is important in accurately and efficiently obtaining their three-dimensional (3D) digital files and shaping parameters. The accurate and efficient reconstruction can be achieved when the proportion of matching points is approximately 50% in the multiview geometric, 3D reconstruction. This conclusion can effectively guide the collection of image sequences based on multiview geometric, 3D reconstruction. The point cloud noise due to the reconstruction is filtered out in HSV color feature space. Furthermore, the detection algorithm removes the outlier based on the standard deviation threshold, which effectively improves the accuracy and the visual effect of the 3D reconstruction. After 3D reconstruction, directed bounding box algorithm is used to calculate the shape parameters of movable cultural relics. In addition, the weighted principal component analysis (PCA) based on the density of the point cloud is used to compute the main direction of the bounding box. The proposed method was used to determine the repeatability standard deviation of shape parameter values for a porcelain vase imitation from the Yuan Dynasty. The repeatability standard deviation was less than 0.15 mm, and the maximum measurement error was less than 0.25 mm, which is higher than the measurement requirements of the shape parameters in the protection and the research of movable cultural relics.
The presence of rain patterns in an image increases the difficulty of target detection and recognition. Rain patterns are the high-frequency parts of the image, which contain several image details. However, a major challenge is in removing the rain pattern while retaining useful details. Thus, we proposed a method based on a multiscale convolutional neural network developed using multilevel and multiattention mechanisms. To avoid the suboptimal effect of rain removal caused by preprocessing, we simulated the imaging process of objects in real scenes, improved the general image restoration model, enriched the network’s receptive field range, and accurately removed rain while enhancing contrast. Furthermore, we extract multiscale feature maps from the network branch using a multiconvolution feature jump connection to compensate for the loss of detailed information in the convolution process and fusion of different levels of feature information. Additionally, we combined attention to form multiple multiscale residual attention submodules to recalibrate the global information in the channel dimension, removing redundancy while enhancing useful information and the primary and advanced features were fused to learn the mapping relationship between the rain and no-rain maps. Considering that the real rain map has no corresponding rain-free map, we used a synthetic dataset for training, and used the synthetic dataset and real scene graphs for verification. The experimental results show that our proposed network achieved a good rain removal effect while retaining detailed information irrespective of the size and density of the rain pattern.
To solve the problem that the Tiny YOLOv4 target detection algorithm has low accuracy and low recall rate in pedestrian detection, the feature extraction network and prediction network are improved. In the part of feature extraction network, the traditional convolution network is replaced by a depthwise separable convolution network to reduce parameters and computation. The attention mechanism module is added in the feature extraction network to enhance the area of interest of detecting object and improve the detection accuracy. A prediction scale is added in the prediction network, and the added scale is enhanced by features to improve the recall of detection of objects. The experimental results show that compared with the original algorithm, the improved Tiny YOLOv4 algorithm improves the accuracy by 7.1%, and the recall rate also increases by 6.6%.
In the target tracking sequences, it is difficult to identify the target because of the complex background and large-scale changes of the target. To solve this problem, a target tracking algorithm based on feature optimization model in the Siamese network is proposed. First, the deep network is constructed to extract the deep semantic information effectively. Then, the hourglass network is used to encode the global features of the multi-scale feature map, and the encoded features are normalized to obtain the effective target features. Finally, a feature optimization model is constructed, and the features obtained by decoding are used as selectors to identify and enhance the effective features of the original feature map. In order to further improve the generalization ability of the model, the attention mechanism is introduced to adaptively weigh the target features to adapt to the scene changes. The proposed algorithm is tested on two standard tracking data sets including OTB100 and VOT2018. The success rate in the OTB100 is 0.648, the prediction accuracy is 0.853, and the real-time performance is 59.5 frame/s; the test accuracy in the VOT2018 is 0.536, the expected average coverage rate is 0.192, and the real-time performance is 44.3 frame/s. The test results prove the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
Multiobject tracking algorithms are frequently affected by the problem of the exchange of pedestrian identity in real congestion situations. To solve this problem, this study proposes a joint network that integrates target detection and person reidentification. Additionally, a track scoring mechanism is introduced to integrate the reidentified feature and time information. By collecting candidates from the detection results and tracking prediction results, the tracking prediction information and reidentified feature information of pedestrian targets can complement each other. To solve the problem of detecting small targets in video images, this study improves the ResNet-34 network by combining the deep aggregation network on the backbone network and replacing the traditional residual block with a multiscale convolutional network to focus on small targets and improve the detection accuracy. In this study, experiments were conducted on the multiobject tracking datasets MOT16, MOT17, and MOT20. The corresponding multiple object tracking accuracy (MOTA) of the proposed network reaches 74.7, 73.7, and 66.4, respectively, and the conversion durations of pedestrian identity are 210, 209, and 1403, respectively. The results reveal that the proposed network has good detection and tracking performances.
To address issues such as position and shape uncertainty in pavement crack detection, as well as similarity between crack features and pavement background texture, an improved crack image segmentation algorithm based on multibranch feature shared structure network is proposed. To improve the detection accuracy while reducing the redundancy of computational parameters, a lightweight feature extraction network is used to acquire high level features, and the multibranch hopping connection method is employed to improve the information utilization between channels. Each branch combines the global convolution network (GCN) module and the boundary refinement (BR) module to improve crack edge segmentation and classification robustness within the crack region, and it employs the recurrent residual convolution (RRC) module to drive crack feature accumulation. Furthermore, the crack morphological parameters are calculated using the median-axis method to extract the crack skeleton, and relative errors of the crack length and width are 4.73% and 5.21%, respectively. The results of multiple datasets of designed comparison experiments show that the proposed improved algorithm can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of pavement crack detection.
The key components of the train are essential for ensuring the safe operation of the train. The current detection algorithm based on deep learning has poor detectability under poor lighting conditions and small component size. To solve this problem, this study proposes a detection algorithm for key components of a train based on improved RetinaNet. First, a receptive field block module was introduced after shallow feature P3 to improve the receptive field and feature quality of the P3 feature layer. Then, the feature pyramid network was replaced with a pixel aggregation net and the positioning ability of the feature pyramid was enhanced by adding a bottom-up feature fusion path. Finally, by adjusting the experimental parameters and the location of the network detection layer, a network model suitable for detecting key components of the train was obtained. Results show that the proposed model is superior to the original RetinaNet in the open dataset PASCAL VOC. Furthermore, it is superior to the current mainstream algorithm in detecting the key components of the train.
Because the circular weld in the pipeline lacks point and straight-line features, research to automatically locate the welds in the pipeline using a monocular vision nondestructive testing robot is still challenging. The localization of positive circular welds under the influence of the robot’s left and right swings is investigated in this paper. The governing equation of the special simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) problem for locating the distance between the positive circular weld and the inspection robot is established using the geometric imaging model of the circular weld in the inspection robot camera and the robot’s motion speed. The problem of solving the governing equation is transformed into a loss function minimization optimization problem. As the optimization problem is highly nonlinear, this paper employs a genetic algorithm to solve it and achieves the positive annular weld location while the robot swings from side to side. Using the synthetic video of the robot detecting the circular weld in the cylindrical pipe and the video captured during the actual operation, experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve good results.
In this paper, we propose a high-precision automatic segmentation method for foreign body defects in high-precision small-field TFT-LCD images to segment TFT-LCD foreign body defects and calculate their size accurately, meeting the requirements of foreign matter defect detection in TFT-LCD industrial production. First, using the spatial distribution of screen pixels and considering the dimensional change of defects, we employ the defect extraction method based on spatial information multiscale saliency detection to automatically obtain the defect areas on the image. Next, combining the spatial distribution relationship between the defects and the gap of screen pixels, the corresponding defect block group truncated by pixel gap is found. Finally, a local convex hull fitting algorithm is used to connect the defect areas to realize automatic segmentation for foreign body defects. Experimental results show that the proposed method can segment foreign body defects more accurately, attaining the accuracy and recall rate of 95.36% and 93.34%, respectively. Furthermore, it obtains the correct size calculation rate of 96.5%, which meets the requirements of TFT-LCD foreign body defect size calculation in industrial production stability, reliability, high precision, high accuracy, and other requirements.
To address the problems of occlusion and postural change in pedestrian reidentification and the low identification rate of current networks, a multibranch pedestrian reidentification network model with different spatial dimensions is proposed. First, IBN-Net50-a serves as the backbone network to extract features. Second, the last two convolution layers are fused with the batch feature-discarding method to enhance the local focal feature learning. Finally, features with different dimensions can be combined to obtain additional valuable information at both the shallow and deep levels. The combined strategy of triplet loss and label smoothing losse is adopted in network training. Further, three commonly used benchmark datasets, Market-1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and CUHK03, are used for experimental verification; the datasets are divided based on the mainstream strategy. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves an effective feature generalization capability. On the Market1501, DukeMTMC-reID, and CUHK03 datasets, Rank-1 and mean average precision (mAP) values of 95.3% and 86.8%, 88.5% and 75.9%, and 80.9% and 77.8%, respectively, are achieved.
To improve the accuracy of light stripe segmentation in the traditional vision measurement system based on line-structured light, an improved light stripe segmentation algorithm based on U-Net is proposed. The proposed algorithm uses the convolution pooling layer of VGG16 instead of that in the U-Net coding block, introduces the coordinate attention mechanism in the hop connection between U-Net coding and decoding layers, and connects the pyramid pooling module at the end of U-Net coding block. Additionally, it uses a combination of Dice function and cross entropy function as the loss function of the network, so as to solve the problem of imbalance of light stripe proportion. Based on the principle of line-structured light measurement, a workpiece size measurement system is designed. Experimental results show that the mean pixel accuracy (mpa) of the improved U-Net algorithm is 95.61% and mean intersection over union (mIoU) is 89.73%, which are higher than other comparison algorithms. The absolute error of workpiece measurement size is less than 0.1 mm, the relative error is less than 1%, and the repetition accuracy is less than 0.2%, meeting the inspection requirements of the workpiece.
To address the issue that there are many characteristics influencing the stray current of a subway track, the conventional feature selection method affects the prediction accuracy of the model, and the interpretability of the model results is poor, this paper proposes a stray current prediction model based on optimal feature improved eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost). Using the flexibility and the strong searchability of the genetic algorithm, we found the first M features that minimizing the mean square error (MSE) of the objective function generation by generation in the set containing the original V features. Simultaneously, the stray current prediction model under the optimal feature selection method (OFS-XGBoost) is established. To address the issue that the prediction results of the OFS-XGBoost are good, however, the machine learning black-box model has an insufficient explanatory ability for the prediction results, an attribution analysis framework based on SHAP theory is proposed to show the influence of feature set on the prediction results of the model in an understandable way based on the marginal contribution of stray current feature samples to improve the inference accuracy. The results show that the prediction error of the proposed model is only 1.684%, which is lower than the prediction models such as random forest and back propagation (BP) neural network under the same optimization strategy. The attribution analysis method based on SHAP value explains the impact of input characteristics on stray current prediction results from a global and individual perspective, helping intelligent subway health management based on improving model interpretability.
In order to realize the fast recognition of charging target in the process of long-distance charging of flying unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) by laser, an improved Yolov3 algorithm is proposed. The lightweight network model is used as the feature extraction network to realize the accurate and fast recognition of charging UAV target by laser launching system. Compared with the original Yolov3 network, the average detection speed is increased from 17 frame/s to 33 frame/s, and the weight of network model is reduced from 236.0 MB to 29.7 MB, which greatly reduces the dependence of Yolov3 model on hardware. The research results show that the improved algorithm has high accuracy and real-time performance, which provides a valuable technical means for real-time remote charging of UAV by laser.
Abnormal state detection of mechanical equipment based on acoustic diagnosis is of great significance in the field of industrial automation. At present,unsupervised abnormal sound detection of mechanical equipment is mainly based on artificial construction algorithms to extract sound signal features, and then use these features for further anomaly detection, which is greatly influenced by the human factors and the lack of universality of the artificial extraction method. To solve these problems, a new feature extraction method based on self-supervised learning is proposed, and the feature is input into the autoencoder (AE) for abnormal sound detection of mechanical equipment. In this method, the sound sample is firstly converted into a time-frequency spectrum, and the time-frequency spectrum of the normal equipment is used as the training sample, then the self-supervised feature extractor (SSFE) is constructed by using the normal time-frequency spectrum and the artificially constructed abnormal time-frequency spectrum. AE is trained by the features of normal samples extracted by SSFE to realize abnormal sound recognition of the unsupervised mechanical equipment. Experiments are carried out with MIMII open data set, and the results show that the proposed method can adaptively extract the sound features of four kinds of mechanical equipment, including fans, pumps, sliders and valves. The average area under curve (AUC) result obtained by the proposed method is 88.5%, which is significantly improved compared with those of the artificial feature extraction methods such as linear sonogram, logarithmic Mel spectrum, and Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients.
The cultural heritage field has developed rapidly based on the use of digital technologies for protecting cultural relics. The point cloud data of cultural relics obtained using three-dimensional laser scanning equipment inevitably contain considerable noise, which directly affects the subsequent processing of the point cloud data. To effectively remove noise points from the disordered point cloud and ensure enhanced recover of point cloud data, a new point cloud denoising algorithm based on the unsupervised network was proposed. First, the outliers are classified and removed from the upper network. Then, a spatial prior term was introduced to guide the data points in the noise cloud to converge to the optimal mode closest to the real point cloud in the multimode on the manifold, enabling the distribution of clean point cloud from the point cloud data of outlier noise points; moreover, the unsupervised denoising of the fine point cloud was realized. Finally, the chamfer distance between the denoised point clouds was estimated for quantitative evaluations. Compared with some classic algorithms, the proposed algorithm can effectively maintain the geometric characteristics of the point cloud model during denoising, and shows a good denoising effect on the point cloud data of cultural relics. The denoised point cloud model considerably restores the original clean point cloud model, which is crucial for the follow-up link of the digital protection of cultural relics.
In this paper, we propose the construction of an extended YOLOv5 model using the infrared camera image datasets of five species to achieve the automatic recognition of massive wild animal images in real-time, accuracy on resource-limited platforms such as infrared cameras. Furthermore, we improve the negative load and low timeliness of data transmission in wildlife monitoring. Here, the dataset constructed is used to train four network structures, namely, YOLOv5s, YOLOv5m, YOLOv5l, and YOLOv5x. By comparing the accuracy, detection speed, and volume of different network structures, the optimal network structure was determined. Simultaneously, we analyzed the recognition effect of the model under the interference of complex background information to evaluate the applicability of YOLOv5 in real-field scenes. Compared with similar algorithms, the advantages of YOLOv5 for wildlife recognition outweighed others. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of the four network structures was high. Moreover, F1-score and average accuracy (mAP) were more than 90%, and the comprehensive performance of YOLOv5m was the best. However, YOLOv5 still has a good recognition effect under the interference of several complex background information and can adapt to real-field scenes. Compared with other algorithms, YOLOv5 has the advantages of high precision, strong robustness, and low resource occupation. It is a lightweight model with superior performance, which provides a new opportunity for real-time wildlife identification on resource-constrained platforms.
To address the localization and the detection accuracy problems of the Faster R-CNN target-detection algorithm, a movable attention (MA) model that can be embedded in the algorithm and trained end-to-end is designed. First, to obtain more accurate spatial location information, MA uses two adaptive maximum pooling operations to aggregate features based on the horizontal and the vertical directions of the input feature and generates two independent directional-sensing feature maps. Second, to prevent model overfitting, the sigmoid activation function is used to increase network nonlinearity. Finally, to fully exploit the obtained spatial location information, the two nonlinear and input feature maps are multiplied successively to enhance the representational ability of the latter. The experimental results show that the improved Faster R-CNN target-detection algorithm based on MA can effectively enhance the network’s ability to locate the target of interest, as well as considerably improve the average detection accuracy.
With the popularization of nonmilitary unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), UAV-detection technology has become a hotspot in security research. This study proposes a low-altitude UAV-detection and -tracking method based on the optimized YOLOv4. This method combines detection technology based on convolutional neural networks with a tracking algorithm for the first time to achieve dynamic detection of low-altitude UAVs. First, the original YOLO network structure is optimized based on multiscale feature fusion. Thereafter, in combination with the DeepSORT multitarget tracking algorithm, the detection and tracking model is constructed. Training and comparative experiments are performed on the self-built LARotorcraft dataset. The experimental results show that the proposed model can effectively reduce the miss detection rate for small targets. Good real-time performance is obtained with an average detection accuracy of up to 77.2%, and stable tracking of visual targets is realized.
An algorithm of multimatching model estimation is proposed for the problem of outliers removed from nonrigid matching images. First, considering the high probability of outlier ratio in the matched point set, the inlier ratio promotion based on the consensus of the distribution of neighbor inliers was applied. Second, to reduce the influence of the inlier distance error threshold on the inlier extraction, a multimodel estimation was applied using the inlier distance error marginalization. Finally, considering the probability of residual outliers in the extracted inlier set, residual outliers were removed based on the consensus of the direction of the matching point position change vector. In the experiments, the proposed method is compared with MAGSAC, NM-NET, P-NAPSAC, SC-RANSAC, Adalam, OANET, SuperGlue, PEARL, Multi-H, Multi-X, and CONSAC, etc. Results indicate over 30% reduction in the inlier distance error, 50% reduction in the outlier residual rate, 8% increase in the recall of inlier, 10% reduction in the running time, and 16% reduction in the misclassification rate of multiplanar estimation.
Aiming at the problems of low detection accuracy resulting from insufficient feature extraction and inaccurate detection box positioning in the Faster R-CNN algorithm, an object detection algorithm based on multiscale feature fusion and anchor adaptation is proposed. First, the high- and low-level features between adjacent levels were fully extracted using the two-way fusion method; then, the multiscale features were balanced so that the integrated features could obtain the same amount of semantic information and detailed information with different resolutions, improving the object recognition ability. Finally, the anchor was generated by adaptively predicting the position and shape of the anchor using the characteristic information of the object in the region proposals network(RPN). The experimental results of the algorithm based on VOC dataset show that compared with the Faster R-CNN algorithm based on ResNet50, the multiscale feature fusion strategy in the proposed algorithm strengthens the detection ability for objects with different scales. The adaptive anchor mechanism can improve the positioning accuracy and avoid missed detection of small objects, and the overall detection results of the proposed algorithm have good performances. The proposed algorithm improves the average detection accuracy by approximately 3.20 percentage points.
Liver segmentation is an important step in computer-aided diagnosis, treatment and surgery of liver diseases. A liver segmentation method based on spatial fuzzy C-means and graph cuts is proposed. Firstly, in order to remove the influence of adjacent organs and tissues on liver segmentation, the spine and ribs are removed from original CT images by thresholding, projection method and 3D region growing, and the right kidney is removed by K-means and binary morphological reconstruction method. Then, liver is segmented by spatial fuzzy C-means from the initial liver slice. The remaining slices are segmented iteratively by graph cuts based on the spatial, shape and gray scale characteristics of CT volumes. Finally, the inferior vena cava is removed by morphological operations and anatomical knowledge. The experimental results show that the proposed method can obtain better segmentation performance than those of other similar methods.
To address the problems of low accuracy, slow convergence, and poor stability in using the back-propagation (BP) neural network for inverse modeling of dual band-notched ultra-wideband filters, this paper proposes an approach to optimizing inverse modeling based on the BP neural network with an improved ant lion optimization (IALO) algorithm and the Huber function. This method improves the ant lion optimization algorithm by serializing the boundary contraction factor, introducing dynamic update coefficients, and adding the Cauchy mutation. Then, the IALO algorithm is applied to optimize the weights of the forward model and thereby speed up the modeling. Subsequently, the Huber function is used to evaluate the neural network. The accuracy and stability of the model are thus improved. This method is used for a double band-notched ultra-wideband filter. Experimental results show that compared with BP inverse modeling, the proposed method reduces the length, width, and frequency mean square errors by 97.44%, 99.43%, and 96.15%, respectively, and shortens the average running time by 66.01%. The multi-solution problem of inverse modeling is solved, and the speed and accuracy of filter design are improved.
To address the problems of poor inter-image correlation and obvious differences in fused brightness in high resolution remote sensing image fusion, this paper proposes a method for fusing domestic high-resolution panchromatic and multispectral remote sensing using the non-subsampled shearlet transform. Remote sensing images of GF-1, GF-2, and GF-7 are selected as the experimental data. The intensity-hue-saturation (IHS) algorithm is used to extract the luminance component of the multispectral image; the non-subsampled shearlet transform (NSST) algorithm is used to extract the high frequency and low frequency information from the luminance component and the panchromatic image; and the relationship between high frequency and low frequency is fully considered when designing an effective image fusion strategy. Finally, the fused image is obtained by the IHS and NSST algorithms. By comparing the proposed method to Brovey, Gram-Schmidt (GS)、Hue-saturation-value (HSV), and Co-occurrence filtering (COF) algorithms, it is determined that the proposed method is a feasible remote sensing image fusion method with the combination of subjective and objective evaluation for the fused images.
Remote sensing satellites commonly use synthetic aperture radar (SAR) and visible light imaging. SAR and visible image data fusion have become an important research field of remote sensing owing to their high complementarity in imaging information. The accuracy of obtaining ground control points is directly influenced by the performance of a heterogeneous data matching algorithm. There are two methods of matching algorithms: two-stage and one-stage. The existing two-stage method is difficult to adapt to remote sensing images with complex terrain and it cannot meet the actual engineering needs in terms of speed, while the one-stage method meets the requirements in terms of speed but lacks in accuracy. To solve this problem, an end-to-end high-precision heterologous remote sensing image matching algorithm based on a residual pseudo-twin convolution cross-correlation network has been proposed. By constructing a pseudo twin network based on residual layer, the proposed algorithm performs convolution cross-correlation operation on the extracted features of SAR and visible images, so as to realize heterogeneous remote sensing image matching. The results show that this algorithm considerably improves the matching accuracy between SAR and visible images, maintaining a high speed and laying the foundation for the engineering applications of depth learning methods in large-scale heterogeneous remote sensing image matching tasks.
The aim of hyperspectral anomaly detection is to find targets that are spectrally distinct from their surrounding background pixels. Many algorithms for hyperspectral anomaly detection have been proposed by researchers. Among these, the low-rank and collaborative representation detector (LRCRD) can not only analyze the hyperspectral correlation between all pixels but also constrain the coefficient matrix of the dictionary using low-rank and l2 norms minimization, which does not require an over-complete dictionary and is more useful for background modeling. However, the LRCRD model ignores the significance of the hyperspectral data’s local geometric information to distinguish between background and anomalous pixels. In this paper, the graph-Laplacian regularization is incorporated into the LRCRD formulation and a novel anomaly detection method is proposed based on the graph regularized LRCRD model to analyze nonlinear geometric information. The proposed preserves local geometrical structure in hyperspectral images, thereby improving detection accuracy. The experiments on synthetic and real hyperspectral datasets demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed method.
The conventional truck point cloud registration algorithm enables point cloud registration by determining the key features among point clouds. However, this method is inefficient because of the presence of repeated scenes and noise points among point clouds. Furthermore, the key features obtained using this algorithm are often inaccurate. Therefore, herein, a multiview point cloud registration method based on laser radar is proposed. In the proposed method, the inertial measurement unit is introduced into point cloud registration to complete the pose correction of the corresponding point cloud without relying on point cloud data. Then, the random sampling consensus algorithm is used to fit the local plane to determine the nearest point, which is integrated with the nearest point iterative algorithm to rapidly identify the corresponding point set and realize the accurate registration of the point cloud. The proposed method is verified via an experiment on a truck data set. The proposed method can complete the registration within 4 s, the maximum translation error is 0.01 m, and the rotation error is within 0.1°. Experimental results confirm that the proposed method exhibits good registration efficiency and accuracy in truck point cloud registration and shows high applicability.
The anti-interference properties of the light detection and ranging (LiDAR) technology is a core aspect for realizing safe unmanned driving. Herein, the principle of modulated LiDAR system using code division multiple access (CDMA) is analyzed, the characteristics of different orthogonal code groups are compared, and the anti-interference performance of the CDMA-modulated LiDAR system is analyzed under different interferences by simulation. Experimental results show that the CDMA-modulated LiDAR system based on the optical orthogonal code (OOC) achieves a low false-alarm rate and can effectively resist the interference of conventional single-pulse LiDAR systems. Furthermore, it can effectively resist the same LiDAR system and the interference of the frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) LiDAR system with low power and a specific frequency. Moreover, for 200 scenes where conventional monopulse LiDAR is used as the dense interferer, the false alarm rate of the CDMA-modulated LiDAR system is only 0.11%, which can meet the anti-interference requirements of large-scale unmanned applications.
To solve the problem of inaccurate segmentation of edge targets and poor classification results in the traditional DeepLabv3+ algorithm in remote sensing image change detection, an improved DeepLabv3+ high-resolution remote sensing image change detection method is proposed. First, a DeepLabv3+ model is developed based on deep separation and hole convolutions, which significantly reduces the amount of calculation and model parameters. Second, the pooling pyramid structure is improved by introducing different receptive fields. Moreover, multiscale feature tensors are added to the decoder module; the intermediate stream structure is reconstructed; and the Xception backbone network is optimized. Then, the network channel is adjusted by setting weight coefficients. The weight configuration is optimized to improve the DeepLabv3+ model. Finally, non-generative and generative sample expansion methods are used to develop the dataset. The detection accuracy and generalization performance of the proposed method are confirmed via experimental comparison and analysis. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively improve the output resolution and detailed characteristics of graphics. This shows that the proposed method has good generalization performance and higher detection accuracy compared to other traditional methods. Furthermore, the proposed method has the highest image detection accuracy compared with other traditional methods, and the overall accuracy index can reach 96.4%.
Accurate extraction of surface water information is important for water resource planning and management and related disaster monitoring. Herein, using Sentinel-2A MSI images as the research data, the water body around Poyang Lake was extracted based on 10 typical spectral band index algorithms and the water body recognition results of synthetic aperture radar images combined with visual interpretation were compared and analyzed as the true value. The experimental results demonstrate that the recognition effect of the normalized, Gaussian normalized, and pseudo normalized difference water body indexes is the best. The average F1-score is greater than 95%, and the threshold stability is high. An improved normalized difference water body index is suitable for water extraction in urban areas. The combined water body index has good recognition effect in paddy fields and river areas. The enhanced water body and shadow water body indices are applicable to mountainous areas. The enhanced water body index is also applicable in urban areas. The revised normalized difference water body index is only applicable to the identification of large-area water bodies. A shadow-oriented automatic water index can effectively eliminate the interference caused by terrain shadows. However, the overall performance of a nonshadow oriented automatic water index is relatively poor.
Aiming at the problem of low accuracy and poor real-time performance of obstacle detection caused by uneven density of point cloud data in the process of obstacle detection by LiDAR, an optimized density noise spatial clustering (DBSCAN) algorithm is proposed to improve the clustering effect of road obstacles. First, lane lines are detected according to the reflection intensity information of point cloud data, and regions of interest are extracted. Then, the slope thresholding algorithm is used to segment the slope ground thoroughly. Finally, an adaptive DBSCAN algorithm is proposed, which selects representative core points and adaptive clustering radius to achieve fast and accurate clustering of dense obstacles with different distances. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can accurately cluster the dense obstacles at different distances. Compared with the traditional algorithm, the positive detection rate of the proposed algorithm is increased by 24.07 percentages, and the average time is reduced by 1.18 s.
Label-free optical imaging technology can perform long-term, noninvasive, high-resolution imaging on living cells owing to its noninvasive characteristics. This technology has promising applications in biomedical research and clinical diagnosis. Label-free imaging technologies can be categorized into specific imaging and nonspecific imaging. In this paper, we review the commonly used label-free imaging. Herein, the imaging principles, advantages and disadvantages, as well as the recent progresses of unmarked imaging are introduced in detail. Furthermore, the future development of the label-free imaging technology is prospected.
Laser point cloud data has the characteristics of high measurement accuracy, fast processing efficiency, strong three-dimensional (3D) vision, and wide application fields. It will be one of the core data sets of the new generation national global topographic database. The rapid advancement of spaceborne laser earth observation technology allows the collection of global 3D point cloud data, as well as a quick and efficient technical method for constructing a high-precision 3D digital geospatial information framework. Herein, we first examined the current state and the issues of global high-precision 3D mapping. Further, the rapid construction setup of 3D digital earth spatial information framework based on global laser point cloud was proposed, mainly including the technical processes of spaceborne photon laser point cloud data detection, processing, and application. Finally, the characteristics and benefits of the rapid construction of 3D digital earth framework, based on point cloud, as well as the main problem and future development directions that must be addressed were discussed.
The rapid development of hyperspectral imaging technology has increased the use of domestic hyperspectral images for the inversion of soil parameters in a wide range. However, the accuracy needs to be improved. Therefore, by considering the Daxigou mining area in Shaanxi Province and taking GF-5 hyperspectral satellite images and measured soil samples as data sources, we proposed an XGBoost inversion model based on genetic algorithm feature selection (GA-XGBoost). First, the preprocessed image data were transformed by continuum removal and logarithm of spectral reciprocal. Then, the Monte Carlo cross-validation method was used to remove abnormal soil samples. Finally, The XGBoost heavy metal content inversion models based on correlation coefficient and genetic algorithm feature selection were established respectively. The results show that the performance of the proposed GA-XGBoost model significantly improved compared with the XGBoost model based on correlation coefficient feature selection under the same spectral transformation. Furthermore, the GA-XGBoost model based on continuum removal transformation has the best inversion accuracy, with a root mean square error of 4.85 mg·kg-1, goodness fit of 0.84, and relative prediction error of 2.0. The inversion results of the spatial distribution of soil Cu content in the study area using the model show that the surrounding of the mining area and both sides of the road are seriously polluted by Cu, which is consistent with the field survey results.
Thermal infrared imaging has an essential application in face recognition, but it has certain limitations, such as low resolution, unclear details, and fuzzy boundaries. Herein, we describe the enhancement effect of polarization detection technology on the texture details of thermal infrared face imaging by analyzing the characteristics of the long-wave infrared polarization images of human faces. Based on the correction of the difference of Gaussian (DoG) edge feature image’s color gamut channel mapping weights, a RGB space fusion framework for the polarized thermal images of human faces is proposed. We use the histogram of oriented gradients (HOG) to obtain infrared polarization facial features and propose a face recognition method based on support vector machine (SVM). Experimental results show that, first, polarization detection technology can enhance the texture and details of the infrared thermal image of the human face, and that RGB color gamut fusion can improve the structural similarity of the long-wave infrared thermal image of the human face. Second, the overall quality index of polarized infrared thermal images is better than ordinary infrared thermal images. Finally, under the framework of this article, the accuracy for face recognition can reach 75.6% using the polarized infrared thermal images of the face.
The Cr, Mn, and Ni content of medium and low alloy steel were analyzed using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (EDXRF) and black propagation neural network optimized by genetic algorithm (GA-BP). EDXRF was used to excite the six standard samples of medium and low alloy steel and the X-ray fluorescence spectra were obtained. The characteristic peak intensity of each element was obtained by subtracting the background using the two-point method. A total of 108 groups of spectral data and their corresponding content-based GA-BP neural network were obtained. To forecast the contents of 36 low alloy steel samples, the training completion of the GA-BP neural network was used. The predicted results and the fundamental parameter method analysis results were compared. The average errors of the chemical analysis results of the standard samples were 0.0287%, 0.0314%, and 0.0423% for Cr, Mn, and Ni, respectively. The experimental results showed that the BP neural network optimized by the genetic algorithm is suitable for the EDXRF analysis of Cr, Mn, and Ni in medium and low alloy steel.