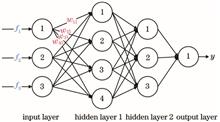
Aiming at the inversion of suspended particulate matter (SPM) concentration using hyperspectral data, this paper proposes a supervised band selection method based on pre-trained neural networks (PNNs), and employs the random forest and neural network to establish an inversion model of SPM concentration. The PNN method needs to perform multiple repeated experiments to obtain sufficient and low-noise expression of band importance. In each experiment, an appropriate number of bands is selected as the features of input data of neural networks. Then, we train a neural network and obtain weights of the first layer in the last training epoch. Finally, we use the L1 norm, L2 norm, and ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) function of the weights to represent the importance of the bands. The experiment results show that the PNN method using L1 norm and L2 norm can obtain a more informative band set, and perform better when used for SPM concentration inversion.
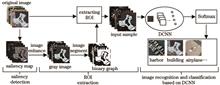
Scene classification of high-resolution remote sensing image is one of the important tasks in interpreting remote sensing image information. In order to extract the target information accurately, we propose a high-resolution remote sensing image scene classification method based on salient features combined with deep convolutional neural network (DCNN) to solve the problems of complex background, diverse targets, and difficult to distinguish between target information and background information in the classification of high-scoring remote sensing image scenes. First, K-means clustering algorithm and super-pixel segmentation algorithm are used to generate the color spatial distribution map and color contrast map of the image, and the different contrast maps are fused to get the saliency map. Then, the features in the saliency map are enhanced through logarithmic transformation, and the adaptive threshold segmentation method is used to improve the discrimination of the target and divide the target area and the background area, and extract the area of interest. Finally, a DCNN model is constructed to extract deep semantic features and classification, and the obtained features are input into the network model for training and classification. Experimental results show that the method can effectively distinguish the main target information from the background information and reduce the interference of irrelevant information. The classification accuracy of the method on the UC-Merced data set and WHU-RS data set are 96.10% and 95.84%, respectively.
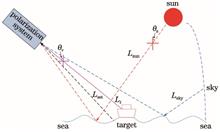
In order to better suppress the influence of solar flare on sea surface target detection, a sea surface solar flare suppression method is proposed based on polarization detection technology and the difference of polarization characteristics among background water body in this paper, solar flare and typical marine targets. The effects of observation zenith angle and solar zenith angle on the polarization of sea surface targets under the background of the solar flare and the contrast between sea surface targets and solar flare background are analyzed. The results show that when detecting sea surface targets in sunny weather, the background radiation is mainly affected by the irradiance caused by the direct reflection of solar radiation from the sea surface. There is no significant difference between the visible light wavelengths of 550 nm and 670 nm in the inhibition effect of solar flare. The inhibition effect of solar flare is better when the observation zenith angle is near 53°, 50°--60° solar zenith angle direction and the sum of solar zenith angle and observation zenith angle is about 106°. This research is of great significance to improve the contrast between the sea surface target and the solar flare background image and the target detection effect under the sea surface solar flare background.
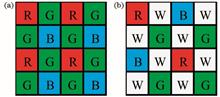
RGBW filter arrays are often used to improve the imaging quality of detectors at low illuminance, but the corresponding color reconstruction methods are still designed according to the characteristics of Bayer array, and do not make full use of the advantages of luminance information, resulting in poor reconstruction results. To overcome this defect, guided filtering is applied to delve the correlation between luminance information and color information first. Then, multi-step residual-based interpolation algorithm with increasing sampling rate is designed, based on the smoothness of residual, which is applied to the spatial characteristics of the SONY-RGBW color filter array. Moreover, combined with the interpolation results in the orthogonal directions, the iterative process is introduced and the pixel-wise evaluation factor is improved to improve the edge adaptability of the algorithm. Finally, the high-frequency component of the luminance image is used to enhance the color image. Experimental results on the Kodak data set and images in real scenes show that the proposed method can reduce color aliasing, reconstruct clear image detail, and the objective criteria with or without reference images are better than the existing color reconstruction methods for RGBW color filter array.
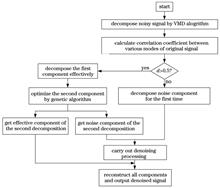
The echo signal of ultrasonic flowmeter usually has noise interference, which makes it difficult to locate the echo signal accurately. In order to filter out the noise in the ultrasonic echo signal, a signal denoising method based on the optimized variational modal decomposition (VMD) algorithm is proposed. Firstly, the information entropy of the mutual information criterion is used to associate the genetic algorithm with VMD. Then, the sample entropy is used as the fitness function to adaptively optimize the parameter combination in VMD algorithm. Finally, the original signal is decomposed, the effective signal is calculated through the correlation coefficient, and the effective signal is reconstructed after further denoising. The simulation results show that the proposed method can effectively filter out the noise in ultrasonic echo signal and retain the useful signal completely.
Aiming at the problem that the conventional point cloud filtering method will cause greater damage to the model in the process of removing the noise close to the model, a point cloud filtering algorithm combining dual tensor voting and multi-scale normal vector estimation is proposed. First, the principal component analysis method is used to estimate the normal vector of each point on a larger scale, and the double tensor voting is performed on each point to extract the feature points. Then, the normal vectors of the extracted feature points are estimated at a smaller scale, and the small-scale noise plane is eliminated by combining the random sample consensus method. Finally, the curvature is used to filter the remaining noise to obtain the final point cloud data. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively eliminate noise points, and better retain the sharp features of the 3D model, which lays the foundation for subsequent point cloud registration and 3D reconstruction.
An improved finger vein recognition method based on ResNet is proposed to solve the problem of finger vein extraction difficulties and insufficient recognition accuracy. First of all, depthwise over-parameterized convolution (DO-Conv) is used to replace the traditional convolution in the network, while reducing the model parameters and improving the network recognition rate. Then, the spatial attention module (SAM) and squeeze-and-exception block (SE-block) are fused and applied to an improved ResNet to extract the detailed features of the image in the channel and spatial domain. Finally, label smoothed cross entropy (LSCE) loss function is used to train the model in order to automatically calibrate the network to prevent errors in classification. The experimental results show that the improved network model is not easily affected by the image quality. And the recognition accuracy of FV-USM and SDUMLA can reach 99.4919% and 99.4485%, respectively, which is significantly higher than that of the previous network. Compared with other models, the proposed method has a significant improvement on the recognition accuracy.
Structured light fringe projection is widely used in three-dimensional (3D) shape measurement technologies. However, even after decades of related research and development, restoring the 3D shape of objects using a single fringe pattern remains a challenge. In recent years, deep learning methods have been used increasingly in computer vision and image processing tasks. Thus, this paper proposes a structured light 3D measurement method based on the U-Net network. The proposed method obtains the depth information of the target object’s surface directly from a single deformed fringe pattern to realize high-speed 3D shape measurement. Simulated and experimental data prove the effectiveness of the proposed method. With the proposed method, 3D data can be calculated from a single deformed fringe pattern; thus, it can be applied to the 3D shape measurement of dynamic objects.
Aiming at the problem of insufficient edge detail preservation in image fusion, infrared and visible images fusion algorithm based on non-subsampled shear-wave transform (NSST) and convolutional neural network image fusion framework (IFCNN) is proposed. First, infrared and visible images are decomposed by NSST. Then, in order to make the low-frequency sub-band image better highlight the contour information, the image is fused using similarity matching fusion rule; for the high-frequency sub-band images, the feature layers are extracted using IFCNN, and the maximum weight image of feature layer can be obtained through L2 regularization, convolution operation, and maximum selection strategy processing, and the high frequency fusion rule can be determined according to the maximum weight image. Finally, the NSST inverse transform is used to obtain the final fusion image. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm retains the details of image edges and textures, reduces artifacts and noises, and has good visual effects.
A lightweight target detection network that integrates scene context is proposed, effectively solving the problem of poor application of existing detection algorithms in the field of unmanned aerial vehicles. In the design of the network, first, the backbone network of YOLOv3 is replaced with MobileNetV3, and scene information is extracted through the 1×1 convolutional layer. Simultaneously, a scene context module is constructed to filter fine-grained object features. Then, complete intersection over union (CIOU) loss is used to optimize the position error of the bounding box in the loss function. Finally, the algorithm is trained and tested on the newly constructed unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photography data set. Experimental results show that compared with the YOLOv3 algorithm, the average detection accuracy of the proposed algorithm increased by 8.4 percent and the detection speed increased by 5.8 frame/s.
Because conventional visual odometry (VO) has cumbersome implementation process and complex calculation problems, a VO based on an improved dual-stream network structure is proposed. The proposed VO uses a dual-stream convolutional neural network structure that can simultaneously feed RGB and depth images into the model for training, use the Inception network structure to improve the convolutional layer, and reduce the number of parameters in the convolutional layer. Simultaneously, an attention mechanism is introduced to the convolutional layer to enhance the network’s recognition of image features and the system’s robustness. After being trained and tested on the KITTI dataset, the proposed improved model is compared with the VISO2-M, VISO2-S, and SfMLearner. The results show that the proposed model’s rotation and translation errors are significantly reduced compared with VISO2-M and SfMLearner when using monocular cameras and comparable to VISO2-S when using binocular cameras.
In the secondary side management ofa substation, the press-plate plays an important role. Aiming at the problem of unsatisfactory results of the existing accurate recognition methods for press-plate states, this study proposes a bilinear fine-grained press-plate state recognition method that incorporates the attention mechanism. First, the attention mechanism is used to focus attention on the contact part of the press-plate; then, the bilinear fine-grained model is used to focus on the key areas related to the opening and closing of the press-plate; finally, effective features are extracted from the key areas to achieve accurate recognition of the state of the press-plate. Experimental results show that the method can realize the end-to-end state recognition of the pressure plate, and the recognition accuracy can reach up to 98%. Compared to the traditional method, the accuracy and recall rate of the method are significantly improved.
As a pixel-level classification technique, image semantic segmentation has been employed in the field of synthetic aperture radar (SAR) image interpretations. U-Net is an end-to-end image semantic segmentation network with a typical encoder-decoder architecture. Among them, the coding part mainly comprises a convolutional layer and a pooling layer, which can effectively extract the features of a target image; however, extracting information such as the target position and direction is difficult. Capsule network is a type of neural network that can obtain the target pose (position, size, and direction) and other information. Therefore, this study proposes an SAR image semantic segmentation method based on the U-Net and capsule network. Moreover, considering the small data set of SAR images, the U-Net encoder is designed to be identical to the visual geometry group (VGG16) to allow the trained VGG16 model to be directly transferred to the encoder. The effectiveness of the method is verified by conducting a segmentation experiment of building targets on two polarimetric SAR image data sets. Results show that the method can achieve improved precision, recall, F1-score, and intersection over union as well as reduce the training time of the network model when compared with the U-Net.
Considering the lack of color constancy (CC) dataset in the field of microscopic images and the failure in achieving the expected effect through the cross-dataset training of the CC algorithm, this study creates a microscopic CC dataset using two steps: camera acquisition and simulation generation. Moreover, this study proposes a microscopic image CC algorithm based on an autoencoder. The algorithm uses an improved UNet structure autoencoder for semi-supervised training and simultaneously introduces a new composite-loss function to optimize network parameters, thereby obtaining an accurate restored image color. Experimental results show that the image resolution trained using the algorithm is higher than traditional autoencoders, and the angle error estimates in the NUS-8, RECommended, and self-built microscope CC datasets are smaller.
Aiming at the problems of block effect and high algorithm complexity in the dark channel prior dehazing algorithm, we propose an improved dehazing algorithm based on the dark channel prior. First, row transmittance is obtained through the dark channel prior dehazing algorithm, and then the haze parameters are adjusted adaptively by the peak signal-to-noise ratio to obtain the optimized transmittance. Then, the above results are trained as the input vector and the target vector of the multilayer perceptron to establish the mapping between the row transmittance and the optimized transmittance and obtain the optimized transmittance. Finally, the image is restored by the atmosphere light value to obtain the haze-free image. Experimental results show that the algorithm can effectively improve the block effect, improve the restoration efficiency, and improve the clarity of image details to a certain extent.
Deep learning-based single-image super-resolution reconstruction method has been relatively perfect. The reconstructed image has a high objective evaluation value or a good visual effect; however, the image perception effect and objective evaluation value cannot be improved in a balanced manner. To address this problem, this paper proposes a single-image super-resolution reconstruction method based on an attention fusion generative adversarial network. In the proposed method, first, the batch layer that destroys the original image contrast information and affects the quality of image generation in the residual network is removed. Then, the residual block of the attention convolutional neural network, which can effectively perform adaptive feature refinement in the feature map, is constructed. To improve the reconstruction results that lack high-frequency information and texture details under large-scale factors, a pixel-loss function is constructed to replace the mean squared error-loss function with a more robust Charbonnier loss function, and a total variation regular term is used to smooth the training results. The experimental results show that compared with other methods on the Set5, Set14, Urban100, and BSDS100 test sets under 4× magnification factor, the average peak signal-to-noise ratio and average structure similarity increased by 2.88 dB and 0.078, respectively. The experimental data and renderings demonstrate that the proposed method is subjectively rich in details, objectively has a high peak signal-to-noise ratio and structural similarity value, and achieves a balanced improvement of visual effects and objective evaluation index values.
In order to improve the accuracy and speed of aerial image target detection, an improved CenterNet aerial image target detection algorithm based on adaptive threshold is proposed. The center point of the target is used as the key point to replace the anchor box for classification and boundary regression, and an adaptive threshold prediction branch is designed to screen and optimize the preprocessing results. At the same time, the encoding-decoding network structure is designed. Through the deformable cavity convolution structure and the convolutional block attention-connection structure based on the attention mechanism, shallow spatial information, and deep semantic information are effectively extracted and fused. In addition, data enhancement is realized by discarding structured information and building new samples with false and missing detection targets, so as to reduce false and missing detection rates. Experiments are performed on the open data set NWPU VHR-10, the results show that compared with CenterNet based on ResNet-50, mean average precision of proposed algorithm increased by 5.17%, and intersection of union of 0.50 and 0.75 are improved by 3.57% and 3.61%, respectively. The detection speed reaches 45 frame·s -1, achieving good detection accuracy and real-time balance.
To improve the visual perception of fused images, a nonsubsampled shear wave transform (NSST) -based perception fusion method for infrared and visible images is proposed. First, the NSST is used to decompose the source image into high- and low-frequency components. Then, to improve image details, a parameter adaptive pulse coupled neural network is used to fuse high-frequency component images. Second, a Gaussian filter and a bilateral filter are used for multiscale transformation to fuse low-frequency component images, and low-frequency components are decomposed into multiscale texture details and edge features to capture more multiscale infrared spectral features. Finally, the inverse NSST is used to obtain the fused image. Experimental results show that the proposed method can not only improve the detail information of fusion image effectively, but also enhance the ability of infrared feature extraction to fit human visual perception.
In the current process of detecting commercial sand and gravel aggregates, the manual detection is inefficient, greatly affected by subjective factors, and the detection accuracy is not ideal. This paper proposes a convolutional neural network (CNN) based on the sand and gravel aggregate image classification model (CNN13). This classification model refers to the classic CNN visual geometry group 16 (VGG16) model to improve the network structure and optimize parameters. The CNN13 model uses the TensorFlow deep learning framework to build a 13-layer CNN structure. The experimental dataset includes 5000 digital images, which is collected from the sand and gravel aggregates in the daily production of a commercial concrete manufacturer. The model uses GPU for high-speed calculation during the training process. Compared with the VGG16 model, the CNN13 model has fewer convolutional layers and parameters, lower requirements for GPU memory, faster training speed, higher classification accuracy, and classification accuracy for each level of sand and gravel aggregates is more than 99%.
The line intercept histogram Otsu method has good segmentation performance, but for the weak-light part of the image, it can only divide it into background, and many details of the image are lost. Based on the analysis of the essence of the line intercept histogram algorithm, a directional fuzzy derivative Otsu method is proposed to segment the weak light part of the image. At the same time, in order to enhance algorithm universality, the segmentation results are fused with segmentation results of the traditional Otsu algorithm. Firstly, the directional fuzzy derivatives are used to replace the neighborhood mean of the pixel to achieve a good performance in segmentation of the weak-light part of the image and suppress noise. Then the segmentation results are fused with the Otsu segmentation results to get more accurate threshold segmentation results. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can segment the weak-light part of the image more accurately in comparison with other segmentation methods, which provides better noise reduction effects.
A color zero-watermarking algorithm based on speeded-up robust features (SURF) to correct geometric distortions and halftone mapping encryption is proposed to address problems associated with poor robustness against geometric attacks in existing digital watermarking algorithms and low efficiency due to excessive embedded color copyright image information. First, the feature points of the carrier image based on SURF algorithm were extracted and feature point information was saved as a key for blind detection. In the copyright verification process, after the feature points of the attacked image were extracted and keys were matched, the geometric correction of the attacked image was implemented based on affine matrix estimated by filtered feature points. Simultaneously, the copyright identification was preprocessed according to the halftone principle. The color image was represented by a three-channel binary matrix with pixel expansion, and the watermark image was encrypted by halftone sub-block mapping according to the encryption rules. In proposed algorithm, the color and structure information of the copyright images were retained while the amount of embedded information was reduced, and the security of the watermark information was increased. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed zero-watermark algorithm is robust against geometric and nongeometric attacks and the generated zero-watermark information is more secure.
The image collected outdoors in a foggy environment is prone to low contrast and loss of details. To solve this problem, our study proposes an image fusion method based on multiscale Retinex theory and wavelet transform to restore foggy images. First, the MSR algorithm was used to enhance the collected foggy image. Then, the “db5” wavelet basis was used to merge the brightness component V of the foggy image and the enhanced image, and the saturation component of the foggy image was constrained. Finally, the defogging image was generated. The threshold value was set, and the fog image with relatively high fog concentration was second iteratively fused using wavelet transform to remove residual fog. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively restore foggy images with different concentrations. Moreover, the image after fog removal can enhance the details of the dark area, improve the image color, and enrich the image information. Using wavelet fusion preserves more image information so that the image color is rich and natural. Thus, the entire smooth fusion image has a good restoration effect.
In person re-identification (ReID) task, some information will be lost in the process of extracting identity-related features, causing the basis for identification become to less and then affects the performance of model. This paper proposes a person ReID method based on double-resolution feature and channel attention mechanism. Firstly, a high-resolution feature branch is added on ResNet, and generate feature vectors corresponding to eight different regions by applying pooling layer on different resolution feature maps. Then a channel attention module is designed based on the situation of feature vectors to enhance the expressive ability of the effective part. Finally, batch normalization is used to coordinate classification loss and measurement loss. In the ablation experiment, the application of each step in the algorithm effectively improves the performance of the model. In the comparative experiments on Market-1501, DUKEMTMC-REID, and CUHK03 datasets, the mean average precision and rank-1 of the proposed algorithm are evidently improved than that of other recent representative algorithms. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can improve the accuracy of person ReID by combining more abundant features.
Character segmentation is an important part in image analysis and recognition of historical Tibetan document. Aiming at the problems of text line slanting, stroke overlapping, crossing, touching between characters, stroke breaking and noise interference of historical Uchen Tibetan document, a character segmentation method for historical Uchen Tibetan document based on structure attributes is proposed in this paper. First, a character block dataset of historical Uchen Tibetan document is established. Then, the local baseline of character block is detected by using syllable point position information or combining horizontal projection and linear detection, and the character block is divided horizontally into two parts above and below the baseline. The improved template matching algorithm is used to detect touching strokes and touching type above the baseline. The multi-direction and multi-path touching character segmentation algorithm is used to realize crossing and touching strokes segmentation. Finally, according to Tibetan structure attribute, to complete the attribution of each stroke. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively solve the challenge problem in character segmentation. The recall rate, precision rate and F-Measure of character segmentation reached 96.52%, 98.24% and 97.37%, respectively.
Crowd density estimation has important application value in the field of intelligent security prevention. A crowd density estimation method with multi-feature information fusion is proposed to address the problems of large difference in viewpoint change of two-dimensional images, loss of feature spatial information, and difficulties in scale feature and crowd feature extraction. The proposed method encodes the multi-view information of images through the attention mechanism-guided perspective of spatial attention (PSA) method to obtain the spatial global contextual information of the feature map and weaken the influence of viewpoint change. Through the multi-scale information aggregation (MSIA) method, the multi-scale asymmetric convolution and the null convolution with different expansion rates are effectively integrated to obtain more comprehensive image scale and feature information. Finally, the spatial information of the high-level feature map and the semantic information of the low-level feature map are complemented by the detailed semantic feature embedding fusion, and the contextual information and scale information complement each other to improve the accuracy and robustness of the model. The experimental validation is carried out using the ShanghaiTech, Mall, and Worldexpo’10 datasets, and the experimental results show that the performance of the proposed method has been improved compared with those of other comparative methods.
There are two calculation formulae in the study of diffraction limited coherent light imaging. One is the formula for calculating the amplitude distribution of the image light field of single lens imaging system under specific approximate conditions. This formula can be extended to the imaging calculation of an optical system composed of multiple elements. The other is the formula which can directly calculate the amplitude and phase distribution of the image light field of an optical system. In order to analyze the practical value of these two formulae, this paper takes the imaging system composed of two lenses as an example, places aperture stops at different spatial positions, and compares the theoretical calculations and experimental measurement results of the two formulae.
The modulation transfer function (MTF) value of complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) image sensors pixels at Nyquist frequency is typically used to evaluate the imaging quality. The MTF is mainly calculated by taking the frequency domain product of the aperture MTF and the diffusion MTF. The aperture MTF is determined by the physical structure of the CMOS image sensor pixel, whereas the diffusion MTF is determined primarily by the process parameters of the p-n junction in the photosensitive region. Simultaneously, the process parameters will affect the quantum efficiency (QE) of pixels, which will then affect the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). The theoretical mechanism of MTF function and SNR is examined in detail in this paper, and the calculation results of MTF and SNR of CMOS image sensor pixels under 8 typical optical wavelengths in the 300--1000 nm spectral band are listed. The MTF of the pixel with L-shaped sensitivity aperture at Nyquist frequency is fixed at 0.67, the diffusion MTF at Nyquist frequency decreases as incident light wavelength increases, the peak value of QE is 85.8% at 800-nm incident light wavelength, and the peak value of SNR is 124 at 800 nm under the same reading noise and dark current.
In order to solve the problems of insufficient viewpoints and narrow viewing angle of the traditional autostereoscopic display technology, a light field three-dimensional (3D) display method with super multiple viewpoints and large viewing angle is proposed. Based on the principle of reconstructing full-parallax light field for integral imaging, the discrete lenticular lens array (DLLA) with a large pitch is used in the proposed method to horizontally modulate the light rays, which emit from pixels of the elemental image (EI), with specific horizontal direction angles to integrate viewpoints in space. As a result, super multiple viewpoints densely arranged in the horizontal direction are reconstructed within a large viewing angle. In addition, the DLLA is optimized for optical imaging to suppress aberrations and ensure high-quality 3D imaging. In the experiment, a 54-inch (1 inch=2.54 cm) light-emitting diode (LED) displayer with a resolution of 1280 pixel×720 pixel is used to achieve a horizontal light field 3D display effect with 42.8° viewing angle and 100 viewpoints, and the distortion rate of 3D imaging is 2.23%. The presented 3D image with continuous parallax of motion and natural expression of depth information verifies the superiority and feasibility of the proposed method.
The non-contact heart rate measurement method based on imaging photoplethysmography is affected by the interference of ambient light, which will seriously affect the identification and extraction of heart rate signals. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes a denoising method of heart rate signal based on a self-optimizing normalized least mean square algorithm. According to the trend of light changes in the original heart rate signal and the background signal, this method can automatically select the control factor through the least mean square error based on the normalized least mean square adaptive filter, which can maximize the removal of light interference in the image. Compared with the actual heart rate results using finger clip pulse oximeter, the Person correlation coefficient between the average heart rate measured by the two methods under the condition of drastic changes in light intensity is 0.95, and the mean absolute percentage error is 2.16%. The results indicate that the method greatly improves the anti-noise ability of the imaging photoplethysmographic against ambient light, which improves the practicability, reliability, and stability of the imaging photoplethysmographic measurement method.
The matching link of the three-dimensional (3D) measurement system based on the dual line-scan camera is easily affected by the surface texture and light source, affecting the point cloud’s accuracy and integrity. This study investigates a grayscale matching algorithm based on Fourier transform to achieve high-precision matching and deal with partial overexposure. Additionally, the imaging model of the measurement system is established and a flexible static calibration method for line-scan cameras is introduced. Finally, an experimental platform is developed to verify the proposed matching algorithm’s effectiveness and the measurement system’s accuracy. The reprojection error of the camera calibration results is better than 0.3 pixel. Based on the proposed algorithm, the measurement point cloud is complete and can reflect the real shape of the depth mutation of the object. The root mean square error of standard plate from the point cloud to the fitting plane is 0.023 mm. Results show that proposed matching algorithm can effectively ensure the integrity of the point cloud and retain the surface details of the measured object.
Rivet flushness is an important indicator of riveting quality parameters; however, efficient and stable methods for actual testing are lacking. We propose a technique for flushness detection based on image-to-point-cloud segmentation algorithm for detecting rivet flushness. First, we propose a separating method of the image noise contour to stably and quickly extract the rivet contour in images. Three neighborhood features at the inflection point of the contour are summarized on the basis of an analysis of the neighborhood features of the rivet contour pixel. According to the neighborhood features, whether the contour point is an inflection point is judged, and the noise contour separation is realized. Second, the rivets features in the image are mapped to the measured three-dimensional point cloud to realize fast and stable segmentation of the rivets after extracting the contours of the rivets in the image. The experiment confirms the excellent stability and accuracy of the rivet flushness detection method proposed in this paper.
To improve the time consumption and low accuracy of traditional manual methods of laser cladding crack detection, an automatic identification method combined with the attention model is proposed to identify and detect laser cladding cracks. The semantic segmentation network of laser cladding cracks based on the U-net network cannot sufficiently extract small local features. By adding the convolutional block attention model (CBAM) layer to extract the feature space and feature channel weight information, we can label the microscopic cracks of the laser cladding zone without any time difference in the pixel level. Experimental results show that the deep learning model combined with the CBAM can improve the accuracy of cladding crack identification and detection by 2.7 percentages. The network fused with the CBAM achieves an accuracy of 79.8% on the cladding area crack test set. Both the labeling accuracy and speed of the deep learning model exceed those of manual labeling, providing an effective method for identifying laser cladding cracks.
Due to the limitation of measuring equipment or the shape characteristics of the model itself, the point cloud data in the triangulated grid generated by three-dimensional (3D) laser scanning point cloud often contains holes, which brings obstacles to the subsequent 3D reconstruction. Aimed at handling the problem of hole repairing, a hole surface repairing algorithm based on laser triangulation point cloud is proposed in this paper. First, the boundary of the triangular patch is determined by traversing the triangular mesh for the closed hole, and the hole is detected. Second, a new triangular patch is generated quickly at the hole polygon based on the minimum angle method to form the initial mesh. Third, the least square network and radial basis function implicit surface are combined. Besides, the curvature of the surface is minimized by using the minimum second derivative. The surface newly generated is consistent with the trend of the original mesh curvature. Finally, the hole repairing of laser point cloud is realized. Experimental results show that, compared with other point cloud repair methods, this method not only reduces the repair error, but also is suitable for hole repairing of various triangular mesh models.
Aiming at the problem of the low recognition rate of the deep learning defect detection algorithm under the condition of small samples, a data enhancement method based on two-channel generative adversarial network is proposed. The generative adversance network is composed of two channels, such as global discriminator and local discriminator. The local discriminator can increase the confidence loss of the defect type and realize the enhancement of local information. The proposed method is used to conduct experiments on the lens defect image dataset. Experimental results show that the nearest neighbor index, maximum mean difference, and Wasserstein distance of the proposed method are 0.52, 0.15 and 2.81, respectively. For the defect type images of pitting, scratches, bubbles and foreign bodies, the generated image quality is better than that of conditional generated adversarial network, Wasserstein distance generated adversarial network and Markov discriminator. The lens image generated by the dual-channel generation confrontation network has diverse global information and high-quality detailed features, which can effectively enhance the lens defect data set.
Aiming at the problem of inaccurate positioning of the SiamRPN (Siamese Region Proposal Network) when the target is temporarily blocked and the appearance changes drastically, a target tracking algorithm combining target tracking buffer and triple loss is proposed. First, the original fixed template is changed into dynamic template to improve the reliability of similarity discrimination in complex environment. Then, the image of the target is sparsely cached in the template buffer to deal with the interference of non-semantic samples in the process of tracking and enhance the robustness of target tracking. Finally, the triplet loss is applied to make full use of the positive and negative sample characteristics of the target to make the tracking more discriminant. Experimental results with OTB100 dataset show that compared with SiamRPN, the area under the success curve of the improved algorithm increases by 0.021, the average center position error decreases by 25.56 pixel, and the average overlap rate increases by 25.2%.
Based on an unsupervised network, a method for cell phone screen defect segmentation is proposed to solve the problem of low accuracy in cell phone screen defect detection. First, an image reconstruction network with multiscale features is constructed through an unsupervised convolutional denoising autoencoder, which reconstructs the multilayer background texture image from the defect image. Then, the defect and multilayer-reconstructed images are subtracted separately to eliminate the influence of the background texture. Finally, adaptive threshold strategy is used for segmentation and the segmentation results are fused to improve the accuracy of defect segmentation. To improve the reconstruction performance, an improved loss function is proposed to train the reconstruction network. Based on an image pixel histogram, the triangle method is used for global adaptive threshold segmentation to improve the segmentation accuracy. The experimental result shows that the proposed method can predict the cell phone screen defect area, reaching 90.30% accuracy. The accuracy and real time of the proposed method meet industrial requirements and it is practical.
A stacked hourglass network (SHN) is a representative research result in human pose estimation; however, it ignores the local information of joints. Therefore, this study proposes a human pose estimation model based on an improved hourglass network. First, multiple residual modules and convolution layer with a step size of 2 are used to obtain low- to high-level features. In order to highlight the local detailed feature information, the number of residual modules and channels are adjusted as the number of network layers deepens. Then, an online difficult keypoint mining module is integrated to extract local features such as texture and shape of the occluded part. Finally, deconvolution is used to maximize the restoration of the original local features. The experimental results show that the average accuracy of the proposed model on the COCO data set reaches 74.6%. In addition, the total parameter amount is 1.5×10 7, which is 5.1 percentage points higher than the average accuracy of superimposing eight SHN (8-SHN), and its total parameter amount is only 1/3 of 8-SHN.
In order to solve the problem of large amount of calculation and time-consuming of the anisotropic Gaussian directional derivative filter, this paper uses the box filter to fit the anisotropic Gaussian directional derivative filter template, and proposes a new fast corner detection algorithm with excellent performance by combining template with the integral image. First, six directional derivative filter templates are designed by using box filter, and the derivative response of input image in each direction is calculated quickly by combining with integral image; second, a coarse selection mechanism of candidate pixels is proposed based on the sparsity of corners, which can quickly receive candidate pixels to reduce the number of pixels involved in subsequent operations. For each candidate pixel, the multi-directional structure tensor product is constructed by synthesizing the derivative response of each direction, and the corner measure map is generated. The performance of the proposed algorithm and 9 classical detection algorithms is evaluated under the conditions of affine transformation and Gaussian noise interference, and time-consuming comparisons are carried out on the test image set of different sizes. The experimental results show that the newly proposed algorithm has excellent detection performance and less time-consuming, and meets the needs of real-time processing.
Aiming at the problem that the anomaly event detection algorithms in the current complex scenes are overly dependent on frame-level labels, and the long time consumption and high memory requirement of I3D model, a M-I3D model based on I3D as a feature extractor is designed, and then an anomaly detection method based on deep spatio-temporal features and multi-instance learning is proposed. The proposed method utilizes normal and abnormal videos as packages and video clips as instances of multi-instance learning. The M-I3D model is employed to extract the features of each video clip, and the extracted feature vectors are input into three fully connected layers to automatically learn a deep anomaly sequencing model, which can predict the scores of abnormal video clips. In addition, in order to better locate anomalies in the training process, the sparse function and constraint function are introduced into the loss function. The results show that, compared with the other methods, the proposed algorithm has higher accuracy and better real-time performance on the UCF-Crime dataset.
The popularization of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) has brought great security risks to people. A UAV video detection algorithm based on the active subspace robust principal component analysis (ASRPCA) fused with the five-frame difference is designed to solve this problem. First, an alternating iteration method combined with the augmented Lagrange multiplier method is used to optimize and solve the ASRPCA model, thereby obtaining the background image of the current frame of the video sequence. Second, the background image replaces the intermediate frame of the five-frame difference. Finally, differential binarization operation is performed simultaneously on the intermediate frames, previous two frames, and subsequent two frames. This makes UAV have a better detection result and a denoising ability. The experimental results show that under different backgrounds, compared with the algorithm of total variation regularized RPCA (TVRPCA), the average of recall rate, precision rate, and comprehensive performance of the proposed algorithm is increased by 5 percent, 4.8 percent, and 5 percent, respectively. The running time is approximately 0.51 s per frame, which meets the offline real-time requirements of the target algorithms.
This paper proposes a reconstruction method for optimized three-dimensional (3D) morphable model parameters to address the instability of the reconstructed model’s shape expression ability due to the inaccurate detection of facial feature points in the face-image reconstruction method based on the 3D morphable model. First, an improved position map regression network is used to extract and locate the facial feature points accurately and on this basis, the initial model parameters are calculated. The parameters obtained using the regression method are then integrated to obtain the optimised model parameters and improve the model’s accuracy and generalisation capabilities. Finally, to obtain the final face model, the 3D morphable model is optimized. This approach can produce accurate 3D face reconstruction using real faces as experimental data.
Circular holes are important features in automated manufacturing and assembly, and accurately estimating the pose of a hole can contribute to high-precision processes. Therefore, we propose a method for circular hole pose measurement based on epipolar constraints of binocular vision. First, to improve the accuracy of contour extraction, a contour purification method based on morphological addition is proposed. Then, the ordinate of the hole is compensated according to the epipolar constraint, and the optimal abscissa is determined via Gaussian fitting to achieve precise matching. Finally, the fitted circle in space is used to determine the hole pose. Experimental results show that the contour extracted using the method closely follows the real hole contour, and the measurement accuracy of the hole position and radius is 0.05 mm. Compared with no compensation, the measurement accuracy of the aperture and hole spacing increases by 31.56% and 34.07% after compensation, respectively. The method provides a strategy to improve the accuracy of hole pose measurement, and meets the actual application requirements of manufacturing and assembly.
Retinal blood vessel segmentation is an important means to detect a variety of eye diseases, and it plays an important role in automatic screening systems for retinal diseases. Aiming at the problems of insufficient segmentation of small blood vessels and pathological mis-segmentation by existing methods, a segmentation algorithm based on the multi-scale attention analytic network is proposed. The network is based on the encoding-decoding architecture and introduces attention residual blocks in sub-modules, therefore enhancing the feature propagation ability and reducing the effects of uneven illumination and low contrast on the model. The jump connection is added between the encoder and decoder and the traditional pooling layer is removed to retain sufficient blood vessel detail information. Two multi-scale feature fusion methods, parallel multi-branch structure and spatial pyramid pooling, are used to achieve feature extraction under different receptive fields and improve the performance of blood vessel segmentation. Experimental results show that the F1 value of this method on the CHASEDB1 and STARE standard sets reaches 83.26% and 82.56%, the sensitivity reaches 83.51% and 81.20%, respectively, and the proposed method is better than that of current mainstream methods.
Aiming at the serious loss of details and poor visual effect in the process of medical image fusion, a pulse coupled neural network (PCNN) medical image fusion algorithm based on non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) and discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is proposed. Firstly, the medical source image is processed by NSCT to obtain the corresponding low frequency and high frequency subbands, and the obtained low frequency subbands are processed by DWT. Then, the PCNN is used to fuse the low frequency subbands, where the input items are the average gradient and the improved Laplacian energy sum. The fusion of high frequency subbands is realized by combining information entropy and matching degree. Finally, the low frequency subband image and high frequency subband image are fused by multi-scale inverse transformation. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the contrast of the fused image and retain the detailed information of the source image, and has excellent performance in both subjective and objective evaluation.
Temporal action detection is a fundamental task in video understanding that is commonly used in the fields of human-computer interaction, video surveillance, intelligent security, and other fields. An improved encoder-decoder temporal action detection algorithm based on the convolutional neural network is proposed. The improved algorithm is applied in two stages: first, the feature extraction network is replaced and the residual structure network is used to extract the deep features of the video frame; and second, the encoder-decoder temporal convolutional network is constructed. The feature fusion is conducted via contact, and the method of upsampling is improved. To improve the detection accuracy of the network, the proposed algorithm employs the appropriate activation function LReLU for training. The experimental results show that the accuracy of the proposed algorithm on the temporal action detection datasets MERL Shopping and GTEA has improved.
In view of the difficulty of automatic port recognition, the ship-wharf-port progressive recognition model is proposed by combining deep learning and geospatial analysis on high-resolution visible light remote sensing images. Firstly, the constructed wharf sample data set is enhanced, and the enhanced data set is used to train the YOLO v3 algorithm. Then, the multi-scale recognition is carried out by the sliding window on the large remote sensing images, and the underlying features of the images are obtained to calculate the wharf categories and pixel coordinates. Finally, the locations of wharves are transformed into geographical coordinates, and the Getis-Ord Gi * statistical method is used to analyze the hot spots. The classical density clustering method is used to identify and extract the locations and ranges of ports. The recognition comparison results in the experimental area show that the proportion of port basin recognition by improved model reaches 82.79% at aggregated threshold of 1000 m .
An efficient localization algorithm is the prerequisite for autonomous robot movement. The traditional adaptive Monte Carlo localization (AMCL) algorithm provides low pose accuracy owing to the complex environment limiting the laser model. Herein, an optimized AMCL algorithm of scan matching (SM) and discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is presented. A weighted average output of the traditional AMCL was used as the initial value of the SM, a matching function model of the lidar observation point and previous map was constructed, and the Gauss-Newton method was used to optimize the solution. Finally, the minor jitter at the localization was filtered through the DFT filter, improving the system’s stability and robustness. Through absolute localization experiments and repeated localization experiments in motion, it is verified that the optimization algorithm is superior to the traditional AMCL algorithm. The optimization algorithm effectively improves the system’s localization accuracy while maintaining its robustness.
Herein, we propose a convolutional neural network based on channel attention mechanism for multiscale feature fusion regarding the characteristics of LiDAR point clouds, such as the complex geometric structure and extreme scale variations among different categories, resulting in the issue of low classification accuracy of small targets. First, low-level features (planarity, linearity, normal vector, and eigen entropy) are calculated for each point by setting a spherical neighborhood, and they are fused with high-level features acquired by the network to improve the geometry awareness of the constructed model. Then, a multiscale feature fusion module is designed based on the channel attention mechanism to learn fusion weight coefficient so that the network can adapt to the receptive field size of different scale objects and realize different scales information filtering, which improves the classification performance of the small-scale object. According to the experiments, the average F1 score using the ISPRS Vaihingen 3D Semantic Labeling benchmark is 72.2%. Compared with other algorithms, our model has the highest classification accuracy in the powerline and car categories with F1 scores of 64.3% and 79.9%, respectively.
Aiming at the problems that most of the current cloud and cloud shadow detection methods are prone to misdetection, serious edge detail loss and insufficient detection accuracy, a remote sensing image cloud and cloud shadow detection method based on the dual attention convolutional neural network model (RDA-Net) is proposed. In the model, the dual attention module is introduced to can effectively capture the dependence of global features, the recursive residual module is used to avoid degradation of the deep network, and the improved atrous spatial pyramid pooling module can extract multi-scale features without changing the size of the feature map. First, the remote sensing image dataset is preprocessed and made the corresponding labels, and then the Gaofen-1 WFV remote sensing image dataset is used for training and testing. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively improve the detection accuracy of cloud and cloud shadow, and can still obtain better edge details of cloud and cloud shadow under complex conditions.
To solve the problems of low detection accuracy for remote sensing images in complex scenes with complex background and small and dense objects, an improved YOLOv3 algorithm is proposed in this paper. Based on YOLOv3, our algorithm is combined with dense connection network (DenseNet) and uses the dense connection blocks to extract deep features and enhance feature propagation. Meanwhile, Distance-IoU (DIoU) loss is introduced as the loss function of coordinate prediction, making the location of the bounding box more accurate. Besides, aiming at the situation of mutual occlusion between targets, we use DIoU instead of IoU in the improved non-maximum suppression algorithm to overcome the problem of false suppression. The proposed algorithm is tested on three classical remote sensing datasets, and the experimental results show that the detection method in this paper has higher detection accuracy.
Recently, the rapid advancements in tissue optical clearing technology have brought new opportunities for modern orthopedic optical imaging research. Tissue optical clearing technology primarily reduces tissue light scattering and light absorption through various physical and chemical methods, allowing light energy to better spread in the tissue in order to increase the depth and contrast of optical imaging. Deeper and higher resolution bone tissue images and 3D spatial microstructure information can be obtained when combined with various fluorescence-labeling strategies, presenting a novel perspective and method for a breakthrough in the molecular imaging study of bone tissue with high scattering and bone disease. In this study, we will discuss the principle and mechanism of tissue optical clearing technology, focusing on the current state, most recent methods, and the mechanism of bone tissue clearing imaging, and prospect the possibility of using this technique in the molecular imaging of bone.
The spectral imaging system on chip has many advantages, such as compact structure, light weight and portability. It can be flexibly mounted on unmanned aerial vehicle and cubic star platform, showing broad application prospects. This paper reviews the research progress and applications of spectral imaging system on chip in recent years, also summarizes the spectrum achieving principle and integration mode of chip-scale spectral imaging system. In addition, some key applications of spectral imaging system on chip in biomedical, environmental monitoring, military equipment, intelligent consumer electronics and other fields are shown in the paper. This paper reveals that the on-chip spectral imaging system is currently facing challenges and development direction in the future.
Herein, we collected the spectra of nine types of common camouflage materials and backgrounds to analyze and extract the spectra of camouflage materials based on reflectance spectra. Then, after envelope removal, we analyzed the original reflectance curves and the spectral curves and used several spectral difference algorithms to calculate the spectral data and then evaluate the camouflage effect. Differences in the spectral characteristics of several groups of camouflage targets, which are difficult to distinguish in visible images, are obtained via experiments, thus providing a basis for selecting bands and camouflage materials.