This paper proposes a method for the scene classification of optical remote sensing images based on the residual network of convolutional neural networks. In the proposed method, two modules, i.e., jump connection and covariance pooling, are embedded in the original network model to achieve multiresolution feature mapping and combine different levels of multiresolution feature information. Experiments are conducted on three open classical remote sensing datasets. Results show that the proposed method can fuse the multiresolution feature information of different levels in the residual network and use higher-order information to achieve more representative feature learning. The proposed method exhibits higher classification accuracy in the scene classification problem compared with the existing classification methods.
In the deep space exploration missions, the detector needs to land in complex terrain areas. Therefore, the rapid detection of on-orbit obstacles is very important, and image segmentation is one of the key processes of on-orbit detection. In view of this, a multi-level threshold image segmentation algorithm based on particle swarm and gray wolf hybrid optimization is proposed. In the optimization process, the proposed algorithm defines the threshold series for different scenes by changing the initial population conditions considering the image energy distribution. In the process of location update, the proposed algorithm increases the perturbation operators to expand the scope of global search, and introduces dynamic weights to balance the global search ability and local search ability of the group, thereby improving the speed and accuracy of optimization and completing image segmentation. The experimental results show that compared with the traditional swarm intelligence algorithm, the proposed algorithm shows better search ability, and it has obvious improvement in dealing with the problem of complex images where the gray histogram does not show bimodal peaks.
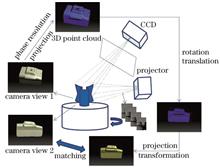
In order to improve the speed and accuracy of point cloud matching in the structured light three-dimensional reconstruction system, a collaborative matching method of two-dimensional view and three-dimensional point cloud across feature points is proposed in this work. First, the normalization of the projected images to be spliced is realized through projection transformation and dimension mapping. After preprocessing, the endpoints and bifurcation points are extracted as key points, and the similar points are triangulated and similarly matched to obtain the initial point set. The initial point set is mapped to three-dimensional space. Second, kd-tree search is used to obtain the centroid of the double neighborhood, and the point set is further screened according to the triangle similarity relationship formed by the three points. Finally, the quaternion method is used to complete the rough splicing, and then an improved iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is used to complete the fine splicing. Experimental results show that the matching accuracy of the proposed algorithm is 98.16%, the matching time is 3 s, and the center of gravity distance error of the coarse splicing overlap area is 0.018mm. The proposed algorithm has high robustness for two-dimensional image perspective transformation, smooth texture, and uneven light.
To address the low detection accuracy and slow speed of traditional flame detection model, a video flame region detection method based on optimal convolutional neural network and hyperpixel segmentation algorithm is proposed. First, the flame image dataset is used to train and verify the model, and the structure of the Inception module is improved by stacking and replacing the convolution kernel. Second, the small convolution kernel replacement is adopted to improve the front-end structure of the network, and the Focal-Loss function is used as the loss function to improve the generalization ability of the model. Next, the parameter complexity optimization experiment of the InceptionV1 model is designed to generate an optimized flame detection network structure. Finally, the flame super-pixel semantic information extracted by the superpixel segmentation algorithm is input into the optimized InceptionV1 model, and the location detection of the video flame area is further performed. Experimental results show that the proposed method can enhance the nonlinear feature extraction of video flames; the accuracy of flame detection is higher than 96%, and the detection speed is 2.66 times that of the original model.
Aiming at the problem that the traditional convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithms only recognize semantics of one-hand gestures and the problems of the poor convergence and low recognition accuracy of the deep learning gesture recognition algorithm, an adaptive one-hand and two-hand gesture recognition algorithm based on double classifiers is proposed to recognize single-hand and two-hand gestures. The core of the algorithm is combining two classifiers for single-hand and two-hand gesture recognition. First, the hand number classifier is used to segment and group the gestures, and the gesture recognition is converted into partial gesture image recognition. Second, the adaptive enhanced convolutional neural network (AE-CNN) is used for gesture recognition, and the adaptive module analyzes the cause of the recognition error and feedback mode. Finally, the parameters are updated based on the number of iterations and recognition results. Experimental results show that the correct probability of the hand number classifier for gesture prediction grouping is 98.82%, the convergence of AE-CNN is better than that of CNN and CNN+Dropout, and the recognition rate of one-hand gestures is as high as 97.87%. The overall model recognition rate of 9 types of single-hand gestures and 10 types of double-hand gestures built based on LSP dataset is 97.10%, and the average recognition rate of gestures under complex backgrounds and different light intensities is 94.00%. The proposed algorithm has certain robustness.
Aiming at the defect of low feature matching accuracy of the ORB algorithm, combined with the optical flow characteristics of the pyramid, this paper proposes a method to optimize the ORB feature matching. First, the region matching method is used to process the matching images, the best trusted matching sub-blocks are selected, and the invalid matching area is narrowed. Then the ORB keywords are extracted from the sub-blocks and the matching descriptors are calculated to obtain the coarse matching point pairs. Pyramid optical flow method is used to track the ORB feature points, and the motion displacement vectors of the feature points are calculated to remove the incorrect matching pairs in the rough matching part. Finally, the random sample consensus algorithm is used to further remove redundant matching points to obtain a more accurate match. Experimental results show that the optimized ORB algorithm can well possess the real-time performance and accuracy. The average time for feature matching is about 87% of the original ORB algorithm, and the average matching rate is over 98%.
In order to well model the long-term time-domain information of human action, a human action recognition algorithm based on sequential dynamic images and two-stream convolution network is proposed. First of all, the sequential dynamic images are constructed by using sequential pooling algorithm to realize the mapping of video from three-dimensional space to two-dimensional space, which is used to extract the apparent and long-term sequential information of actions. Then, a two-stream convolution network based on inceptionV3 is proposed, which includes apparent and long-time motion flow and short-time motion flow. The input of the network is sequential dynamic images and stacked frame sequence of optical flow, and it combines data augmentation, pre-trained model, and sparse sampling. Finally, the classification judgment scores output by each branch is fused by average pooling. Experimental results on UCF101 and HMDB51 datasets show that, compared with the traditional two-stream convolution network, this method can effective use the temporal and spatial information of the action, and the recognition rate can be improved greatly, which shows effectiveness and robustness.
In the Tibetan historical document images, there usually exist adhesion and overlapping between adjacent text lines, which makes text line segmentation become a difficult task. We propose a method for line segmentation of Tibetan historical document images, which combines the text core regions and expansion growth. First, the non-syllable points are removed according to the area and roundness of the connected components in the binary Tibetan historical document images and thus the syllable point images are obtained. Second, through the syllable point image via horizontal projection and the binary original image via vertical projection, the scope of the text line baselines and the number of text lines are obtained and the text core regions are generated. Meanwhile, the text core regions are combined with the binary original images via the or operation of pixel values to obtain the pseudo-text connected regions. Finally, based on the breadth-first-search algorithm, the expansion growth from the text core regions to the pseudo-text connected regions is realized and the pseudo-text line connected regions are obtained. The non-literal regions are removed to obtain the pseudo-text lines, and the final text lines are obtained through an effective algorithm for the line attribution of broken strokes. The experimental results show that the proposed method achieves relatively good text line segmentation effect and effectively solves the problems in text line segmentation of Tibetan historical documents, such as overlapping between text lines, partial adhesion between lines and stroke breaking.
Aiming to solve the problems of complex drug-grabbing tasks and low efficiency of existing pharmacists, a vision-based drug-grabbing robot system is designed, and a drug-identification algorithm based on the fusion of local feature matching and based on Mean Shift algorithm is proposed. The complete system realizes drug identification, positioning, and grabbing tasks. The drug-grabbing robot installed between the drug racks receives information of the medicine sent by the upper computer, identifies the medicine through its camera, matches the medicine on the transporter using the AKAZE algorithm, obtains the coordinates of the medicine, and grabs and places the matched medicine on the transporter. After the sorting robot located in the designated area for taking the medicine obtains information of the medicine sent by the upper computer, the dynamic medicine on the transporter is identified twice via the improved Mean Shift algorithm, and the identified medicine is grabbed and placed in the designated area for taking the medicine to complete the taking function of the whole system. Experiments show that the system can accurately identify the drugs with the guarantee of secondary sorting and can accurately locate drug information with a small error, which is suitable for drug grabbing in pharmacies.
This study proposes a new network framework based on a lightweight attention mechanism and the YOLOv3 backbone network. When designing the feature extraction network, the standard convolutions of the YOLOv3 backbone network are replaced using depthwise and pointwise convolutions, thereby accelerating the model training and increasing the detection speed. Next, the speed and accuracy of the model are weighted using an attention mechanism module. Finally, multiple-scale prediction layers are added to extract more feature information; simultaneously, the network parameters are optimized using the K-means++ clustering algorithm. In an experimental evaluation on face-detection performance, this method considerably improved the face-detection performance, achieving 94.08% precision and 83.97% recall on the Wider Face dataset. The average detection time is 0.022 s, which is 4.45 times higher than that of the original YOLOv3 algorithm.
A novel demosaicing algorithm based on deep learning is proposed to address the problems of zippers and artifacts that often occur in the traditional Bayer demosaicing algorithm. First, the proposed algorithm decomposes, removes, and combines pixels in the red, green, and blue channels of mosaic images to obtain two color images. The two color images are then inputted into a designed convolutional neural network to reconstruct the complete color image. The network can make the full use of the feature information generated by the convolutional layer. The experimental results show that the quality of the whole color image reconstructed by the proposed algorithm is relatively high, and the zippers and artifacts are relieved to a certain extent. The objective index and subjective evaluation of the proposed algorithm are better than the contrast algorithms.
In this study, we propose a shared lightweight convolutional neural network (CNN) to automatically identify vehicle colors and types. In the basic network, an improved SqueezeNet is employed. Further, we compare the classification performances of different “slimming” SqueezeNets on the training set. In addition, the characteristics of the fully shared, partly shared, and no-shared networks are discussed. Experimental results indicate that the fully shared lightweight CNN not only reduces the number of parameters but also realizes high-precision recognition of the multiple attributes associated with the appearance of vehicles. Subsequently, an experiment was conducted on the Opendata_VRID dataset. The accuracy of vehicle color and type recognition is 98.5% and 99.1%, respectively. A single picture can be recognized on a personal computer without GPU in only 4.42 ms. Thus, the shared lightweight CNN considerably reduces time and space consumption and is more conducive for deployment in resource-constrained systems.
In view of the low contrast and many noise points of the mesh fabric image, the segmentation results have the problems of mesh connection and incompleteness. A segmentation algorithm based on the minimum gray value of the region is proposed to improve the segmentation accuracy of the mesh. First, the image is processed with Gaussian pyramid scaling and histogram equalization algorithm to enhance the texture contour and contrast of light and dark of the image. Then, a segmentation algorithm based on the minimum gray value of the area is used to solve the problem that the mesh cannot be segmented correctly only by the gray value. Finally, a multi-image fusion algorithm is used to solve the problem of difficult threshold selection in the segmentation algorithm based on local gray scale minima. A variety of mesh fabric images with different illumination levels are selected for experiments. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has a good segmentation effect, which can effectively solve the problems of mesh adhesion and incompleteness in the segmentation results. The segmentation error rate of the mesh fabric is 0.24%.
The pedestrian detection algorithm based on the histogram of orientation gradient (HOG) feature and the local binary pattern (LBP) operator adopts the sliding window search strategy. The scanning area is too large and the calculation is complex, which will cause the detection speed to be slow. In view of this, a pedestrian detection algorithm is proposed. First, a selective search algorithm is used to locate the target area, and the aspect ratio of the candidate area is limited to a certain range to filter out invalid windows. Then, in order to make up for the defects of LBP operator in texture expression, a complete local binary pattern (CLBP) operator is introduced to improve the expression ability of texture features. Then, considering that the dimensionality of the HOG feature and the CLBP operator is too high to affect the recognition ability of the classifier, the principal component analysis method is used to reduce the dimensionality of the HOG feature and the CLBP, respectively, and series fusion is conducted after dimension reduction. Finally, the mining process of hard examples is introduced to train the support vector machine classifier, which can make the model more fully trained and thus reduce the false detection rate. The simulation results on the INRIA dataset show that the proposed algorithm has a certain improvement in recognition rate and recognition speed.
The traditional mosaicking technology exhibits insufficient utilization of the image information. Therefore, a hyperspectral image mosaicking technique based on the double-layer fusion of image and data is proposed. In case of the image layer, the scale-invariant feature transformation algorithm is used to extract the image features and the Euclidean distance is used to determine the feature matching range. Further, the features are matched according to the coordinate conversion relation to complete image layer mosaicking. In case of the data layer, the data is divided into high and low data. Then, the weighted sum method is used to calculate the new value of data and stitch it, and the high and low data are merged via the displacement operation to complete the mosaicking of the data layer. Finally, the image and data are stored in the BIL mode for completing the double-layer fusion of image with data. The hyperspectral image mosaicking experiment is conducted in a certain area. Experimental results demonstrate that the average mosaicking accuracies of the image and data layers are 0.9214 and 0.9663, respectively, indicating the effectiveness and accuracy of the proposed technique.
A single-layer long short term memory (LSTM) network is not generalizable to solve complex speech emotion recognition problems. Therefore, a hierarchical LSTM model with a self-attention mechanism is proposed. Penalty items are introduced to improve network performance. For the emotion recognition of video sequences, the attention mechanism is introduced to assign a weight to each video frame according to its emotional information and then classify these frames. The weighted decision fusion method is used to fuse expressions and speech signals to achieve the final emotion recognition. The experimental results demonstrate that compared with single-modal emotion recognition, the recognition accuracy of the proposed method on the selected data is improved by approximately 4%, thus the proposed method has a better recognition results.
Aiming at the problems of super-resolution convolutional neural network (SRCNN) with fewer convolutional layers, long training time, difficulty in convergence, and limited expression and generalization capabilities, a residual deconvolution SRCNN (RD-SRCNN) algorithm is proposed in this work. First, different size convolution kernels are used for convolution operation to better extract the detailed features in low resolution images. Then, the acquired image features are input into the residual network composed of convolution layer composed of convolution kernels of different sizes and activation layer of exponential linear unit, and each feature extraction unit is connected by short path to solve the problem of gradient disappearance and realize the feature reuse, and reduce the network redundancy. Finally, a clear high-resolution image is obtained by adding a deconvolution layer to increase the receptive field. Experimental results show that the RD-SRCNN algorithm achieves good results in both visual and objective evaluation criteria.
Aiming at the identification problem with poor robustness based on current finger-knuckle-print recognition methods, a finger-knuckle-print recognition method using non-subsampled Shearlet transform (NSST) and Tetrolet energy features is proposed in this paper. First, histogram equalization is used to adjust the gray level of the image to reduce the influence of uneven light distribution on the recognition system. Second, the NSST and its inverse transform are used to obtain the reconstructed image after denoising, and Tetrolet transform is performed on it to establish the energy surface of low-frequency image. Finally, the energy difference surface is obtained by subtracting the energy surface of different images, and the variance of the surface is further calculated. Based on this, the classification and recognition of different finger joint print images are carried out. The experiment results on the HKPU-FKP, IIT Delhi-FK, and HKPU-CFK databases and their noise databases show that the correct recognition rate of the method is 98.0392%, the shortest recognition time is 0.0497 s, and the lowest equal error rate is 2.5646%. Compared with other algorithms, the algorithm improves the performance of the finger-knuckle-print recognition system, which is feasible and effective.
In order to solve the problem that the scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) has a large amount of calculation and cannot meet the requirements of accuracy and real-time in the navigation algorithm, a parallel SIFT algorithm FG-SIFT based on fast Gaussian blur is proposed. First, the two-dimensional Gaussian kernel function, which constructs the Gaussian pyramid, is separated into two one-dimensional Gaussian functions to reduce the computational complexity. Then, two infinite impulse response filters are used in series to approximate each one-dimensional Gaussian kernel function to further reduce the computational complexity. Finally, using the advantage of parallel processing, the parallel computing scheme of each part of the algorithm is designed. Simulation results show that the computational efficiency of FG-SIFT algorithm is 15 times higher than that of the original SIFT algorithm, and the running efficiency of FG-SIFT algorithm on graphics processing unit is nearly 2 times higher than that of SIFT without fast Gaussian blur. This algorithm greatly reduces the calculation time of feature point extraction and improves the real-time performance.
Hyperspectral image clustering has always been a hot topic in the field of image processing. Spectral clustering algorithm, as one of the most popular clustering algorithms, is widely used in hyperspectral image clustering. However, due to the large computational complexity of the spectral clustering algorithm, it is difficult to process large-scale hyperspectral image data. Because the binary tree can select anchor points very fast, the spectral and spatial characteristics of a hyperspectral image are fully utilized to ensure the clustering performance and reduce the computational complexity based on the binary tree anchor graph. However, the clustering algorithm generally adopts the kernel clustering method, therefore it is inevitable to introduce parameter adjustment. Thus, based on the selection of anchor points in the binary tree, we proposes a hyperspectral fast clustering algorithm based on the binary tree anchor graph. This algorithm innovatively applies the method of binary tree anchor selection and coreless clustering to the hyperspectral images. First, the binary tree is used to select some representative anchor points from the hyperspectral data. Second, a coreless similarity map is constructed based on these anchor points, which effectively avoids the artificial adjustment of the thermonuclear parameters to construct the similarity map. Third, the spectral clustering analysis is performed to obtain the clustering results. Finally, this algorithm is used for hyperspectral image clustering. This algorithm not only improves the clustering speed, but also reduces the necessity of original thermonuclear parameter adjustment. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can obtain better clustering accuracy in a shorter time compared with the traditional clustering algorithm.
Aimed at the problem of traditional semantic segmentation algorithms having large parameters and slow running time, which are not conducive to their practical application for contraband identification technology, this paper proposes a prohibited item identification algorithm based on a lightweight segmentation network. A dilated convolution module is used in a shallow feature layer of the model to enlarge the receptive field of the network, reduce misclassification, and improve segmentation precision. To reduce computational complexity, an asymmetric convolution module is used in a deep feature layer to replace the traditional single convolution operation. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves balanced performance for identification accuracy and speed, the mean intersection over union (mIoU) is 73.18×10 -2, and the frames per second rate (FPS) is 27.1.
The simple linear iterative clustering (SLIC) method does not perform well in edge detail processing in image segmentation. Thus, a modified color image segmentation algorithm is proposed combining a “parameter-controlled modified simplified” pulse coupled neural network (PC-MSPCNN) and SLIC. The proposed algorithm works in two steps. First, the weighted matrix and connection coefficient of the MSPCNN model are improved, and the auxiliary parameters are added to improve the accuracy of the segmentation. Then, the color image is input into the PC-MSPCNN model, and the edge of the object is divided according to the distribution of the output Y value in the improved model so that the segmentation results appropriately fit the edge of the object, and the proposed similarity criterion is used to merge the scattered fragments to reduce the complexity of subsequent processing. Second, based on the measurement similarity of the SLIC, the internal activity term U values of the three RGB channels in the PC-MSPCNN are introduced to achieve weighted fusion clustering for the remaining parts of the image to improve clustering. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can accurately fit the edge of an object, considerably reduce the number of pieces, and effectively improve adherence of the image edge.
Aiming at the low efficiency of GrabCut algorithm in image segmentation, and the problems of under-segmentation and over-segmentation, an improved GrabCut algorithm based on probabilistic neural network (PNN) (PNN_GrabCut) is proposed in this paper. The algorithm replaces the Gaussian mixture model (GMM) in the GrabCut algorithm with PNN model to calculate the weight of t-links to improve the calculation efficiency of the algorithm. By constructing the foreground and background histograms, the pixels with higher pixel values are selected as training samples of the PNN model to improve the segmentation accuracy of the algorithm. In the public ADE20K data set, images are selected for segmentation experiments. The results show that the segmentation accuracy of PNN_GrabCut algorithm is better than other comparison algorithms, and the efficiency is higher. For image segmentation experiments with high similarity between foreground and background, the results show that the segmentation accuracy of PNN_GrabCut algorithm is significantly higher than that of GrabCut algorithm.
A simultaneous algebraic reconstruction technique based on group sparse regularization (GSR-SART) algorithm is proposed in this study to address the problems of large positioning error of the fluorescent light source and incomplete morphological information in fluorescence diffuse optical tomography. The algorithm uses nonlocal self-similarity and intrinsic local sparsity to construct the self-adaptive similar group. Then, the similar group is considered the basic unit to learn the adaptive dictionary. Finally, the target function is solved using the iteration shrinkage threshold algorithm. The experimental results show that compared with the other advanced algorithm, the proposed algorithm yields better results in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio and root mean square error.
The collapse of trees can be mainly attributed to the decay and hollow in standing timber. The internal structure of standing timber is verified to determine the internal defects. In this study, a method is proposed to detect the internal defects in standing timber based on microwave tomography. First, a microwave tomography system comprising 16 antennas is developed. Second, a healthy wood model and two wood models with different defects are simulated at a frequency of 1 GHz. Third, the finite element analysis software is used to simulate the internal electric field characteristics of the standing timber, based on which image reconstruction can be performed using the linear backprojection image reconstruction algorithm, thereby reconstructing the dielectric constant distribution map inside the wood. Then, the reconstructed image is analyzed based on the average structural similarity index. Finally, qualitative and quantitative analyses of the different trunk models and reconstructed image are conducted. Simulation results demonstrate that the position and size of a defect can be directly identified using the proposed microwave tomography system based on the visualization effect of the reconstructed permittivity distribution map.
To improve calibration accuracy, this paper proposes a light plane calibration method based on a line transformation in space. First, a cross-correlation template and a 5-point moving-average method are used to extract the center of the laser stripe, and the linear regression equation of the light bar in the images is then fitted by the orthogonal regression method. A straight line equation for the target surface light bar is obtained by a plane homography transformation, and the straight line equation in the target coordinate system is converted to Plücker matrix form. According to the pose transformation relationship, the straight line equations in the camera coordinate system are obtained and statically indeterminate line-plane co-planar constraint equations are established. A singular value decomposition(SVD) is used to solve the parameters of the light plane equation. The root mean square (RMS) of the standard step block length obtained by the proposed method is 0.065mm, and the average error is less than 0.030mm. The measured average error of cylinder diameter and RMS are less than 0.050mm. The results show that the proposed method uses the overall information of the light bar itself to fit the light plane, which can achieve higher calibration accuracy. This represents a simple calibration process that avoids the separate solution of each feature point.
Matching difficulty and the occurrence of large errors in the weak and repeated texture areas of an image are the problems associated with the stereo matching algorithm. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a stereo matching algorithm based on improved cost calculation and a disparity candidate strategy. First, the improved Census transform and adaptive weighted bidirectional gradient information are combined to estimate the initial matching cost, improving the reliability of cost calculation. Here, inner circle coding is added to the traditional Census transform for improving the utilization of neighborhood information while reducing the impact of noise. The adaptive weight function is used to combine the horizontal and vertical gradient costs for reducing the mismatching rate of the object edge areas. Second, after cost aggregation with an adaptive cross-window, the initial disparity can be obtained by establishing candidate disparity sets and introducing neighborhood disparity information. Finally, the disparity is optimized via two-round interpolation. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can improve the stereo matching of the weak and repeated texture areas and that the average mismatching rate on four standard stereo image pairs in Middlebury is 5.33%.
Aiming at the problems of low accuracy and complex parameter setting in the traffic sign segmentation of a pulse-coupled neural network, we propose an improved pulse-coupled neural network with adjustable parameters (PA-MSPCNN) in this paper. By analyzing the color characteristics of traffic signs, the PA-MSPCNN preprocesses the image with reddening and distinguishes traffic signs and the environmental background. The influence of neighboring neurons on central neurons improves the weighing matrix and the connection coefficient of the MSPCNN. We analyze the relationship between the dynamic thresholds and adjust these more reasonably by adding an auxiliary parameter. The experimental results show that the segmentation accuracy of the PA-MSPCNN on traffic sign images is 85%. The PA-MSPCNN not only reduces the number of parameters in the traditional PCNN model but also accurately segments the image, which has better applicability for complex situations such as changes in illumination conditions, scale changes, and geometric rotation of traffic signs.
The RetinaNet and Libra RetinaNet object detectors based on deep learning employ feature pyramid networks to fuse multiscale features. However, insufficient feature fusion is problematic in these detectors. In this paper, a multiscale feature fusion algorithm is proposed. The proposed algorithm is extended based on Libra RetinaNet. Two independent feature fusion modules are constructed by establishing two bottom-up paths, and the results generated by the two modules are fused with the original predicted features to improve the accuracy of the detector. The multiscale feature fusion module and Libra RetinaNet are combined to build a target detector and conduct experiments on different datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that the average accuracy of the added module detector on PASCAL VOC and MSCOCO datasets is improved by 2.2 and 1.3 percentage, respectively, compared to the Libra RetinaNet detector.
Stereo region-convolutional neural networks (Stereo R-CNN) algorithm has the characteristics of accuracy and efficiency. It has better detection performance in certain scenes, but there is still room for improvement in the detection of distant targets. In order to improve the vehicle detection accuracy of the binocular vision algorithm, an improved Stereo R-CNN algorithm is proposed in this paper. The algorithm uses deterministic network (DetNet) as the backbone network to enhance the network's detection of long-term targets; for the potential key points of the left and right eye views, the consistency loss function of the key points of the left and right views is established to improve the location accuracy of the potential key points, and then improve the accuracy of vehicle detection. Experimental results on the KITTI data set show that the performance of the algorithm is better than Stereo R-CNN, and the average accuracies of two-dimensional and three-dimensional detection tasks are improved by 1%-3%.
In order to solve the problem of the spatial dislocation caused by person detection error in person re-identification, the local-based deep neural networks model only learn the adjacent local relationship, resulting in lack of long-distance local correlation. This paper proposes a person re-identification algorithm based on first-order and second-order spatial information. On the backbone network, first-order spatial mask is learned to fine-tune the spatial weight of the input image to reduce the background interference. The second-order spatial mask is used to model the long-distance dependency relationship, and local features are integrated into the dependency model to obtain the global feature representation. In the local branch, DropBlock is introduced to regularize the pedestrian features to avoid the network model relying too much on specific part features. In the training stage, the whole network is optimized by the label-smoothed cross-entropy loss and the triple loss with positive samples’ center. Experimental results based on Market-1501 and DukeMTMC-reID data sets show that compared with other mainstream algorithms, the person re-identification accuracy of the algorithm is higher, and the extracted pedestrian features are more discriminative and robust.
For current correlation filter target tracking algorithm, the spatial regularization weight is not connected with an object, and the temporal regularization term fails to update adaptively. To resolve this problem, a correlation filter based on adaptive spatiotemporal regularization was proposed. The adaptive spatial regularization term first obtains the spatial regularization weight connected with the object by initial-frame saliency aware reference weight. Second, the reference value of the temporal regularization parameter is calculated using the altered response score between two adjacent frames. Thus, the adaptive temporal regularization term can be continuously updated by the changing regularization parameter. Finally, the algorithm is optimized by the alternating direction method of multipliers, which reduces the number of iterations and solves the related parameters (filtering function, spatial regularization weight, and temporal regularization parameter). In an experimental evaluation on OTB-2015 dataset, our algorithm outperformed comparable algorithms, achieving a distance precision of 86.4% and a success rate of 65.6%. The proposed algorithm also showed higher robustness in complex scenes with deformation, rotation, occlusions, and out of view than the competing algorithms.
Binocular stereo matching transforms plane vision into three-dimensional stereo vision based on the parallax principle, which is one of the core steps of three-dimensional reconstruction. Aiming at the problems of local stereo matching algorithm in the depth discontinuity, low matching accuracy in weak texture areas, and easy to be interfered by factors such as light and noise, an improved stereo matching algorithm is proposed in this paper. First, in the cost calculation stage, the improved Census cost and the gradient cost are fused, and the guided filtering algorithm is used to perform multi-scale cost aggregation on the image; then, the winner-take-all algorithm is used to calculate the initial disparity; finally, the left-right consistency detection, middle value filtering performs disparity post-processing to obtain the final disparity image. Experimental results show that the average mistake match rate of the algorithm on the Middlebury2.0 test platform is 5.11%, and it has good robustness and practicability.
The deep learning method based on convolutional neural network plays a very important role in promoting the automatic detection of rail surface damage. Therefore, a method based on convolutional neural network for rail surface damage detection is proposed. First, a branch network is added between the contraction path and extension path of the classic U-Net can assist U-Net to output the ideal segmentation graph. Then, the type-I RSDDs high-speed railway track dataset is taken as the test sample, and the test sample is amplified by means of data enhancement and fed into the improved U-Net for training and testing. Finally, the evaluation index is used to evaluate the proposed method. The experimental results show that the detection accuracy of the proposed method reaches 99.76%, which is 6.74 percentage higher than the highest level of other methods, indicating that the proposed method can significantly improve the detection accuracy.
This paper aimed to solve the problems of road edge detail information loss and inaccurate road extraction due to multiple downsampling operations of the fully convolutional neural network. Thus, a road extraction method of GF-1 remote sensing images based on dilated convolution residual network with multiscale feature fusion is proposed. First, numerous labels for road extraction are generated through visual interpretation. Second, dilated convolution and multiscale feature perception modules are introduced in each residual block of the residual network, namely, ResNet-101, to enlarge the receptive field of the feature points without reducing the feature map resolution and losing the detailed edge information. Third, through superposition fusion and upsampling operations, the road feature maps of various sizes are fused to obtain the feature maps of the original resolution size. Finally, for classification, the feature maps are input into the Sigmoid classifier. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method is more accurate than the conventional fully convolutional neural network models, with the accuracy rate being more than 98%. The proposed method effectively preserves the integrity and detailed edge information of the road area.
Tree species investigation has been faced with problems such as high cost, low efficiency, and low precision. The use of remote sense can greatly increase the work efficiency of tree species investigation and save cost. Although convolutional neural network (CNN) has made many breakthroughs in natural image classification area, few people have used CNN model to carry out individual tree species classification. Based on the above considerations, this paper builds CNN models, and integrates them with high-resolution remote sensing imagery to classify individual tree species. In the course of semi-automatically constructing the sample set of remote sensing imagery of individual tree species with high-resolution imagery, the crown slices from imagery (CSI) delineation, manual annotation, and data augmentation are used. Meanwhile, in order to train the sample set of remote sensing imagery of individual tree species, five CNN models are adapted. Through comparative analysis, it is found that LeNet5_relu and AlexNet_mini cannot achieve the best classification effect. GoogLeNet_mini56, ResNet_mini56, and DenseNet_BC_mini56 have the best classification effect for different species respectively. DenseNet_BC_mini56 has the highest overall accuracy (94.14%) and the highest Kappa coefficient (0.90), making it the best classification model from all aspects. The research proves the effectiveness of CNN in the classification of individual tree species, which can provide a critical solution for forest resource investigation.
Aiming at the problem that remote sensing images with complex environmental backgrounds and small targets are difficult to perform accurate target detection, based on the single-stage detection model (SSD), a single-stage target detection model based on attention and feature fusion is proposed in this paper, which is mainly composed of detection branch and attention branch. First, the attention branch is added to the detection branch SSD. The fully convolutional network (FCN) of the attention branch obtains the location characteristics of the target to be detected through pixel-by-pixel regression. Second, by using the method of adding corresponding elements to the detection branch and attention branch, the feature fusion of detection branch and attention branch are carried out to obtain high-quality feature image with more detailed information and semantic information. Finally, soft non-maximum suppression (Soft-NMS) is used as a post-processing part to further improve the accuracy of target detection. Experimental results show that the mean average accuracy of the model on the UCAS-AOD and NWPU VHR-10 data sets are 92.52% and 82.49%, respectively. Compared with other models, the detection efficiency of the model is higher.
When a coherent beam propagates through a strong scattering medium, a speckle pattern of the output field can be formed due to random scattering. As a consequence, it is impossible to directly acquire the original information of the input beam from the output scattering field. However, in the random scattering process, the output speckle pattern still contains the original information of the incident beam. The acquirement of the original information based on speckle patterns for the reconstruction of an object has become a hot research topic. As for this problem, the techniques including speckle correlation, transmission matrix, wavefront control as well as time reversal and phase conjugation have been proposed. The scattering imaging technique based on correlation holographic theory is mainly introduced, in which its principle, history and recent new progress are included. In addition, its future development is prospected.
Flammable liquids are widely used in food, chemical industry, energy, and other fields, and have created great economic value. However, these liquids are flammable and explosive and sometimes generate toxic vapor, and thus their nondestructive detection is of great importance for promoting industrial production and guaranteeing personal and property safety. Spectroscopic methodologies have the advantages of fast response, online and nondestructive detection, no need of sample pretreatment, and high precision, playing an important role in the detection of flammable liquids. In this paper, we expounded the technical principles of the spectroscopic methodologies for flammable liquids and highlighted the development history and application status of five typical spectroscopic methodologies for flammable liquids, including near-infrared spectrometry, Raman spectrometry, ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry, fluorescence spectrometry, and terahertz time-domain spectroscopy. Furthermore, we discussed the future potential applications of these spectroscopic methodologies in combination with their advantages and disadvantages.
With the wide applications of three-dimensional (3D) meshes in digital entertainment, television animation, virtual reality, and other fields, there are more and more processing techniques for 3D meshes, including compression, simplification, watermarking, and denoising. These processing techniques will inevitably lead to various distortions in 3D meshes. Therefore, how to preferably evaluate the visual quality of 3D meshes becomes an urgent problem to be solved at present. This paper reviews the objective quality assessment methods for 3D meshes developed during the past 20 years. First, some technical indexes for 3D mesh quality assessment and several public databases are introduced. Second, the quality assessment methods for existing typical three-dimensional meshes are classified, and their respective characteristics are introduced. Then, the typical algorithms introduced in the commonly used databases are tested and compared. Finally, the objective quality assessment methods of 3D meshes are summarized and prospected.