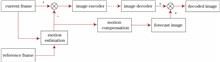
An optimal solution of motion estimation can be obtained using the full search algorithm. However, its implementation requires a large number of operations. This paper introduces a new three-step method, in which, by adding an inner loop search within the search for the first time and applying the abort discrimination technique, the acceleration of stationary block matching can be realized, and the search process can be completed quickly. The algorithm reduces the total number of searches to ensure a certain precision and thus greatly improves search efficiency. Given the process description of the algorithm, search template, etc., the soft core design of the field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is completed using a hardware programming language, and the function simulation is completed using a software tool. The results show that the algorithm utilizes 2177 FPGA logic units and 37112-bit block memory. The soft core can quickly acquire motion vectors and complete the search process.
This paper proposes an asymmetric optical color-image encryption system based on vector decomposition and chaotic random phase mask. The introduction of vector decomposition makes the first phase mask also act as the main secret key when the input image is a real-value image, which makes the encryption system asymmetric. The two chaotic phase masks generated by the 2-D Henon chaotic map replace double random phase masks. The chaotic system’s initial values and control parameters were used as secret keys to increase the key space and provide more security for the encryption system. The following parameters were tested: key sensitivity, correlation coefficients of two adjacent pixels, occlusion attack resistance, noise attack resistance, and chosen-plaintext attack resistance of the encryption system. Test results validate the feasibility and security of the proposed encryption system.
In this study, the gray standard deviation and filter window of the traditional bilateral filter model are improved. First, the noise standard deviation with respect to each pixel in a picture is calculated using the probability distribution and maximum likelihood functions in a fixed square window. Subsequently, the median of the noise standard deviation of the whole picture is considered to be the threshold value. The window of the pixel will contain an edge if the noise standard deviation of a pixel point is greater than the threshold value. Thus, the noise standard deviation and filter window of the pixel point are recalculated using the half-edge rotating window method. Then, each pixel point is filtered using a bilateral filter, where twice the noise standard deviation of this pixel point is considered to be the gray standard deviation. Finally, a strong noise can be judged based on the regional similarity model, and the median filter is used to eliminate the noise. The experiments denote that the edge-preserving and filtering performances of the proposed algorithm are excellent under different noise intensities, and the proposed algorithm can effectively eliminate the strong noise.
This work proposes a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) target-recognition algorithm based on bidimensional empirical mode decomposition (BEMD). BEMD can extract multilevel bidimensional intrinsic mode functions (BIMFs) from the original image, which facilitates a more accurate description of target details. Therefore, a combination of the original SAR images and BIMFs can provide more useful information for further classification. Support vector machines (SVMs) are employed to classify the original SAR images and BIMFs. Afterwards, the outputs from all SVMs are fused using Bayesian theory to obtain more robust recognition results. Some typical experimental setups are designed based on the MSTAR dataset to test the performance of the proposed method. The results validate the superiority of the proposed method over several current SAR target-recognition algorithms.
Existing fusion algorithms for infrared and visible images face issues such as low contrast and clarity of fused image and loss of detailed texture information. To address these problems, a fusion algorithm combining robust principal component analysis (RPCA), compressed sensing (CS), and non-subsampled contour transform (NSCT) is proposed. Firstly, two original images are pre-enhanced, and the pre-enhanced images are decomposed via RPCA to obtain the corresponding sparse and low-rank components. Secondly, the sparse matrices are compressed and sampled using the structural random matrix. Gauss gradient-differential contrast of information (GG-DCI) is used to compress and fuse the images, and the reconstruction is conducted using the orthogonal matching tracking method (OMP). Then the low-rank matrices are decomposed into low- and high-frequency components via NSCT. The low-frequency components are fused using the regional energy-intuitionistic fuzzy set (RE-IFS), the highest-frequency components are fused using the maximum absolute value rule, and other high-frequency components are fused using the adaptive Gaussian region variance. Finally, the fused images are obtained by superimposing the fused sparse and low-rank components. Experimental results show that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm can more effectively improve the contrast and clarity of fused images, retain abundant detailed texture information, possess generally better objective evaluation indexes, and efficiently improve the fusion effect of infrared and visible images.
Existing depth-learning target detection algorithms are unsuitable for air-to-ground target detection because the results are degraded by the single imaging angle, target size changing with imaging height, and complexity of the background interference. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a attention learning mechanism in key areas, which enhances the expressive ability of the feature maps and alleviates the interference of complex background features. This paper first establishes the proposed learning mechanism, which enables the network to select and utilize the features of the target regions in images. Second, it designs a loss function coupled with regional attention and target detection for synchronous optimization of the regional attention loss and target detection loss, which is then achieved by data mining. The proposed algorithm is experimentally evaluated on air-to-ground target detection datasets. The algorithm effectively focuses on and utilizes the feature information of the target key areas, reduces the interference of the background information, and improves the accuracy and anti-interference ability of air-to-ground target detection.
Target detection for optical remote sensing images has always been one of the hotspots in the field of remote sensing. However, the accuracy of the existing detection methods for targets with complex background and small size is low. Aiming at the problem, a target detection method based on Mask-RCNN framework is proposed. The algorithm uses ResNet50 as the feature extraction network and uses the feature reuse technology to realize better extraction of the semantic features of the target. In view of the fact that the size ratio of different types of aircrafts is not fixed, a set of more suitable candidate frame scales is designed. The experimental results show that this method has higher detection accuracy for small object detection compared with the previous detection algorithms.
The disadvantages of the nearest point iterative algorithm (ICP) are low registration efficiency in the big-data point cloud and strong dependence on the initial position of the registration point cloud. To overcome these disadvantages, this study proposes a method that combines the fast point cloud coarse registration method with the ICP algorithm. First, the original point cloud is sampled according to the voxel, and after extracting the key points with the normal vector feature, it is described by the fast point feature histogram (FPFH) algorithm. Subsequently, according to the vector angle feature of the key matching pair in the local neighborhood, the matching point pair is further simplified. Next, the reduced key sequence pair set is used to obtain the transformation parameter with the most interior points using the random sampling consensus algorithm (RANSAC), thereby completing the point cloud coarse registration. Finally, accurate registration is performed using the ICP algorithm on the basis of the point cloud coarse registration. Experimental results show that the registration efficiency and accuracy of the algorithm are improved for high-density point clouds.
A crime scene sketch plays an important role in forensic science as an important part of investigation records. However, in real life, unqualified sketches are developed in many cases. Therefore, this study proposes an automated method to classify crime scene sketches based on a convolutional neural network. First, 64098 crime scene sketches and 27162 photos used as negative samples are collected from the national criminal scene investigation information system (crime scene survey system for short), and are manually labeled to build a crime scene sketch dataset. Then, a new convolutional neural network called XCTNet is designed by introducing “Inception” into AlexNet. Finally, the performance of XCTNet is measured with respect to many aspects, and the images misclassified by XCTNet are extracted. The results denote that XCTNet achieves an accuracy of 98.65% on the test set, which is 3.78 percentage points higher than that of AlexNet; meanwhile, it only uses one tenth of the parameters of AlexNet. However, the recognition accuracy of the proposed method for self-drawn location sketches should be improved.
It takes significant time and a large amount of data for a traditional convolutional neural network-based target-detection algorithm to train its network parameters. Considering that forest fire data are small samples, this work investigates and implements a forest fire detection algorithm using the transfer learning method to train a convolutional neural network. Experiments on the forest fire dataset in this work show that the detection accuracy of this algorithm can reach 97%. In addition, the algorithm is more adaptable for forest fire detection as it has the advantages of high accuracy, low false alarm rate, and short detection time.
A model pruning method based on gray correlation analysis is proposed to solve the problem that the convolutional neural network cannot be deployed on embedded devices due to the huge computation and memory space. For the weight model file after data training, the importance of each convolution kernel is quantized by using the pruning method based on gray correlation analysis. In each pruning, the convolution kernel with the minimum quantization result is deleted from the model so as to reduce the computation and accelerate the inferential speed. Iteration training is used to compensate for the performance loss of the new model. The experimental results show that compared with APoZ method and L1 method, the accuracy of the proposed method increases by 5.3% and 10.4% at the same inferential speed, the acceleration effect of VGG-16 model is 2.7 times that of the original model, and the memory space is reduced to 1/13.5.
To solve problems of leak classification of small targets, unable to extract occluded targets, and missing details of remote sensing image existing in deep convolution networks, a remote sensing image segmentation method based on multi-level channel attention (SISM-MLCA) is proposed. This deep convolution coding-decoding network-based method initially adds the channel attention mechanism in the network coding stage and obtains more effective features through self-learning to solve the problem of target occlusion in remote sensing images. Next, feature map fusion of channel attention is applied at different scales to extract abundant context information and deal with target scale changes. This solves the problem of small target segmentation and improves the performance of segmentation. In this study, experiments conducted on two datasets demonstrate that SISM-MLCA has high accuracy for target segmentation and good segmentation results for small and occluded targets. Good results are achieved in target segmentation of remote sensing images with limited training data, complex and diverse backgrounds, and large-scale changes. These results demonstrate that SISM-MLCA is applicable to the target segmentation of complex remote sensing images.
A three-dimensional (3D) deformable convolutional neural network is proposed based on the C-3D convolutional neural network for realizing detection of pulmonary nodules. A 3D deformable convolution and pooling is used in the main structure of the model. It solves the problem that the traditional square convolution and pooling cannot collect the pixels of pulmonary nodules efficiently when dealing with irregular pulmonary nodules. By adjusting the input of the 3D convolutional neural network, the scanning and recognition of 32×32×32 pixels of a sample image are realized step by step by using a convolutional neural network, thereby realizing pulmonary nodule localization. As for the output of the model, the first full connection layer of the C-3D network is replaced by the convolution layer based on a full convolution neural network, to solve the problem of memory overflow during training. In terms of model parameters, three different learning rates and optimization functions are designed for experimental comparison, and the parametric comparison diagrams of three different learning rates and optimization functions are drawn. According to the experimental results, the optimal learning rate and parameters of optimization functions of the convolutional neural network are selected. The experimental results show that the area under the receiver operating curve, classification accuracy, recall, and F1 value of the proposed method have been significantly improved.
To reduce the time consumption in the training process with mesh segmentation method based on the deep learning, this paper proposed a mesh segmentation based on optimizing extreme learning machine with ant lion optimization. This paper utilized the dual influence of the elite ant lion and roulette strategy in the ant lion optimization algorithm, iteratively updated the ant colony, sorted the ant lion colony and ant colony in descending order, considered the optimal N to update ant lion colony, and used the optimal ant lion to update the elite ant lion to keep the elite ant lion as the optimal solution. Therefore, the input weight matrix and the hidden layer bias randomly generated by the extreme learning machine were optimized, and a high-precision segmentation classifier was obtained using the improved extreme learning machine method. Considering six models in Princeton Shape Benchmark (PSB) dataset, the results show that on the model dataset such as Airplane, Ant, Chair, Octopus, Teddy, and Fish, the training time of the models with the number of faces ranging 200000-300000 is approximately 1000 s. The proposed method has high segmentation accuracy, with the highest segmentation accuracy being 99.49%.
Aiming at the remote sensing images with target intensive, multi-scale, and occlusion, a remote sensing image segmentation model based on the attention mechanism is proposed herein. The proposed method is based on the deep image segmentation model. The channel attention mechanism is used for weighting the low-level features before high-low layer feature fusion, thus enhancing the target features, suppressing the background features, and improving the information fusion efficiency. A positional attention mechanism is proposed to process the final features of the decoding phase for further enhancing the responsiveness of the model to the target features. At last, weighted and aggregated feature maps are up-sampled to the original image size for pixel label prediction. Experiments on two remote sensing road datasets and comparisons with related models show that the proposed model displays excellent performance in remote sensing image road extraction and can be employed to complex remote sensing image segmentation.
A plant image recognition method, which is based on effective region screening through a convolutional neural network (CNN), is proposed with an aim to improve the accuracy of plant image recognition in complex backgrounds. First, image (flower, leaf) datasets are used to train an effective region-screening model through a CNN, which is designed to allow the datasets to retain effective areas such as flowers and leaves after screening through the model. Subsequently, the effective areas are extracted from the plant image data sets by Mask R-CNN. Then the effective area screening model is used to screen the effective areas that can represent the plant image categories. The effective areas are divided into training sets and test sets in a ratio of 4∶1. The CNN plant image recognition model based on effective region selection (MRC-GoogleNet) is obtained after training in GoogleNet. Finally, the recognition accuracy is obtained through the model. The experimental results and data reveal that the recognition model, which is based on effective region selection, can more effectively extract image features and improve the recognition accuracy compared with the classical CNN plant image recognition model.
Existing robust estimation methods of the fundamental matrix possess some limitations such as low accuracy. This study presents a fundamental matrix estimation method that uses multi-kernel learning to improve density peak clustering. First, from the viewpoint of the shortcomings in the density peak algorithm, such as the need to select parameters and inability to automatically cluster, multi-kernel learning and γ distribution map are introduced. Second, with the feature of epipolar distance, the proposed method eliminates the anomaly of the matching dataset to obtain a better internal point set. Finally, the M estimation method is used to exclude the positioning noise error, conduct further optimization processing on the internal idea set, and estimate the final base matrix. The INRIA dataset is used to validate and analyze the proposed method. Results show that the calculation accuracy and correctness of the fundamental matrix are improved using the proposed method.
Traditional image segmentation methods mainly rely on the low-level features, such as image spectrum and texture, and are easily disturbed by occlusion and shadow. To address these problems, a CV (Chan-Vest) image segmentation model combining the convolutional restricted Boltzmann machine is proposed. The target shape a priori information is modeled and generated using the convolutional restricted Boltzmann machine. Then the energy function of the CV model is constrained by the added a priori shape term to guide image segmentation. Better segmentation results are obtained in remote sensing datasets Satellite-2000 and Vaihigen, whose training data are limited while target shapes and sizes are different.
A computational ghost imaging method based on orthogonal sinusoidal speckle was proposed herein to solve the problem of low signal-to-noise ratio caused by the non-orthogonality of random speckle distributions. This method combines the orthogonal property of a matrix, superimposes two orthogonal oblique sinusoidal distribution patterns, and constructs an orthogonal sinusoidal speckle field to image unknown targets by adjusting the upper-frequency limit. Experimental results and numerical simulations show that the ghost image quality obtained by the proposed method has significantly improved as compared with that obtained by the computational ghost imaging based on the Gaussian speckle pattern, and the peak of signal-to-noise ratio is increased by 4 dB--7 dB. Furthermore, the structural similarity is improved by 280%.
Resultson multiple datasets show that the proposed method achieves superior performance compared with 10 algorithms proposed in recent years.
This paper proposes a backbone network for object detection aiming at the difference between object detection and image classification, to solve the problem that most object detectors are excessively dependent on the classification network. The network mainly includes the initial block, feature fusion module, and mix down-sampling module. The initial block can reduce information loss of the input image. By concatenating the outputs of different convolution layers, the feature fusion module not only enhances the robustness of the network to detection objects with various sizes but also provides more context information for object detection, which effectively improves detection accuracy. In the down-sampling part of the network, a mix down-sampling module is introduced, which balances the ability of the backbone network to classify and locate objects. Experimental results show that the mean value of average precision of the proposed model can reach 81.0% on the PASCAL VOC 2007 test set after training on PASCAL VOC 2007 and PASCAL VOC 2012 datasets, and the detection speed of the model is 85 frame/s, which ensures good performance in terms of accuracy and efficiency.
The existing one-stage regression networks can obtain the multi-level information through the fusion of multi-branch response maps. However, the algorithms for response map fusion are mostly based on a simple element-wise sum or a multiplication operation. In this paper, a novel tracking model that includes a novel response map fusion method based on bilinear convolutional neural network, is proposed. The proposed model can obtain position correlation and information interaction of response maps, which is useful for achieving more accurate target tracking. The proposed algorithm is tested on the OTB2013 benchmark. Results show that, a competitive performance can be achieved by using the proposed model, compared to the state-of-arts tracking models.
To solve the target tracking problem in computer vision, this study proposes a strategy based on a convolutional neural network (CNN) that extracts depth features and adaptively blends with edge features to realize the tracking algorithm for video targets. The low-level network of CNN can acquire a part of the spatial structure and shape of the target. High-level network of CNN can obtain relatively abstract partial semantic information. Herein, depth features are extracted by the second convolutional layer Conv1-2, the fourth convolutional layer Conv2-2, and the last convolutional layer Conv5-3 in VGG16 neural network. The above mentioned features are fused with the edge feature adaptively to achieve video object tracking. Herein, the experimental verification and analysis of the proposed method are conducted on the OTB100 dataset. Results show that the proposed method can achieve accurate positioning of the target.
The global localization algorithm for an indoor mobile robot based on monocular vision is significantly complex at present. To solve this problem, this study proposes a global localization method for an indoor mobile robot based on binocular vision. To ensure stable feature extraction during the motion of the indoor mobile robot using binocular vision, a calibration board-based global localization scheme is presented. The center of the calibration board is used as the localization point of the mobile robot. Based on this, to improve real-time localization and reduce the extraction range of corner points on the calibration board, the motion area detection of the mobile robot is achieved using the Gaussian mixture model background subtraction method and morphological method. Further, according to the established criterion of corner points on the calibration board, image coordinates of four corner points on the calibration board are obtained by screening the corner points extracted from the mobile robot. The coordinates of the localization point are calculated by combining the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters of the binocular camera and the global localization mathematical model, and the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed method are verified by experiments and analysis. This provides a new idea for the global vision localization of indoor mobile robots.
The VDSR (very deep super resolution) model has some problems such as neglecting the interconnection between feature channels, inability to fully utilize the features of each layer, excessive parameter quantity, and computational complexity. To solve these problems, this paper proposes a network structure based on a residual channel attention mechanism and multilevel feature fusion. By introducing residual channel attention, the channel's characteristic response is adaptively corrected to improve network representation ability. A recursive structure is adopted in the network and parameter sharing is implemented in each recursive block, which reduces the number of parameters. The proposed multilevel feature fusion method can fully extract image features; traditional convolution is replaced by group convolution to further reduce the number of parameters and computational complexity. The algorithm reduces the number of parameters and complexity of the model while ensuring the quality of image reconstruction. When an image is enlarged four times, parameter quantity and computational complexity are approximately 0.33 and 0.02 times, respectively, those of VDSR.
Most of the existing statistical a priori image blind deblurring methods have limited edge and detail recovery ability. To solve this problem, we proposed a new blind deblurring algorithm. First, by using the downsampling, the multi-scale decomposition of an image was performed based on pyramid decomposition. Then, in each image layer, the significant intensity a priori was used to extract the image edge, and the low gradient rank a priori was employed to suppress the blurring effect and noise. Next, the coarse-to-fine strategy was used to alternatively iterate the blur kernel and latent image to obtain an accurate final blur kernel. Finally, a clear image was recovered by a non-blind deconvolution method. Further, to reduce the iteration time of the multi-scale iteration, an adaptive iterative strategy was proposed. In this strategy, the number of iterations was adjusted by the similarity evaluation of the estimated blur kernels, and the computational cost was effectively reduced. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can accurately estimate the blur kernel and effectively suppress the influence of noise; also, the recovered image contains more edge and detail information.
This work addresses the challenge of obtaining world coordinates when estimating the pose of curved objects through monocular vision. An efficient method for estimating the pose of curved objects is proposed herein. The proposed method combines binocular vision with the cooperative target. A point cloud of the target object in various poses is generated using a binocular camera in order to rapidly extract the world coordinates of the corner points of the target. Unlike the traditional point-cloud registration pose-estimation methods, the mean value of the corresponding point coordinate difference is used to represent the translation vector in the proposed method. The normal vector of the tangent plane comprising the target corner points is used to form a matrix of the target coordinates in different poses; thus, the rotation matrix is derived. The proposed method not only ensures the accuracy and stability of the pose estimation results but also improves the efficiency of the algorithm significantly. The experimental results show that the efficiency of the proposed method is 98.24% and 97.58% higher than those of the ICP algorithm and NDT algorithm, respectively. The proposed method to estimate the pose of curved objects has various practical applications that are reviewed in this work.
The existing internal calibration methods of a linear array CCD camera generally depend on the distortion parametric model, and the calibration accuracy is limited by the correlation of internal parameters of the model. Herein, an internal calibration method of linear array CCD camera using a nonparametric model is proposed to improve the internal calibration accuracy. Through the pinhole imaging model and the perpendicular method, a nonparametric model of linear array CCD camera imaging is constructed, and the mapping relationship between spatial feature points and imaging points and the size of the distortion between the ideal imaging point and the actual imaging point are directly determined. The reprojection error is used as the evaluation standard to compare the proposed method with the internal calibration method using the parametric model. The experimental results show that the root mean square, average value, and maximum value of the reprojection errors obtained using the proposed method are 0.42, 0.00, and 0.95 pixel, respectively, which are 0.80, -0.10, and 2.47 pixel less than that obtained using the internal calibration method using the parametric model.
Herein, a context-aware correlation filter tracking algorithm based on the Gaussian output constraint (OCCACF) is proposed to reduce the occurrence of drift in the target tracking process. This algorithm assumes that the output response of the tracking target obeys Gaussian distribution. A form of constraint output is derived from the properties of Gaussian distribution and an iterative parameter is obtained using the constraint output and correlation filter knowledge. The filters in this tracker are selectively updated according to setting constraints. The effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified using 50 video sequences in the OTB-2013 evaluation benchmark and the proposed algorithm is compared with other tracking algorithms. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can significantly improve the overall performance of target tracking and has obvious advantages than other algorithms that have been proposed in recent years.
In view of low accuracy and poor real-time performance of the existing target detection methods, a real-time road target detection method based on depth neural network on the unmanned aerial vehicle(UAV) flight control platform is proposed. The method combines the advantages of YOLOv2 and YOLOv3 networks, and proposes a model of object detection which introduces the Darknet-19 network with residual block and multi-scale features, considering the current situation that YOLOv2 has a low accuracy of road target detection and is difficult to detect small target, and YOLOv3 has a poor real-time performance. The regression classifier is proposed to achieve multi-label classification of overlapping images. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a detection frame rate of 20 frames/s or more on the UAV flight control platform for the video image with a resolution of 416 pixel×416 pixel, the mAP reaches 82.29%, and the recall rate reaches 86.7%, basically meets the requirements of road target detection accuracy and real-time performance on the UAV flight control platform.
Point cloud registration is one of the key technologies for indoor scene reconstruction based on the RGB-D(RGB-depth) sensor. To solve the point cloud registration problem among key frames in sparse mapping, this study proposes a coarse registration algorithm with scene classification based on improved random sample consensus (RANSAC). First, geometric information and photometric information are used to detect, describe, and match keypoints. Then, the scene classification algorithm determines the scene category, and geometric and photometric correspondences are adaptively combined. Finally, the improved RANSAC is proposed to estimate the transformation among key frames by biased random sampling and adaptive hypothesis evaluation. The whole coarse registration algorithm is experimentally verified by the public RGB-D dataset and compared with several algorithms. Experimental results show that the coarse registration algorithm can achieve robust and effective transformation estimation, which is helpful for subsequent fine registration and overall indoor scene reconstruction.
The traditional three-dimensional (3D) model classification method relies on the overall shape characteristics of cultural relics, which causes the problem of low efficiency, high cost and low accuracy for the classification of cultural debris with serious damage, missing details and irregular shapes. The depth information of local surface around the feature points of cultural relics and the regular geometric texture of the surface can be used as the discriminative features of classification. Therefore, a local point cloud information and significant multi-feature descriptor are proposed. The surface regularity geometric feature, combined with the rotation projection feature, are used as the discriminant features of the classification of cultural relics; then the similarity metric rule is proposed and the weight of two characteristics are adaptively calculated according to the measurement results of each type of feature, to achieve the classification of cultural debris. The debris data set of terracotta warriors is used as experimental data for the classification, the results show that the proposed method occupies small memory and calculates fast. Multiple cross-validation methods are used to verify the results, the accuracy rate is 74.78%, which is 15.64% higher than that of the traditional 3D model matching method.
In this study, we propose a scale-adaptive correlation filter tracking algorithm based on the fusion of multiple features to handle the problems that the single feature of the kernel correlation filtering algorithm cannot adapt to the complex scenes observed during the tracking process and that the kernel correlation filtering algorithm cannot handle the scale changes of the target. First, under the framework of the correlation filtering algorithm, the fast histogram of oriented gradient and local binary pattern features are weighted adaptively based on the reliability of the feature response graph for localizing the target. Second, the scale estimation process estimates the scale of target using a scale pyramid to ensure good adaptability with respect to the target with scale change. The proposed algorithm and five other tracking methods are verified by testing on the OTB-50 dataset. Apart from outperforming the existing methods in terms of the accuracy and success rates, the proposed algorithm exhibits good robustness and a stable tracking performance.
Herein, a facial expression recognition method based on local feature fusion of convolutional neural network (CNN) is proposed to improve recognition rate and real-time performance of facial expression classification. First, a CNN model is constructed to learn the local features of the eyes, eyebrows, and mouth. Then, the local features are sent to a support vector machine multi-classifier to obtain their posterior probabilities. Finally, a particle swarm optimization algorithm is used to optimize the fusion weight of each feature, realize the decision-level fusion with the optimal accuracy rate, and complete the expression classification. Experiments show that the average recognition rates of the method on the CK+ and JAFFE databases are 94.56% and 97.08%, respectively. Compared with other recognition methods, results show that the proposed method has superior performance, improves the recognition rate and robustness, and ensures the real-time performance of the classification.
Camera calibration is an important premise for accurate positioning in robot machine vision systems. To solve the problem of low accuracy of traditional camera calibration, this paper proposes a camera calibration optimization method based on an improved particle swarm optimization algorithm. This method uses Zhang Zhengyou calibration method to obtain the initial value of camera intrinsic parameters and realizes the nonlinear self-adaptive adjustment of inertial weight parameters in different iteration stages, balancing the local and global search capabilities. Dynamic self-adjusting strategies of sines and cosines changes in different iteration stages are adopted for global and local learning factors to further improve the global search ability further and late search accuracy. When a particle swarm is about to fall into the local optimum, the dispersing mechanism is used to enlarge the spatial range of the particle swarm to avoid premature convergence of the algorithm. Experimental results show that the proposed method has better precision and repeatability as compared with the traditional methods.
Faster RCNN has poorer performance in terms of accuracy and robustness for detecting small targets. For this reason, an improved Faster RCNN was proposed to detect the defects in mugs. The Faster RCNN and feature pyramid network (FPN) were combined to increase the use of detailed shallow features, so as to achieve better detection effect for small targets. Faster RCNNs before and after improvement were used to conduct simulation on Caffe. The results show that Faster RCNN performs well in defect detection for mugs, but it misses some small targets. The improved Faster RCNN increases the detection accuracy by 2.485 percent at most for gaps and scratches and performs better in small target recognition.
To reduce the noise in remote-sensing images, seven typical filtering operators are selected to separately process the remote-sensing images. Combined with the classification method of support vector machine (SVM), we analyze the variation of images’ brightness values after filtering and compare their accuracy with that of unfiltered remote-sensing images. The results show that the filtered remote-sensing images have a higher classification accuracy for the extraction of soil salinization compared with untreated remote-sensing images. Of the several selected filtering operators, the soil-salinity extraction model that uses Gaussian low-pass filtering and SVM can improve the classification accuracy and the Kappa coefficient from 86.7285% and 82.21% to 89.6950% and 86.20%, respectively, which is the best classification accuracy to date. To summarize, the filtering operation suppresses noise, improves image quality, effectively improves the monitoring ability of salinization. Grasping the spatial distribution characteristics and temporal and spatial variation principle of soil salinization is of practical significance for preventing and mitigating soil salinization to protect fragile ecological environments in arid and semi-arid regions.
The three-dimensional (3D) imaging techniques of robotic vision in the field of intelligent manufacturing robot vision perception are reviewed. The characteristics and limitation in practical applications of some typical robot vision imaging methods are systematically summarized. The content involves time-of-flight imaging, point and line scanning imaging, chromatic confocal imaging, structured light projection imaging, deflectometric imaging, monocular and multi-view stereo imaging, and light field imaging. The tree map of various robotic vision imaging methods are drawn. The best 3D imaging methods of eye-in-hand robotic system are discussed.
Over the recent years, the popularity of depth sensors and three-dimensional(3D) scanners has enabled the rapid development of 3D point clouds. As a key step in understanding and analyzing three-dimensional scenes, semantic segmentation of point clouds has received extensive research attention. Point cloud semantic segmentation based on deep learning has become a current research hotspot owing to the excellent high-level semantic understanding ability of deep learning. This paper briefly discusses the concept of semantic segmentation, followed by the advantages and challenges of point cloud semantic segmentation. Then, the point cloud segmentation algorithms and common datasets are introduced in detail. This paper also summarizes the deep learning methods based on point ordering, feature fusion, and graph convolutional neural network in the field of point cloud semantic segmentation. Finally, it analyzes the quantitative results of proposed methods and forecasts the development trend of point cloud semantic segmentation technology in the future.
Diffuse optical tomography (DOT) is a low-cost, non-radiative damage, deep detection in vivo optical functional imaging technology that uses near-infrared light to detect biological tissue optical structures. Due to the strong scattering, low absorption characteristics, and high spatial resolution of the biological tissue itself, the inverse problem of DOT reconstruction has serious ill-conditioned characteristics. The traditional inverse problem solution is mainly based on the algebraic iterative reconstruction method. With the development of artificial intelligence and the arrival of the era of big data, deep learning research has set off to reach another new climax. The inverse problem-solving method based on a deep learning network model is gradually used in the DOT reconstruction process. On the basis of combing the traditional DOT reconstruction algorithm, this manuscript focuses on the research progress of the latest deep learning for DOT reconstruction and provides reference for relevant research teams in this field.