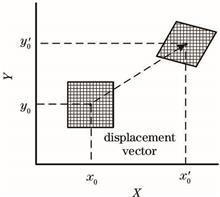
A dynamic loading instrument and medical computed tomography (CT) machine are used to perform a single-axis in situ compressive stress-layered scan of a concrete. The CT image of the middle layer of the concrete specimen is selected as the object, and the concrete components are divided into CT thresholds to analyze the occurrence and development of cracks. The internal displacement and strain fields of the concrete are measured using the digital image correlation (DIC) method, and the displacement and strain fields are combined to analyze the generation and development process of the localized deformation area. The results reveal that the high-strain generation area is consistent with the crack generation area of the CT image. Combined with the CT value, the curve of the average value and maximum principal strain versus stress are analyzed. Moreover, the various stages of the concrete failure process are analyzed. The evaluation reveales that the CT-scale crack stage started at 70.3% of the peak load. Experimental results show that the combination of DIC method and advanced CT technology can present the stress and strain process inside the concrete specimen in the form of images, providing effective visualization for studying the deformation, failure, and stability of the internal structure of the concrete.
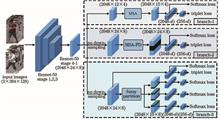
The traditional method based on deep learning does not focus on sub-significant information. Therefore, a multi-branch network based on multi-scale attention (MSA) mechanism was proposed to coordinate significant and sub-significant information. Firstly, the proposed algorithm combined the multi-scale feature fusion module (MSFF) with the attention mechanism to get an MSA module. This module enables the network to adaptively adjust the size of the receptive field according to the input information so as to make full use of information of different scales. Additionally, a multi-branch network was established to realize the coordination of global features and multiple local features. Using the MSA module, weighted enhancement of global information and local detail information can be achieved separately, and a more discriminative feature is obtained for final recognition. The experiment results show that the proposed method performs well on multiple datasets.
In order to quickly obtain a wide range of pavement images with sufficient clarity, a stitching algorithm for aerial pavement images is proposed, which can quickly and accurately process the images to obtain the stitched images of the pavement surface so as to provide convenience for the application of unmanned aerial vehicle aerial photography in the field of pavement transportation. When pavement images are stitched, the images contain large similar areas, resulting in a low registration accuracy, a large amount of image information, and a long stitching time. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes to determine the overlapping area of adjacent images before feature point extraction. Scale-invariant feature transform feature points combined with sparse representation matching method in the overlapping area to register adjacent images. Then, wavelet transform method is used fuse the images to improve the stitching effect. Experimental results prove that the proposed method can effectively process aerial pavement images and obtain better pavement stitching images.
The goal of low-illuminance image enhancement is to increase the overall illuminance of the image, thereby presenting more useful information. Aiming at the problems of low illumination, low contrast and high noise in low-illumination images, a method of image enhancement method based on attention mechanism and Retinex algorithm is proposed. This method first decomposes the low-illumintion image into an invariant reflection map and a slowly-varying smooth illumination map. Then, it uses the attention mechanism to extract the spatial and local object information of the image, so as to ensure that the spatial and local object information is used for constraints during the enhancement process. Moreover, it increases the color loss function to improve the image saturation to compensate and calibrate the contrast details in the enhancement process. Furthermore, it improves the low-illumintion image and synthesis method, add real noise, and efficiently expands the training data set. Finally, the experiments on the LOL and SID data sets show that the subjective and objective evaluation indicators of the proposed method improved.
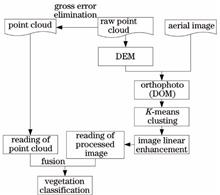
Since it is difficult to automatically distinguish between vegetation and buildings from non-ground point cloud data, this research work proposes a method to automatically classify vegetation in airborne LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) point clouds, which is assisted by aerial image. Based on the fact that the spectral characteristics of vegetation are clearly different from other ground objects, digital orthophoto generation and K-means clustering algorithm are employed to cluster and enhance the images. Then, the enhanced image and the point cloud data of the corresponding area are fused. Finally, the airborne LiDAR vegetation point cloud data is classified using the image processing results. Experiments are carried out on airborne LiDAR vegetation point cloud data and aerial images of a particular city. Quantitative analysis results prove that total classification accuracy of the proposed method is 96.47%, and the Kappa coefficient is 0.9248. The introduced method can pave the way for automatic classification of the vegetation in LiDAR point clouds.
In order to solve the problem that the shadow in remote sensing images leads to the loss of ground object information and the degradation of image quality, we propose a shadow compensation method by combing logarithmic transformation with local enhancement in the high resolution remote sensing images. First, based on the shadow detection results, we design an improved logarithmic transformation image enhancement method and construct the logarithmic transformation compensation model to effectively increase the brightness of shadow areas. Then, we use the local compensation model and weighting treatment to improve the contrast of shadow areas. Finally, we obtain the automatic parameters of the compensation model using the information of similar points on both sides of the shadow boundary and realize the automatic compensation. The experimental results indicate that the proposed method can be used for shadow compensation, to improve the brightness and contrast of shadow areas, and to recover the true ground object information of shadow areas correctly.
In view of the serious detail loss and poor visual effect in the process of infrared and visible image fusion, a fusion method based on the multi-scale geometric transformation model is proposed. First, the improved visual saliency detection algorithm is used to detect the significance of infrared and visible images and construct the saliency matrix. Then, the infrared and visible images are transformed by the non-subsampled shearlet transform to obtain the corresponding low-frequency and high-frequency subbands. Simultaneously, the low-frequency subbands are adaptively weighted by the saliency matrix and the high-frequency subbands are fused by the simplified pulse coupled neural network combined with the multi-direction sum-modified-Laplacian. Finally, the fusion image is obtained by inverse transformation. The experimental results show that this method can effectively improve the contrast of the fusion image and retain the details of the source image. The fusion image has a good visual effect and performs well in a variety of objective evaluation indicators.
In the spinal computed tomography (CT) image segmentation problem, owing to the low contrast between the spine and tissues, and the influence of noise, the traditional segmentation algorithms have problems such as poor segmentation accuracy and low degree of automation. Aiming at solving the above-mentioned problems, a method of locating the spine through AttentionNet and then using improved DenseUnet to perform spinal CT segmentation is proposed herein. First, preprocessing operations such as cropping, resampling, and normalization of gray values are performed on all spinal CT sample data; the samples are trained using AttentionNet to obtain Attention maps with position information. Second, the traditional DenseUnet is improved, and each Dense block adds the Shuffle operation to increase the network robustness. After each Dense block, a 1×1 convolution is added to reduce the number of channels and network parameters. Third, the training samples are pretrained using the improved DenseUnet to obtain the prediction maps with prior information. Finally, the Attention map, prediction map, and the original images are fused into three-channel training samples as the input, and the improved DenseUnet is used to train segmentation model and is verified against the test set. Consequently, the spinal CT automatic segmentation is realized. The experimental results show that the segmentation accuracy of the proposed method is better than that of the traditional DenseUnet, and the proposed method is an effective automatic segmentation method for spinal CT.
In the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images, there are many complex background problems, such as speckle noise, close contact of floating ice in drift-ice area, and more small pieces of ice. Here, we describe a SAR flow ice separation algorithm based on background-suppression saliency detection. This algorithm obtains a preliminary saliency map by learning the random forest regression based on the saliency detection of images. Then the image region is constructed by using super pixels. Additionally, discrete Fourier transformation is performed, after which the frequency domain features of the region are extracted, and the chi-squared distance is calculated. The proposed algorithm then suppresses the boundary background to generate a background-suppression module diagram, followed by fusion of the two-stage graph to obtain the enhanced saliency graph. We evaluate the proposed algorithm and compare its performance against seven saliency algorithms and three sea-ice-segmentation methods using a SAR sea-ice dataset. The results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively detect isolated ice floes and suppress background areas.
At present, most of the precipitation nowcasting production is unable to consider the problems of high coverage, high accuracy, and low cost. Therefore, we herein propose a method based on outdoor monitoring images and deep neural network to forecast the rainfall intensity in the next 1 h. We design a dual-flow 3D convolutional neural network to extract high-dimensional features of rainfall information in images. The local information is adaptively generated at a low computational cost, and the temporal and spatial characteristics of rainfall information are extracted by the proposed network which integrates the whole network and the local network using a double loss function. The experimental results show that the neural network based on the dual loss function is better than that based on the single loss function in precipitation intensity forecasting. Percent of doom, false alarm rat, critical success index, and the accuracy of the proposed network are better than those of other models in most cases. In terms of visualization of the model effect, the proposed network can effectively extract the feature information of the precipitation images. Therefore, the proposed precipitation nowcasting method is capable of fine and low-cost precipitation prediction.
Visual simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) systems that use cameras as input can retain the spatial geometry information of a point cloud in the map construction process. However, such systems do not fully utilize the semantic information of objects in the environment. To address this problem, the mainstream visual SLAM system and object detection algorithms based on neural network structures, such as Faster R-CNN and YOLO, are investigated. Moreover, an effective point cloud segmentation method that adds supporting planes to improve the robustness of the segmentation results is considered. Finally, the YOLOv3 algorithm is combined with ORB-SLAM system to detect objects in the environment scene and ensures that the constructed point cloud map has semantic information. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method constructs a semantic map with complex geometric information that can be applied to the navigation of unmanned vehicles or mobile robots.
Image segmentation is the focus of mobile phone film defect detection. However, the low contrast of captured images often makes image segmentation difficult. In this regard, this paper proposed an improved Retinex enhancement method. The method used Gaussian convolution to estimate the illumination component of defect image to obtain the reflection component, performed adaptive nonlinear transformation on the reflection component, employed contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) correction to improve the contrast, used the top-hat transform to eliminate the influence of lighting background, and enhanced the defect image of the mobile phone film. Then, aiming at the incomplete segmentation of the dark details of the defect edge by Otsu's algorithm, a gradient image of the enhanced image was introduced to achieve effective segmentation of mobile phone film defects images. The experimental results show that in the case of low contrast, compared with the original defect image, the image processed by this algorithm has an improved information entropy of about 20%, a contrast of about 100%, and an excellent segmentation effect.
In this paper, we presented the Intelligent Domestic Garbage Recognition using Faster RCNN to realize high-precision identification of domestic garbage. Specifically, 6 kinds of domestic garbage were selected to build the dataset. The data augmentation technique was adopted to expand the quantity and category of the targets, and improve balance on the size of the targets. Moreover, we used three different types of backbone networks including VGG-16, Res101, and MobileNet_v1 to analyze and compare the accuracy, speed, and generalization performance. The research used end-to-end training network finely tuned by the special layer, and carried out enhanced training on low recognition rate samples to obtain a minimum mean average precision (mAP) of 92.85%. Subsequently, we captured three typical errors and optimized from the misidentified samples, and thus the highest recognition mAP increased to 99.23%. To analyze the generalization performance of different backbone networks embedded in the algorithm, we built a dataset with 816 pictures derivatized from the different backgrounds and used it to test the impact of changing the background on garbage detection. As a result, we found that the complex backgrounds from surrounding garbage put the greatest impact on detection accuracy. Thus, the generalization performance takes the same trend as convergence performance, which changes Res101, VGG-16, MobileNet_v1 from good to bad. Therefore, the setting method of the optimal probability threshold for algorithm detection was analyzed and obtained based on the principles of the high-precision requirement for recyclable garbage and high recall requirements for hazardous garbage.
In the three-dimensional point cloud registration, when the surface of the point cloud is relatively flat and the geometric features are fuzzy, the iterative closest point algorithm has poor registration results, even often fails to register. The point cloud data obtained by the three-dimensional laser scanner includes geometric coordinate information and RGB information. Here, by making full use of point cloud coordinate information and RGB information, we propose a new point cloud registration method, which first convert RGB values into grayscale values, set the weighting factor according to the sum of the variance of the gray value and the sum of the variances of each curvature, and then adaptively adjust the impact of color information and geometric information on registration in the light of the weighting factor to achieve an organic combination based on color information and geometric information. Experimental results show that the proposed method can achieve stable and accurate registration of different point clouds.
With the aim of denoising the results of the existing image-fusion algorithms and making them more uniform with respect to quality, we propose a fusion image enhancement method. First, the source image is mean-filtered and salient area of the target image is obtained using the digital subtraction technology. The subtracted image is then decomposed in two-scale using an improved Laplacian operator to obtain the corresponding coarse and refined focus areas. Further, an initial decision graph is generated according to the pixel-level linear mixing rules, and the final decision graph is obtained by refining the initial decision graph using the consistency check algorithm. Finally, the results are synthesized to reconstruct a new fusion image. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves different degrees of enhancements of the fusion image generated using the existing fusion algorithms, the image has improved robustness to noise, and processing time is less than 0.4 s. The small defocus or focus area in the fusion image is more. With good recognition ability, the edge information of recognition increases in clarity and smoothness, and specific verification results are given for objective indicators.
Compared with traditional target tracking algorithms, the target tracking algorithm based on correlation filter has great advantages in tracking accuracy and real-time performance. However, when the target is blocked or out of view, it is difficult to extract target features and correctly locate the detection window, which may easily lead to target tracking failure or drift. Therefore, in this paper, a parallel correlation filter tracking algorithm based on confidence is proposed. First, the paper proposes a new confidence evaluation method to determine whether the target is blocked or out of view. Second, on the basis of confidence, two different trackers are fused with the combination weight of confidence to construct a parallel correlation filter tracking algorithm in order to improve the tracking accuracy and robustness. Finally, in order to prevent model pollution, an adaptive weight update strategy is adopted for the two filter models. Experiments on OTB-2013 and OTB-2015 datasets show that compared with traditional algorithms, this algorithm has significantly improved tracking accuracy and success rate.
To solve the problem that it is difficult for military unmanned aerial vehicles to acquire synthetic aperture radar images of important ships at sea, this paper introduces an unconditional image generation network which can learn the internal distribution of images from a single image. The network adopts the idea of a pyramid of multi-scale generative adversarial networks (GAN). In each layer of pyramid, there is a GAN responsible for the generation and discrimination of image blocks at this scale, and each GAN has a similar structure. The head of generator contains Inception modules connected with different sizes of convolution kernels to obtain image features at different scales. In order to make full use of these features, a residual dense block is added. The discriminator uses the idea of Markov discriminator to capture images distribution at different scales. All the generated images are made into data sets for training different target detection algorithms, the results show that the average accuracy of the model is improved to a certain extent, which verifies the effectiveness of the network model.
In this paper, we proposed the Dunhuang inpainting mural restoration algorithm based on the combination of sequential similarity detection algorithm and cuckoo search algorithm to improve the incorrect filling problem of the Criminisi algorithm and low efficiency in Dunhuang murals restoration. First, we improved the priority calculation formula with the method of redefining data items using a P-Laplace operator to eradicate the priority calculation tends to zero. Second, we improved the efficiency of mural restoration using the sequential similarity detection algorithm based on the dynamic threshold for searching matching blocks. To make the matching block more reasonable, we used a cuckoo optimization algorithm to determine the best matching block. Finally, mural restoration was completed through iterative updates. The results of restoration experiments on Dunhuang mural inpainting show that compared with similar comparison algorithms, the proposed algorithm in this paper achieves better subjective and objective restoration effects, and improves the restoration efficiency.
Aiming at the problem of low location accuracy and detection accuracy of fire detection, a fire detection method based on localization confidence and region-based fully convolutional network is proposed. First, expanded separable convolutions are used to improve the receptive field, reduce the amount of model parameters, and improve the detection speed. Second, the prediction candidate frame is translated and stretched to improve the integrity of the candidate region. Then, for non-maximum suppression method, the classification confidence degree is used as a sorting standard, which leads to the error suppression problem, so as to improve the location accuracy and detection accuracy of the candidate frame. Finally, new tags are added, they represent the weak fire with no obvious characteristics and the strong fire with obvious characteristics, respectively. The weak fire samples are strengthened to distinguish the weak fire from the bright background, so as to reduce the sample missing rate. Experimental results show that the proposed method, based on the public fire data set of Bilkent University and the test data collected from the internet, can make the fire area detected to be more complete. The fire position is more accurate, and the fire detection rate is higher.
To improve the clarity of low-light images and avoid color distortion, a low-light image enhancement algorithm based on the attention mechanism and convolutional neural network (CNN) is proposed to improve image quality. First, the training data is synthesized based on the Retinex model, and the original image is transformed from RGB (red-green-blue) color space to HSI (hue-saturation-intensity) color space. Then, an A-Unet model is constructed to enhance the brightness component by combining the attention mechanism and CNN. Finally, the enhanced image is obtained by transforming images from the HSI color space to the RGB color space. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively improve the image quality, improve the image clarity, and avoid the color distortion. Good results can be obtained in the experiments of synthesizing low-light images and real low-light images, and the subjective and objective evaluation indexes are better than that of the comparison algorithm.
The model based on fuzzy C-mean (FCM) clustering has the advantage of retaining most of the information of the original image for image segmentation. The adaptive dual-channel spiking cortical model (ADSCM) has the advantages of global coupling, pulse synchronization, less parameters, and high computational efficiency, and can process the information of darker images well. An infrared and visible light image fusion algorithm based on FCM and ADSCM is proposed. After the source image is decomposed by non-subsampled shearlet transform (NSST), the corresponding sub-band images are fused by combining FCM and ADSCM, and finally the new image is reconstructed by inverse NSST. Experimental results show that compared with other traditional methods, the proposed method can effectively extract the target information of the infrared image while retaining the visible light background information, and has obvious improvement in average gradient, mutual information, and edge retention factor.
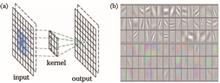
Hyperspectral image classification is one of the research hotspots in the field of remote sensing. It is an important means of earth observation and has important applications in areas such as fine identification of ground objects. The use of convolutional neural networks (CNN) can effectively extract advanced features from the original image with high classification accuracy. However, CNN has a huge amount of calculations and requires high-performance hardware. In order to improve the computational efficiency of the model, the CNN model can be trained on the GPU. Existing parallel algorithms such as GCN (GPU based Cube-CNN) cannot make full use of the parallel capabilities of the GPU, and the algorithm acceleration effect is not ideal. In order to further improve the efficiency of the algorithm, the GGCN (GPU based Cube-CNN improved by GEMM) parallel acceleration algorithm based on the general matrix multiply (GEMM) algorithm is proposed. G-PNPE(GEMM based Parallel Neighbor Pixels Extraction) reorganizes and arranges the input data and convolution kernel to achieve parallel calculation of convolution, which effectively improves the utilization of GPU and increases the training efficiency of the algorithm. By analyzing the experimental results on the three datasets, the classification accuracy of the improved algorithm is consistent with the original algorithm, and the training time of the CNN network is shortened by about 30%, which proves the effectiveness and superiority of the algorithm.
Considering the large amount of calculation, low efficiency, and poor real-time performance of mobile scanning registration when using the traditional point cloud registration method to process large point cloud models, a point cloud registration method based on the convolution neural network combined with the improved Harris-SIFT (Scale Invariant Feature Transform) is proposed. First, the Harris-SIFT algorithm is improved so that it can extract the stable key points of a point cloud model in three-dimensional space. Second, the weighted adjacency matrix of the key points is used as the input feature map for the convolutional neural network. This allows for prediction matching of the key points from the source point cloud and the target point cloud. Then, based on the key points of the matching, the iterative closest point (ICP) algorithm is used to achieve precise registration of the point cloud data. Compared with the traditional point-to-point registration, the proposed method does not need to generate corresponding point descriptors, thus avoiding the problem of a high global search overhead. The experimental results reveal that when compared with the ICP algorithm, the proposed method can better complete real-time point cloud registration, needs minimal calculation, takes a short amount of time, and is highly efficient.
Speckle design is the key to high quality image reconstruction in compressive sensing based computational correlation imaging. Aiming at the problems of high redundancy and low quality of correlation imaging in traditional speckle pattern generation methods, we propose a speckle design method based on principal component analysis (PCA). In this method, the data in the high-dimensional space are projected into the low-dimensional space. Combined with image prior knowledge, a set of measurement matrixes are obtained by sample training method, which can improve the image quality at low sampling rate. The experimental results show that, compared with traditional methods, when the sampling rate is the same and lower than 0.5, this method can increase the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the image by 5 dB, and the structural similarity can be increased by 0.2. It provides a new idea for similar scenes that obtain high-quality images at low sampling ratio.
During lidar detection of obstacles, owing to the characteristics of near dense and far sparse point clouds, the movement with variable speeds of vehicles results in point cloud drifting in the object segmentation. Moreover, objects close to each other are difficult to be segmented, resulting in omissions or incorrect detections. To address these problems, this study proposes an improved Euclidean clustering algorithm based on the point cloud shot-line angle constraint to make obstacle detection more rapid and accurate. The proposed algorithm effectively solves the problem of low success rate in detecting obstacles owing to the uneven point cloud density. Simultaneously, experiments are performed on the proposed algorithm. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can quickly and accurately segment and cluster obstacles within a certain range compared with the traditional Euclidean clustering algorithm.
Computational ghost imaging (CGI) can easily penetrate a static scattering medium. However, when the scattering medium changes dynamically, the measured light intensity is subject to nonlinear changes caused by the medium; as a result, the light intensity of each measurement exhibits a drift, and the reconstructed image contains lot of noise due to the interference. To improve imaging results penetrating a dynamic scattering medium, this study proposes a method to correct the measured value of each point. In this method, patterns with the reflectivity of 1 are added to a measurement matrix. The attenuation factor is obtained at each time by recording the change of light intensity after projecting the pattern, and the compensation coefficient at the middle time is calculated. According to the compensation coefficient, the light intensity distortion caused by the change of the medium’s attenuation factor is corrected for each point, and finally, the transformed values are restored and calculated. The reconstruction results show that the proposed method can effectively deal with the aforementioned noise problem of the CGI technology encountered while penetrating a dynamic scattering medium.
Aiming at the problems that there exist poor accuracy of the optical flow method and time consumption of the feature point method in traditional visual odometers, we propose the model of a visual odometer by integrating optical flow with feature matching. This model mainly fuses the LK optical flow pose estimation based on inter-frame optimization with the optical flow / feature point pose optimization based on key frames. In addition, aiming at the problem that there occur accumulation errors in the traditional reference-frame/current-frame tracking method, we introduce a local optimization algorithm on the basis of the optical flow method to preliminarily estimate the camera's pose. Simultaneously, aiming at the problems that the image insertion frequency is too high and time consumption in the feature method, we construct a unified loss function of optical flow/feature points on the basis of the key frames to optimize the camera’s pose. The position accuracy test results of the algorithm on the EuRoC dataset show that the position accuracy of the proposed algorithm in simple environments is equivalent to that of the feature point method, and in the case of missing feature points, the proposed algorithm possesses position accuracy higher than that of the feature point method and has certain robustness. The running time test results show that on the basis of ensuring the positioning accuracy, the running time of the proposed algorithm is 37.9% less than that of the feature point method, and the algorithm has the certain real-time performance.
This study proposes a method for detecting slipping of stockbridge dampers based on key point training and learning. First, an improved SSD model is used to identify and locate the stockbridge damper. Thereafter, the key points of the stockbridge damper are selected, the MobileNetV3 network is trained, and the input area is set by the upper positioning results of the stockbridge damper to realize the detection of key points. Finally, discrimination rules are formulated according to the characteristics of line images. For m(m≥2) stockbridge dampers, the geometric constraint relationship among the key points is used to realize determination. For a single stockbridge damper, the EPnP algorithm is used to estimate the multiangle pose of the camera. Moreover, the spatial coordinates of the nearest points are obtained from the relationship between the pose and the pixel coordinates of the key point of the damp to determine whether the distance between the nearest points and the stockbridge damper is within the threshold range. The experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively identify slip faults and provide new ideas for detecting defects in transmission lines.
Existing point cloud registration algorithms cannot solve problems of variable scale and registration accuracy of point cloud models simultaneously. Hence, this paper proposes a two-stage variable scale point cloud model registration algorithm. In the first stage of the algorithm, a dynamic scale factor is added to approximately estimate and adjust the scale of the target point cloud model. Spatial rotation transformation is then performed at three angles to divide the grid points, and the grid point spacing is set to 30°. This improves the convergence speed of the algorithm and prevents a local optimum, thus providing a good initial position for the second stage of registration. The second stage is optimized based on a scale iterative closest point (SICP) algorithm to match the point cloud model more precisely. A comprehensive comparison experiment is performed on different registration algorithms, and the experimental results show that in the case where there is a large rigid body transformation between two point cloud models and the scales are significantly different, the proposed algorithm has an order of magnitude of registration error of 10 -30--10 -4.
Aiming at the problem of color distortion and edge blur in RetinexNet low illumination image enhancement algorithm, we propose an improved RetinexNet algorithm. First, using the relatively independent characteristics of each channel in the HSV (Hue, Saturation, Value) color space model to enhance the brightness component. Then, the correlation coefficient is used to adaptively adjust the saturation component with the change of the brightness component to avoid changes in image color perception. Finally, aiming at the edge blur problem of the enhanced image, Laplace algorithm is adopted to sharpen the reflectivity image to enhance the ability of detail expression of the image. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm could effectively enhance the details of the image, keep the overall color of the image consistent with the original image, and improve the visual effect of the image.
The detection and recognition of small targets are always difficult for researchers in the field of target detection, resulting in the feature extracted from the model not having good expression ability, so the detection result of small targets is poor. This paper presents a modified algorithm based on feature pyramid network(FPN). Specifically, the parallel branch is devised on the original basis to fuse the feature information of two different up-sampling methods to enhance the representation ability of small objects. Meanwhile, a multiple threshold detector named Cascade R-CNN is added to prompt the localization ability of small objects. Experiments are conducted on UAV aerial image datasets. The experimental results reveal that the average precision of the proposed algorithm under MS COCO dataset increases by 9.7 percentage compared to that of the initial FPN algorithm; hence, the proposed algorithm has a good detection performance.
In this paper, we proposed an action recognition algorithm based on the adaptive fusion of RGB and skeleton features to efficiently improve the accuracy of action recognition. However, the conventional action recognition algorithms based on RGB and skeleton features generally suffer from the inability to effectively utilize the complementarity of the two features and thus fail to focus on important frames in the video. Considering this, we first used the bidirectional long short-term memory network (Bi-LSTM) combined with a self-attention mechanism to extract spatial-temporal features of RGB and skeleton images. Next, we constructed an adaptive weight computing network (AWCN) and computed these adaptive weights based on the spatial features of two types of images. Finally, the extracted spatial-temporal features were fused by the adaptive weights to implement action recognition. Using Penn Action, JHMDB, and NTU RGB-D dataset, the experimental results show that our proposed algorithm effectively improves the accuracy of action recognition compared with existing methods.
To solve the problem of low accuracy and low efficiency in manual detection of woven bag defects, an efficient online detection method for woven bag defects is proposed. The method collects images of woven bags online and performs image processing to eliminate interference items and accurately detect defects in woven bags. The image is preprocessed by using the mean filter and gray-scale open and close operations to eliminate black and white stripes and gray-scale unevenness that interfere with defect detection in the image, and reduce noise. Use differential image binarization to perform background segmentation on the image, and extract hole defects, wire drawing defects, and excessive wire gaps, wrinkles, and black objects. At the same time, open and close operation is used to connect the broken defects and eliminate the excessive wire gaps in the silk thread, so as to avoid the omission of small defects. Feature extraction and defect detection are used to eliminate the interference of folds and black objects, and detect holes and drawing defects. Experimental results show that the average correct detection rate of 500 samples reaches 97.20%, the detection efficiency is 720 m/h, and the detection accuracy and efficiency are high.
An improved F-PointNet (Frustum PointNet) for 3D target detection on image and lidar point cloud data is proposed. First, the 2D target detection model of the image is used to extract 2D region of the target, and it is mapped to the point cloud data to obtain the candidate region of the target. Then, the 3D target mask of the candidate region is predicted. Finally, the 3D target is detected by using mask. When the mask is predicted, the proposed wide-threshold mask processing is used to reduce the information loss of the original network, the attention mechanism is added to obtain the points and channel layers that require attention, the Focal Loss can solve the imbalance between the target and the background problem. Through multiple comparison experiments, it is proved that wide-threshold mask processing can improve the accuracy of 3D target detection, and the attention mechanism and Focal Loss can improve the accuracy of prediction.
Aiming at the problem of inaccurate estimation results caused by the complexity of limbs and environment in human pose estimation, a human pose estimation method based on secondary generation adversary is proposed in this work. The stacked hourglass network (SHN) is trained for generation adversary through two stages. First, the SHN is used as a discriminator in the first generation adversarial network model, and the on-line adversarial data is used to strengthen training to improve the estimation performance of the SHN. Then, the SHN acts as a generator in the second generation adversarial network model, and the limb geometric constraints are used as the discriminator. The estimation performance of the SHN is improved again through the second adversarial training, and the final SHN is obtained. The proposed method is tested on the public data sets LSP and MPII, and the results show that it can effectively improve the estimation accuracy of the SHN.
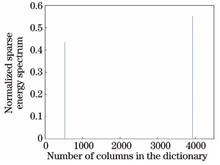
Aiming at the problems of the co-analysis of multiple 3D models in the function space and the co-segmentation of the whole model cluster, we propose a co-segmentation method based on point cloud sparse coding. First, the point cloud feature is extracted and the 3D information is transformed into the feature space. Second, the dictionary matrix and sparse vectors are constructed after the decomposition of the feature vectors into the base vectors by the deep learning network. Finally, the test data is represented by dictionary sparseness and the category of each point in the point cloud model is determined. To get the co-segmentation result, the homogeneous points are divided into the same region. The experimental results show that the segmentation accuracy on ShapeNet Parts dataset obtained using the proposed algorithm is 85.7%. Compared to the current mainstream algorithms used for segmentation, the proposed algorithm can not only compute the relational structure of model clusters more effectively, but also improve the segmentation accuracy and effect.
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EG) is a gastrointestinal disease characterized by an increase in peripheral blood eosinophil (EOS). The main diagnosis of EG is based on whether the number of eosinophils in the pathological section of a digestive tract mucosa specimen exceeds the standard. In this study, a computer image analysis algorithm was used to identify and count eosinophils in pathological section images, with the aim to assist pathologists to manually calculate the number of EOS and reduce the workload and improve the work efficiency of doctors. A robust watershed algorithm was used as the core algorithm for identifying EOS, and the over-segmentation problem in the traditional watershed algorithm was solved using an improved distance transform algorithm and foreground and background markers. The accuracy of the watershed algorithm for recognition and counting was improved. The improved watershed algorithm was used to identify and count EOS, and its results were compared with a pathologist's standard. The average accuracy of the algorithm is 95.0%. Compared with the traditional watershed algorithm, the relative standard deviation of the improved algorithm improved from 5.8% to 2.2%, the over-segmentation rate reduced from 13.4% to 3.7%, and the running time of the algorithm reduced from 40 s to about 27 s.
Taking 3ds Max script (MAXScript) as the main modeling and manual assembly of substation buildings as a supplement, a method for constructing 3D substation models based on 3D laser scanning point cloud data is proposed. The proposed method can solve the problems of low efficiency of manual modeling of substation 3D modeling and poor model scalability. Taking the 3D modeling of a 110 kV substation in Fuyuan County, Yunnan Province, as an example, the experimental results show that the proposed method can meet the accuracy requirements of the model to a certain extent and can reduce the modeling cost of the substation and improve its modeling efficiency.
The surfaces of caves are complex and irregular. Many existing modeling methods are based on an overall-resolution 3D reconstruction. Although the overall model resolution is guaranteed, the efficiency of 3D reconstruction is substantially low, and the model file is too large, which makes it considerably difficult for the follow-up professional application. Therefore, a multi-resolution 3D reconstruction technology based on 3D laser point cloud feature line extraction was proposed for the karst cave. First, the enhanced geometric features of neighboring points were used to extract the eigenvalues and increased the normal vector angle as a basis for detecting the feature points. Second, the standard particle swarm optimization(SPSO) and fuzzy C-means clustering algorithms were used to realize the point cloud classification. Third, the broken line growth method was used to connect the feature points into the feature lines and project them onto 3D point cloud; finally, the classified point cloud was used for modeling as per different resolutions. The 3D reconstruction of the karst cave was realized with high precision, high quality, and high efficiency. The experimental results show that this method can improve the efficiency of the 3D reconstruction of karst caves, realize modeling according to different resolutions, reduce the amount of data after the 3D reconstruction, improve the efficiency of 3D reconstruction, and has high practical value.
Hyperspectral image classification has been recognized as a basic and challenging task in hyperspectral data processing, wherein the rich spectral and spatial information provides an opportunity for the effective description and identification of the surface materials of the earth. There are many parameters in convolutional neural network (CNN). In order to avoid overfitting problem, a large number of training samples are needed in CNN. In addition, the Log-Gabor filtering can effectively extract spatial information, such as the edge and texture, which reduces the difficulty of CNN feature extraction. To leverage the advantages of CNN and Log-Gabor filtering, a hyperspectral image classification method that combines the Log-Gabor filtering and CNN is proposed herein, and two real hyperspectral image datasets are used for comparison experiments. Experimental results show that the proposed method has a higher classification accuracy than that of the traditional support vector machine and CNN.
The quantitative phase microscopy is sensitive to environmental disturbance. It has been a hot topic that how to get rid of the influence of environmental disturbance on quantitative phase imaging. This review focuses on the common-path digital holography microscopy (DHM) and single beam quantitative phase microscopy. The former mainly includes Fizeau interference microscopy, Mirau interference microscopy, off-axis and coaxial point diffraction interference microscopy, DHM of double spherical illumination, and spatially-multiplexed DHM. The latter mainly includes coaxial digital holography, and quantitative phase-contrast microscopy based on parallel light illumination, ultra-oblique illumination, and multi-point off-axis illumination. We hope that this review will provide useful reference for the construction of high stability and practical quantitative phase microscopic devices.
Existing edible oil detection technology cannot quickly and accurately identify edible oils sold in markets. Hence, in this paper, we propose a quick method of identifying edible oils. Fluorescence spectrum data of oil samples were obtained using the laser induction fluorescence(LIF) technique. Principal component analysis was used to extract characteristic information. Next, a multiclassification learning model was developed through the fusion algorithm of moth-flame optimization and kernel extreme learning machine (KELM) to identify the type of oil samples. Five types of oil samples were selected for experimental purposes, and 150 groups of fluorescence spectra were collected from each sample. Next, 600 samples were randomly selected to train the learning model, and the remaining 150 samples were used to test the trained model. Experimental results show that KELM model , extreme learning machine model and back propagation neural network model have similar average classification accuracy on the test set. However, the standard deviation of KELM model is less than those of other two models. This shows that KELM model has a stable classification performance and can quickly identify edible oils.
For quick, nondestructive, and cheap testing of the volatile oil of Zanthoxylum bungeanum, Chinese prickly ash samples were selected as the experimental object and collected from Hanyuan County for hyperspectral analysis in the 400-1000-nm wavelength. Standard normal variable transformation (SNVT)was used to preprocess the spectral data and the method of iteratively retains informative variables (IRIV) was used to extract the feature variables. The regression model of extreme learning machine (ELM) was established. The following results were obtained using the model: the coefficient of determination ( RC2) and root-mean-square error of the calibration set (RMSEC) were 0.8522 and 0.3475 and the coefficient of determination ( RP2) and root-mean-square error of the prediction set (RMSEP) were 0.8365 and 0.5737. To improve the prediction performance of the model, the fruit fly optimization (FOA) algorithm was used to optimize the input weights of ELM. Finally, RC2 and RMSEC of the optimized model (IRIV-FOA-ELM) were 0.8792 and 0.3323, respectively, and RP2 and RMSEP were 0.8659 and 0.3621, respectively. The results show that the hyperspectral imaging technique can be used for the rapid nondestructive testing of the volatile oil of Z. bungeanum, providing a new method and concept for the testing of volatile oil of other agricultural products.