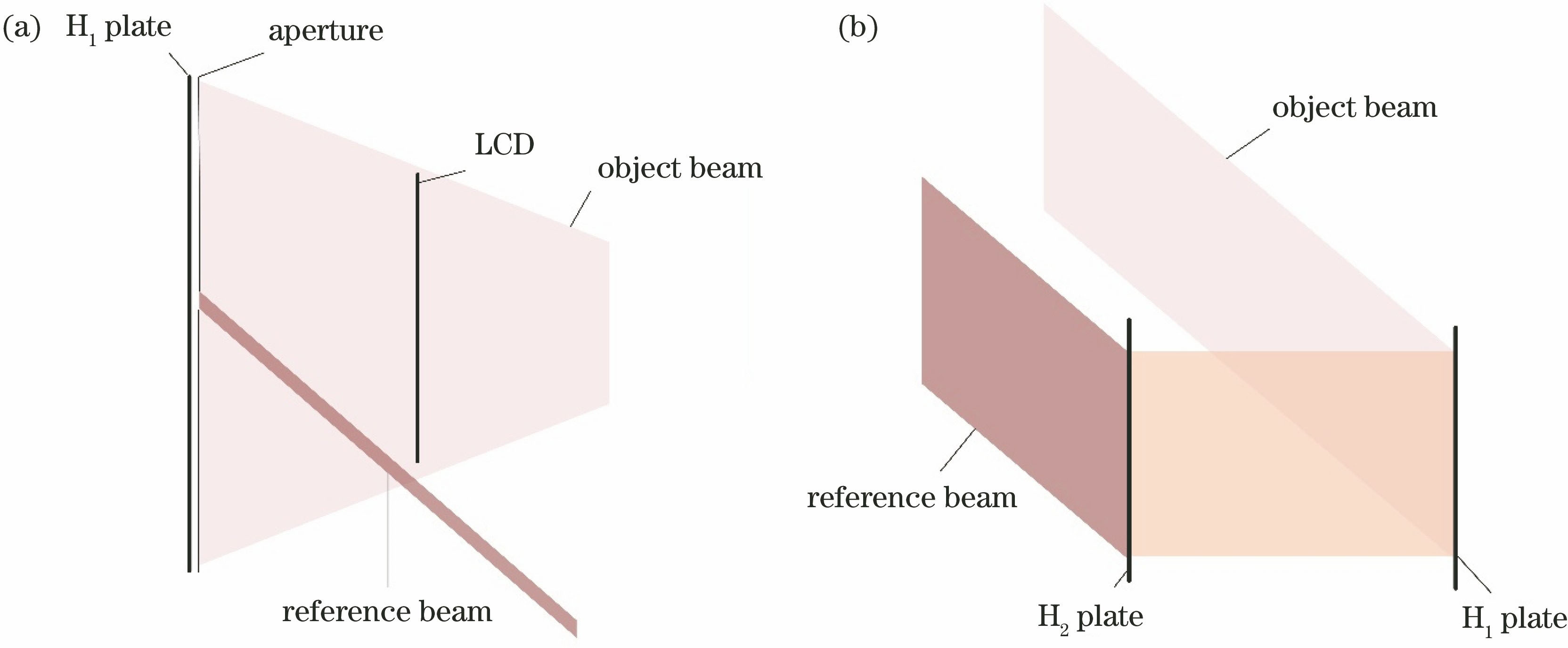
Holographic stereogram printing technology is a research hot spot of holographic display technology. This paper briefly introduces a single-step holographic stereogram printing method based on effective perspective image segmentation and mosaicking (EPISM). The single-step printing can obtain reconstructed image protruding from the holographic plate and achieve the printing effect of traditional two-step method. In order to realize white light reconstruction and improve the practicability of the EPISM method, the influence of the reference light intensity on brightness of the reconstructed image and the influence of scene depth on the quality of the reconstructed image are analyzed. The conditions of white light reconstruction are proposed, and the white light reconstruction of holographic stereogram by EPISM method is realized.
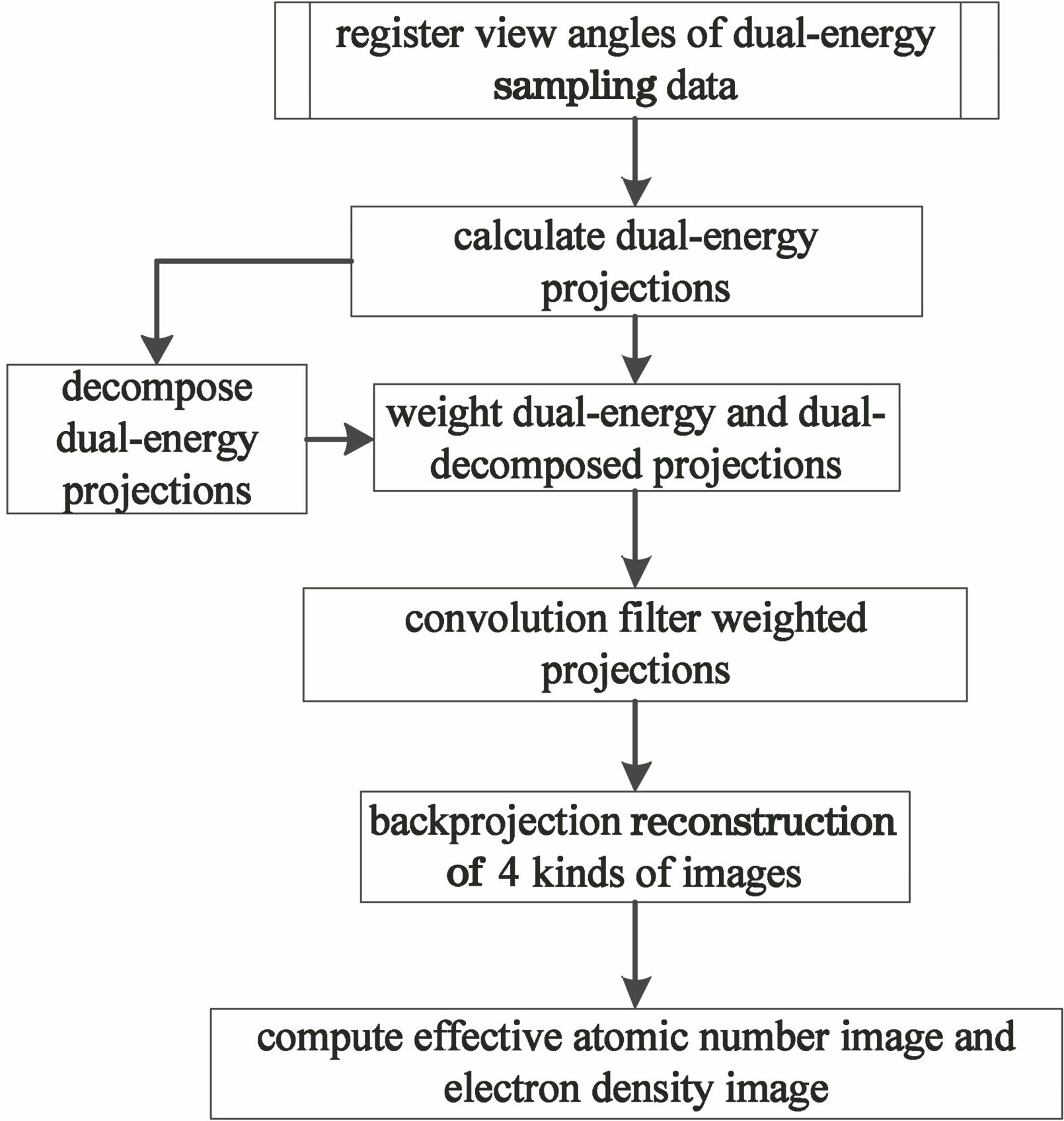
A complete solution for parallel accelerated reconstruction of dual-energy computed tomography (CT) based on graphics processing unit (GPU) is proposed. By integrating the view angle registration steps of dual-energy sampling data into the basic reconstruction process of dual-energy CT, the accuracy of dual-energy projection decomposition is granted, and the accuracy of dual-energy CT reconstruction is improved. Several images are back-projected simultaneously in the back-projection step to avoid repeated calculation of projection addresses, and GPU parallel algorithm is used in each step in the whole reconstruction process to improve the reconstruction speed of dual-energy CT. When the reconstructed images are two and four types, compared with the reconstruction speed of repeated reconstruction by single-energy CT, the speedup ratio of the reconstruction process of the proposed method is 1.88 and 3.24, respectively, and the speedup ratio of the most time-consuming back-projection step is 1.90 and 3.66, respectively. Experiments and practical application prove that the proposed method can effectively improve the accuracy and speed of dual-energy CT reconstruction.
A fine-grained image classification method based on multiscale feature fusion is proposed. By using feature pyramid structure, the scales of different levels of features are transformed, and the information fusion is then carried out. After that, the first three regions with the most detailed features are screened out, combining with the global feature of the image to determine the subclass category of the image. The experiments are conducted on the open fine-grained data sets CUB-200-2011 and Stanford Dogs, and the classification accuracy is 85.7% and 83.5%, respectively. Experimental results show that the method has certain advantages for fine object classification.
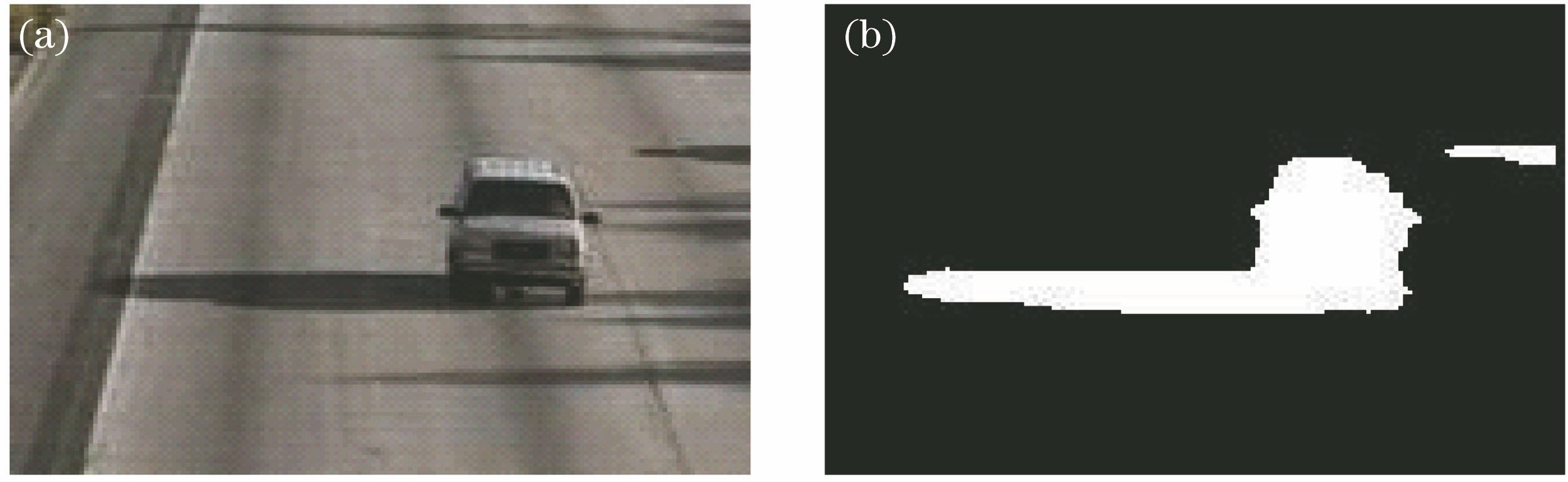
Shadows seriously affect the target detection accuracy in a complex scene. A traditional target-detection method can easily misidentify moving shadows as moving targets. To solve this problem, this study proposes an improved video-shading removal algorithm combining the Laplace-Gaussian (log) operator with the ViBe algorithm. A two-dimensional (2D) digital filter based on the log operator was used for filter detection. The coefficient matrix of the 2D digital filter was rotated by 180° to create a convolution kernel, which was convoluted with the input image matrix to achieve image edge detection. Finally, the improved log operator was used to extract the outer contour and foreground target edges. The two edges were subtracted to obtain the inner edge, which was the moving target edge with the shadow eliminated. Experiment results reveal that the improved algorithm is robust and can effectively eliminate shadows.
In this study, we designed a repair algorithm to satisfy the requirement for repairing the defects in images. Based on the Criminisi algorithm, we introduced the marker-controlled watershed algorithm to segment an image into parts based on the scene for improving the image defect repair accuracy. Further, based on the nearest best matching principle, the image was repaired and a control function was introduced with respect to the pixel distance for reducing time for searching matching blocks. Then, we optimized the priority calculation method of the Criminisi algorithm by introducing the local color variance, and improved matching degree between the filled segments and the sections to be repaired based on the covariance. Subsequently, the confidence formula with respect to image repair was reset to reduce the magnifying error when the confidence value was continuously updated. Additionally, we considered many defect images as examples to verify the repairing effect, and the obtained results demonstrated that the designed algorithm has an excellent repair effect. Experimental results show that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm can considerably reduce the time required to repair the damaged image and more effectively restore the original image information.
Generally, deep learning methods are used to identify and classify the foreign fibers in cotton. First, a target recognition framework is adopted based on Faster RCNN to develop a foreign fiber dataset according to the characteristics of foreign fiber size and shape diversity. Next, the original VGG16 is replaced by RseNet-50 as the feature extraction network in the foreign fiber classification model, and the size of the mark box is improved using the k-means++ clustering algorithm. Subsequently, the model is trained to identify and classify the foreign fibers in cotton. The trained model achieves an accuracy rate of 94.24%, a precision of 98.16%, a recall rate of 95.93%, and an F1 score of 0.970 with respect to the verification set. When compared with the original model, the recognition effect is observed to improve in case of small sizes, large aspect ratios, and dense occurrences when the proposed model is used. Furthermore, the accuracy, precision, recall rate, and F1 score of the proposed model improve by 3.21%, 0.90%, 2.51%, and 0.017, respectively, when compared with those of the original model.
A periodic structural parameter inspection method based on spectrum characteristics is designed herein by utilizing the unique spectrum distribution of periodic texture images. A static image inspection interface and a real-time acquisition and inspection system are built, and multiple experiments are conducted based on fabric density inspection. The ratio of relative error of experimental data less than 1% is 96.7%, the average error is about 36% lower than that of the existing algorithm, the inspection time of single frame image is approximately 150 ms, and the inspection speed is suitable for industrial inspection. The proposed method is applied to the field of paper counting, wood texture inspection, and micro-structure array inspection. The experimental results show that the periodic structure parameter inspection method based on spectrum characteristics has high accuracy, wide application range, and high detection efficiency.
In this study, we propose an improved YOLOv3 network detection method to solve the problem that gear defects are difficult to detect in industrial manufacturing. First, a gear defect image database is constructed by performing various activities, including image acquisition and expansion and defect labeling. Second, the feature extraction ability is improved using the DenseNet network structure instead of the original network structure. Finally, the small-size defect detection ability is improved by increasing the network prediction scale. When compared with the YOLOv3 network, the mean average precision and the missing-part precision of the gear increased by 3.87% and 5.7%, respectively, using the proposed method. This experiment demonstrates that the proposed method exhibits several advantages and that the gear defects can be effectively detected.
For the problem of a few feature points and low registration accuracy in multi-mode magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) tumor image registration by speeded up robust features algorithm. Harris detection method is used to extract and detect the feature points of reference image and floating image, and then circular 64-dimensional vector method is used to generate feature descriptors and carry out Euclidean distance matching to enhance the extraction of feature points. The initial parameters of registration image are set to ensure that particles search near the optimal value. The mutual information is used as the measure function of particle swarm optimization to enhance the global optimal solution of the objective function. The average maximum value is introduced to prevent this algorithm from falling into premature phenomenon. Simulation results show that compared with the existing algorithms, the proposed optimization algorithm can increase the number of multi-mode MRI image feature points with higher accuracy.
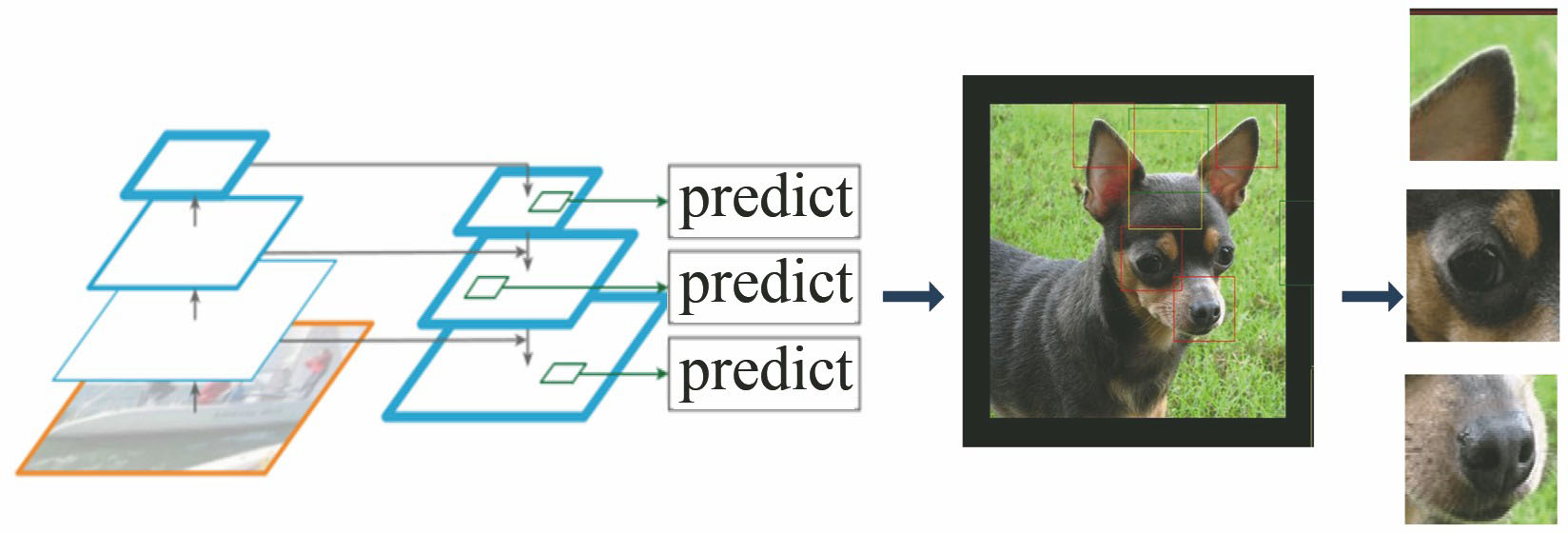
Fine-grained images have a highly similar appearance, and the differences are often reflected in local regions. Extracting discriminative local features plays a key role in fine-grained classification. Attention mechanism is a common strategy to solve the problems above. Therefore, we propose an improved bilinear residual attention network based on bilinear convolutional neural network model in this paper: the feature function of the original model is replaced by deep residual network with a stronger feature extraction capability, then channel attention module and spatial attention module are added between the residual units respectively to obtain different dimensions and richer attention features. Ablation and contrast experiments were performed on three fine-grained image datasets CUB-200-2011, Stanford Dogs, and Stanford Cars, the classification accuracy of the improved model reached 87.2%, 89.2% and 92.5%, respectively. Experimental results show that our method can achieve better classification results than the original model and other mainstream fine-grained classification algorithms.
Aiming at the problem of insufficient expression ability of traditional single manual feature and model degradation caused by error accumulation in the process of model updating in complex scenes, Based on this, the object tracking algorithm based on correlation filtering and convolution residual learning is proposed. The multi-feature correlation filtering algorithm is defined as a layer in the neural network, and the feature extraction, response graph generation, and model update are integrated into the end-to-end neural network for model training. In order to reduce the degradation of model during online updating, the residual learning mode is introduced to guide model updating. The proposed method is validated on the benchmark datasets OTB-2013 and OTB-2015. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively deal with motion blur, deformation, and illumination in the complex scene, and has high tracking accuracy and robustness.
In order to improve the adaptability of intelligent vehicles to quickly detect objects in various scenes, a joint method of multi-task sharing the same feature extraction network is proposed. First, ResNet-50 network is used to extract image features of the encoder. Then, multi-scale feature prediction and fast regression in single shot multibox detector target detection algorithm are used to decode the detection results. A pyramid pool structure of porous space in DeepLab v3 is used to process the multi-scale mapping, bilinear sampling and batch normalization of the image features after ResNet-50 sampling so as to complete segmentation and decoding. Finally, the training of the joint method is completed under the set training parameters. Experimental results show that the mean average precision of the method is 89.00%,the mean intersection over union is 83.0, and the number of frames per second is 31 frame, which can support intelligent vehicle to complete certain tasks.
Aiming at the problem of low registration rate in image feature point extraction and matching algorithm, an image registration algorithm is proposed to optimize the grid motion statistics. The algorithm first uses oriented fast and rotated brief algorithm to extract the feature points, and then rough feature point registration is carried out by Brute-Force matching algorithm. According to the size of the image and the number of feature points, the image is divided into multiple grids, and the number of feature points in the grid is moved for statistics. A score statistics template is created by using Gaussian function through the distance between the nine-square grid feature points and the central feature points. The score statistics of the nine-square grid is compared with the set threshold. If the threshold is exceeded, it is considered to be a correct matching point, otherwise it will be filtered out. Experimental results show that the number of exact matching points between the proposed algorithm and the grid-based motion statistics algorithm is increased by 18.17%, and the speed can be increased by about 41.3% compared with the traditional feature point extraction matching algorithm. This method can effectively eliminate false matches and improve the matching rate.
Facial features extracted by a deep convolutional network are susceptible to background, individual identity, and other factors, which are mixed with unnecessary features that interfere with facial expression recognition. To solve this problem, an attention model-based facial expression recognition algorithm is proposed in this paper. To avoid overfitting, this method is based on a lightweight convolutional neural network. Moreover, the channel attention model and the spatial attention model are employed to strengthen or suppress the feature map elements. A residual learning unit is used to enable the attention model to learn rich features and obtain an excellent gradient flow. In addition, a key area crop scheme for facial expressions is proposed to solve the problem of noise interference in non-expressive regions. The proposed method is validated on two commonly used expression datasets: CK+ and MMI. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method.
To solve the problem of color cast and detail blur in low-illumination underwater images, a low-illumination underwater image enhancement algorithm based on white balance and relative total variation is proposed. According to the characteristics of selective attenuation of light in water, the algorithm firstly performs global illumination compensation for underwater images to improve image brightness and uses gray world algorithm to correct underwater image color. Then a new relative total variation constraint is constructed according to the edge preserving smoothness of guided filtering to estimate the illumination map. Finally, a reflection image, namely an enhanced underwater image, is obtained based on the low-illumination imaging model. The subjective effect, objective analysis, and application comparison experiments all prove the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm in correcting color cast and enhancing image details.
A new adjustable adaptive local dimming method is proposed. In the proposed method, backlight brightness values calculated by existing local backlight algorithms are used to construct the constraint condition. Then, the backlight obtained by the local backlight algorithm is adjusted according to human visual characteristics. Based on the light-emitting diode-liquid crystal display (LED-LCD) prototype, the brightness of the backlight with the best quality is chosen as the highest backlight brightness of the image under the condition that the display image is not distorted. Finally, pixel compensation is conducted based on the optimal backlight. Experimental results show that the proposed method can make the displayed image closer to real scene perception and improve the image contrast to a certain extent.
This study proposes an enhancement method based on non-subsampled contourlet transform (NSCT) and multi-scale guided filtering to solve the shortcomings of lack of brightness, blurry edge details, and unsatisfactory visual effects for partial remote sensing images. First, the multi-scale sub-band image was obtained using NSCT. Then, global dynamic mapping was applied to a low-frequency sub-band image to adjust the brightness. Accordingly, a weighted guided filter was used to replace the Gaussian filter in Retinex to obtain the detail and base components. Scale factor was utilized to adjust the ratio of the two components in the low-frequency sub-band image. The adaptive Bayesian threshold based on the features of each direction and the enhanced nonlinear gain function were employed to improve the high frequency sub-band coefficients. Finally, the processed sub-band was inversely reconstructed by NSCT to obtain an enhanced image. Compared with traditional enhancement algorithms, the proposed method herein improves definition and information entropy, preserves detail features, and enhances the visual effect.
Faster R-CNN algorithm cannot achieve accurate ship detection. Therefore, a ship detection algorithm based on a deep feature pyramid and cascade detector is proposed in this study. First, the small-target data enhancement algorithm is used for expanding the data to ensure that sufficient features are learned by the detection model. Then, the deep feature pyramid network is used for improving the feature extraction network of the original target detection algorithm, suppressing the coherent speckle noise, and effectively extracting the ship features. Further, a cascading structure is adopted to adjust the improved network according to the sparse features of the ship targets obtained from the synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images. Based on the aforementioned improvements, some images from the ship target detection dataset and the SAR images of the Bohai Bay captured in February are selected for performing the experiments. Experimental results show that, the proposed algorithm achieves good detection results, proving its effectiveness with respect to ship detection.
In view of the insufficient consideration of structural information in the priority calculation of the Criminisi image inpainting algorithm and the fact that matching only relies on the color distance selection, the mural repair process is prone to structural propagation errors and pixel mismatches. To address this, a mural inpainting algorithm based on information entropy and structural characteristics is proposed in this study. First, when calculating the priority function, the information entropy of measuring the complexity of the pixel block is introduced, and the optimal block to be repaired is determined by improving the priority function to preferentially repair the regions with rich structural information. Then, the matching block is determined by combining the sample color feature and the covariance similarity between blocks, and then the best matching block is determined through the Euclidean distance between the blocks. Finally, the mural inpainting is completed through iterative updating. Experiments on damaged Dunhuang murals show that the proposed algorithm overcomes the problem of the Criminisi algorithm mismatching and filling. Subsequent to the repair, good visual effects are obtained, and objective evaluation values such as peak signal-to-noise ratio of the image are improved.
Non-reference image quality evaluation is a research hotspot in recent years. At present, the commonly used evaluation algorithms are extracting features from gray space. In order to increase the reflection of the color channel information on the image quality, the mean subtracted contrast normalized (MSCN) coefficients of each channel in the RGB(Red, Green, Blue), LAB(Luminosity, A, B), and HSV(Hue, Saturation, Value) color spaces are extracted, respectively, and fitted through asymmetric generalized Gaussian distribution model. The statistical features of the fitted MSCN coefficients are trained by gradient boosting regression algorithm to obtain a non-reference image quality evaluation model. The predicted scores of each color channel training model and gray space training model are individually compared with subjective scores. The results show that the monotonicity, subjective and objective consistency, and stability of the non-reference image quality evaluation model under some color channels are improved to some extent compared to the gray space. The model trained with the features extracted under the RGB_B channel has the best performance, Pearson related coefficient increases from 0.63 to 0.70.
It is difficult to determine the size and number of sub-blocks in a hyperspectral image using the existing methods because of the low rank of the sub-blocks and other associated disadvantages. Therefore, we propose a hyperspectral image denoising method, which combines the features of the ground objects with the low-rank characteristics. Further, the number of sub-blocks are divided with respect to the number of categories of prior knowledge of ground object data, and optimal parameters are specified for determining the size of the blocks. Then, the low-rank characteristics of the same object space spectrum are obtained based on the correlation of the pixel space and spectrum with respect to the same feature. Finally, the spectral low-rank characteristics of the entire hyperspectral image are combined, and the noise-reduced image is obtained according to the low-rank matrix recovery model. Experiments conducted on the Washington DC Mall and Indian Pines datasets demonstrate that the proposed method not only improves the noise reduction effect with respect to each type of ground noise but also targets mixed noise containing more severe random noise and sparse noise.
The measurement precision of charge coupled device (CCD) is the main factor affecting the accuracy of wavefront reconstruction. Due to the limitations of camera manufacturing technology and environmental impact, it is inevitable that noise data will be collected, which will affect the image information collection with low signal-to-noise-ratio and high spatial frequency. An improved phase diversity wavefront sensor based on image compensation is proposed to reduce the influence of noise on wavefront reconstruction. First, two images are collected under the normal exposure time and saturated exposure time of CCD respectively. And then they are sewed into an image containing accurate high spatial frequency and low spatial frequency light intensity information. At the same signal-to-noise ratio, the improved phase diversity wavefront sensor and the traditional phase diversity wavefront sensor are simulated. The results show that the wavefront inversion accuracy of the improved phase difference wavefront sensor is significantly improved. Finally, the effectiveness of the method is further verified through experiments.
Aiming at the problem of low accuracy of the segmentation algorithm for three-dimensional (3D) point cloud data, a new segmentation algorithm combining point cloud skeleton points and external feature points is proposed. This method can effectively segment local small-scale convex objects, which cannot be segmented by traditional methods. This would make the segmentation of 3D point cloud data more perfect and provide a new idea for the segmentation of 3D point clouds. In this paper, C++ and its open source point cloud library are used to program. First, L1 median algorithm is used to extract skeleton points from 3D point clouds. At the same time, feature points are extracted by scale-invariant feature transform algorithm. Then, a segmentation plane is constructed based on skeleton points and feature points, segmentation is conducted, and the remaining feature points are detected. At last, a segmentation plane is constructed again for segmentation, therefore getting the final result. Experimental results show that the algorithm can efficiently segment small-scale convex surface of 3D point clouds and improve the accuracy of segmentation.
Aiming at the problem of low accuracy of the segmentation algorithm for three-dimensional (3D) point cloud data, a new segmentation algorithm combining point cloud skeleton points and external feature points is proposed. This method can effectively segment local small-scale convex objects, which cannot be segmented by traditional methods. This would make the segmentation of 3D point cloud data more perfect and provide a new idea for the segmentation of 3D point clouds. In this paper, C++ and its open source point cloud library are used to program. First, L1 median algorithm is used to extract skeleton points from 3D point clouds. At the same time, feature points are extracted by scale-invariant feature transform algorithm. Then, a segmentation plane is constructed based on skeleton points and feature points, segmentation is conducted, and the remaining feature points are detected. At last, a segmentation plane is constructed again for segmentation, therefore getting the final result. Experimental results show that the algorithm can efficiently segment small-scale convex surface of 3D point clouds and improve the accuracy of segmentation.
This paper studies P4P localization algorithm based on quick response (QR) code recognition, and proposes to use the coordinates of the four coplanar vertices stored in the QR code and the pixel coordinate in the QR code images to locate. The pixel coordinates of the four coplanar vertices of the corrected QR code are obtained through camera calibration and image correction, and the actual position coordinates of the four coplanar vertices are obtained through decoding program analysis. The rotation matrix and translation vector output by the P4P algorithm are used as the following iterative initial values of the next algorithm. In perspective N points projection algorithm, the optimization on manifold is converted into optimization in tangent space by means of local isomorphism between Lie group and Lie algebra, and the optimization method in linear space is used to optimize the target value. In any gradient direction of the tangent space, the parameter value is in the space, that is, the matrix is all on the manifold. Experimental results show that during the navigation movement, the camera coordinate position error is less than ±2 mm, and the rotation angle error is less than ±0.5°, showing that the algorithm has high positioning accuracy and stability.
With the continuous development and wide applications of deep learning, target detection algorithms based on deep learning have become a new mainstream. To further improve the detection accuracy of the convolutional neural network YOLO v3 (You only look once v3), a convolution layer module was added to the network structure of the original algorithm to classify the target background of the sample and the anchor frame size of the feature map was roughly adjusted. To resolve the challenge of unbalanced proportion of positive and negative samples in the original algorithm, samples with background probability value less than the set threshold value were filtered by the module after outputting the target background probability. The adjusted anchor box was used to replace the anchor box of fixed sizes directly generated by clustering in the original algorithm. This process provides a better initial value for bounding box prediction. Experimental results on VOC dataset indicate that the improved YOLO v3 shows higher detection accuracy than the original algorithm.
A point cloud registration algorithm based on cosine similarity (PCR-CS) is proposed. This algorithm mainly solves the problem of point cloud rigid registration, which involves finding the rotation matrix R and the translation matrix T of the point cloud registration to realize registration between the original point cloud P and the target point cloud Q. In the proposed algorithm, first, the two points clouds to be registered are decentralized and the cosine similarity of the point clouds is studied. Then, the two three-dimensional point clouds to be registered are projected onto the XY plane and rasterized on the XY plane. The data points on the statistical grid form the statistical matrices SP and SQ. Moreover, the differential evolution algorithm is used to find the optimal R under the condition of the cosine similarity of the two points clouds to achieve point cloud registration. Finally, the center point is used to calculate T. Experiment results show that compared with other algorithms, the proposed algorithm has higher registration accuracy. In addition, even when the point cloud data are accompanied by noise or missing data, it can achieve good registration results.
For extracting the road under complex illumination environment, a road region extraction algorithm is proposed based on color invariant and dark primary color segmentation. The illumination invariant image is obtained with orthogonal decomposition method, and the road information such as vanishing point of image can be extracted based on the clustering segmentation of the dark primary color prior road image. The road region is identified by a constructed soft voting function, and the final accurate road is obtained after morphological processing. In order to effectively evaluate the accuracy and efficiency of the road region extraction algorithm on complex illumination scenes, we construct a complex illumination road scene image dataset for road region extraction and builds benchmark for nine road area extraction algorithms. Experimental results show that the proposed method can effectively reduce the influence of other interference factors such as shadow. Compared with the other eight algorithms, the proposed algorithm can achieve similar accuracy or more accurate than the latest algorithms. Moreover, when the extraction of vanishing point position is accurate, the road extraction performance is more complete and accurate than other algorithms. In addition, the dataset and benchmark built in this paper can effectively evaluate the performance of road region extraction algorithms in complex illumination environment.
In order to solve the problems of premature convergence, uneven search ability, and tendency to fall into local optimality in differential grey wolf prediction algorithm, an improved hybrid grey wolf optimization (HGWO) prediction algorithm is proposed, which can adaptively improve and adjust the mutation operator, crossover operator, and mutation strategy. Support vector machine (SVM) with classification prediction function is embedded, while Levy flight global search is used to update the position of the wolves, and the SVM kernel function parameter γ and penalty factor C are optimized. Thus, an HGWO-SVM prediction algorithm is built to predict the large lane of the coke pusher. The results show that, compared with the existing algorithms, the relative errors of position prediction of pedestrian, bicycle, battery car, electric tricycle, and large, medium and small four-wheel vehicle are reduced by 4.21, 4.14, 7.91, 2.03, and 25.53 percentage points, respectively, and the prediction time is reduced by 8.8-10 s. It can overcome the harsh environmental impact of coke oven, accurately predict the trajectory of the moving targets in the lane of the coke pushing vehicle, and provide an active and safe predictive control method for the unmanned operation of coke pushing truck.
Aiming at the problem that the traditional 2D deep learning method can not realize the 3D point cloud classification, this study proposes a novel classification method for airborne LiDAR point clouds based on 3D deep learning. First, airborne LiDAR point clouds and multi-spectral imagery are fused to expand the spectral information of point clouds. Then, 3D point clouds are placed on grids to make the LiDAR data suitable for the 3D deep learning. Subsequently, the local and global features in different scales are extracted by multi-layer perceptron. Finally, airborne LiDAR point clouds are classified into semantic objects using the 3D deep learning algorithm. The data sets provided by the International Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing (ISPRS) are used to validate the proposed method, and the experimental results show that the classification accuracy can be increased by 13.39% by fusing the LiDAR point clouds and multi-spectral images. Compared with some of the methods submitted to ISPRS, the proposed method achieves better performance by simplifying the process of feature extraction.
Based on the excellent hole convolution performance observed using the obtained image information, we propose a framework for performing hyperspectral image classification based on the dual-channel dilated convolution neural network (DCD-CNN) to improve the classification accuracy. The receptive field of the filters can be expanded via dilated convolution, which effectively avoides the loss of image information and improves the classification accuracy. In this proposed framework, one-dimensional CNN and two-dimensional CNN, exhibiting an empty convolution, are used to extract the spectral and spatial features of the hyperspectral images. Subsequently, these extracted features are combined using a weighted fusion method. Finally, the combined features are input into the support vector machine for performing final classification. The expreimental results on the two commonly used hyperspectral image datasets by the proposed framework are compared with that by the four existing classification methods, showing that the proposed framework exhibits improved classification performance.
Laser intensity is affected by factors such as atmospheric environment, scanning distance, target characteristics, thus the laser intensity values of the similar targets have a large deviation. In order to eliminate the impact of the scanning distance on the intensity of terrestrial laser scanning, based on Lidar ranging equation, experiments with the same material, different distance, and reflection intensity of point cloud, are designed. The relationship between the laser scanning distance and the laser intensity of point cloud and the mathematical model are obtained. The models with better experimental data correction effects (including Taylor interpolation polynomial model, Sectional polynomial model, Section al Gaussian function, and polynomial mixed model) are used to modify the laser intensity of the point cloud. The results show that the Taylor interpolation polynomial model has the best correction performance, which effectively eliminates the deviation of point cloud intensity caused by the distance factor, and makes the laser intensity of the same kind of target tend to be consistent, and the laser intensity difference of heterogeneous targets is obvious.
Fluorescence microscope has always been the main method in biomedical researches due to its advantages such as less damage to samples, specific labeling, and being suitable for in vivo imaging. However, the defects of optical system itself, the optical inhomogeneity of biological samples, and the change in the refractive index at the interface between the sample and the microscope's immersion medium have caused aberrations and reduced the imaging contrast and imaging resolution. Adaptive optics (AO) technology uses active optical components such as deformable mirrors and spatial light modulators to correct distorted wavefronts (aberrations), eliminate dynamic wavefront errors, and restore diffraction-limited performance. In recent years, many researchers have combined AO system with fluorescence microscope to correct the aberration caused by sample inhomogeneity and improve the imaging quality. In this paper, the basic principle of the AO technology is introduced, the applications of AO technology in fluorescence microscopic imaging in recent years are reviewed, and its future development trend is prospected.
Precise object detection and recognition plays an important role in information-based warfare. Due to panoramic vision sensors’ large field of view (LFOV), they are gradually applied to security and military areas. In this paper, first, the difficulties and challenges in the development of object detection and recognition in LFOV are presented from three aspects: camera imaging model, image imaging quality, and asymmetry of object. Then, based on whether the distortion correction preprocessing is carried out or not, the object detection and recognition algorithms in LFOV are classified into two categories: distortion correction based algorithms and original LFOV image based algorithms. These two kinds of algorithms are comprehensively combed and summarized. Finally, the paper analyzes the unity and difference of various algorithms for object detection and recognition in LFOV and discusses their future development trend.
Image saliency is the most important information source to realize visual information perception. The detection of image saliency information has always been a hot topic in computer vision research. With the great improvement of data acquisition capability, the demand of three-dimensional or stereoscopic vision is becoming more and more urgent. The effective extraction of deep sensitive information is an important element that affects the current stereoscopic vision experience. Therefore, it has been paid attention by many researchers and obtained some research achievements. In this paper, through extensive research on the relevant detection templates and technologies of image saliency detection and depth sensitive information extraction research, the current status of depth sensitive information extraction research is classified and summarized, and several typical depth sensitive information extraction algorithms are analyzed through comparative experiments. Finally, the problems and development trends of depth-sensitive information extraction techniques are discussed.
As a new imaging technology, photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has attracted more and more attention in biomedical imaging due to its unique multi-scale imaging abilities of label-free, high resolution and high contrast, and has been rapidly transformed into clinical trials. Benefitting from the rapid development of ultrasonic detection technology and laser technology, the PAT system has gradually achieved real-time, large field of view, high resolution and high penetration depth of tissue structure and functional imaging. In this paper, we mainly summarize the advances of the circular array PAT system in biomedical imaging and the problems it faces in preclinical and clinical practices.
As one of the important tasks in machine vision, object detection is a technology branch with important research value in artificial intelligence systems. The three mainstream object detection models of convolutional neural network framework, anchor-based model, and anchor-free model are analyzed. First, the network structure and the advantages and disadvantages of the mainstream convolutional neural network framework, and the related improvement methods are reviewed. Second, the anchor-based model is deeply analyzed from one-stage and two-stage branches, and the research progresses of different object detection methods are summarized. The anchor-free model is analyzed from three parts: early exploration, key points, and intensive prediction. Finally, the future development trend of the field is considered and prospected.