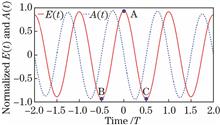
By using the improved strong field approximation method combined with the time window function, the effect of hydrogen atomic electron wavepacket (EWP) interference in above-threshold ionization by a strong laser field on the photoelectron energy spectra and two-dimensional (2D) momentum spectra is analyzed. It is found that the general characteristics of photoelectron energy spectra and 2D momentum spectra are formed by the interplay of inter-cycle and intra-cycle interferences. The fanlike structure in the 2D momentum spectra is caused by the long-range Coulomb potential and the intra-cycle interference. A numerical solution of the time-dependent Schr dinger equation (TDSE) is used to analyze the reason why the intra-cycle interference is suppressed in multi-cycle pulse ionization and it is found that this special fringe appears in the 2D momentum spectra only when the Keldysh parameter is close to 1. These results show that the long-range Coulomb potential has an important influence on the formation of these fringes.
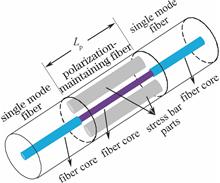
A high sensitivity optical fiber curvature sensor with a fiber structure is proposed based on single mode-polarization maintaining-single mode (SPS), which is fabricated by splicing a piece of polarization-maintaining fiber (PMF) between two sections of single mode fiber. The curvature sensing performance and the effect of the length of PMF on the curvature sensitivity of this sensor are studied in experiments. The results show that, the output spectrum of this sensor shows an obviously red-shift phenomenon with the increase of curvature. In addition, the length of PMF has a significance influence on the curvature sensitivity of this sensor. In the curvature range from 0.43 m-1 to 1.37 m-1, the maximum sensitivity can reach to 59.849 nm/m-1 when the length of PMF is 11 cm. This sensor has advantages of simple structure, easy fabrication and high sensitivity compared with the other optical fiber sensors with an optical fiber structure, and it can be used in the field of the structural health monitoring.
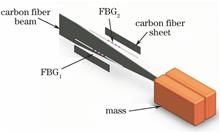
A new inclination sensor based on embedded fiber gratings and carbon fiber equi-strength beams is proposed. The measuring principle and the manufacture methods of this sensor are first introduced. Then this sensor is fully tested. The research results show that, within a measurement range of ±30°, the sensor possesses a sensitivity of 49.73 pm/(°), a measurement accuracy of 0.101°, a repeatability error of 0.62%, and a fitting linear correlation coefficient of 0.99992. Furthermore, the creep resistance and the good temperature compensating abilities are good. The requirement of long-term inclination monitoring under complex electric environments is met.
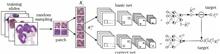
Automatic pathological image diagnosis is an important topic in medical image analysis, and the prerequisite for an accurate pathological image diagnosis is to capture the distinctive morphological features of normal and abnormal tissues. With a deep neural network as a tool, a boosting convolutional neural network is proposed, in which a pair of complementary networks is trained to optimize the accuracy of a pathological image diagnosis. To reduce the risk of over-fitting caused by the scarce training examples due to the high cost of obtaining pathological images, in the proposed algorithm, a basic classifier is first trained to estimate the probabilities of local tissues being abnormal, and then another heterogeneous network is trained to correct the predictions made by the basic one. The extensive experiments are carried out on the Cancer Metastasis Detection on Lymph Node dataset and the Animal Diagnostics Lab dataset provided by Pennsylvania State University which contains the pathological images of three organs (i.e., kidney, lung and spleen). The experimental results show that the proposed model can be used to achieve a high accuracy on the pathological images of different organs.
An electro-optical imaging system is a typical optical-discrete sampling system. Usually, the spatial resolution of the electro-optical imaging system can be improved by means of the technical routes such as the increase of objective lens focal length, the increase of detector array consumption, the size reduction of detector elements, and the increase of detector filling rate. Due to the restriction of device level,the effective data processing method can be used to improve the resolution of an imaging system. The sub-pixel imaging technique and the super-resolution image processing technique based on the discrete CCD/CMOS plane array detectors are mainly introduced, which are widely concerned at home and abroad.
A saliency detection model is proposed based on Log-Gabor filtering and saliency map fusion optimization of stereoscopic images, in which the image saliency is detected by the planar image saliency combined with the texture and depth features. First, the left view saliency map is calculated by the improved graph-based manifold ranking algorithm. Second, the left view texture features and the depth features from stereoscopic images are extracted, and the texture and depth saliency maps are computed by the Log-Gabor filtering method, respectively. Third, the above three saliency maps are integrated into a stereoscopic (3D) saliency map by the weighted linear combination (WLC) method. Finally, the 3D saliency map is enhanced by the center-bias factor and visual acuity. The experimental results on a public eye tracking dataset show that the proposed model possesses a good detection performance and is superior to the existing 3D visual saliency detection models.
To solve the problems of low disparity accuracy in local stereo matching, a secondary guided filtering model is proposed and applied to the local stereo matching algorithm. The newly designed secondary guided filtering model overcomes the deficiency of traditional guided filtering and further suppresses the noises because the result of the first guided image filtering is used as the guiding image of the second guided filtering. In the cost aggregation phase, the introduction of the secondary guided filtering further improves the matching accuracy because the cross-scale framework is used to aggregate the matching cost volume at each scale. The experimental results demonstrate that the local stereo matching algorithm based on the secondary guided filtering possesses a high accuracy in the detection of standard stereo image pairs on the Middlebury benchmark. Moreover, the temporal complexity of the cost aggregation phases is independent of the filtering kernel size, and the proposed algorithm achieves good performances in speed and accuracy. The idea of the secondary guided filtering has potential applications in stereo matching and others.
Based on by the Dijkstra farthest point sampling (DFPS) algorithm, the initial sampling points of the three dimensional (3D) model cluster are obtained. The correspondence between two models is obtained by the calculation based on the functional mapping theory. The matching between two models is transformed into the multi way correspondence of a 3D model cluster by use of the cycle consistency constraints. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can reduce the isometric errors of the correspondence among 3D models to a certain extent. Moreover, this algorithm is not only capable of the correspondence calculation of two models, but also the correspondence calculation of an isometric or approximately isometric 3D model cluster.
A method for detecting the tower components from far to near is proposed based on the histogram of the gradient (HOG) along the tower gradient direction by analyzing the structural characteristics of hollowing-out of a tower. The multi-layer perceptron (MLP) is first trained by using the HOG feature of the tower under different orientations to obtain a trained classification model, then the aerial image is input into this classification model to identify the orientation of the tower, and the detection of a local target is finally realized. Compared with that of a deep learning neural network, the classification feature of the proposed method is clear and representative. The experimental results show that the detection accuracy of the proposed method is 27.9% higher than that of the Faster RCNN (Regions with Convolutional Neural Networks) method, but the computation time is 70.9% lower than the latter. The proposed method is suitable for the accurate detection of the tower orientation and its local parts by the unmanned aerial vehicle in an open environment.
The traditional image processing algorithms used for the location of Chinese chess pieces have high complexity and the traditional character recognition methods used for the recognition of chess pieces have low generalization and accuracy. A segmentation method based on chess piece color features and an improved binary image filtering algorithm are proposed to achieve the fast location of chess pieces, and the second correction of positions is not needed. A recognition method of chess pieces based on a convolutional neural network is proposed, which can be used for the recognition of chess pieces with different fonts. In the case of chess piece replacement, this method can still recognize chess pieces quickly and accurately. The experimental results show that as for the proposed method, the location error is 0.51 mm, the average location time is 0.212 s, and the average recognition accuracy of chess pieces with four types of fonts is about 98.59%. The effectiveness and practicability of this method are confirmed.
The principle of a true color low light level night vision system based on full-wave and three-wave bands is briefly described. Combining with the general image fusion algorithms, four image fusion algorithms for low-light-level night vision, including the weighted average method, the Brovey method based on linear transformation enhancement, the HIS (hue, intensity and saturation) space method, and the HIS method based on edge segmentation are studied. The realization methods and processes of these fusion algorithms are described in detail. The research results show that by the Brovey method based on linear transformation enhancement, the comprehensive objective evaluation indexes of fusion images for Scene 1 and Scene 2 are 27.9647 and 31.2756, respectively, larger than those by the other three algorithms. Among these four fusion algorithms, the visual effect of fusion images obtained by the Brovey method based on linear transformation enhancement is the best.
The influence of ultrasonic wave excited by a laser point or line source on the detection of rail surface defects is investigated. In addition, the sound fields, acoustic signals and the detection effectiveness of rail surface defects under these two types of excitation modes are compared by the finite element method. The detection of horizontal, vertical, and oblique 45° rail surface defects is simulated by the finite element method and the corresponding experimental test is also conducted. The consistency between experimental and simulated results shows that the acoustic surface wave excited by a laser line source possesses good directionality and a high signal amplitude, which is more conducive to the detection of rail surface defects and has a good detection ability for different types of rail surface defects.
The YLS-3000 fiber laser is used to laser cladding of the Co-based superalloy. The macro-morphology, microstructure and microhardness of Co-based superalloy after laser cladding are characterized by the optical microscope and the microhardness tester. The results show that due to the preheating effect of the preceding cladding process on the subsequent cladding process, the widths of the cladding layer gradually transit from the initial 4.84, 5.17, 5.88 mm to the cladding-terminal 5.28, 6.61, 6.78 mm, respectively under the effects of different laser cladding parameters. The upper surface morphology of laser cladding area is horn shape. The morphology of laser cladding is asymmetric crescent shape due to the powder feeding direction during laser cladding and the preheating effect of adjacent laser cladding on the substrate. The equiaxed grains are observed in the central area of surface cladding layer and the non-uniform dendrites are observed in the middle of inner cladding layer. Because of the non-equilibrium solidification in the process of laser cladding and the differences between heating rates and cooling ones in different sections, the hardness of the cladding layer presents a non-uniform distribution, and is always higher than the hardness of its substrate.
A method for measuring laser linewidth at Fourier limit based on time resolution and Fourier transform is proposed, whose resolution is limited by Fourier transform. In experiments, the linewidths of a fiber laser and a semiconductor laser are measured by the time-resolved method, which are compared with those by the traditional radio frequency (RF) spectral methods. The linewidth measurement results of these two lasers under different integration time show that the proposed measurement method at Fourier limit has smaller measurement errors than those by the RF spectral analyzer. Moreover, the acquisition of spectral information by the time-resolved method has the advantage of real-time acquisition.
A monocular visual depth estimation method is proposed based on deep convolutional neural networks, in which an end-to-end learning framework is used to construct a model. A residual network (ResNet) is used as the coding part of the neural network model framework to extract the depth information features. The encoded information is decoded by a densely concatenated convolution network (DenseNet). The integration of the encoded and decoded information streams is realized by Skip-Connections, which avoids the loss of inter-layer information under transmission. The experimental results show that the depth convolution neural network can be used to estimate visual depth more effectively and accurately than other monocular visual depth estimation methods.
The far-field unidirectional scattering properties of silicon nanocross dimers are investigated systematically by the finite element method. The multipole decomposition method is used to explain the scattering properties of nanocross dimers. By the analysis of the effects of different resonance modes on the scattering properties of nanoantennas, it is found that the coupling of these resonance modes of silicon nanocross dimers leads to the formation of magnetic hotspots and the far-field unidirectional scattering. The adjustable optical properties of nanocross dimers may provide a solid theoretical foundation for achieving far-field unidirectional controllable nanoantennas.
The coherent control of multi-dressed four-wave mixing (FWM) Autler-Townes (AT) splitting is mainly investigated. It is shown that the transformation of the FWM signals from singly-dressing to cascade doubly-dressing is realized by controlling the quantity of the additional dressing fields. Moreover, the AT splitting phenomena of the singly-dressed or doubly-dressed FWM signals can be observed when the frequency detuning of probe field is scanned. The second-order AT splitting phenomena of the doubly-dressed FWM signal is also observed. The factors influencing the position and linewidth of AT splitting are finally analyzed. The research results show that the position and linewidth of AT splitting can be coherently controlled by Rabi frequency or frequency detuning of the dressing field.
Aiming at the economic and optical performances of the compound parabolic concentrator (CPC), the CPC structural design is optimized. According to the parameter equation, the effect of the intercept ratio for the same area on the total CPC arc length and the number of receiving tubes is analyzed. The research results show that an intercept ratio value of 0.15-0.25 for CPC can effectively reduce the use of CPC arc surface material. Based on the Tracepro software, two-dimensional ray tracing of CPC is implemented, and a simulation and calculation method for the direct optical efficiency of CPC is proposed. Four seasonal dates, January 1, April 1, July 1, and October 1, are selected as the simulation dates. The simulation results show that the average direct optical efficiencies of CPC with an interception ratio of 0.16 are 13.77%, 15.24%, 9.30% and 11.54% higher than those of CPC with an interception ratio of 0.56, respectively. The increase of solar altitude angle and the decrease of azimuth angle are both helpful to reduce the end ray loss of CPC. The increase of the CPC length is helpful to reduce the effect of terminal light loss on CPC optical efficiency. The experimental results confirm the correctness of the simulation ones. The proposed method can be applied to the optimization design of a CPC structure for the improvement of optical performances.
A design method of curved light-emitting diode (LED) array is proposed. Based on the principle of light superposition, the LEDs are arranged on the free-form surface, and the LED light-emitting angle is controlled through curvature. Based on the analytical formula of off-axis illumination distribution of the LED curved array, a particle swarm optimization algorithm is introduced based on simulated annealing, the constraint conditions are set, a uniformity evaluation function is constructed, and the numerical model of LED curved array is optimized. A physical light source is produced for the illuminance measurement and the defect detection. Both the theoretical simulation and the real detection show that when the inclination angle is 45° and the ratios of the target surface area to the light-emitting surface area are 1∶0.85 and 1∶4,the illumination uniformity is 91.79% and 98.4%, respectively. The results for leather defect detection show that the proposed curved LED array light source can highlight specific defects, quickly and accurately identify defects, and is easy for image processing.
The effects of current, temperature or their joint stress on the reliability of LED bulbs are studied and the failure mechanism of LED bulbs under each stress is investigated as well. It is found that the degradation of blue chips is the main failure mechanism of LED bulbs at room temperature when the current is as the accelerated stress. With the increase of current stress, the degeneration of phosphor gradually becomes the main failure mechanism, which resulted in the increases of both the correlated color temperature and the color rendering index of LED bulbs. Under the temperature stress or the joint current-temperature stress, the degeneration of phosphor is serious and the phenomenon of blackening appears. In addition, the yellowing and blackening occur in the lamps, driving power sources, LED brackets and aluminum substrates. It is indicated that the temperature stress accelerates the failure of LED bulbs more than the current stress. Finally, the lifetime of LED bulbs under the current stress is predicted by the extrapolation method.
A scheme of classical-quantum signal transmission in a shared fiber is proposed based on a measurement-device-independent protocol. The counting rate formula of spontaneous Raman scattering noise is deduced and the effects of the incident power of classical signals, channel number of quantum signals and average photon numbers of quantum signals on the quantum key distribution (QKD) performances are analyzed. The numerical simulation results show that the maximum safe transmission distance for the QKD by the proposed scheme is up to 141 km when the incident power of classical signals is 0 dBm (i.e., the communication capacity of 84.8 Gbit/s). Even when the incident power increases to 11 dBm (i.e., the communication capacity of 1.068 Tbit/s), it is still up to 100 km. Compared with the existing optimal transmission scheme, the maximum safe transmission distance of the QKD by the proposed scheme is extended by 26 km. Although the QKD performance decreases with the increase of the incident power of classical signals, the performance can be compensated by the multiplexing channels of quantum signals and the optimization of the average photon numbers of quantum signals.
The bit error rates (BERs) of both the free space quantum communication system and the classical optical communication system are analyzed. A free space quantum-classical signal coexistence transmission system is designed based on the wavelength division multiplexing technology, whose feasibility is investigated by the software simulation. The 15 bits quantum information and 128 bits classical information are totally transmitted within 256 ns and the BER of classical information is 4.07×10-15. The results show that the designed system can effectively realize the coexistence transmission of free space quantum and classical signals in the same channel and simultaneously expand the channel capacity of the free space quantum key distribution system.
The infrared dim small target detection technology has become a research focus in the infrared field at home and abroad. The characteristics of infrared dim small targets are introduced. The principles, main steps and features of the existing infrared algorithms for the dim small target detection in single-frame images are reviewed from three aspects of filtering based on spatial domain and transform domain, human visual systems, and image data structures. The development trend of infrared dim small target detection technologies is analyzed.
The basic principle of the photoelectric mixing technology is elaborated. The research progress of the photoelectric mixing technology is traced and summarized from two ways of the independent photoelectric devices and the combined photoelectric devices. Inspired by the microwave photon frequency conversion technology, a photoelectric mixing method is proposed based on the bulk electro-optic modulator. This method uses the electro-optic modulator to demodulate the frequency mixing on the optical field and uses the high-resolution and low-cost image sensors at the back end, which breaks through the limitation of the array size on the image resolution and achieves the advantages of high energy efficiency and high signal-to-noise ratio.
Photonic crystal is a kind of artificial structure crystal formed by a plurality of dielectric materials with different dielectric constants arranged in a certain spatial period, whose photonic band gap has high reflectivity to electromagnetic waves. The photonic crystals can alter the radiation characteristics of targets. The study of infrared stealth materials based on photonic crystals is one of the research hot spots of the current infrared stealth technologies. The structures and characteristics of photonic crystals are introduced in detail and the current application status of photonic crystals in infrared stealth is systematically reviewed. The outlook for the study of novel infrared photonic crystal materials is also discussed in order to provide some solutions for the needs of wide-band stealth, multi-band compatibility, and band gap adjustment of photonic crystal infrared stealth materials.
The interactive holographic display technology, due to its unique true three-dimensional (3D) display ability, can bring users a natural and real human-computer interactive mode. As an important part of the interactive holographic display system, the gesture recognition module has an important impact on the success, nature and comfort of the interaction process. There are mainly three gesture recognition ways in the interactive holographic display system, recognition based on wearable devices, recognition based on visual inspection, and 3D touch detection based on holographic 3D display. The research progress of the interactive holographic display system is firstly reviewed, then the development, merits and faults of these three interactive modes are discussed, and the current problems and development prospects of the interactive holographic display system are finally analyzed. This study can provid a reference for the further research on the interactive holographic display.
The basic principle of recording and reconstructing for the coded aperture correlation holography is clarified, and the existing systems and methods for recording the coded aperture correlation holography are introduced. The imaging resolution and reconstruction quality are mainly analyzed. The existing problems and the research directions for this technology are also discussed. Coded aperture correlation holography has been demonstrated its potential applications in the fields of dynamic three-dimensional imaging, multi-spectral imaging, adaptive optics, biomedicine, and military.
Taking different requirements for image motion detection as orientation, the development of image motion detection methods is traced, and the whole detection process of image motion is clarified as three stages: image motion calculation based on engineering parameters, image motion estimation based on joint optical correlators, and image motion detection based on remote sensing images. For each stage, the existing solved problems and the remaining technical bottlenecks are analyzed objectively. In combination with the development trend of space cameras, three pivotal scientific problems that need to be solved in the existing image motion detection methods are deeply analyzed. This study provides a possible research thought for wide-band image motion detection.
A fast and high precision imaging registration method is presented, which can be used to improve the speed and accuracy of spectral recovery in a hyperspectral imaging process. In this method, two local upsampling phase correlation methods are adopted. One is to estimate the rotation and scaling parameters in a log-polar space, and the other is to estimate the translation parameters in a Cartesian space. A gradient preprocessing process is introduced to make the method more robust. The principle of Fourier-Mellin transform is introduced and this transform can decouple the rotation and scaling parameters. Based on the traditional phase correlation method, the local upsampling phase correlation method is introduced. The necessity of the gradient preprocessing process is verified. The simulation results show that the proposed method can be used to achieve high precision image registration.
The infrared spectroscopy method is employed to analyze the corn leaves infected by the southern corn leaf blight disease and the molecular structure information of infected corn leaves is obtained. The research results show that the fungal pathogens have certain effects on the protein structure of the leaves. The two-dimensional correlation infrared spectral analysis indicates that the β-sheet conformation of the protein secondary structure in healthy corn leaves changes with the growth and metabolism of corn leaves, while in the infected corn leaves is the change of the β-turn conformation. Two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy can be used to reveal the change of molecular structures of corn leaves invaded by the fungal pathogens and provide a reference for the prevention and control of corn diseases.
With the help of optical aberration theory, grating dispersion theory and pixel resolution matching theory, we design an initial structure of a wide-spectrum high-resolution grating spectrometer. Based on the comprehensive consideration of the mechanical processing and the efficiency of the spectrometer, this method is applied to the initial structural design of the optical system of a Czerny-Turner grating spectrometer with a wavelength range from 200 nm to 1000 nm and a resolution of 0.01 nm. The ZEMAX software is used to simulate and optimize the optical structure of this spectrometer. The results show that this design method can simultaneously meet various design requirements such as spectral detection range, resolution and clear aperture, so that the instrument design performance can meet the requirements of various indicators.
A novel algorithm for component identification in mixtures based on Raman spectroscopy is proposed, in which background correction and de-noising operation on the Raman spectra of mixtures are firstly performed, the Voigt function is then used to fit the Raman peaks to obtain the Raman shifts, full widths at half maximum, and peak intensities as the feature parameter vector of mixtures, and finally, the effective component identification of mixtures is finally realized via the correlation analysis of the feature vectors between the mixtures and the pure substances in the database. The Raman spectral data of 18 pure substances are used to build a standard database, and the component identification experiment of 6 kinds of mixtures are conducted. The experimental results show that the recognition accuracy of the proposed algorithm is up to 100%.