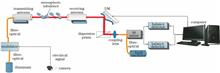
As for the wave-front sensorless adaptive wave-front correction system based on the stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm, its convergence speed is too slow to satisfy the real-time requirement of a wireless optical coherent communication system. The parallel processing base on the SPGD algorithm is introduced and the graphics processing unit (GPU) parallel computing is used to improve the convergence speed of the correction system. The average gray value of the surrounding 400 pixels centered on the centroid of the real-time spot detected by CCD camera is employed as the value of system performance index. GPU multithreading operation is used to accelerate the solving process of the performance index and the updating process of the deformable mirror control voltage vector. The results from the indoor experiments and the external coherent light experiments show that the Strehl ratio is larger than 0.8 and the maximum time acceleration ratio is up to 8.6. Moreover, the convergence speed of the GPU accelerated wave-front correction system is improved and simultaneously the correction effect is ensured.
Based on the scalar diffraction theory, a binary annular phase plate is studied by means of the coherent superposition method, which is used for the generation of a hollow focal field. The analytical expression of the radius for each ring is derived. The influence law of the ring radius on the hollow focal field is also investigated by the numerical calculation method. The research results show that, in the focal plane, the ring radius of this phase plate has a great influence on the side lobe ratio and the maximum light intensity ratio, but has a little influence on the radius of the hollow focal field. The increase in the number of rings reduces the side lobe radio, but increases the maximum light intensity ratio. In contrast, in the axial direction, the increase in the number of rings cannot increase the maximum light intensity ratio. Both the number of rings and the ring radius have relatively great influence on the side lobe ratio and the maximum light intensity ratio. For a binary annular phase structure, the side lobe ratio and the maximum light intensity ratio only depend on the ring radius and are independent of numerical aperture. In the focal plane, the radius of the hollow focal field is inversely proportional to the numerical aperture. In the axial direction, the radius of the hollow focal field is inversely proportional to the square of numerical aperture.
The distillability evolution of qutrit-qutrit systems in an amplitude damping channel is investigated. The research results show that the lasting time of free entangled states is longer than that of bound entangled states, which is quite different from the former results. The free entangled states evolve to the separable states directly, and the sudden death phenomenon of distillability is not observed in the proposed model.
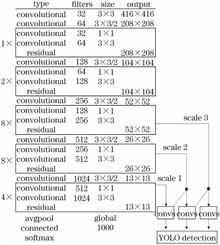
The popular target recognition method YOLOv3 is deeply studied, and the Inception module is integrated into the feature extraction network darknet-53 to get a new network darknet-139. Compared with YOLOv3, the new network has better ability in feature extraction. The data set required by the algorithm is collected and made, and were trained and tested on YOLOv3 and the proposed algorithm, respectively. The experimental results show that the average recognition rate of the proposed algorithm is about 2% higher than that of YOLOv3.
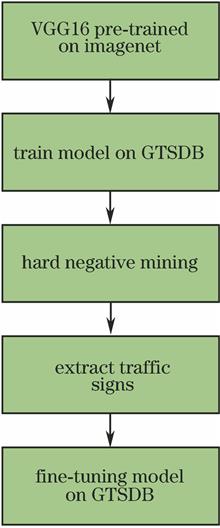
A detection method of traffic signs is proposed based on a modified convolutional neural network. The model is pre-trained to produce the negatives, and hard negative mining is used to add the negative samples into the network to improve the discriminating ability of the model. A feature concatenation strategy during the multi-scale training process is employed to further enhance the performance of the model. On the German traffic sign detection dataset, the effectiveness of the proposed method is simulated in the TensorFlow framework. The research results show that compared with the existing methods, the proposed method can be used to obtain a high detection rate and processing time of only 0.016 s for each image.
A no-reference stereo image quality assessment algorithm based on image fusion is proposed. The algorithm reconstructs the left and right views of the stereo image by wavelet transform and fuses them into one image. The luminance coefficient of the fused image is normalized, which keeps the brightness of each part in balance and preserves the structural information of the fused image. Finally the convolutional neural network is used to extract feature and predict regression. The experimental results show that the predicted scores of the proposed method are in good agreement with the human subjective assessment scores.
A scene text detection method based on color clustering of textual pixels is proposed, in which the initial textual regions of original images are extracted by the maximally extremal stable regional algorithm, and the stable textual pixels are screened out by the stroke width transform algorithm and the angle features. The multi-scale color clustering is conducted in these stable textual pixels, which is combined with a support vector machine for the realization of character regional verification. The text line aggregation is finally adopted to achieve the goal of text detection. The tests are conducted on two public datasets of ICDAR2011 and ICDAR2013, and the F-scores of this algorithm are 0.76 and 0.77, respectively. Compared with the existing text detection methods, the proposed method obtains a good text detection performance.
Aiming at the problem of low recognition rate because the single descriptor cannot accurately obtain the effective palmprint features, a palmprint recognition method is proposed based on subspace and texture feature fusion. The subspace feature and texture feature of a palmprint image are obtained by robust linear discriminant analysis and local direction binary pattern, respectively. The weighted concatenation method is used for the subspace and texture feature fusion. The chi-square distance among the fused feature vectors is used for identification matching. The experimental results on the PolyU and the self-built non-contact databases show that the recognition time is 0.3069 s and 0.3127 s, respectively, and the lowest equal error rate is only 0.3440% and 1.4922%, respectively. Compared with other methods, the proposed method can accurately obtain the effective feature information of a palmprint image and improve the system recognition performance under the premise that the real-time performance is ensured.
A reflection ghost imaging scheme based on the superimposed speckle pattern is proposed. The speckle particles of different sizes are randomly inserted into the speckle patterns with the speckle particle size of 1 pixel×1 pixel. The superimposed speckle pattern is applied as the illuminating source for ghost imaging. The numerical simulation and experimental results show that, compared with the traditional ghost imaging scheme, the superimposed speckle pattern formed by random mixing of speckle particles with different sizes significantly improves the contrast-to-noise ratio of the spatial information of the recovered object. The proposed scheme can not only reduce the number of samplings, but also significantly recover the image space information, and further promote the practical application of ghost imaging technology.
Aiming at the problem of serious lack of effective samples in the automatic discovery of camouflage targets, a simulation training method is proposed based on the sample simulation of a deep neural network and the technical idea of AlphaGo. A simulation synthesis model of camouflage scenes is established. The compound algorithm in the image space, the deep feature extraction strategy of scene images, the measurement strategy of target fusion degree, and the sampling algorithm for graph clustering are designed, respectively. Thus the representative samples for camouflage scene simulation are batch generated, which can be used for the deep neural network training and learning. Moreover, a discovery model of camouflage targets is designed based on a deep residual neural network, in which a multi-scale network training strategy is considered. The experimental results on the simulated samples and real scene images show that the proposed method can be effectively used for the automatic discovery and evaluation of camouflage targets.
To improve the lateral resolution and contrast and restrain the peak sidelobe energy of ultrasonic echo images, a sidelobe canceller algorithm applied to the ultrasonic imaging is proposed. The proposed method calculates the weight vector by eigenspace-based generalized sidelobe canceller algorithm. The coherence factor of the ultrasonic echo signal is used to optimize the obtained weight vector. Then, the common point target and dark speck are imaged. The simulation results show that the proposed method improves the lateral resolution by 60% compared with delay-and-sum algorithm, and has a improvement of 112% in contrast compared with the eigenspace algorithm. Experimental results based on an actual ultrasonic system agree well with the simulated results, which proves the effectiveness of the proposed method.
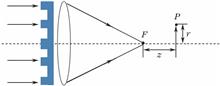
A light stripe center extraction algorithm is proposed based on Gauss-Lorenz peak fitting, which is suitable for different types of light stripe images. The cross-sectional energy model of a light stripe is built and the cross-sectional energy compositions of light stripes with different image qualities are analyzed, thus the Gauss-Lorenz decomposition fitting model is constructed. Based on the constructed model, the successive gray normalization, extraction of regions of interest, Gauss-Lorenz decomposition peak fitting and removal of Lorentzian components are acted on the light stripe images. The accurate light stripe center can be extracted with the gray centroid method. The contrast experimental results show that the proposed method has the characteristics of high extraction accuracy, strong applicability, but long time-consumption for different types of light stripe images. However, if it is applied to strong diffuse reflection and specular reflection light stipes, its time consumption is only half of that of Steger algorithm with the best effect at present.
The stereo micrography and three-dimensional (3D) measurement methods with super-large depth of field based on ultra-short depth of field microscopic imaging techniques are systematically summarized. The comparison is conducted aiming at the typical focus evaluation functions, focus search strategies, image sequence fusion and 3D reconstruction methods in 3D measurement methods with focus variation microscopic imaging. Some experimental verifications are also implemented. Research results are of reference to implementing 3D imaging with focus variation and measurement methods.
With the two-dimensional displacement measurement as an application example and based on the analysis of the generation mechanism and characteristics of laser beam drifts, a method for laser beam drift compensation is proposed by the combination of differential compensation with the common path compensation. In addition, these two compensation methods are analyzed in detail and verified by experiments. The experimental results show that, the compensation effects of the angular drift and total drift of the beam for the differential compensation method are 35.2% and 54.4%, respectively. In contrast, the compensation effect of the total drift of the beam for the common path compensation method is 42.2%. The research results can providea technical support for solving the common problem of beam drift compensation in laser alignment measurement.
To improve the microstructures and properties of Ni-based laser cladding layers, the Ni-based laser cladding layers with different mass fractions of nano TiO2 and CeO2 are prepared on the Q235 steel substrate surfaces by the synchronous feeding of laser cladding powder. The surface morphologies, microstructures and phase compositions of laser cladding layers are analyzed and the microhardness and corrosion resistance of laser cladding layers are measured as well. The research results show that the simultaneous addition of TiO2 and CeO2 in the Ni-based alloy powder can fully integrate the properties of both and make well-distributed, fine, crack-free and corrosion-resistant laser cladding layers obtained.
A saliency detection method is proposed based on a cascaded full convolutional neural network. This network is mainly composed of two full convolutional neural networks. In the first stage, a full-convolutional neural network with a pyramid pooling module encoding and decoding architecture is constructed, and the pyramid pooling module can be used to effectively suppress the interference of background noises. In the second stage, an edge detection network is designed to learn the edge information of a salient region, and the accurate boundary saliency map is obtained by the fusion of two-stage saliency maps. The experimental results show that the proposed method has high accuracy, high recall rate, and low average absolute error in image significance detection dataset ECSSD and SED2, which provides the reliable pretreatment results for target recognition, machine vision and other applications.
A decision-level fusion tracking method based on deep learning for infrared and visible spectra is proposed. By building the parameter transfer model, the visible detection model of the specified objects is extracted from the existing deep-learning-based detection model. This visible detection model is used as the infrared detection pre-training model, and the fine-tuning training on a collected infrared image dataset is done to obtain the infrared detection model based on deep learning. On this basis, a decision-level fusion tracking model based on deep learning is built. An comparison experiment between single-band tracking and dual-band fusion tracking is carried out. The research results show that the proposed method improves the tracking accuracy and success rate compared with the single-band tracking, and has good robustness.
A seismic signal blind denoising algorithm is proposed based on W-weighted nuclear norm minimization. The noise level of seismic signals is estimated by principal component analysis and the denoising is realized by weighted nuclear norm minimization (WNNM). In denoising, the shrinkage degree of singular values of a matrix is controlled by weight assignment, and the performances of the algorithm is improved. Three kinds of seismic signals are denoised, respectively. The performance is compared with double tree complex wavelet transform, curvelet transform and the WNNM algorithm. The research results show that the proposed algorithm can effectively remove the noises contained in seismic signals when the noise level is unknown. Moreover, the denoising effect is superior to those of the traditional denoising algorithms.
According to tumor features under gastroscope, the template matching tracking algorithm based on speeded up robust features (SURF) are adopted to track the tumor image. Mismatching points of features are removed to improve the tracking accuracy. In matching tracking algorithm based on SURF, the clustering center of matching feature points and smallest circular position around the feature point are used to measure tracking effect of each frame. Video frames of two groups of gastroscopic lesions are regarded as experiment dataset for target tracking tests. Results show that the improved matching tracking algorithm based on SURF has good stability and tracking accuracy.
A deep learning network structure based on the convolutional neural network and long short term memory (LSTM) neural network is proposed. The feature fusion is used to extract the shallow features and deep features through the convolutional network, and the features are fused by convolution, and the the obtained vector information is input into the LSTM unit. Networks are trained separately using the optical flow images and the red green blue information, and the results from each network are fused with weights. The experimental results show that the proposed model effectively improves the accuracy of behavior recognition.
Based on the ANSYS finite element simulation software, a three-dimensional solid finite element model of laser melting RuT300 is established, in which the effects of laser absorption rate, thermophysical parameters of materials and latent heat of phases are all considered. The effect law of preheating temperature on temperature distribution, temperature gradient, cooling rate, and so on is obtained by the analysis of the transient temperature fields of laser fusion under different preheating temperatures. The results show that the maximum temperature at the same position increases with the increase of preheating temperature. The preheating temperature has a more obvious influence on the temperature field at the low part of the sample. With the increase of preheating temperature, the temperature gradient at the same position of the sample decreases. When the depth from the upper surface of the sample is about 2 mm, the temperature gradient of the sample is not obviously influenced by preheating temperature. In addition, the preheating treatment of samples can be used to reduce their cooling rates, and it is found that the cooling rate decreases as preheating temperature increases.
With the Chinese medicinal material Radix Scrophulariae as a carbon source, the fluorescent carbon quantum dots are prepared by the high temperature calcination method. The carbon quantum dots solution under the excitation at 270 nm wavelength has the maximal fluorescent light emission wavelength at 418 nm. The fluorescent light intensity of the carbon quantum dots solution can be effectively quenched by the introduction of the nitrate ions (NO3-). Based on this, a novel method for detecting NO3- is developed using carbon quantum dots as the fluorescent probes. Under the optimal experimental conditions, the signal shows a good linear relationship with the concentration of NO3- when this concentration is in the range from 0.4 μmol/L to 80 μmol/L. The limit of detection is 65 nmol/L. When the 5.0 μmol/L or 50.0 μmol/L N O3- solution is added to the real water samples for the standard adding recovery experiment, the recovery rate is in the range from 98.0% to 104.0%.
A refractive index sensor based on the trapezoidal dielectric grating and the metallic film structure is proposed. The reflectivity of liquid to be analyzed is studied by the finite element method with different grating thicknesses, trapezoidal parameters and refractive indices. The angular sensitivity of the sensor is derived by optimizing the structure parameters. In consideration of the doubling effect of the angular sensitivity caused by the symmetrical movement of reflection resonance peaks, the angular sensitivity can reach 845.23(°)/RIU as the refractive index of liquid to be analyzed is changing from 1.33 to 1.34, and 1283.14(°)/RIU as the refractive index is changing from 1.34 to 1.35. The sensor has detection applications with a wide range of refractive index. The trapezoidal parameter plays a key role in the angular sensitivity of the sensor. A standing wave structure of the electric field distribution with the largest contrast corresponds to the highest sensitivity of the sensor structure.
A model framework called DenseNet-SE is proposed based on a multi-featured dense convolutional neural network. Compared with the conventional methods, the DenseNet-SE adopts the data-driven approach and the manual extraction of features is not necessary. It contains the dense residual blocks so that the deep features can be acquired. In the jump-joining way, the fine-grained features are obtained from the shallow layers to assist the deep features. The fused features can help the network structure obtain more global information and better represent the categories of formula symbols. The standard mathematical formula symbol library provided by the competition organization on recognition of online handwritten mathematical expression (CROHME) is used to verify the proposed algorithm, results show that the recognition rates of CROHME2014 and CROHME2016 are 93.38% and 92.93%, respectively, higher than those of the existing algorithms.
A tree species classification and mapping method is proposed based on the deep transfer learning with unmanned aerial vehicle high resolution images. The image features of tree species are extracted using a large convolution neural network trained on ImageNet. The features of tree species images are compressed by the global average pooling. A simple linear iterative clustering method is used to generate the super-pixel, which are used as the minimum classification unit to generate tree species maps. The experimental results show that the proposed method can accelerate the convergence of the training process. The overall accuracy and Kappa coefficient are increased by 9.04% and 0.1547, respectively, compared with the small convolutional neural network method in the case of small inter-class gap and the large intra-class gap, and the boundary of the super-pixel tree mapping is more accurate.
Photoacoustic imaging technique overcomes the strong scattering effects of light when transmitting in organisms by detecting the ultrasonic signals based on the photoacoustic effect, which avoids the limitations of low depth of traditional optical imaging and low contrast of acoustic imaging. This technique has potential applications in early cancer diagnosis and it can possibly become an effective method for tumor diagnosis, locating, staging and treating. The principle of photoacoustic imaging and the research status of its clinical applications in early cancer diagnosis and treatment at home and abroad are mainly described. The potential application of photoacoustic imaging technique in biological medicine is prospected, and its future development trend and limitations are also analyzed.
The crystal structure and optoelectrical properties of two-dimensional layered perovskite materials are introduced. The latest applications of two-dimensional layered perovskite materials in the fields of solar cells, light-emitting diodes and photodetectors are summarized. The main problems and future development prospects of these materials are given, aiming to guide the design and fabrication of high performance two-dimensional layered perovskite optoelectronic devices.
The technical characteristics and development history of magnetic-optical-electric hybrid storageis are reviewed, and its key technologies and research status are summarized, including storage system structure, some key technologies of software and hardware, as well as related standard formulation and patent applications. And the development trends of hybrid storage technology are described. The future for the development of magnetic-optical-electric hybrid storage is prospected. This review will help researchers to understand magnetic-optical-electric hybrid storage more systematically, clearly and accurately, and contribute to the development of big data storage in the future.
The D-type photonic crystal fiber (PCF) refractive index sensors, the multi-core porous PCF surface plasmon resonance (SPR) refractive index sensors with a large dynamic refractive index measurement range, and the dual-channel SPR-PCF refractive index sensors are introduced. Their advantages are summarized and their inherent limitations are analyzed. The SPR-PCF sensors are expected to make breakthroughs in the technical fields such as biomedical testing, food safety testing, mine exploration testing, and environmental chemical testing.
Label-free microscopic imaging technology includes the optical coherence tomography, photoacoustic imaging, nonlinear imaging, and microsphere lens imaging technology. The commonly used label-free imaging techniques are introduced, and the traditional and advanced imaging principles are summarized. The advantages and disadvantages of such various of label-free imaging technologies and the latest research progress are introduced in detail, including the applications of such imaging technology in various fields. Finally, the future development of multi-modal imaging technology based on unmarked microscopy technology is prospected.
The investigation of various soliton dynamics in a mode-locked fiber laser is briefly summarized, especially the recent progress of soliton transient dynamics in an ultrafast laser based on the dispersive Fourier transformation (DFT) technique is introduced. In addition, the multi-scale detection of ultrafast phenomena simultaneously using a time lens and the DFT technique is also briefly discussed, which helps to completely understand the physical nature of optical solitons. The development of real-time diagnostic methods can greatly inspire researchers to explore the soliton dynamics, and thus further promote the investigation of soliton dynamic characteristics as well as the development of ultrafast laser technologies.
Three kinds of white, pale-pink purple and light-blue purple jadeite samples from Myanmar are selected for the test and analysis of elements and optical absorption spectra, and their color origins are preliminary studied. The results show that the lavender jadeite samples contain a small amount of iron, manganese and titanium, while the contents of chromium, vanadium and copper are extremely low. In addition to the absorption peak of Fe3+, the pale-pink purple jadeite has a broad absorption band peaking at 566 nm, and the light-blue purple jadeite has a broad absorption band peaking at 534 nm and a shoulder band at 625 nm on the long-wave side. It is inferred that the pale-pink purple and light-blue purple jadeite are mainly colored by Mn3+ and Ti3+ ions, respectively.
In order to improve the detection sensitivity for the technique of laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) of liquid matrix, the key parameters of the spectroscopic detection system must be optimized. The liquid jet sampling technique is adopted. The analysis lines of six metal elements of Pb, Cr, Cd, Mn, Ca, and Al mixed in an aqueous solution are selected. The maximization of the signal-to-noise ratio of LIBS signals for each metal element is used as the optimizing criterion. When the gate width of an intensified charge-coupled device (ICCD) is 0.3 μs, the key system parameters of laser pulse energy, ICCD gate delay and liquid sample flow rate, are optimized as 50 mJ, 2.0 μs and 40 mL/min, respectively.