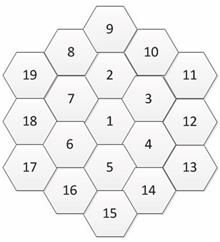
A location method for minor damages of aircraft skins based on a marked honeycomb model is proposed. A CCD camera is used to capture the damage location, and the image is processed at sub-pixel level to obtain its coordinates. According to the principles of harmonic conjugation and the invariance of cross-ratios, the actual position of the damage can be determined to achieve accurate positioning. Then, based on this, the base point is transmitted and the infinite and seamless extensibility of the honeycomb model are used to compare and match of main base points and other base points on the surface of the aircraft skin so as to achieve accurate detection of the aircraft skin damage. The comparative experimental results show that the proposed method has high accuracy and less time consuming, and can effectively realize damage detection and location for aircraft skins.
Aiming at the problem that using RGB images for vehicle detection are affected by complex conditions such as road shadow, vehicle reflection and insufficient light. The paper proposes a vehicle detection algorithm based on convolutional neural network and combination of RGB and depth images. Two improved models of single-channel RG-D and double-channel RGB-D fusion networks are designed to improve detection speed and accuracy respectively. The algorithm is tested with (Grand Theft Auto) vehicle dataset and compared with other popular algorithms based on RGB images. The results show that compared with Yolo v2 algorithm based on RGB images, detection accuracy and recall rates increase 5.69% and 6.31% respectively by double-channel RGB-D fusion network, and the fastest detection speed of single image reaches 24 ms with single-channel RG-D fusion network. Experiments show that the improved network model based on RGB-D images can achieve real-time detection and effectively improve vehicle detection accuracy.
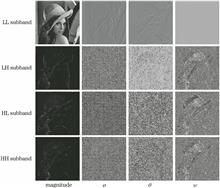
First, the left and right views of stereo images are decomposed by quaternion wavelet transform to obtain the amplitude and phase information of different scales and directions, and then cyclopean images are generated by combining human visual characteristics. The left views, right views, and cyclopean images are processed via mean subtracted contrast normalization (MSCN). The MSCN coefficient map is then obtained. The MSCN coefficient and the product of MSCN four-direction neighborhood coefficients are fitted via a generalized Gauss distribution model to extract statistical parameter features. The feature vectors are formed by combining the kurtosis, skewness, standard deviation, and energy. The image quality perception score is then predicted using the XGBoost model. Experimental results show that the proposed stereo image quality assessment algorithm is superior to other reported methods in the LIVE 3D image database and it greatly improves the running speed.
Under complex sea conditions, ship detection from remote sensing image is easily affected by the ship wake, sea clutter, oil, and thin cloud, which may lead to poor detection results and difficulty in the detection of small ships. Herein, we propose a saliency optimization ship target detection model based on an adaptive robust background. The proposed method uses the Tophat algorithm for preprocessing of the original image to suppress interference from the ship wake and sea clutter. Further, an adaptive superpixel segmentation method is proposed to optimize the robust background detection model. An improved Otsu segmentation method based on the mean information is proposed to determine the area where the ship is located. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method can effectively detect the location of a ship under various sea conditions. The proposed algorithm demonstrates high detection precision (91.20%), recall (79.31%), and comprehensive evaluation index (84.00%). When compared with the existing saliency detection algorithms in ship detection, the proposed algorithm exhibits obvious advantages; therefore, it is suitable for small ship detection based on the remote sensing images under complex sea conditions.
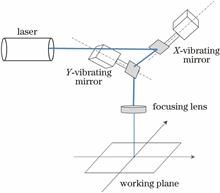
To solve the problem of laser surface processing not forming high-chromatic-aberration and high-contrast black patterns on aluminum alloys, a fiber laser machine with a 4-ns pulse width is used to mark 5052 anodic aluminum oxide (AAO) alloy at a scanning speed of 130 mm/s, a frequency of 300 kHz, a scanning pitch of 0.005 mm, and a setup power of 27%P0-33%P0 (P0 is the rated power of the laser). We obtain a black pattern with a high chromatic aberration and high contrast. The effect of the laser power on the contrast and micro-morphology of the pattern is studied, and the mechanism of pattern formation by laser surface processing on the AAO is analyzed. Results show that when the laser power exceeds 1.64 W, the laser energy reaches the melting threshold of aluminum and a pattern is formed on the surface. With the increase of laser power, the contrast gradually increases. When the laser power increases to 2.13-2.76 W, the AAO surface forms a fine-crack micro-morphology by melting and evaporation, the macroscopic display is black, and the contrast reaches the maximum. When the laser power increases to 3.32 W, the surface of the aluminum material melts completely, the fine-crack micro-morphology disappears, the macroscopic display is grayish white, and the contrast decreases. These results contribute to further research on the mechanism of laser surface processing on aluminum, which is helpful for promoting the development of the Internet of Things.
Loop closure detection algorithm is essential for the visual simultaneous localization and mapping (VSLAM) systems to reduce accumulative error and build a globally consistent map. When detecting loops under the change of viewpoint and scene appearance, the precision and robustness of traditional loop closure detection algorithms decline and some algorithms based on deep learning are difficult to extract features and perform loop closure detection in real time. To overcome these problems, we propose a novel loop closure detection algorithm based on convolutional autoencoder fused with Gist feature, forcing the encoder to reconstruct the Gist feature to enhance the expressive ability of the model when the scene appearance changes. In the same time, we warp images with randomized projective transformations to make the training pairs to improve the precision and robustness of the model when the viewpoint changes. Our model is relatively lightweight which is capable of extracting keyframe features and detecting loops in real time. The results of experiments on Gardens Point and Nordland datasets show that our model can achieve better precision and robustness compared with traditional methods, like bag of visual word (BoVW), Gist, and some other methods based on deep learning.
A high-transmittance broadband millimeter wave metasurface structure with gradient phase is presented, and the metasurface structure works in the 55-75 GHz frequency band. This proposed structure comprises two dielectric layers and three metal layers. The intermediate metal layer is notched rectangular ring which can adjust the phase in the range of 0-2π by adjusting the geometry. The function of the notched rectangular ring is to achieve polarization conversion. The transmission phase difference of construction units with different notched rectangular rings basically remains unchanged in working frequency band, thereby ensuring the broadband property. The grid layer ensures the high transmission performance of the metasurface structure. The proposed metasurface structure is successfully applied to the metasurface designs of a planar lens and orbital angular momentum beam.
The relationship between diffuse reflectance R measured close to the source and parameter γ related to collecting aperture , reduced scattering coefficient μ's,and scattering phase function is discussed. According to different biological tissues, different scattering phase functions are selected, and the diffuse reflectance data of photons passing through biological tissues are obtained by Monte Carlo simulation. The relationship between the reflectance R and dimensionless reduced scattering coefficient μ's , where is the collection aperture of scattered light, is validated by the data obtained. It is found that when μ's < 2, R is sensitive to the change of the scattering phase function and has a linear relation with μ's . The slope of R is a quadratic function with respect to γ. Results demonstrate that the diffuse reflectance R of the micro-area near the light source is sensitive to the change of γ. This provides a simple method for measuring γ related to the microstructure of biological tissues.
We propose a method to design two-dimensional photonic crystal all-optical logic gates based on the linear interference effect and ring resonators. The phase difference is generated by introducing the optical path difference in the ring cavity, which leads to the constructive or destructive interference of light waves. Thus, optical logic gates, such as OR, AND, XOR, NOT, NOR, and NAND, are realized. The plane-wave expansion and time-domain finite-difference methods are used to simulate the logic devices and verify the logic functions. The results demonstrate that small-sized devices can be realized. In addition, the devices have a high transmittance rate, high contrast ratio, and fast response time(less than 218 fs). The design has potential application in the field of integrated optics.
Doppler wind lidar can ensure non-contact measurement of the atmospheric wind field based on optical Doppler effect. Doppler wind lidar is scalable with high resolution in time and space and exhibits large coverage and wide detection range. Further, it is suitable for mobile, foundation, vehicle, shipboard, airborne, and spaceborne platforms and is extensively used in flight safety, wind power generation, weather forecasting, scientific research, military defense, and so on. Herein, the main systems, technologies, latest developments, and applications of Doppler wind lidar at home and abroad are introduced and analyzed. Further, two techniques for direct and coherent detection are compared and summarized based on our analysis. In addition, the development trends, research hotspots, and application development of Doppler wind lidar are briefly summarized.
Terahertz (THz) waves have great application potential because of their unique atmosphere sensitivity features and spatial transmission properties. This study summarizes the research achievements of major research institutions at home and abroad in THz space exploration. Further, we describe the parameters, working environment, and detection results of large ground-, aircraft-, and space-based THz space exploration platforms and compare the experimental results of these platforms. In addition, the features of THz remote sensing equipment are also analyzed. Finally, we present the application prospect and future development trends of THz space exploration. The THz space exploration technique can obtain unique information that cannot be acquired using optical methods or microwave technology, which makes it a prospective research area in the future. The development of THz space exploration technology will lay an important foundation for high-resolution space remote sensing.
Insufficient or excessive oxidation of the Spiro-OMeTAD layer can lead to a low efficiency of the perovskite solar cell. The effect of the hole transporting layer on Spiro-OMeTAD oxidation is investigated to solve such problem. Four different methods are primarily utilized to oxidize the hole transporting layers. Then, the optoelectrical performances of the hole transporting layers before and after oxidation are studied to determine the optimum oxidation method and its conditions. Subsequently, planar devices with a ITO/SnO2/CH3NH3PbI3/Spiro-OMeTAD/Ag structure are fabricated. The photoelectric properties are characterized and compared before and after oxidizing the devices. The result shows that an efficient oxidation decreases the pinholes on the surface of the Spiro-OMeTAD layer and makes it fully dense. Thus, the fill factor (FF) of the perovskite solar cell is increased. Furthermore, the oxidation treatment reduces the parasite absorption of light by the Spiro-OMeTAD layer and improves the effective optical absorptance of the perovskite solar cell. In addition, the oxygen oxidation in the Spiro-OMeTAD precursor is apparently superior to the other oxidation modes. Compared with the air-oxidized device, the FF of the oxygen-oxidized device rises from 0.43 to 0.63, and the photon conversion efficiency increases from 9.06% to 14.19% under the optimum operating conditions.