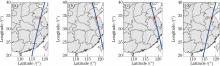
Aiming at the region of 33.5°N-34.5°N on the satellite transit route, we compare the aerosol vertical distribution characteristics during clean period, haze, dust, and pollution caused by fireworks based on CALIPSO satellite laser radar data. The results show that, in the sunny day, most of aerosols are clean continental aerosols at high altitude; in haze, most of aerosols are polluted continental aerosols whose backscatter and extinction are strong, and most of aerosol particles are spherical particles with small diameters; in dust, aerosols have a wide vertical distribution from the ground to the high altitude, and most of aerosol particles are non-spherical particles with big sizes; in pollution caused by fireworks, aerosol particles are the small size particles at low altitude, whose types are the polluted continental aerosol and the polluted dust aerosol. It is concluded that the vertical distributions of aerosol under different population types are different. We can use CALIPSO satellite laser radar data, together with meteorological element and HYSPLIT model to characterize the category of the atmospheric aerosol.
The calibration method is an indispensable key element in the study of three-dimensional measurement systems of line-structured light. We focus on three issues in the calibration method of line-structured light sensors,the calibration target, calibration method of light plane, and evaluation of calibration accuracy. At first, the commonly used calibration target type and its calibration characteristics are summarized, which provide a reference for the selection of calibration target. Then, the current main calibration methods of light plane are divided into three kinds according to the relative motion relation between the calibration target and the sensor, namely the calibration method with fixed position between calibration target and the sensor, the calibration method with controllable relative motion between the calibration target and the sensor, and the calibration method with freely motion between calibration target and the sensor. Subsequently, we systematically summarize the existing evaluation methods of the calibration accuracy, and analyze the principles and characteristics of them. Finally, we summarize the development status of the line-structured light calibration method, and point out that the line-structured light self-scanning measurement system and the underwater calibration are the development trend of line-structured light sensor.
Due to the limitations of waveguide structure, chip packaging and other factors, the beam quality of diode lasers in fast axis is different from that in slow axis. Diode lasers are usually used as pumping source, i.e., luminance converter, and cannot directly act as a high-brightness laser source. We introduce an incoherent beam combining technology, called wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) beam combining technology, and it can improve the output optical power density and output beam quality of diode lasers. We summarize its development status and some important trends at home and abroad. The study provides a reference for the development of diode laser WDM beam combining technology.
The free-space quantum key distribution (QKD) technology has become one of the research hotspots in the field of quantum communications, and the continuous variable QKD and the discrete variable QKD are two major technical branches of this technology. The recent research progresses of free space QKD technology at home and abroad are reviewed. From the viewpoint of practical applications, the technical difficulties of these two branches are compared and analyzed. The phenomena like the background light interference, the single photon depolarization characteristics in the atmospheric channel and the phase distortion caused by turbulence are analyzed emphatically, and the development foreground of free space QKD technology is prospected.
Phase-shifting interferometry is an important technology in both wavefront and phase measurements by virtue of its advantages of non-invasive, no damage, high sensitivity and high speed. And phase-shifting interferometry technologies have been widely used in many fields related to the optical imaging and metrology. In this paper, according to the characteristics of the phase-shifting and optical path introduced in the imaging system, the phase-shifting interferometry technologies are classified. And the typical phase-shifting interferometry technologies in both cases of temporal and spatial domains are analyzed comparatively. Then, a lot of typical phase retrieval methods are listed, on the basis of the development of the phase-shifting interferometry technology. For the general phase-shifting interferometry technologies, typical phase shift extraction methods are classified according to the characteristic of phase shift. Then, aiming at the common problems existing in the general phase shift extraction methods, the corresponding solutions are discussed. At last, the trends of the phase-shifting interferometry technology and phase-shifting extraction method are predicted.
In order to broaden applications of microwave photonic filter (MPF), we review existing techniques to improve the out-of-band suppression ratio of the MPF implemented in incoherent or coherent operational regime. A single bandpass MPF is proposed based on carrier-suppressed single sideband (CS-SSB) injected distributed feedback (DFB) laser. Four-wave mixing effects have been reduced through optical carrier suppression. The out-of-band suppression ratio of the single bandpass MPF increases from 20 dB to 32.3 dB. The methods to improve the out-of-band suppression ratio of the MPF are discussed.
The principle of optical phased array is briefly discussed. The development of optical phased array is reviewed, especially the research progress of silicon photon phased array in recent years. Large-scale integration has been achieved by using silicon-on-insulator (SOI) technology compatible with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) process lines. And the largest silicon photon phased array has been reported abroad, and its size is up to 4096 elements. The two-dimensional beam scanning angle achieved on silicon photons can reach 46°×36°, the beam width is only 0.85°×0.18°, the antenna loss is less than 3 dB, and the sidelobe suppression is greater than 10 dB. In addition, the steering speed of the optical phased array made of micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices is more than 0.5 MHz. Advantages and disadvantages of various methods to realize optical phased array are expounded, and the future development prospect is prospected. Finally, the applications of optical phased array in laser radar, imaging and military are introduced.
Regenerated fiber Bragg grating (RFBG) is prepared from an ordinary fiber Bragg grating (FBG) through a high temperature annealing process, which has a high temperature resistant. The RFBG can work under a high temperature environment since the grating degeneration does not exist in RFBG. RFBG has attracted much attention due to its easy fabrication process, low cost, and excellent sensing performance. We review the development of RFBG from formation mechanism, fabrication, regeneration of specific FBG, and mechanical strength protection and forecast the high temperature sensing applications of RFBG.
Laser wireless power transmission (LWPT) technology has advantages such as long transmission, high power density, high conversion efficiency and dispense with energy transmission lines, and it has potential application prospects in the spacecraft, unmanned aerial vehicle, space solar power station and so on. With the technology development of laser and photovoltaic cell, the feasibility of LWPT technology is greatly enhanced. We present the development status and tendency of LWPT technology and analyze the key technologies of LWPT system and the response characteristics of the photovoltaic cell under laser illumination. We design and optimize optoelectronic conversion devices for high power density and specific wavelength laser to improve the conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells, which can support the practical application of LWPT technology.
The low light level remote sensing imaging technology uses image intensified CCD (ICCD), to make up of the existing CCD remote sensing camera. The technology features are wide spectral response, low noise, high sensitivity, large dynamic range, and intelligent electronic control. The ICCD as well as its applications, will significantly expand the applicable luminance conditions and work time of various spacecraft, from 105-102 lx in the daytime (10:00-16:00 for 6 h effective remote sensing time) to 105-10-1 lx under daylight/dawn/dusk/moonlight conditions (06:00-18:00 for 12 h effective remote sensing time). The remote sensing equipment can provide real-time information in a wider period through its observing, reporting, and early warning ground emergencies, such as natural disasters, terrorist activities, as well as some necessary demands in geography, geology and mapping fields. In the paper, we have reviewed the basic principle, system composition, key technique, performance test, overall evaluation and the latest research progress and achievement in application of the low light level remote sensing imaging technology.
The free manufacture from powders to parts can be realized by the technique of selective laser melting (SLM), and the formed parts have a high size accuracy and a low surface roughness. SLM is especially suitable for the formation of the moulds with complex structures. The research status of SLM and forming of mould steels as well as their molding materials, process characteristics, microstructure evolution and performance optimization are mainly summarized. The application status such as the application of conformal cooling channels is briefly described. The existing problems in the SLM and forming of mould steels are summarized and the future research direction is prospected and discussed.
In speckle vision measurement, markers are usually used to improve the measurement efficiency. To overcome long matching time and low matching accuracy in traditional marker matching process, we propose a new method for marker matching by using improved Kanade-Lucas-Tomasi (KLT) algorithm. Firstly, we measure the marker to establish initial matching point based on the improved speeded up robust feature (SURF) algorithm. Secondly, we use the improved KLT algorithm to achieve the marker matching. Thirdly, we use the constraint condition based on max bidirectional error to delete the mismatched points and improve the reliability of maker matching. Finally, we make a matched experiment to verify the marker coated on the speckle region of the wing model during the wing flutter measuring. The results show that, compared with traditional scale-invariant feature transform (SIFT) and SURF matching methods, the proposed method reduces the matching time by 75.9% and 42.8%, and improves the matching accuracy by 30.6% and 22.2%, respectively.
In the progress of laser scanning projection calibration, the accuracy of the calibration is directly affected by the light spot size of the laser projection, and then affects the projection accuracy of the projection system. In order to meet the requirements of the laser projection scanning system for accuracy, a method of improving the accuracy of the laser scanning projection is proposed. That is, the method of combining the fixed magnification collimation beam expander lens group and the dynamic focusing lens group reduces the laser beam divergence angle and laser projection spot at the same time, and the projection system in the projection of the working distance has sufficient depth of focus. Which can obtain a larger laser energy density, and then achieve the field of focus. The theoretical results are simulated and verified by using the ZEMAX optical design software through the experiment. In 4-5 m working distance, after the laser beam passes through a fixed radio collimating beam expander and the dynamic focusing lens group, it effectively reduces the laser beam divergence angle and projection light spot size, then improves the energy density of projection spot on the target locating point. Finally, the laser scanning projection system meets the requirements of the projection accuracy.
According to the digital spiral imaging method, the information of the object is recorded by the orbital angular momentum of light. Through analyzing the orbital angular momentum spectra, we obtain the information of the phase object. Characteristics of the orbital angular momentum spectra of a simple canonical phase object are studied when different Laguere-Gaussian (LG) beams are used in detection. The results show that we can obtain the phase and transmittance information effectively by analyzing the orbital angular momentum spectra. Spectral components with different diffraction orders produced by the LG beams with different topological charges and radial node numbers are analyzed. The results show that the high-order LG beam is more conductive to probe the information of a simple canonical phase object.
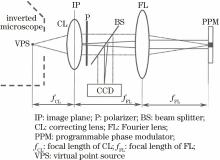
We use single-lens imaging system to analyze whether the specific function of 4f lenses system in the particle field in-line holographic diagnosis (ie, the magnification of 4f lenses system is the same constant for each position of the particles) is unique or not to 4f lenses system. The experimental results show that when the positions of the recording surface and the lens are relatively fixed, the hologram recorded by the single-lens optical system can also be precisely reproduced by the plane wave, and its magnification has nothing to do with the object distance of the object. So we can see that the above advantages of 4f in particle field in-line holographic diagnosis are not unique to the 4f. That is to say, we record the particle field by a single-lens imaging system without different reproduction or particle size calibration methods.
The angular accuracy of ship borne theodolite is significantly affected by its own shafting error, inertial navigation attitude error and unknown ship deformation. In order to reduce the influence of these factors, the optical axis spatial calibration method based on airborne light source simulating stellar theodolite is proposed. The proposed method effectively combines star sensor and carrier phase differential technique of global position system(GPS). Two unmanned aerial vehicles are used to carry out accompanying flight, which make two airborne light sources appear in the field of view of calibration telescope. Thus, two high precision base lines are built, and the calculation of optical axis space pointing of calibration telescope is finished by using double-vector altitude determination. Finally, the calibration and calculation of optical axis in the theodolite system accurately pointing at horizontal coordinate system are realized. The simulation results show that the optical axis space pointing calibration accuracy is better than 10″ by optimizing the parameter configuration. This method can realize the accurate calibration of theodolite optical axis space under the dynamic condition of the sea.
Based on the measurement principle and the method of Mueller matrix and Stokes vector, the phase retardation and fast axis azimuth of wave plate are measured rapidly and simultaneously. After the laser passing through the polarizer and the standard 1/4 wave plate, the standard right rotation circular polarized light is produced and then passes through the wave plate sample. The Stokes vector of the laser after passing through the sample is recorded by the Stokes polarimeter, and the phase retardation and fast axis azimuth are obtained simultaneously. The influences of standard 1/4 wave plate parameter error and system stability on measurement results are analyzed. By using this experimental system, the average standard deviations of the phase retardation and fast axis azimuth of wave plate are ±0.05° and ±0.03°, respectively. The experimental relationship between the parameters of mica wave plate and quartz wave plate and temperature is also obtained. The proposed method has the characteristics of simple measurement process, high precision and real-time measurement of phase retardation and equivalent fast axis azimuth of unknown anisotropic material.
In order to study the effect of sample temperature on the characteristic parameters of laser induced breakdown aluminum (Al) plasma, we use a double-pulse laser to induce the Al sample heated in intermediate frequency furnace to form plasma. And then we analyze the intensity changes of different characteristic spectral lines and the morphology changes of plasma plume collected by CCD camera when the Al sample temperature changes. Under the assumption of local thermodynamic equilibrium, we use Boltzmann oblique line method and Stark broadening method to analyze the evolution law of plasma electron temperature and electron density with the sample temperature. The full widths at half maximum (FWHMs) of different spectral lines varing with different sample temperatures are analyzed by Lorentz linetype fitting. The experimental results show that the morphology and size change of plasma plume is a direct reflection of the change of the characteristic parameters of plasma such as electron temperature and electron density. As the sample temperature increases, morphology of plasma plume, spectral line intensity, FWHM, electron temperature, and electron density will become saturated. For ionic and atomic lines, the sample temperature has different enhancement effects on the spectrum intensity and FWHM.
Two new methods for etching quartz glass by infrared-laser-induced chemical reactions of barium compounds are proposed, where the two barium compounds are BaCrO4 and Ba (OH)2,respectively. Via the deduction by the energy dispersive X-ray spectrometer and the analysis and test by the X-ray diffraction (XRD), it is found that micro-cracks and edges occur in the micro-channels obtained in the process of etching quartz glass by laser-induced chemical reactions of BaCrO4. Meanwhile, the decomposition of BaCrO4 produces BaO, which has a chemical reaction with SiO2 to generate BaSiO3 at high temperature, and thus this method can be used for etching quart glass directly. In the process of etching quartz glass by laser-induced chemical reactions of Ba(OH)2, both Ba(OH)2 and its decomposed BaO have chemical reactions with SiO2 at high temperature to generate BaSiO3, and thus this method can also be used for etching quartz glass directly. Different etching mechanisms for these two methods lead to relatively obvious difference of etching quality.
Ni-based WC stripes on the W6Mo5Cr4V2 high speed steel (HSS) specimen surfaces are fabricated by the laser cladding technique. The friction and wear tests of HSS specimens and specimens with Ni-based WC cladding stripes are carried out, respectively. The friction coefficients of specimens are measured and the friction reducing mechanism of HSS specimens with Ni-based WC stripes is investigated. The results show that the friction coefficients of specimens with Ni-based WC cladding stripes are lower than those of HSS specimens, and they decrease with the decrease of cladding stripe space. Graphite precipitation and Ni meltal self-contained within the specimens with Ni-based WC cladding stripes have a better friction reducing effect, and the friction-reducing mechanism of Ni-based WC cladding stripes is the combination of hard phase with soft substrates.
A V-model unstable optical resonator is designed, and the rule of the output spectrum of continuous wave hydrogen fluoride (HF) laser is discussed on the condition of different oxidant excess indexes. Spectral lines corresponding to wavelength over 2.87 μm, such as 2P8 and 2P9, are obtained efficiently under appropriate reaction formula and optical resonator parameters. We can partly regulate the distribution of HF laser output spectrum by adjusting the combustor oxidant excess index and controlling the amount of free fluoride atom lasing reaction. The output power of laser is closely related to the gain coefficient. The maximal output power of a single spectral line is determined by its maximal gain coefficient, while the maximal output power of the laser depends on the maximal value of the sum of all spectral lines gain coefficients.
A scheme for eliminating the autocorrelation and broadening the bandwidth of chaotic laser from semiconductor lasers (SL) is proposed. In this scheme, a SL with single-channel phase modulation optical feedback is taken as the master laser, and a SL with double-channel filter optical feedback is taken as the slave laser. The laser from the master laser is injected into the slave laser. We numerically investigate the influences of parameters, such as the pumping factor, external light injection coefficient and frequency detuning between master and slave lasers, on the autocorrelation and bandwidth of chaotic laser from slave laser. The results show that the proposed scheme can effectively reduce the autocorrelation and broaden the bandwidth of chaotic laser form slave laser under the selected parameter conditions. The bandwidth maximum value of chaotic laser can reach 18.45 GHz.
The laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) based on the C element is investigated by the spectroscopic imaging and plasma monitoring techniques, and the ablation quality and repeated heating of the sample are studied in depth. The research results show that the spectral intensities of the C element under single and double pulse LIBS are obviously different. The double pusle signal enhancement is not only attributed to the increase of the ablation mass, but the change of plasma forming environment caused by the physical change of the double-pulse signal reheating.
The effects of different process parameters on the deformation mode and deformation amount of single-curvature forming parts and S-shaped double-curvature special-shaped parts of 2024 aluminum alloys are studied by the laser peen forming experiments, the manufacturing methods of S-shaped double-curvature special-shaped parts are analyzed, and the three-dimensional distortion part is obtained in experiments. The results show that, if increasing the laser pulse energy or decreasing the sample thickness, the concave deformation of samples is more likely to occur, otherwise the convex deformation occurs. The deformation amount of sample increases when the shock area and the coverage rate increase, but the deformation mode dose not change. The formation regularity of S-shaped double-curvature special-shaped parts is consistent with that of single-curvature forming parts. In order to obtain S-shaped double-curvature special-shaped parts of 2024 aluminum alloys, a "concave+concave" deformation mode can be adopted for thin plates, while for thick plates, the "convex+convex" deformation mode can be adopted.
The effects of laser power on droplets and weld sizes under different transfer modes are investigated by using the experiment of laser-MAG (metal active gas arc welding) hybrid welding of SUS301L stainless steels. The results indicate that, with the increase of laser power, the metal vapor recoil force increases, the resultant electromagnetic force direction changes, and the droplet transfer is affected. In the short-circuiting mode, the droplets transfer difficultly and are deviated from the wire to laser spot when laser power exceeds 2000 W. In the globule and spray transfer modes, there exist an unstable phenomena in the droplet transfer and welding voltage when laser power is beyond 3000 W. In different transfer modes, the weld penetration and width increase with laser power. After the laser power approaches 2000 W, the weld penetration changes linearly with laser power, while the weld width remains constant.
In order to investigate the distribution characteristic of residual stress in targets directly irradiated by high power laser, the experiments of laser irradiation on 7075 aluminum alloy samples under the condition with or without absorbing layers are respectively conducted by means of Nd∶YAG laser, and the experimental results are compared. The results show that there are remelting layers and ablation spots on the sample surface after direct laser irradiation. The maximum tensile residual stress (TRS) distributed on the surface of samples reaches 116.2 MPa, the residual stress distribution in the depth direction of the sample is TRS-compressive residual stress (CRS)-TRS, the maximum CRS in the depth direction is 153.6 MPa, and the maximum micro-hardness in the depth direction is 174.5 HV. When the absorbing layer is included, there is a circular ablation zone on the surface of the absorbing layer, and the smooth dent appears on the sample surface after the removal of the remaining absorbing layer. The maximum CRS distributed on the surface of samples is 264.7 MPa, the residual stress distribution in the depth direction of the sample is CRS-TRS, the maximum CRS in the depth direction is 258.3 MPa, and the maximum micro-hardness in the depth direction is 193.6 HV.
By use of the laser-welding technique, the tailor-welded joints of DP980 and 22MnB5 are fabricated, and their microstructures and properties are researched. The results show that an obvious softening occurs in the heat-affected zone (HAZ) of DP980 and the minimum hardness of the softening zone is about 75% of that of the DP980 base material, however, there is no softening phenomenon in the HAZ of 22MnB5 where the hardness is increased to 2-2.4 times that of 22MnB5 base material. The tailor-welded joints have fractures at the 22MnB5 base material, whose tensile strength is around 670 MPa. The softening zone of the HAZ of DP980 is composed of temper martensite and ferrite, the two-phase zone is of a small amount of quenched martensite and ferrite, and the hardening zone is basically of lath martensite. The incomplete quenching zone of the HAZ of 22MnB5 has a similar composition with the two-phase zone of DP980 side, the complete quenching zone is of all lath martensite, and the weld zone is of coarse lath martensite.
Self-mode-locked Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) vortex beams are studied based on Nd∶GdVO4 crystals. The stable picosecond self-mode-locked laser with Hermite-Gaussian (HG00 and HG02) modes can be obtained through the continuous adjustment for cavity loss. The stable picosecond self-mode-locked vortex pulse can be converted from HG02 mode to LG02 mode with a mode converter. The frequency of mode-locked pulse is 1.35 GHz. The average output powers of LG00 and LG02 modes are 484 mW and 371 mW respectively, and the slope efficiencies are 30.3% and 19.3% respectively.
In order to improve the bonding strength between substrates and thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) of hot components of aircraft engines and prolong service life of coatings, the laser rapid prototyping technology is applied to fabricate a network structure on a superalloy substrate, and the plasma spraying method is for ceramic coatings. The thermal shock resistance of these TBCs is studied experimentally and compared with that of traditional coatings with a two-layer structure. To further analyze the effect of the network structure on the stress distribution of TBCs, a two-dimensional finite element numerical model is established based on the thermo-elastic-plastic theory. The results show that the TBCs with a traditional two-layer structure and a network structure fail after 45 and 111 thermal shocks, respectively. Due to the thermally grown oxide layer (TGO) along the interface between the layers of ceramic and bond coating, a spalling of the ceramic layer near the edge is observed for both kinds of TBCs. Further numerical analysis results show that the concentration of stress on the boundary region is relatively released with the help of the network structure. Accordingly, the cracks originated on the boundary are effectively suppressed, which reasonably makes the thermal shock resistance improvement of TBCs.
It is not an optimal solution to optimize kerf width of laser cutting Ni-based alloy steel by orthogonal method, so it is suggested to take effects of interaction, which is a combination of factors, into consideration. Design of orthogonal test include evaluation index determination of cutting quality, levels determination of each factor, interaction table top design. After that, in order to avoid test contingency, two groups of orthogonal experiments are performed. L8(2 7) table is used to analyze the effects of gas pressure, defocusing distance, cutting speed and the interaction between the factors on cutting quality, and L16(2 15) table is used to analyze the effects of cutting speed, current, pulse width, frequency and the interaction between the factors on cutting quality. Finally, according to the test results, We can get a conclusion that interaction analysis can accurately find the optimal solution in a comprehensive experiment by a contrast of intuitive analysis and interaction analysis. The significant interaction that impacts on quality of laser cutting Ni-based alloy steel is summarized. The optimum technological parameters of the two groups and important factors are obtained.
The surface of AerMet100 steel is treated by semiconductor laser melting, and the influences of laser melting on microstructure, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of materials are investigated. The results indicate that the melting layer with a good metallurgical quality and without cracks can be obtained by laser melting. In the power range of 750-1650 W, the thickness, hardness, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the melting layer increase with the increase of laser power. When the laser power is 1650 W, the hardness, corrosion resistance and wear resistance of the melting layer are optimal. The phase of AerMet100 steel does not change significantly after laser melting, but the austenite content decreases and the martensite content increases.
Three groups of cross-shaped terahertz band-pass filters with different central frequencies are designed by using the finite difference time domain method. A femtosecond laser micro-machining system is built and the substrateless terahertz filter on a single-layered aluminum foil is fabricated. The transmissivities of these band-pass filters are tested by using the time-domain terahertz spectroscopy system. The experimental results are in a good agreement with the simulated results. All the transmissivities at central frequencies of these filters are over 85%, which reaches the commercial level of terahertz filters.
Applying nanostructure is one of the main approaches to improve the light extraction efficiency (LEE) of organic light-emitting diodes (OLED). When the nanostructure is located between the organic layer and indium tin oxide(ITO) anode, the mode overlap can be guided, the scattering can be enhanced, and the LEE of OLED can be improved. Gold thin-film annealing technology and wet etching technology are adopted to prepare random distributed nanopatterns on the ITO glass for the orange OLED device. The influence factors of nanopatterns on the luminous performance of devices are studied. Meanwhile the standard OLED device is fabricated for contrast. The experimental results show that, compared with the OLED without nanopattern, the performance of OLED with nanopattern is improved in brightness by 17%, current efficiency by 34%, power conversion efficiency by 32%, and external quantum efficiency by 35%, while the gold film thickness is 10 nm, the annealing temperature is 570 ℃, the annealing time is 240 s, and the etching depth is 30 nm. It is indicated that nanopatterns can effectively improve the LEE of OLED device.
An indoor visible light single-source full-duplex communication system is designed and constructed based on inverse modulation of defocused cat eye aiming at hard realization problem of all-optical communication link in indoor visible light communication system. The uplink and downlink of system are independent on each other. It overcomes the disadvantage that traditional single-source duplex communication system needs coordination of transmitter and receiver at the two ends with communication, and can realize the duplex communication of all-optical link without adding additional light source. The experimental results show that the system can realize the downlink 5.0 Mbit/s and uplink 2.0 kbit/s data transmission under the condition of 3.0 m communication distance.
We design a multipurpose laser communication optical antenna to develop and debug the space multi-node laser communication system. The laser communication optical antenna and autocollimator can be switched when the lens or the optical beam splitter in the classic Cassegrain system is chosen. The primary mirror room is designed to improve the overall stiffness of the system and can be used as the lens hood of the system. The front end of the primary mirror room is connected with the disc-type secondary frame so as to assemble and debug the optical system conveniently. The primary mirror is fixed through six bonding points in the primary mirror room. The back end is connected with the backboard of the primary mirror room to provide the installation interfaces for lens assembly, optical beam-splitting assembly, and primary mirror auxiliary support. The finite element analysis results show that when the first order mode frequency of this structure is 345 Hz and the ambient temperature is 20 ℃±5 ℃, the root mean square (RMS) value of surface shape error of the primary mirror is less than λ/28. Tested by a 4D interferometer, the RMS value of wavefront aberration of the system is less than λ/14 under work mode of laser communication optical antenna, which can meet the requirements of laser communication system.
A multi-channel continuous photonic time-stretched analog-to-digital converter (PTS-ADC) system based on the time and wavelength interweaved technology is designed. And the effect of complementary dual Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) structure on PTS-ADC is studied. The principle of complementary dual-MZM which can suppress second-order harmonic in PTS-ADC is verified by theoretical deduction. A continuous PTS-ADC system based on complementary dual-MZM is designed. We simulate the analog to digital conversion of 6 GHz radio frequency (RF) signal by Optisystem. The simulational results show that the system can realize the down-conversion processing and continuous sampling of the RF signal, and the effective number of bits (ENOB) of 4.69 is achieved.
We analyze states of polarization in the fiber with different pitches and the influence of the environmental temperature on the fiber from the high-birefringence pitch and the structure of the sensing fiber. We compare the temperature characteristics of PANDA fiber, elliptical core fiber, and polarization-maintaining (PM) microstructure fiber, and make the conclusion that for a given fiber optic current sensor (FOCS), when the pitch of the sensing fiber LT is twice as long as the beat length Lp of the fiber in non-helical state, the temperature characteristic is the worst; when LT decreases, polarization-maintaining ability and anti-physical-interference ability weaken; when LT≈Lp, the sensing fiber has good temperature characteristics and strong anti-physical-interference ability. The sensing fibers with different structures have different ratio errors. Without compensation at the temperature of -40-+70 ℃, the sensing fiber based on PM microstructure fiber has a minimum value of ratio error ±0.32%.
We get the binary Taylor expansions of the effective refractive index and period of fiber Bragg grating (FBG), verify theoretically that the temperature-strain and strain-temperature cross sensitivities are the same, and make a conclusion that the thermo-optical coefficient and the elasto-optical coefficient are both proportional to the square of the effective refractive index. The calculation equations of temperature and strain are listed, and the method of calculation is expatiated. The wavelengths of FBG under different temperatures and strains are measured, and the cross sensitivity coefficients of temperature-strain and strain-temperature are -1.4743×10-6 nm/(℃·με) and -1.3948×10-6 nm/(με·℃). We place the FBG hydrostatic leveling instrument on the open-air balcony for one day, monitor the wavelength changes of FBG, and then calculate and get a more accurate solution to the changes of liquid depth in the hydrostatic level instrument. The experimental results show that using the calculation equations of temperature and strain can improve the measurement accuracy of FBG.
A semi-direct monocular visual odometry (SVO) algorithm with point-line feature fusion is proposed to solve the problem of localization and mapping in underground engineering for patrol robot. The proposed algorithm is divided into feature extraction, state estimation and depth filter. The point-line feature of image is extracted in the feature extraction thread. The camera pose with 6 degrees of freedom is obtained with different matching and tracking strategies of point-line feature, and it is further optimized by the constraint relationships between frame and frame, feature and feature, and local frames. And the depth information from three-dimensional landmarks to the camera optical center is described through the depth of filter threads with probability distribution. The proposed method can improve the robustness of depth estimation with respect to the fixed depth values. The average positioning accuracy of the proposed algorithm increases by 17.6% on the Euroc dataset compared with that of the LSD-SLAM algorithm, and increases by 6.4% on the Tum dataset compared with that of SVO algorithm. We adopt the robot camera platform to test, and the actual positioning error of about 1.17% meets the actual requirements.
The roller missing defect in the assembling process of deep groove ball bearings is detected automatically with the machine vision method. Three lighting schemes are presented for acquisition of bearing images. The image noise is removed by median filter. The Hough transform algorithm and the polar coordinate expansion method are used for circular detection and rectangular expansion of bearing images. 80 perfect bearings and 60 roller missing bearings are selected for test. The results show that the lighting system of coaxial light source combined with backlight can effectively reduce the surface reflection of bearings. The pre-processing of the image with the median filter can eliminate the isolated noise and make the image less vague. The Hough transform algorithm can quickly obtain the images of bearing inner and outer rings and locate them. The Cartesian polar coordinate expansion method can expand the roller bearing images into rectangles. The detection and recognition of the roller missing position are realized by setting the gray threshold. The recognition rates of the proposed method for 80 perfect bearings and 60 roller missing bearings are 92.5% and 93.3%, respectively.
The convolutional neural network structure fails to consider the independence and correlation between RGB images and depth images fully, so its detection is not high. A new double flow convolution network is proposed for the joint detection of RGB-D images. The RGB image and depth image are inputted to the two convolutional networks and the two networks have the same structure and weight sharing. After several convolutions, the independent features are extracted. According to the optimal weights in the convolution layer, the two convolutional networks are fused. The fused features are extracted continuously using convolution kernels, and the output is obtained by full connection layer finally. When the detection time is similar, the detection accuracy and the success rate are increased by 4.1% and 3.5% respectively, compared with the previous early and late fusion methods.
Endovenous laser treatment is one of the most promising techniques for treating varicosity. We can select the proper treatment parameters, and avoid complications at the time of closing veins, after understanding the transmission of laser in vessels and perivenous tissues. Based on structure features of veins and perivenous tissues, an optical model of 3D tubular structure is established. The 3D Monte carlo algorithm is used to study the distribution of light with different wavelengths and discuss the influences of vessel thickness, irradiation site, and optical parameters on treatment curative effect. The results show that the selection of wavelength should consider the diameter of vessels. The laser with wavelength of 1500 nm has a small injury on perivenous tissues of veins, but the fluence attenuation is relatively quick, so it is available for treating thin vessels. The fluence attenuation of 1320 nm laser is relatively slow, so it is available for treating thick vessels. During the treatment process, the light source should be kept in the central axis, avoiding ulceration and perforation of vessel wall. It is likely to damage the tissues around the vein through reducing absorption coefficient and scattering coefficient in blood. The proposed simulation method may be helpful to the optimization and design of vein laser treatment in clinical medicine treatment plan.
In order to solve the problem of the thickness and uniformity of the light emitting diode (LED) lens coupler for the existing lighting fiber bundle, a new type of Fresnel lens coupler according to the Fresnel theory and the total reflection principle is designed. The Fresnel rotating surface and the free-form surface total reflection rotation surface are used to shape the light beam emitted by the LED Lambert light source to obtain a flattened light beam, which is then coupled to the fiber bundle for uniform illumination. Using 1 W 3535 white LED as the light source, TracePro software is used to simulate the Fresnel lens coupler model. The results show that when the maximum diameter of the Fresnel lens is 14.9 mm, the thickness is 7.8 mm and the output beam divergence angle is 60°, a uniform light field with diameter of 10 mm and luminance uniformity of 92% is obtained on a receiving screen with a coupling distance of 2 mm.
When using the existing methods of depth learning to study the vegetation extraction, there are some problems that the adjacent objects are in the same window, and some useless crushing plots and the salt and pepper phenomenon appear. We propose a method by combining the optimal segmentation scale with the deep belief network to study the vegetation extraction, and comparison experiments are carried out with spectral-texture features and other information. Experimental results show that the overall accuracy of the proposed method is 91.92% and the Kappa coefficient is 0.8677, and the proposed method can effectively improve the classification accuracy compared with the existing deep learning methods. The classification results show that the proposed method can effectively reduce the salt and pepper phenomenon, and clear express the boundaries of objects.
We propose a new human action recognition method based on quaternion three-dimensional (3D) skeleton representation,in order to accurately describe the movement details of human skeletons and 3D geometric relationship of skeletons. Firstly, we obtain skeletal sequences with the same frame quantity by applying linear interpolation and quadratic polynomial interpolation to normal key frames and variable key frames, respectively, on the basis of the captured key frames. Secondly, we use quaternions to represent 3D geometric skeletal relationship of the obtained skeletal sequences to generate quaternion feature descriptors. Finally, we use the support vector machine classifier to train and test the quaternion feature descriptors to realize recognition. Experimental results based on three standard datasets prove that the quaternion feature descriptor is robust to noise, changes of moving rate and viewpoint, and time domain misalignment, and it is able to improve the identification accuracy of human behavior significantly.
In the research of three-dimensional imaging technology, the extraction of image depth is not affected by the illumination direction of the light source and the launch characteristics of the object surface, meanwhile with no shadow, and it can accurately show the three-dimensional depth information of the object surface. We propose a depth acquisition method to obtain the high-quality depth images, using the optimal entropy threshold image segmentation method based on improved genetic algorithm to segment the image and then obtain the depth image. This method can obviously improve the accuracy and real validity of the obtained depth image. The improved genetic algorithm can quickly approximate the optimal threshold, greatly shorten the threshold time of the optimal threshold image segmentation, and improve the accuracy of segmentation efficiency and depth acquisition.
In order to achieve a better denoising effect, we analyze the advantages and disadvantages of the existing denoising model based on the partial differential equations in spatial domain, and propose a double-fidelity total variation denoising model on the basis of L p adaptive denoising model. We introduce the adaptive parameter as the weight of the fidelity item to control the fidelity intensities of different regions and improve the adaptive denoising ability. To overcome the 'ladder' effect in smooth areas, an adaptive gradient-fidelity item is added so that the denoising images have the similar gradient structure to the original images. The experimental results show that the proposed model has better effects in the peak signal to noise ratio, structural similarity, and visual effects.
Deep convolutional neural networks are widely used in the image classification. Current convolutional neural networks architectures based on the simplified convolution can reduce the number of network parameters, but it will lose some of the important information, which decreases the performance of the networks. The two-stream convolutional unit is proposed, in order to improve the accuracy of image classification. The two-stream convolutional unit contains two convolutional filters, which extracts the features containing the information in and across the channels, respectively. Based on the proposed two-stream convolutional unit, a deep convolutional neural network called CTsNet is constructed. Experiments of image classification are conducted on the databases of CIFAR10 and CIFAR100. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed two-stream convolutional unit can extract features containing the information in and across the channels separately, increase the diversity in features and reduce the information loss. The CTsNet based on the two-stream convolutional unit can improve the recognition performance effectively.
High-resolution image acquisition is the premise and foundation of automatic pattern recognition. We study the multi-focus image acquisition problem of stereoscopic pests, taking the rice field insect as the object. Harris corner detection and image entropy are taken as the image quality detection standard. The influence of step displacement in image acquisition on the resolution of image fusion is analyzed with image fusion method based on wavelet transform for different scales of rice pest images. According to the experimental comparison, we obtain the best image acquisition and image fusion strategy and the relation of magnification and optimum step displacement. The experimental results show that this strategy is reliable to acquire the extended-depth-of-field image for stereoscopic pests, which provides an effective measure for establishing a high-quality image database of rice pest samples.
Color image quality assessment (CIQA) is a hot spot in researching image quality assessment (IQA). Chromatic information has a certain effect on the human visual system (HVS). Based on the conversion of RGB images to another color space YIQ, we obtain SSIM and GSSIM of the color image (C-SSIM and C-GSSIM) by extending the structural similarity index (SSIM) and gradient-based SSIM (GSSIM) of the grayscale image. In addition, considering HVS as a complex nonlinear system, two general pooling strategies are used to describe HVS characteristics to improve the evaluation effect of C-SSIM, C-GSSIM and feature similarity of the color image (C-FSIM). The numerical results, performed in TID2013 image database, demonstrate that C-SSIM, C-GSSIM and C-FSIM based on the general mean pooling strategy can effectively improve the accuracy of IQA.
Automatic classification of histopathological image is vital in medical image processing field, and the effective feature extraction plays an key role to realize accurate diagnosis. A feature extraction algorithm based on Product of Experts (PoE) is proposed to realize the feature representation of the histopathological image. The maximum likelihood and Monte Carlo random sampling methods are used to train PoE models corresponding to different kinds of images, and the responses of image samples in the two models are concatenated as their eigenvectors. Finally, a support vector machine (SVM) classification model is built based on the eigenvectors of the trained image samples. The experiments are carried out to classify histopathological images of healthy and inflammatory organs of kidney, lung, and spleen, which are provided by the Animal Diagnostics Lab at Pennsylvania State University. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can achieve high accuracy in three organ image classifications.
In order to improve the visual effect of underwater images, an underwater image restoration algorithm based on red-dark channel prior (RDCP) and inverse filtering is proposed. Firstly, the Jaffe-McGlamery underwater optical imaging model is simplified. On this basis, the RDCP is used to eliminate the foggy appearance of images resulting from backward scattering during the imaging process. Secondly, considering the mathematic relation between the transmission map of each channel and optical transfer function, inverse filtering is applied to remove the forward scattering component. Finally, the proposed algorithm adopts linear stretch based on Gaussian distribution to improve image contrast. The proposed algorithm and several main underwater image processing algorithms are employed in processing underwater images captured in various underwater environments, and the information entropy and other objective evaluation factors are calculated. The experimental results prove that the proposed algorithm has superiority for balancing the color, contrast and saturation of the images, and the visual effects are more similar to images captured in natural settings.
Traditional image contrast enhancement technology can easily cause over-enhancement or under-enhancement in the local area of images. Thus, an image contrast enhancement method combining nonseparable wavelet analysis and curve fitting is proposed. The method uses mean and standard deviation of the standard clear image as the ideal target for image contrast enhancement. Firstly, four-channel nonseparable wavelet is used to decompose standard clear image and low contrast image of the same target. Next, the predictive ability of curve fitting is used to get the relationships among mean values and the relationships among standard deviations of sub-images with same frequency channel and same direction. Then, the ideal enhanced sub-images can be obtained by the functional relationships and histogram matching formulas. Finally, these new sub-images are reconstructed by nonseparable wavelet. The performance of the method is evaluated with clarity and standard deviation. The experimental results show that the proposed method has a good enhancement effect for low contrast image, and can obtain high definition images.
In the process of workpiece circular arc radius measurement on binocular vision, the circular arc contour feature extraction is the key to match follow-up edge contour point and reconstruct space arc. Affected by the surface texture of the workpiece, the interference of the surrounding environment, and uneven illumination, the existing algorithm cannot accurately extract the circular arc contour feature. Based on the edge detection by Sobel operator, we use adaptive convolution operation and double local binary pattern texture feature to generate the fusion gray value, which can be used to screen out the edge contour points in the previous detection result by Sobel operator. The polar coordinate distribution histogram is obtained and processed as a normal distribution, which can eliminate the interference of noise points in the complex background and distinguish the outer contour feature from the inner contour feature. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm overcomes the influence of illumination and becomes accurate and robust.
In order to design a wideband bandwidth-tunable filter, we design four kinds of filters with two types of micro cavities through different coupling structures between the waveguide and the micro resonator in the two-dimensional photonic crystal structure. By means of the coupled mode theory (CMT), we qualitatively analyze the influences of phase detuning factor and ratio of coupling quality factors on the fiber performances. We use finite-difference time-domain (FDTD) method to study the transmission spectra of the filter by adjusting rod radii of the 5×5 micro resonators. The simulated results show that the three symmetrical filters have high normalized transmission (85.3%-99.9%), narrow bandwidth (1.8-5.6 nm), and broad tunable range for extracting peak wavelength (1308.0-1582.3 nm) at each peak wavelength. Compared with the asymmetrical filter, symmetrical filters have higher normalized transmission at peak wavelength. The symmetrical structures have potential value in the designs of optical signal extraction interfaces, optical sensing, and optical interconnection networks.
To realize the active light control with compact structure, we design an optical switch based on plasmonic demultiplexer. The device is composed of metal-Kerr nonlinear material-metal waveguide and resonant cavities, providing the function of active optical regulation. With the multiple parameter optimization, the signal with wavelength of 1310 nm can be controlled by pump light with wavelength of 735 nm. The signal can realize output and cut off at two output. The directional extinction ratio can reach to 29.4 dB and the response time is only 50 fs. The dual-channel all-optical switch has the advantages of simple and compact structure, easy integration, fast response, and so on, it will has importance application in naono-integrated optics.
It is demonstrated that, in the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) detection system, the thermal effect generated by the variation of environmental temperature will affect the resonance condition and correlated output. The SPR detection system based on the liquid prism is set up, in which the thermal performance of each dielectric layer is analyzed in detail. Based on the theoretical model on the relationship between the refractive index of the dielectric layer and the temperature, the influences of the environment temperature variation on both the resonance curve and resonance angle of each dielectric layer are numerically simulated. The simulated results show that the thermal effected refraction variation of deionized water are 1-2 orders higher than that of glass substrate and metal film. By exploiting self-build resonance detection system, we experimentally explore the dependences of both the resonance angle deviation and the refractive index change of water on environmental temperature variation. The results indicate that when the variation range of the environment temperature is 29 K, the resonance angle offset is 0.216° and the refraction change of the water reaches up to 4.02×10-3. Also, the formula of the relationship between the refraction of the water and the temperature is attained. The experimental results basically agree with the theoretical calculations, which lay foundation for further improvement of the sensitivity of the detection system.
Reflection intensity information is an important component of data acquired by airborne light detection and ranging (LiDAR) system. The main difficulty in realizing road point cloud extraction using reflection intensity information is that road point cloud is always contained in ground point cloud, whereas the reflection intensity threshold to discriminate road point cloud and non-road point cloud is hard to obtain. To solve this problem, an extraction algorithm of road point cloud based on skewness balancing is proposed, which can obtain the reflection intensity threshold automatically, accurately and parameter-freely. After that pure road point cloud can be obtained. We adapt two datasets of LiDAR point cloud located in somewhere of Shanxi province and a certain city in Germany to test the effectiveness of the proposed algorithms at different environments, respectively. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm is easy and effective, and has a good performance of road point cloud extraction.
Aiming at the problem that the shallow machine learning algorithm commonly used in remote sensing image classification application cannot satisfy the classification accuracy in the current mass remote sensing image data environment, we propose a method to apply the fully convolution neural network to the remote sensing image classification. To reduce the loss of image feature map in the pooling process, we add the fusion of the pool layer and the deconvolution layer. To improve the reliability of fusion, we add the scale layer. To obtain finer edge classification results, considering the spatial correlation between pixels mean-shift clustering is used to obtain the spatial relationship of pixels. Classes of regional objects are determined by the maximum sum and the minimum variance of the regional pixel probabilities. Images of typical regions are chosen to carry out the classification experiments, and the classification method proposed in this paper is compared with those of the fully convolution neural network, support vector machine, and artificial neural network. The results show that the accuracy of the classification method proposed in this paper is obviously higher than that of the traditional machine learning methods.
To solve the problem that the exact position relation between three-dimensional lidar and global positioning system/inertial navigation system integrated navigation system cannot be obtained directly and the relative rotation angle between them cannot be directly measured, a method based on simultaneous matching of multiple-point clouds is proposed to calibrate the extrinsic parameters. Firstly, the lidar point clouds, which are similar in position and opposite in direction, are selected as the calibration data. Secondly, we set the parameters of the initial regional center, the initial step length and the step counts, then traverse the combination of parameters to find the optimal target function when the corresponding extrinsic parameters are updated to the optimal iterative regional center. We shorten the step length continuously, until optimal extrinsic parameter that satisfies accuracy requirement is obtained. The experiment collects two different data in different environments, and uses better and worse parameter initial iterative center and different step counts to calibrate. Results show that the proposed calibration method has a short time duration, and can get good calibration results for non-ideal initial parameters. The method is simple, and can achieve required calibration accuracy without special calibration object.
Feed with copper can accelerate the growth of pigs significantly, so it is common to find feed with excess copper content, but excess copper brings serious consequences. Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) technology is used to quantificationally analyze the copper in pig feed rapidly. Competitive adaptive reweighted sampling (CARS) algorithm screens 22 important wavelength variables which are associated with copper in pig feed with compression ratio of 1.1%. Finally, partial least squares (PLS) regression method is applied to establish the prediction model of copper content in pig feed based on the 22 important wavelength variables, and the copper content in prediction set pig feed samples is predicted. The results show that the CARS-PLS model has higher prediction accuracy and prediction ability than full spectrum-PLS model. The correlation coefficient, the root mean square error of cross validation and the relative error are 0.978, 19.25, 5.59%, respectively. CARS algorithm can effectively optimize the LIBS online detection model of copper in pig feed and improve the prediction accuracy.
Laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) is proposed to identify tea variety rapidly. LIBS spectra of seven kinds of teas are collected at 200-480 nm wavelength. Two approaches in preprocessing spectra are applied to decrease noise and eliminate disturbance. One is nine-point smoothing (NPS), the other is NPS combined with first derivative (FD). Principal component analysis (PCA) is adopted to reduce the dimensions of processed spectra. Three models like discriminant analysis (DA), radical basic function (RBF) and BP-ANN (multi layer perception, MLP) are selected to discriminate the tea variety. The results demonstrate that the recognition accuracy of tea variety is improved while NPS, FD and PCA are utilized according to priority. And the recognition accuracy of MLP is higher than that of DA and RBF. The recognition accuracy of MLP is 99.6% in training set and 99.1% in test set. It is feasible to select suitable LIBS spectra preprocessing and model construction method to identify tea variety.