View fulltext
View fulltext
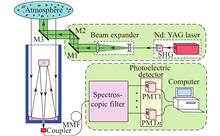
Lidar is an active remote sensing instrument, which has the characteristics of high precision and high spatial-temporal resolution. It has been widely used in the detection of atmospheric environmental parameters (aerosol, CO2, ozone, etc.) and meteorological parameters (temperature, water vapor, pressure, wind speed and direction, etc.). In recent years, atmospheric phenomena such as haze and climate change have been widely concerned by the public, and the national environmental governance and meteorological forecasting departments have an urgent demand for atmospheric observation technology. Atmospheric Lidar has been developed rapidly in China, and has achieved good research achievements. The research progress and development status of Lidar for atmospheric detection in recent years were introduced and summarized in this paper. According to the different detection objects detected by Lidars, Lidars can be classified as Mie scattering Lidar, Raman Lidar, high-spectral-resolution Lidar, differential absorption Lidar and et al. The advantages and disadvantages of all kinds of atmospheric detection Lidars and their applications in different detection objects were comprehensively introduced in this paper. Finally, the bottlenecks of Lidar technology were summarized, and the development trend of Lidar was also prospected.
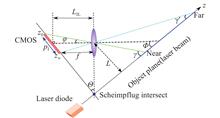
When the object plane is not parallel to the lens plane in an imaging system, if the image plane, the object plane and the lens plane intersect into a straight line—satisfying the Scheimpflug imaging principle, the imaging system can still clearly image the object and achieve infinite depth-of-focus (DoF). The newly developed Scheimpflug lidar (SLidar) technique based on the Scheimpflug imaging principle can thus utilize continuous wave diode lasers as light sources and image sensors as detectors, featuring short blind range, compact structure, low maintenance and high cost performance, etc. In recent years, the SLidar technique has gradually been applied to the fields of atmospheric environment monitoring, three-dimensional (3D) target imaging, fluorescence(hyperspectral) lidar detection, ecological studies, combustion diagnosis, and water-body optical measurements, etc. This article will thoroughly explain the basic principles of the SLidar technique, discuss latest progresses in these fields and present its perspectives.
The tracking algorithms based on the Siamese networks show great potential in terms of tracking accuracy and speed. However, it is still challenging to adapt the offline trained model to online tracking. In order to improve the feature extraction and discrimination ability of the algorithm in complex scenes, a Siamese network real-time tracking algorithm that combines channel, interconnection and spatial attention mechanisms was proposed. First a Siamese tracking framework with a deep convolutional network VGG-Net-16 as the backbone network was built to increase feature extraction capabilities; then the channel-interconnection-spatial attention module was integrated to enhance the adaptability and discrimination capabilities of the model; then the multi-layer response maps were weighted and fused to obtain more accurate tracking results; and finally the large-scale datasets were used to train the end-to-end network, and tracking test on the benchmark OTB-2015 was completed. The experimental results show that compared with the current mainstream algorithms, the proposed algorithm is more robust and better adapt to complex scenes such as target appearance changes, similar distractors, and occlusion. On the NVIDIA RTX 2060 GPU, the average tracking speed reaches 37FPS, which meets real-time requirements.
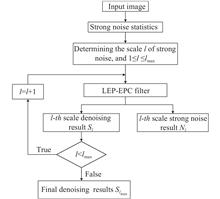
The detection of mine targets will be interfered by the underwater non-uniform strong noise (organic matter, suspended particles, etc). To solve this problem, a novel denoising method was proposed. Firstly, the local edge preserving filtering algorithm was optimized and the local edge preserving filtering based on edge perception constraint was proposed. A spatially adaptive edge perception constraint regularization term was introduced into the model to better represent the edges and details of the image, so that the edge-preserving and smoothing property could be better. Secondly, the multi-scale strategy was used to solve the heterogeneity of strong noise, the optimized model was iteratively applied to the noise removal results of each scale to generate multi-scale decomposition, and the denoising scale was gradually increaseed in the process of multi-scale decomposition. The noise of different scales was gradually separated from the denoising results of the previous scale. The experimental results show that, compared with other classical denoising methods, the proposed algorithm can better remove the underwater non-uniform strong noise while retaining the mine target information, which also has a certain guiding significance for real-time mine operation.
Infrared imaging technology has been widely used for object tracking in military, remote sensing, security and other fields. However, thermal infrared images generally suffer from low contrast and blurry targets. Therefore, it has great importance of fusing infrared images with visible images. Compared with single-modal RGB trackers, dual-modal RGBT(RGB/Thermal infrared) trackers are more robust to illumination variation and fog. In this paper, a RGBT dual-modal siamese tracking network with feature fusion was proposed. Convolutional features extracted from the visible image and infrared image were fused to improve the appearance feature discrimination. The network can use the training data for end-to-end off-line training. Experimental results on the public RGBT234 dataset demonstrate that our tracker achieves robust and persistent tracking in complex scenarios.
In view of the infrared datasets which has limited scale and few labeled samples, a semi-supervised transfer learning method was proposed for the training of infrared object detection neural network. It aimed at improving the training efficiency and generalization ability of object detection neural networks on infrared datasets with limited scale, and increasing the adaptability of deep learning models in scenarios with few training samples such as infrared object detection. Firstly, the ability of unlabeled samples in improving model generalization and suppressing overfitting under few labeled samples was described. Then, the process of semi-supervised transfer learning for infrared object detection neural network was proposed: a pre-trained model was trained on large scale RGB dataset, and next it was fine-tuned using a few labeled and unlabeled IR images. Moreover, a pseudo-supervised loss function with feature similarity weighting was proposed, where the predictions from same batch was used as labels to each other, thus making full use of the feature distribution of similar objects in unlabeled images. To reduce the computation of semi supervised learning, the pseudo-supervised loss of object was limited on the objects within the neighborhood of its feature vector. Experimental results show that the test accuracy of object detection neural network trained by proposed method is higher than that trained by supervised transfer learning, it achieves an improvement of 1.1% on Faster R-CNN and a significant improvement of 4.8% on YOLO-v3, which verifies the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Latest generation of dual-channel spaceborne hyperspectral imager based on visible near infrared (VNIR) and short wave infrared (SWIR) uses the field slitter to separate VNIR and SWIR channels into several sub-fields, and each sub-field image has different ground area at the same time. When using motion compensation technology to improve signal to noise ratio of the instrument, the observation angles of each sub-field are different, which leads to more complicated mismatch of images and make it impossible to get the continuous VNIR-SWIR spectrum of the ground pixel. The rule of image distortion and dual-channel mismatch quantitatively was analyzed by Rigorous imaging model, and the registration scheme by using geometric orientation of each sub-field separately as well as the phase correlation method was proposed on this basis. Verification based on dual-channel spaceborne hyperspectral simulated data of Dongtianshan under motion compensation was performed. The result shows that registration accuracy of traditional scheme based on correlation of images reaches 3.9 pixel, which means the continuous VNIR-SWIR spectrum of the ground pixel is still unavailable. The registration accuracy of the scheme proposed by this paper reaches 0.3 pixel, and the reflectance spectrum overlap ratio error of the overlapping bands of VNIR and SWIR reduces from 41.5% to 1.2%.
Remainders with a certain size in the infrared detector assembly easily cause the diffraction phenomenon in the optical path of infrared detector in service, which would change the local luminous flux distribution on the focal plane, resulting in 'black spot' and 'Poisson bright spot ' on the image. In order to reduce the occurrence of such abnormal images, according to Fresnel diffraction theory, the remainder particles diameter satisfying the diffraction spot formation for several typical detector Dewar assemblies was calculated, and the relationship among the remainders dimension, Dewar structure, wavelength and diffraction spot was also analyzed. The results show that diffraction is more likely to happen for longer wavelength and smaller distance between remainders and focal plane; for different detector Dewar assembly, the position inclined to diffraction is the region where the distance denoted by "L" between remainders and focal plane satisfies the equation "LLC". Besides, combined with the production practice, some corresponding measures to control the remainders were offered. These conclusions in the article provide a reference for the infrared detector production design and engineering application.
The cold shield structure has direct effects on stray lights suppressing in infrared detector. In order to further improve the cold shield efficiency, the cold shield height and containment structure influence on stray radiation suppressed were offered based on the analysis. Building mathematical models, DF20 cold shield was chosen as an instance to be calculated by the program. Compared with the test results of the infrared detector, when the cold shield height is 25 mm, the test result is 5.46%. When the cold shield height is 29 mm, the test result of cold shield which restraining the stray radiation effectively 4.87%, the test result of cold shield which restraining the stray radiation ineffectively 6.11%. A creative idea of cold shield structure design was proposed. Just increasing the cold shield height, may not increase the cold shield efficiency. When the baffles restrained the stray radiation effectively, with the cold shield hight increased, the stray radiation suppression capability became stronger, the cold shield efficiency increased, the infrared detector performance was improved. At the same time, changing the cold field structure will not influence the efficiency of the cold shield.
In order to solve the problem of low contrast between the target and the background and blurred details in infrared images, an improved infrared image clearing algorithm based on dark channel prior theory was proposed and FPGA was used to design the hardware system of the proposed algorithm. The dark channel image was obtained based on nonlinear filtering of the current pixel and the neighborhood data of the input image. Moreover, the correction function was used to optimize the transmission to generate a look~~up table. Then the transmission was looked up in the look~~up table and the proposed algorithm enhanced the image with the atmospheric scattering model, thereby reducing or eliminating the block effects and the color distortion of the sky or other bright areas generated by the traditional dark channel algorithm. The design of FPGA hardware could work with an estimated frequency of 188 MHz by occupying only 4% of LUT and 8% of I/O resources, which was much higher than the operating frequency of 27 MHz of the camera used. Therefore, the design was realized to meet the requirements of real-time application of video images.
A novel micro bridge structure for uncooled vanadium oxide infrared focal plane array (IRFPA) detector was developed. This micro bridge used common-leg structure, which was shared by column adjacent pixels. Common-leg structure greatly increased the leg length, reducing the thermal conductivity, which could effectively improve the response rate and reduced the negative electron-transfer dissociation (NETD). Furthermore, the micro bridge adopted double-layer process to increase the area of the deck and the vanadium oxide, which could improve the filling rate and the detector performance. The detector array was 384×288 with 12 μm pixels. The readout integrated circuit (ROIC) adopted rolling-shutter mode for integration and a pixel-by-pixel mode for readout. The high reliability metal vacuum package was used for the device. The results showed that the NETD of the detector was less than 15 mK, and the response rate was greater than 44 mV/K. Its performance index could meet the requirements of civil and military applications.
For the target recognition of infrared imagery, a method was proposed via the combination of convolutional neural network (CNN) and joint sparse representation (JSR). CNN learned the deep features of the infrared target imagery, which described the multi-layer properties of the target. Different layers of deep features described the target charateristics from differnt aspects, so they can well complement each other. The joint use of multi-layer deep features could provide more valid information for target recognition. During the classification, JSR was employed to represent the multi-level deep feature vectors and the inner correlations among different features was used to improve the overall representation precision. Therefore, JSR not only made use of individual deep features but also considered their inner correlations. According to the outs from JSR, the target label of the input sample was determined based on the minimum error. The experiments were conducted based on mid-wave infrared (MWIR) dataset under the conditions of original test samples, noise test samples, and small training set. Simultaneously, the proposed method was compared with four previous methods. According to the experimental results, the proposed method achieves better performance under the three conditions, validating its potential in infrared imagery target recognition.
Depolarization mechanism and compensation scheme of radially polarized beams under non-uniform pumping were investigated. Theoretical analysis shows that, for the non-uniform pumping status, the thermal induced shear birefringence caused by the thermally induced shear stress within the cross-section of the isotropic crystal is the main reason for the depolarization of the radially polarized beams. Related experiments were designed to evaluate the depolarization of the radially polarized beams under non-uniform pumping conditions by using two methods of thin-film polarizer (TFP) measurement and purity measurement, in which the TFP measurement method was used to detect the overall depolarization of radially polarized beams and the purity measurement method was used to detect local depolarization of radially polarized beams. With a peak pump power of 1.1 kW, the depolarization measured by the two evaluation methods was 2.34% and 2.53%, respectively. Based on the theoretical analysis and evaluation results, a combination of phase modulation and spatial mode matching was considered in the design of the depolarization compensation scheme, which improved the depolarization of the radially polarized beams by 59%. Meanwhile, a picosecond radially polarized beam with a pulse energy of 19.36 mJ, a purity of 90.13%, and a beam quality M2 factor of 3.8 was achieved.
During the measurement procedure of laser structure light vision, the measurement object material surface difference and geometric curvity would both affect the laser light-spot image quality, and influence the precision accuracy of measurement data processing. For adapting to application various circumstances of industrial measurement, the current controlling of laser diode of structure light was adopted. A low cost miniwatt semiconductor laser controller design solution was submitted based on the analysis of laser diode performance. The PWM signal driving technique was researched in this paper, which applied ARM MCU to generating PWM output signals, and then signals were transformed into analog laser controlling signal by cascade circuits of the resistance-capacitance filter circuit with optoisolator, operational amplifier follower and voltage controlled constant current source (V-I) circuit. The ratio and reference frequency of PWM signal could be set by the modbus serial agreement between host machine and laser controller. A series of imaging experiments with laser structure light projection were be done, which indicated adjusting laser structure light output at the right level would be able to optimize the measurement result and improve the adaptability of laser vision system. The experimental results show that the system can run stably.
For the precise measurement, a femtosecond mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser with a 6 MHz repetition rate tuning range at a fundamental repetition rate of 26 MHz was reported, corresponding to 23% tuning ratio. With chirped fiber Bragg grating, the mode-locked fiber laser could run at different dispersion regimes. The influence of the net cavity dispersion on output characteristics and repetition rate tunability was studied. In a range of negative cavity dispersion, the mode-locked fiber laser could output the nearly same spectrum when the repetition rate was tuned, and the output spectrum was nearly Gaussian-type. Based on this result, a simple scheme, spatial optical path structure, and optimized cavity parameters was designed, which promised the large tunable range and stable mode-locking. The mode-locked fiber could stably output 3.23 mW ultrashort laser pulses with 347 fs dechirped pulse duration. Furthermore, the Yb-fiber laser was locked to the Rb atomic clock so that the repetition rate could be stabilized. The Allan deviation is 2×10-10 when the average time was 1 s.
A high power 755 nm continuous-wave (CW) laser with high beam quality based on the Alexandrite crystal was demonstrated. The Alexandrite lasers single-end-pumped by 638 nm laser diodes (LDs) and 532 nm solid-state laser were studied comparatively, then the CW output power, optical-to-optical conversion efficiency, and slope efficiency pumped by 638 nm LDs were 3.9 W, 19.7%, and 23.7%, respectively, while they were 2.1 W, 10.0%, and 12.9%, at nearly the same conditions except that it was pumped by 532 nm solid-state laser. The results show that the Alexandrite laser pumped with 638 nm LDs can obtain higher CW output power and higher conversion efficiency. Moreover, a CW output power of 6.2 W at 755 nm of Alexandrite laser double-end-pumped by a 638 nm LDs was achieved with the optical-to-optical conversion efficiency and the slope efficiency of 16.3% and 24.2%, respectively. The beam quality factor M2 was better than 1.47 at the CW output power of 5.0 W, which was the highest CW output power of Alexandrite laser with the diffraction limit to the best. This high power and high beam quality 755 nm Alexandrite laser provides the fundamental frequency source for the development of CW ultraviolet lasers.
To reveal the mechanism of shock wave drag reduction by single nanosecond-pulse laser energy deposition, the interactions between single laser energy deposition and normal shock wave, the single laser energy deposition and bow shock wave in supersonic flow field were studied numerically. Dissociation and ionization of air usually were not taken into consideration in typical simulation method, so appropriate space distribution of laser energy deposition induced plasma cannot be obtained. Tear-drop initial energy distribution and finite rate reaction model were adopted in this work. The simulation results of shock wave and hot core evolution processes are in good accordance with those of experiments, which verifies the rationality of the proposed simulation method. The normal shock and bow shock wave under the condition of Maher number 1.92 are selected respectively. The incident laser energy is 10.1 mJ and 12 mJ. Results show that the hot core of laser energy deposition induced plasma cloud turns into low pressure symmetrical vortex ring after the interaction with normal shock wave. In the condition of bow shock wave, the shock wave drag induced by low pressure vortex ring is reduced, which formed after the shock wave. It is the main mechanism of shock wave drag reduction.
Modern aircraft is equipped with airborne photoelectric detection system. Infrared thermal imager is used to search the azimuth of aircraft target in airspace, and pulsed laser rangefinder is used to measure the radial distance of target. Airborne pulsed laser target detection is a dynamic process. When the light spot moves on the target or the atmospheric turbulence refraction causes the echo beam to deviate from the receiving antenna, sometimes the target is absent, which makes it impossible to track the target stably. Only the amplitude information of target echo pulse is used to detect, which limits the effective range of laser target. In the dynamic clutter background of airborne platform, the problem of dynamic target detection can be solved by considering the pulse laser target as the range extended target and the echo signal as the target waveform image. In view of this, a multi pulse laser range extended target echo filtering algorithm based on wavelet transform was proposed. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can keep the waveform characteristics well.
GaSb thermophotovoltaic cells were epitaxially grown on GaSb substrates by the Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE) method. And two kinds of GaSb TPV cells with 1 cm×1 cm dimensions that had different electrode shape were fabricated. In order to obtain high quality GaSb epitaxial layer, the growth conditions of MBE were optimized continuously. The quality of epilayers was good which was shown in the surface morphology characterized by AFM. The root mean square (RMS) of surface morphology was only 1.5 Å (1 Å=0.1 nm). Device characteristics including open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current density, external quantum efficiencies, fill factor and dark current density of the TPV cells were measured and compared. Under solar simulation, the TPV cells exhibited an open-circuit voltage of 0.303 V and a short-circuit current density of 27.1 mA/cm2. Compared with the TPV cell that had a simple electrode, the TPV cell having the grating electrode showed better performance in short circuit current density and fill factor. Under infrared light illumination, the TPV cell with a grating electrode exhibited an optimal fill factor of 56.8%.
With the increasing development of light and small satellite technology, high-density optical payload has become a new hotspot research in space optical field. The field-bias and multi-light-channel coupled coaxial four-mirror optical system has the advantages of long focal length, large field of view and high degree of lightweight, which can satisfy the high-resolution, multi-function and low-cost applications of the optical payloads. Therefore, it has a widely application prospect in the field of light and small optical remote sensing payloads. Based on Gaussian optics and third-order aberration theory, the initial configuration of the coaxial four-mirror optical system was analyzed. An example of field-bias with visible spectrum and MWIR spectrum coupled optical system which was suitable for push-scanning was given. The visible channel has a focal length of 4 m, working spectrum of 0.45-0.85 μm, relative aperture of 1∶10, the MWIR channel has a focal length of 1.6 m, working spectrum of 3.7-4.8 μm, relative aperture of 1∶4, and the FOV of both channels are 1.4°×0.2°. The imaging quality and tolerance of the system were analyzed, from the results of the analysis, the imaging quality of each channel approaches the diffraction limit, the total length of the optical system is less than f’visible/5.48, the system has higher compression ratio, and has easily implemented quality because of the relatively loose tolerance about processing and assembling.
In order to meet the increasing demand for beam quality of laser weapons, a design and aspheric optimization method of optical collimation system was proposed. This method was successfully applied to the lens design of a laser cauterization gun, so that the gun could obtain a higher quality collimating beam in a farther range. First, the initial structure was obtained based on the analysis of tactical and technical parameters and the calculation of the optical path, then the aspherical optimization was performed, the two simulation results were compared and analyzed based on ZEMAX. Numerical results show that the optimized structure has significant advantages. Its aspheric coefficient and curvature radius are 0.584 mm and 115.37 mm respectively, and the light energy utilization rate can reach 99.92% when the GB 1316-88 anti-reflection film is used. After tolerance analysis, the lens was processed and combined with the gun body for a board ablation experiment. The experimental results are in good agreement with the simulation results. The superiority of lens performance proves the feasibility and rationality of the proposed design and optimization method, and also provides a certain reference value for similar problems in other fields.
The temperature of aerial camera varies greatly in the working environment, and the temperature change will produce a temperature gradient in the optical lens of the camera, which will affect the image quality of the camera. In order to ensure the image quality of the optical system, the lens need to be designed for dissipate heat within a certain temperature range. The thermal analysis of an aviation camera optical system was accomplished by ZEMAX optical design software. According to the analysis results, the integrated optical-mechanical design of passive athermalization of multi-chip and large-field optical len was realized with ANSYS software. The image compensation at different temperature was achieved through micro-displacement variation between the compensation link inside the lens along the axial direction. At the same time, an optical non-contact online detection method was proposed with high precision, and the accuracy is ±1 μm. And then heat dissipation compensation test piece was developed to achieve micro displacement test, which showed the test data of micro displacement was consistent with the analysis data. Finally, the effectiveness of the design was verified by the image quality testing of the actual aerial lens with this integrated design, and the lens performs well at working temperature.
In order to improve the efficiency of observation and the quality of staring imaging, satellite-borne wide field infrared camera has a strict requirement on the scanning mirror control system. The scanning mirror is required to achieve fast steering in tens of milliseconds and trajectory tracking with arc second level control precision. Due to the limit of control system bandwidth, the motion performances are difficult to realize by algorithm based on classical control theory. For the scanning mirror with pivot supporting, a trajectory tracking control method for high order controlled plant based on iterative learning algorithm was proposed. The design and optimization process of learning law was given. By using anticipatory learning scheme, the calculations of high order derivatives for tracking error were avoided. Furthermore, the convergence condition and the key parameter of control algorithm were derived by frequency domain analysis. Its application effect was verified by both simulation and prototype test. The prototype test results show that, in the scanning mirror closed-loop control system with less than 2 Hz bandwidth and no identification for high order characteristics of the controlled plant, the tracking error of a desired trajectory with above 106 (°)/s3 angular jerk is reduced to ±1.5" after adopting the iterative learning algorithm, which meets the performance requirements of infrared camera system.
In order to solve the problems of the large number of components and complex structure in the mid-long wave infrared dual-band system, the structural characteristics of the annular folded imaging system was analyzed, and the calculation method of the obscuration ratio was explained. An infrared dual-band annular aperture ultrathin imaging system with common path was designed. The focal length is 50 mm, the field of view is 14°, and F number is 1. The system is made up of only one optical element, so it has simple structure and compact optical path. The ratio of total optical length to focal length is 0.48. At the spatial frequency of 20 lp/mm, the modulation transfer function (MTF) of the full field of view is more than 0.45 in medium wave infrared 3-5 μm, and that is more than 0.30 in long wave infrared 8-10 μm. The athermalization of system is realized in the range of -40-80 ℃. According to the tolerance results, this system is machinable. The chalcogenide glasses used for the substrate material can be precision molded to achieve batch processing. The study provides a new idea for the realization of low-cost and miniaturized infrared dual-band system.
Aiming at the shortcomings of the design of the underwater laser peripheral scanning ring window, a design method of the transmitting optical system that shifted the scanning base point was proposed. This method was based on the structure of Kepler telescope. The divergence angle of the beam and its distribution uniformity were optimized by adopting the image-side telecentric method for the conjugated design and distortion control of the objective lens and the eyepiece group. On the basis of the optimized design, the influence of the flat window and the conformal window on the beam quality and the influence of the coating on the energy transmission efficiency were simulated and analyzed respectively. Finally, tolerance analysis and hydraulic simulation of different window designs were carried out. The simulation results of optics and mechanics show that the method effectively reduces the window area of the shell surface, avoids the blind area of the fan-shaped detection caused by the design of the ring window, and has certain guiding significance for the engineering design of the underwater laser peripheral scanning emission system.
The roughness of the material surface affects the THz nondestructive testing results. Roughness of the surface can be ignored in the microwave region, but should be considered in the terahertz frequency domain. The effect of scattering caused by rough surface at terahertz frequency on the reflection spectrum was studied and discussed. By consideration of the reflection model of a single sample, the reflection signal of a rough surface can be correlated with that of a smooth surface by using the Kirchhoff approximation. In addition, the glucose tablets with different roughness were measured by THz-TDS (Terahertz time domain spectroscopy) system and their reflection spectra were analyzed. The reflection spectrum results show that due to the roughness of the surface, diffuse scattering generated by the rough surface weakens the intensity of the reflection spectrum at the receiver. In order to reduce the influence of the roughness on the spectrum, a spectral Gaussian compensation method was proposed, which can restore the spectral characteristics of the smooth surface. The power spectrum of 360 mesh roughness was increased by about 3 dB and 9 dB at 0.5 THz and 1 THz, respectively. Therefore, it can be envisaged that the proposed rough-surface spectral compensation method has a specific reference value in the development of the THz nondestructive testing technology in the future.
The submarine movement underwater can produce special internal wave which will rise and arrive at the water surface and make up a kind of the special weak texture. The texture makes it possible to detect through infrared remote sensing device. But the texture signal usually has very low contrast and is always mixed with intensive clutter in the sea surface background. Therefore, it is very difficult to extract these special textures from all the captured information. After comparing the advantage and disadvantage in the state of art for the texture extraction, optical filtering based on incoherent light was used for enhancing Signal-Clutter-Ratio(SCR) of the weak texture on the water surface. That will make the extraction much easier. Based on the optical principle of interference filtering and SCR evaluation method for the ability of the device to extract the weak texture signal on the water surface, optical filtering method for signals with different frequency was analyzed and evaluated by SCR. The optical transfer function of interference light was optimized according to the target frequency of the weak-texture signals. The simulation and experiment were implemented for verifying the feasibility. The optimized double-aperture optical system has better ability to extract the weak texture, which has showed that 7% SCR enhancement can be derived for the weak texture model and signal from this system. Combined with the digital contrast method, the ability for extracting the weak texture from the sea surface can be further improved.
A control algorithm based on disturbance estimation and compensation theory was proposed in order to meet the design requirement of apparent axis velocity stationary-error in advanced airborne target indication equipment. An improved extended state observer (ESO) was designed to reduce the phase delay of the high order observer and to improve the control accuracy of the line of sight (LOS). The step response and velocity stability capability of the improved control algorithm were tested in the experiment, and were compared with the classical control algorithm. By analyzing the step experiment results, it can be seen that the designed control algorithm can achieve shorter stability time and lower overshoot under different closed-loop control bandwidth. Under the closed-loop bandwidth of 35 Hz, the stability time of PID algorithm was reduced by 49.1% and the overshoot was reduced by 88.4%, and the dynamic performance of the system was significantly improved. The velocity stability experimental results show that the designed control algorithm can significantly improve the rejection capability of different disturbances of amplitude of 1° and frequency within 2.5 Hz, the velocity error of the LOS was controlled within 0.1(°)/s, and the disturbance residuals were less than 0.1(°)/s. The designed control algorithm meets the design requirements of advanced target indication equipment and has high practical value for improving the dynamic performance of the system and the velocity stability of the LOS.
Doppler wind measurement lidar reverses the wind speed by the Doppler frequency shift of the echo signal of the system. In order to improve the detection accuracy of the wind field, the research was carried out from the aspect of frequency stabilization technology. During the frequency stabilization process, measures were taken to eliminate the long-term drift and short-term jitter of the laser frequency. For the long-term drift of the laser frequency, a temperature control box for the seed laser was designed and developed, which greatly reduced the long-term laser frequency shift by controlling the temperature of the water bath. The laser frequency was stabilized within ± 50 MHz. For short-term jitter of the laser frequency, a frequency stabilization system with an iodine molecular absorption cell as the core device was adopted to accurately control the temperature of the iodine molecular absorption cell through semiconductor temperature control, with a temperature control accuracy of 0.03 ℃, the frequency stabilization accuracy was improved, and the laser frequency was further stabilized within ± 8 MHz to meet the design accuracy requirements within ± 10 MHz. Through the establishment of Doppler wind measurement lidar system, the launching laser frequency stabilization device was verified. The observation results of 4 consecutive sets of wind field show that the detection height of the system was 17 km, and most of the variances were below 4 m/s. It meets the requirements of wind lidar measurement indicators.
Due to the limitation of laser pulse width, traditional lidar cannot achieve shallow water measurement of tens of centimeters. A polarization lidar with dual Geiger-mode avalanche photodiodes (Gm-APD) was designed to achieve high-precision depth image of shallow water layer by using a wide laser pulse. The surface of the shallow water layer was smooth and had good polarization-maintaining characteristics, whereas the bottom surface was rough and had certain depolarization characteristics. According to this feature, by emitting horizontal linearly polarized light, a polarization beam splitting prism was used in the receiving system to separate the front and rear surface signal lights, and then they were detected by two Gm-APDs respectively. The system was not limited by the pulse width of signal light, and made full use of the dead time mechanism of Gm-APD to realize the depth measurement of ultra-thin shallow water. Using the principle of polarization transmission of the Stokes parameter and Muller matrix, the principle of light splitting of the dual Gm-APD polarization lidar was theoretically analyzed. Signal restoration & center-of-mass algorithm method was used to restrain the range walk error to obtain high range precision. The thin shallow water layer had a gradient from 4.5 cm to 8 cm in depth, and the bottom surface of which was covered with black and white sand. In the experiment, a 6 ns width laser pulse was used to obtain a high-precision depth image of the thin shallow water layer at the detection distance of 5 m with the accuracy of 0.8 cm. This effectively verifies the feasibility of the scheme. This scheme can provide certain reference for the measurement of shallow ocean water layer in in airborne lidar bathymetry systems.
A Rayleigh scattering lidar for measuring the atmospheric density and temperature has been deployed at Zhongshan Station (69.4° S, 76.4° E), Antarctica. Lidar transmitter was a frequency doubled Nd:YAG laser with ~400 mJ pulse energy and 30 Hz repetition rate. A telescope with 0.8 m diameter pointing to the zenith direction served as the lidar receiver. This lidar was capable of profiling the density and temperature in the Upper Stratosphere and Lower Mesosphere (USLM) region. At the vertical resolution of 300 m and the temporal resolution of 30 min, the lidar measurement uncertainties, mainly due to the photon noise, were calculated to be within 1.5% and 1 K for density and temperature, respectively. Since March 2020, this lidar has been routinely operated at Zhongshan station for exploring the atmospheric density and temperature variations and wave propagation characteristics in the polar USLM region.
Though the measurement precision of the traditional LiDAR is gradually increased, it is still limited by the quantum noise of the optical field and the extra noise introduced by the detection process. To improve the detection performance of LiDAR, a new scheme using quantum squeezed state light field as local oscillator of LiDAR was proposed and the key factors for improving the detection precision of LiDAR was analyzed. Then an integrated low-noise squeezed light field was prepared, and the experiment of LiDAR Doppler information measurement was carried out. The results show that the Doppler information detection sensitivity by using quantum squeezed state is 3 dB higher than the traditional scheme of the coherent state light field as the local oscillator, which paves a research path for the detection of weak signals such as Doppler information.
Lidar has the advantages of long detection distance, high detection accuracy, high temporal and spatial resolution, and diverse detection parameters, which is an important method for atmospheric detection. Compared with the lidar working at visible wavelength, 1.5 μm atmospheric detection lidar has unique advantages, including eye-safe, all-fiber structure, able to penetrate clouds and fog, and 24 hour continuous detection. In 2015, the world's first single-photon frequency up-conversion aerosol detection lidar was born, achieving continuous detection of aerosol distribution with high spatial and temporal resolution at a distance of 6 km. The representative development of 1.5 μm atmospheric detection lidar in recent years was introduced. In terms of detection methods, direct detection lidar and coherent detection lidar were introduced respectively. Direct detection lidar includes single-photon frequency up-conversion aerosol detection lidar, single-photon frequency up-conversion wind measurement lidar, superconducting dual-frequency wind measurement lidar, superconducting polarization lidar, multimode fiber-coupled single-photon cloud detection lidar and single-photon sensitivity free-space distributed spectral detection lidar. Coherent lidar includes the polarization detection coherent lidar, Golay coding coherent wind lidar and the atmospheric multi-parameter detection coherent lidar. The detection targets of these lidars include atmospheric aerosol (cloud), visibility, polarization, wind profile, gas concentration, precipitation (raindrop size distribution), etc.. Some of them have the ability to detect multiple parameters simultaneously.
A vehicle-mounted sodium fluorescence scattering Doppler lidar and a vehicle-mounted 532 nm Rayleigh scattering Doppler lidar have been developed for wind and temperature observations in near space region. Three-frequency-ratio Doppler measurement method was used to obtain wind and temperature from 80 km to 100 km in the sodium fluorescence scattering Doppler lidar. And Iodine absorption line edge technique was employed to measure wind speed below 70 km, integration method was used to measure temperature below 80 km in the 532 nm Rayleigh scattering Doppler lidar. When the range resolution was 1 km and the temporal resolution was 1 h, the uncertainties of measured temperature and wind speed were about 0.2 K and 0.4 m/s at 40 km, 1.5 K and 5.5 m/s at 70 km, 0.3 K and 1.0 m/s at 92 km. The two lidars have carried out long-term observations in Beijing, Qinghai, Gansu. The data are used for near space environmental characteristics researches.