View fulltext
View fulltext
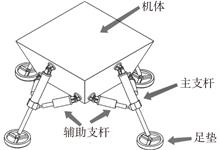
Based on a four-legged walkable lander with a series-parallel hybrid leg-foot mechanism, the Newton-Euler method is applied to study the dynamic modeling of the joint energy consumption problem during walking in order to understand the problem of joint energy consumption during walking. Firstly, the D-H method is used to establish the joint coordinate system of the series-parallel mixed leg-foot mechanism, and the forward kinematics and inverse kinematics are derived. Secondly, on the basis of the kinematic model, the Newton-Euler method is used to establish a full-state dynamic model of the lander, which takes the relative trajectory of the foot end as the input to obtain the change curve of the force in each joint during the movement of the lander. Finally, the five-order spline interpolation method is used to plan a section of motion trajectory, and the ADAMS simulation software is used to simulate the virtual prototype of the lander. It is verified that the theoretical calculation value of the dynamic model and the numerical simulation result of the virtual prototype have the same change trend, which proves the validity of the model and can be used as the basis for the establishment and optimization of subsequent energy consumption model.
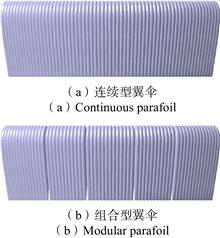
With the increasing demand for aerospace recovery system applications, the recovery mass is increasing, the requirement of parafoil area is becoming increasingly high, and oversize parafoils are paid more and more attention. However, there is not enough research on oversize parafoil at home and abroad. This paper intends to establish the physical model of oversize modular parafoil and oversize continuous parafoil. Based on the k-epsilon turbulence model, the CFD method is deployed to calculate the aerodynamic features of continuous parafoil and modular parafoil under the conditions of no pull-down, single side pull-down and double side pull-down respectively. Results show that there is obviously air supplement in the modular parafoil, which can improve the flow separation, and increase the stall angle of attack. Therefore, the oversize modular parafoil are more suitable for the flight mission with high attack angle and have a wider range of applications. This paper can provide some reference for the selection of oversize parafoils in the future.
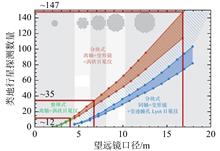
Large aperture space optical telescope is a significant scientific instrument to achieve high resolution remote sensing and high sensitivity detection. The traditional monolithic space telescope with an aperture of more than four meters will be difficult to break through the limitation of the effective envelope of the fairing of the existing launch vehicle. The segmentation technology can maximize the aperture under the premise of satisfying the carrying capacity, which is the best choice to solve the high resolution and high information collection ability of the current telescope. The research status of the segmented space telescope technology is reviewed from the deployment form, the types and characteristics of the segmented space telescope in the technical realization route are summarized, and technical connotation and realization methods are analyzed for the high-precision mechanism development technology, robot intelligent assembly technology, wavefront detection and control technology and ultra-light segmented mirror technology, respectively. Finally, facing the future vision goal, the technical development of the segmented space telescope is prospected.
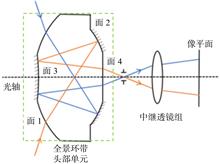
The panoramic band optical system has been widely used in the field of ultra-large field of view optics due to the characteristics of real-time imaging around the view range. For the traditional panoramic ring optical system integrating the refraction and reflection surfaces in a block lens, the light is repeatedly folded and reflected inside the lens to limit the size reduction of the head unit. Moreover, the infrared lens material has high density, low transmittance, and poor refractive index temperature stability, which is contradictory to the needs of high stability and lightweight optical remote sensors. Based on the aberration theory, the initial structure design method of the head unit of the infrared optical system with a panoramic ring and two mirrors is discussed in this paper. Q-Type aspherical surface was introduced into the panoramic head unit to increase the optimization variables. A panoramic band infrared optical system with two mirrors as the head unit is designed to describe the difficulty in aspherical surface processing. The modulation transfer function of the system is better than 0.5 at Nyquist frequency (20 lp/mm). The energy concentration of full-field pixels (within 25 μm×25 μm) is better than 65%, and the image quality evaluation results show that the image quality is good. This design has great improvement in reducing the size of the system and improving the efficiency of optical design optimization and meets the application requirements of real-time imaging with large field of view.
Railway disaster monitoring and evaluation by using satellite remote sensing technology is of great significance for ensuring the safety of railway construction and operation, and enhancing railway disaster prevention, reduction, and relief capabilities. Analyzing the current problems in the application of satellite remote sensing for railway disasters, combined with the development of satellite remote sensing in China and the actual emergency management work in the new era, this paper explores the practical application requirements of satellite remote sensing technology in the entire process of railway disaster management, including disaster reduction, preparedness, emergency response, and recovery and reconstruction. Aiming at the main disasters affecting railway safety, the application methods and capabilities of satellite remote sensing monitoring and evaluation technology in railway emergency management are analyzed. With regard to typical examples of disasters such as floods, geology, forest fires and snowstorms, technical processes for monitoring and assessing railway disasters by satellite remote sensing have been established, and the effects of satellite remote sensing on railway disaster emergency management have been further analyzed. The results show that satellite remote sensing technology can realize pre-disaster risk monitoring and post-disaster loss evaluation of major railway disasters, and can effectively support the whole process of railway disaster management. The integrated application of multiple means and dynamic monitoring can improve the decision support effect of remote sensing information, which has a broad application prospect in the emergency management of railway disasters.
With the continuous increase in the operational mileage of railways in our country, the external environment of railways is becoming increasingly complex. Hazards in the external environment of railways, mainly consisting of color steel tile houses, dust-proof nets, plastic greenhouses, ground films, and plastic waste, emerge frequently. These hazards, which frequently lead to major railway traffic accidents, have become a significant constraint on the safe operation of railways. The efficient monitoring of hazards in the external environment of railways is a crucial prerequisite for governance, and remote sensing technology is currently the optimal means to achieve large-scale, low-cost monitoring of external environmental hazards in railways. In this regard, this paper systematically reviews four categories of remote sensing monitoring technologies: optical remote sensing, synthetic aperture radar, lidar, and ground-based video surveillance. The paper discusses the advantages, limitations, and current applications of these technologies. It analyzes two types of monitoring and identification methods: those based on artificial features and those based on deep learning, highlighting their characteristics and shortcomings. Finally, the paper looks forward to the intelligent monitoring of railway external environmental hazards based on the fusion of multi-source remote sensing data at multiple levels, the construction of precise identification models for railway external environmental hazards, and knowledge-guided intelligent dynamic monitoring of railway external environmental hazards.
With the deepening of the application of remote sensing technology in the railway industry, the application of multi-source remote sensing to observe the state of railway facilities has become a hot topic in academia and industry. In order to solve the problem of quantitative monitoring of the state of railway facilities, the settlement information of railway facilities can be obtained by applying InSAR technology, and the analysis and extraction of settlement information often rely on the attributes such as the type and location of the facilities, otherwise the settlement of specific railway facilities cannot be further quantitatively evaluated. In this paper, satellite-based optics and microwave remote sensing images are used to automatically extract railway facilities through target detection technology, and the correspondence between microwave scattering points and categories and locations in the optical properties of railway facilities is determined. The results show that the extraction accuracy of railway facilities is increased by 2.8% compared with that of optical remote sensing images, and 9.2% is higher than that of SAR images, at the same time, the facility extraction results are more accurate in terms of location compared to SAR image extraction results.It can reduce the impact of driving safety caused by incorrect monitoring of facilities, and provide a reference for the quantitative monitoring of deformation of InSAR railway facilities.
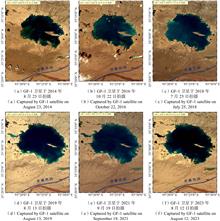
Glacial lake outburst floods (GLOFs) are a serious mountain natural disaster, threatening residents and important infrastructure such as railways and highways in China’s high-altitude regions. Automatic and efficient glacial lake remote sensing mapping methods are the basis for glacial lake disaster assessment, monitoring and early warning. However, the existing automatic mapping method is difficult to achieve the accuracy of traditional manual and semi-automatic ice lake extraction methods in actual ice lake extraction applications, and it still needs to be further improved. This study is based upon the original U-Net model and incorporates polar self-attention mechanisms at various bridge connections. The input image features with high resolution are maintained both spatially and channel-wise and refined through the synthesis of nonlinear output features. Then, an improved U-Net glacial lake remote sensing deep learning mapping method is constructed and successfully applied in key areas of the plateau railway. The results are as follows. 1) Compared with three classical models, namely PSPNet, DeepLabV3+, and the original U-Net, the improved model has improved performance on various metrics in the glacial lake prediction dataset, with the precision, recall, IoU, and F1 values reaching 0.972 5, 0.966 5, 0.940 8, and 0.969 4, respectively. Relative to the original U-Net network, the precision, recall, IoU, and F1 values of the revised model have been increased by 5.01%, 6.05%, 10.73%, and 5.53%, respectively. 2) Using Landsat-8 satellite remote sensing data, the improved model is applied to automatically and efficiently extract glacial lake information in the Palong Zangbo and Yigong Zangbo case study areas from 2013 to 2022. The mapping glacial lakes in 2020 have an overall accuracy of 98.16% and an overlap rate of 96.66% with the user-interactive mapped reference data, meeting the research requirements for GLOF assessment and monitoring. This method can be used in the practice of glacial lake disaster prevention and control in major engineering projects such as railways.
Feature point extraction and matching are crucial aspects of remote sensing image processing. Currently, most mature algorithms are designed for remote sensing images of Earth’s surface, with little consideration for the imaging conditions and the influence of the detection platform on spatial target images. As a result, the quality of feature point matching for spatial target images is often poor. To address the issue of low matching accuracy for spatial targets, this paper proposes a clustering-based feature point matching algorithm. First, feature points are extracted and described based on the repetitive weak textures of spatial targets. Then, clustering is performed using the spatial positions of the feature points, and matching is carried out for the clusters of feature points. Subsequently, the main direction of each feature point cluster is adjusted by subtracting the overall direction of the target. This adjustment is used to further group the points within each cluster, facilitating feature point matching. Finally, outliers are eliminated using the nearest neighbor-to-second-nearest-neighbor ratio method and the Random Sample Consensus algorithm (RANSAC). Simulation experiments with imaging data using this feature point matching method demonstrate that, for spatial target images, clustering-based feature point matching outperforms direct matching. The improvement in the number of matches can reach up to 50%, and the reprojection error is better than 1/4 pixel. The method proposed in this paper utilizes various commonly used feature descriptors, significantly enhancing the quantity and accuracy of feature point matching for spatial target images.
Aiming at the problem of intricate road shape and structure in high-resolution remote sensing images, where narrow and small roads are extracted incorrectly or omitted, a lightweight remote sensing image road extraction method based on Atrous Space Pyramid Pooling and Attention Mechanism is proposed. Firstly, based on the original HRNet network, multi-scale road information fusion is realized by introducing the ASPP. Secondly, the Squeeze and Excitation channel attention mechanism (SE-networks) is introduced to enhance the quality of network feature representation. Finally, using deep separable convolution to improve the network residual module to realize the model lightweight and reduce the complexity of model calculation. Experimental results on the publicly available dataset show that the accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score and the MIoU of the proposed algorithm was improved respectively by 5.35%, 2.15%, 4.1%, 3.15% and 14.34%, compared with the original HRNet network, and reduce the number of parameters by 35.6%. Compared with other networks, the algorithm highlights the characteristics of small roads, and the prediction results have good continuity and integrity. As the small size, the proposed model is easier to deploy in real-time detection equipment. The proposed model effectively reduces the road extraction fault and missing, implements a stronger adaptability, higher segmentation accuracy, more lightweight multi-scale road semantic segmentation algorithm.
Aiming at the problems of high cost and low precision of traditional bare rock extraction methods in karst areas, this paper constructs a bare rock extraction method based on improved DeepLabV3+. This method first uses CA-DC-MobileNetV3 to replace DeepLabV3+ backbone network Xception in the encoder for feature extraction, which greatly reduces the amount of model parameters. Secondly, the features extracted by the encoder are enhanced through the feature pyramid network and the coordinate attention mechanism to obtain more small target information and reduce the loss of image details. Finally, in the atrous spatial pyramid pooling module, the features of the convolutional layers with different dilation rates are fused to improve the utilization of information. The results show that the method in this paper performs best in the bare rock extraction tasks in different scenarios, the number of model parameters is about 1/13 of that of DeepLabV3+, and the intersection ratio and F1-Score are 72.46% and 84.04% respectively. Compared with the DeepLabV3+ model, the above two indicators have improved by 4.62 and 3.19 percentage points, respectively, and are superior to other commonly used semantic segmentation models, improving the accuracy of bare rock extraction.
Accurate and efficient building information extraction from high-resolution remote sensing images is of great significance for land planning and mapping. In recent years, great progress has been made in building information extraction based on convolutional neural networks. However, there still exists the problems that the advanced semantic features of the images are not sufficiently utilized and it is difficult to obtain detailed and high-precision segmentation images when processing high-resolution remote sensing images. To solve the above problems, a deep learning network architecture, Atrous Space and Channel Perception Network (ASCP-Net), is proposed for automatic building extraction. The Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) and Spatial and channel-wise Attention (SCA) modules are integrated into the encoder-decoder structure. Multi-scale context information is captured and aggregated through the ASPP module. Meanwhile, the SCA module is used to selectively enhance the more useful information in specific locations and channels, and the high and low-layer feature information is input into the decoding network to achieve efficient building information extraction. Experiments on the WHU Building Dataset show that, for the overall accuracy and F1 score, the proposed method reachese 97.4% and 94.6% respectively, and can obtain clearer building boundaries compared with other models, especially for the extraction of incomplete buildings at image edges, and effectively improving the accuracy and integrity of building extraction.
The research on real-time automatic identification technology for landslides is of great significance for protecting people’s lives, property, and ecological safety. It can solve the problem of poor timeliness in landslide risk investigation and prevention due to the lack of timely identification of landslides at present. Considering the changes of vegetation coverage index (NDVI) as one of the important criteria for landslide detection, the article combines NDVI change detection technology, automatic threshold selection algorithm, and morphological technology to achieve real-time and automatic recognition of landslides. Compared with existing research algorithms, Compared with existing research algorithms, it adds some important parameters in the automatic landslide recognition process (such as NDVI, mountain shadows, etc.). The adaptive automatic threshold selection algorithm reduces manual involvement and significantly enhances its timeliness while ensuring high recognition accuracy. This article is based on two optical images and takes a certain area in Mentougou District, Beijing as the research area. Real time and automatic recognition of landslides in this area from September 7, 2021 to September 7, 2022 is carried out, using the results of manual visual interpretation as the correct standard. The recognition results of the article are compared with their accuracy, and the landslide detection rate reached 92.31%, proving the accuracy and high efficiency of this method for detecting landslides. Finally, the method is applied to the central part of Dujiangyan City, which further proves the effectiveness and generalization ability of the method.
Aiming at the problem that the traditional threshold algorithm have low accuracy of cloud detection due to spectral differences caused by characteristic differences such as cloud diurnal variation, cloud type, cloud phase state, and cloud optical thickness, This paper proposes a cloud detection algorithm model that takes into account optimal selection of samples, coupled with the physical threshold method and machine learning, and uses the data of Himawari-8 for daytime cloud detection. Through sample optimization selection, the samples include cloud features in different situations as much as possible, providing a good sample basis for the machine learning model and increasing the model generalization ability. At the same time, in addition to considering factors such as albedo, brightness temperature, brightness temperature difference, and zenith angle, the input features also add cloud recognition results based on the physical threshold method based on albedo and brightness temperature difference. And cloud detection is carried out based on the Extremely randomized trees (ET) model. The results show that cloud detection cross-validation accuracy of the model is 96.41%, with the total omission error of 2.08% and total commission error of 0.91%, respectively. The results are compared with the product data based on CALIPSO with an overall detection accuracy of 97.1%.
The use of satellite remote sensing inversion of suspended matter concentration in water bodies is of great significance in water quality monitoring and protection. In the process of suspended matter concentration inversion, it is technically difficult at present to avoid or minimize the interference of chlorophyll-a and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in the water body. Aiming at the "Sustainable Development Goals scientific satellite 1" (SDGSAT-1) MII sensor and using the Hydrolight radiative transfer model, the article theoretically excavates the inversion factor that is only strongly related to suspended matter, constructs an inversion model of Lake Taihu suspended matter concentration suitable for MII images, and applies the model to both measured and sensing image data for verification. The results showed that: the inversion factor$ R'{\text{(}}{B_{\text{5}}}{\text{/}}{B_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}} $ was strongly correlated with the suspended matter concentration, while weakly correlated with chlorophyll a and CDOM concentration; the power function model constructed by using $ R'{\text{(}}{B_{\text{5}}}{\text{/}}{B_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}} $ as the inversion factor was the optimal inversion model; the power function model was applied to the measured data and the SDGSAT-1 MII data of Lake Taihu on May 4, 2022, respectively, and the two verification experiments showed that the inversion results and field measurement results had a strong consistency, and the applicability of the power function model was good. This research can provide a technical reference for the SDGSAT-1 satellite in monitoring suspended matter concentration in lake water bodies, water resources assessment , and protection, etc.