View fulltext
View fulltext
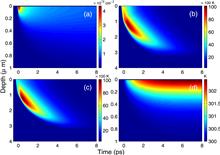
The ultrafast dynamic process in semiconductor Ge irradiated by the femtosecond laser pulses is numerically simulated on the basis of van Driel system. It is found that with the increase of depth, the carrier density and lattice temperature decrease, while the carrier temperature first increases and then drops. The laser fluence has a great influence on the ultrafast dynamical process in Ge. As the laser fluence remains a constant value, though the overall evolution of the carrier density and lattice temperature is almost independent of pulse duration and laser intensity, increasing the laser intensity will be more effective than increasing the pulse duration in the generation of carriers. Irradiating the Ge sample by the femtosecond double pulses, the ultrafast dynamical process of semiconductor can be affected by the temporalinterval between the double pulses.11474129), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education in China (grant no. 20130061110021) and the Project 2015091 Supported by Graduate Innovation Fund of Jilin University.
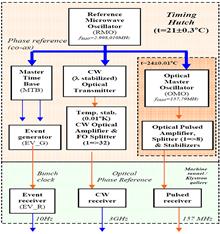
FERMI, the seeded free electron laser (FEL) in operation in Italy, is providing the User Community with unique fully coherent radiation, in the wavelength range 100–4 nm. FERMI is the first FEL fully synchronized by means of optical fibers. The optical timing system ensures an ultra-stable phase reference to its distributed clients. Several femtosecond longitudinal diagnostics verify the achieved performance; the bunch length monitor (BLM) and the bunch arrival monitor (BAM) will be presented in this paper. Feedback systems play a crucial role to guarantee the needed longterm electron beam stability. A real-time infrastructure allows shot-to-shot communication between front-end computers and the servers. Orbit feedbacks are useful in machine tuning, whereas longitudinal feedbacks control electron energy, compression and arrival time. A flexible software framework allows a rapid implementation of heterogeneous multiinput–multi-output (MIMO) longitudinal loops simply by selecting the appropriate sensors and actuators.They also acknowledge all funding sources that made the FERMI construction and operation possible, among others: the Italian Minister of University and Research (MIUR),the Regione Autonoma Friuli Venezia Giulia, the European Investment Bank (EIB), the European Research Council (ERC) and the European Commission (EC).
Laser drivers are an enabling factor to inertial confinement fusion, because laser diodes must be used instead of flash lamps. We discuss the limitations of laser diode arrays and show what steps the industry is taking. The pump power requirements of large-scale projects such as LIFE or HiPER are within reach of semiconductor laser diode assemblies. Pulsed light output powers per laser bars have been around 300Wper bar, as in the Jenoptik 940 nm bars previously used for pumping the Yb:YAG slabs in the DiPOLE project. By redesigning the semiconductor laser structures 500W per bar is now commercially available for 808, 880 and 940 nm pump wavelengths. The construction of one inertial fusion power plant will require an amount of semiconductor laser chips in excess of the current annual production by two orders of magnitude. This adds to the engineering task of improving the device characteristics a challenge to production capacity. While the industry benefits from the recent boost in solid-state lighting that acts as a technology driver, cooperation between manufacturers will be imperative, and to this end we propose standardization efforts.
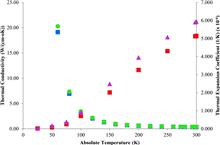
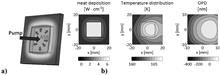
Using cryogenic laser technology, it is now possible to design and demonstrate lasers that have concomitant high average and peak powers, with near-diffraction-limited beam quality. We refer to these new laser systems as HAPP lasers. In this paper, we review important laser crystal materials properties at cryogenic temperature, with an emphasis on Yb lasers, and discuss the important design considerations, including the laser-induced damage threshold, nonlinear effects and thermal effects. A comprehensive model is presented to describe diode pulsed pumping with arbitrary duration and repetition rate, and is used with the Frantz–Nodvik equation to describe, to first order, the performance of HAPP laser systems. A computer code with representative results is also described.
We present the workflow of the design, realization and testing of deformable mirrors suitable for high power diode pumped solid-state lasers. It starts with the study of the aberration to be corrected, and then it continues with the design of the actuators position and characteristic. In this paper, we present and compare three deformable mirrors realized for multi-J level laser facilities. We show that with the same design concept it is possible to realize deformable mirrors for other types of lasers. As an example, we report the realization of a deformable mirror for femtosecond lasers and for a CW CO2 laser.Regional Development Fund, the European Social Fund and the state budget of the Czech Republic (project HiLASE: CZ.1.05/2.1.00/01.0027, project DPSSLasers: CZ.1.07/2.3.00/20.0143). This research was partially supported by the grant RVO 68407700.
Fast magnetic field annihilation in a collisionless plasma is induced by using TEM(1,0) laser pulse. The magnetic quadrupole structure formation, expansion and annihilation stages are demonstrated with 2.5-dimensional particle-in-cell simulations. The magnetic field energy is converted to the electric field and accelerate the particles inside the annihilation plane. A bunch of high energy electrons moving backwards is detected in the current sheet. The strong displacement current is the dominant contribution which induces the longitudinal inductive electric field.were provided by the MetaCentrum under the program LM2010005, IT4Innovations Centre of Excellence under projects CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0070 and LM2011033 and by ECLIPSE cluster of ELI-Beamlines. The EPOCH code was developed as part of the UK EPSRC funded projects EP/G054940/1.
A new specially correlated partially coherent beam named nonuniform multi-Gaussian correlated (NMGC) partially coherent beam is introduced. The correlation functions of such beam in x and y directions are different from each other, i.e., nonuniform correlation function in one direction and multi-Gaussian correlated Schell-model function in the other direction. The propagation properties of an NMGC partially coherent beam in free pace are demonstrated, and we find that the intensity distribution of such beam exhibits self-focusing and self-shifting effect in one direction and self-shaping effect in the other direction on propagation. The correlation-induced self-focusing and self-shaping effect will be useful in some applications, where the high power and shaped laser is required, such as material thermal processing and laser carving.of China under grant no. 11274005 and the project of the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
We demonstrate that the methodology of frequency-resolved optical gating (FROG) is applicable to time-resolved reflection spectroscopy of a plasma mirror in the vacuum-ultraviolet (VUV) region. Our recent study [R. Itakura et al. Opt. Express 23, 10914 (2015)] has shown that a VUV waveform can be retrieved from a VUV reflectionspectrogram of a plasma mirror formed on a fused silica (FS) surface by irradiation with an intense femtosecond laser pulse. Simultaneously, the increase in the reflectivity with respect to the Fresnel reflection of the unexcited FS surface can be obtained as a time-dependent reflectivity of the plasma mirror. In this study, we update the FROG analysis procedure using the least-square generalized projections algorithm. This procedure can reach convergence much faster than the previous one and has no aliasing problem. It is demonstrated that a significantly chirped VUV pulse as long as 1 ps can be precisely characterized.(Grant No. ZE26B-27).
We produced 5-mJ, 6.5-fs visible pulses at a repetition rate of 1 kHz using filamentation in a gas cell filled with kryptonfollowed by spectral selection and phase compensation by a combination of dielectric mirrors. The visible pulses have a smooth spectrum from 520 to 650 nm with a shot-to-shot stability in each spectral component of better than 2% (standard deviation). This pulse compression scheme is simple and robust, and can be easily integrated into intense ultrashort-pulse laser systems.Program for Leading Graduate Schools (MERIT) by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.