View fulltext
View fulltext
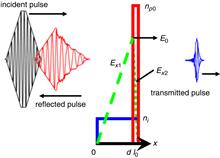
The effects of ion motion on the generation of short-cycle relativistic laser pulses during radiation pressure acceleration are investigated by analytical modeling and particle-in-cell simulations. Studies show that the rear part of the transmitted pulse modulated by ion motion is sharper compared with the case of the electron shutter only. In this study, the ions further modulate the short-cycle pulses transmitted. A 3.9 fs laser pulse with an intensity of 1.33×1021 W cm-2 is generated by properly controlling the motions of the electron and ion in the simulations. The short-cycle laser pulse source proposed can be applied in the generation of single attosecond pulses and electron acceleration in a small bubble regime.
An overview of the Czech national R&D project HiLASE (High average power pulsed laser) is presented. The project focuses on the development of advanced high repetition rate, diode pumped solid state laser (DPSSL) systems with energies in the range from mJ to 100 J and repetition rates in the range from 10 Hz to 100 kHz. Some applications of these lasers in research and hi-tech industry are also presented.
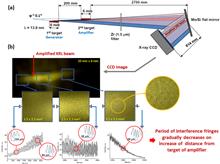
In the far field of the intensity distribution of the beam delivered by a two-stage transient–collisional excitation X-ray laser (XRL), a non-expected interference pattern that is stable from shot to shot has been discovered. It is demonstrated that the interference is caused by the emergence of an imaginary source in the amplifying plasma, which is phase matched to the radiation of the generator. The observed phenomenon is called an X-ray coherent mirage. To explain the obtained results, a new theoretical approach is developed. The basic essential conditions for formation of the X-ray mirage are formulated, and possible applications are discussed. This paper details the experiments, including the formulation of the necessary and sufficient conditions for formation of the X-ray mirage, and possible applications are discussed.
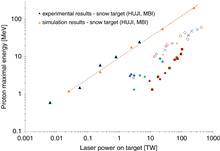
This paper presents a new method to control the position of a micro-column snow target. This target enables the measurement of the mean electron density of the pre-plasma created by a pre-pulse with different time delays. This research will allow a better understanding of the generation of fast protons from the interaction between a structured pre-plasma and a high intensity laser.
A short overview of the theory of acceleration of thin foils driven by the radiation pressure of superintense lasers is presented. A simple criterion for radiation pressure dominance at intensities around 5×1020 W cm-2 is given, and the possibility for fast energy gain in the relativistic regime is discussed.
We develop a splicing technology of Ti:sapphire crystals for a high-energy chirped pulse amplifier laser system that can suppress the parasitic lasing to improve the amplification efficiency compared to a large-size single Ti:sapphire crystal amplifier. Theoretical investigations on the characteristics of the amplifier with four splicing Ti:sapphire crystals, such as parasitic-lasing suppression and amplification efficiencies, are carried out. Some possible issues resulting from this splicing technology, including spectral modulation, stretching or splitting of the temporal profile, and the sidelobe generation in the spatial domain (near field and far field), are also investigated. Moreover, the feasibility of the splicing technology is preliminarily demonstrated in an experiment with a small splicing Ti:sapphire crystals amplifier. The temporal profile and spatial distribution of the output pulse from the splicing Ti:sapphire crystal amplifier are discussed in relation to the output pulse from a single Ti:sapphire crystal amplifier.
The use of the Laser MegaJoule facility within the shock ignition scheme has been considered. In the first part of the study, one-dimensional hydrodynamic calculations were performed for an inertial confinement fusion capsule in the context of the shock ignition scheme providing the energy gain and an estimation of the increase of the peak power due to the reduction of the photon penetration expected during the high-intensity spike pulse. In the second part, we considered a Laser MegaJoule configuration consisting of 176 laser beams that have been grouped providing two different irradiation schemes. In this configuration the maximum available energy and power are 1.3 MJ and 440 TW. Optimization of the laser–capsule parameters that minimize the irradiation non-uniformity during the first few ns of the foot pulse has been performed. The calculations take into account the specific elliptical laser intensity profile provided at the Laser MegaJoule and the expected beam uncertainties. A significant improvement of the illumination uniformity provided by the polar direct drive technique has been demonstrated. Three-dimensional hydrodynamic calculations have been performed in order to analyse the magnitude of the azimuthal component of the irradiation that is neglected in twodimensional hydrodynamic simulations.
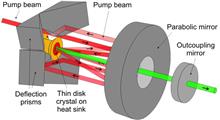
We present the results of performance modeling of a diode-pumped solid-state HiLASE laser designed for use in inertial fusion energy power plants. The main amplifier concept is based on a He-gas-cooled multi-slab architecture similar to that employed in Mercury laser system. Our modeling quantifies the reduction of thermally induced phase aberrations and average depolarization in Yb3C:YAG slabs by a combination of helium cryogenic cooling and properly designed (doping/width) cladding materials.