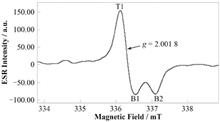
BackgroundGamma source irradiation is the most commonly used way at present for the equivalent dose (DE) determination of fossil samples in electron spin resonance (ESR) dating. However, it is facility-limited and time-consuming in many cases.PurposeThis study aims to establish the standardised growth curves (SGCs) of fossil enamel samples for determining the DE by ESR without gamma irradiation.MethodsFirst of all, we analyzed 20 tooth samples from the Late Pleistocene sites, and they exhibited similar dose response characteristics. Then, based on our preliminary work, we attempted to establish the SGCs of these Late Pleistocene fossil teeth using three different methods: (1) a simple method (fitting the natural dose points of fossil samples from Middle to Upper Pleistocene sites with exponential functions), (2) an average method (fitting the dose points with averaged ESR signal intensities), and (3) a representative sample method (establishing a SGC by using a representative sample). Finally, dose values obtained by each method were compared with those determined by the additive dose method (ADM).ResultsThe results of DE determined by the simple and average methods are close, with a deviation of less than 32% from the ADM results. The dose values obtained by SGC using the representative sample method generally agree with those of the ADM, with a deviation within 26%, which is the smallest among the three methods.ConclusionAlthough the uncertainties of the dose values obtained for the SGCs are not very close to those obtained using the ADM, it indicates the potential to quickly determine a more reasonable Dmax for irradiation, identify the possible intrusion of fossil samples, and analyze small or precious fossil samples.
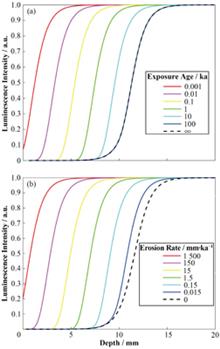
BackgroundRock surface luminescence dating has developed rapidly in the past decade. It has been widely used to obtain exposure ages and erosion rates of various rocks in archaeology, geology, and geography, such as stone artifacts, glacier bedrock, gravel, and bedrock fault surfaces. However, these is little study on the effect of parameters related to this method, such as attenuation coefficient μ, decay rate of the trapped charge at the rock surface σφ0ˉ, environmental dose rate D˙, and characteristic saturation dose D0 on exposure age and erosion rate results.PurposeThis study aims to quantitatively investigate the impact of relevant parameters on exposure age and erosion rate, and examine the limits of exposure age and erosion rate obtained by the method under different parameters.MethodsFirst, parameters that might have an impact on age and erosion rate results were determined through theoretical analyses. Then, the relationship among the parameters, depth of half saturation and exposure age (erosion rate) were studied using numerical simulations. The impact of each relevant parameter on exposure age and erosion rate was observed for varied parameter values. Finally, the dating limit was determined from the inflection point in the simulated profiles.ResultsThe smaller μ value is, the greater the rate of change in the depth of half saturation would be when increasing the same exposure time. However, the rate of change in the depth of half saturation remains constant for different σφ0ˉ values when the same erosion rate is increased.ConclusionsAmong the parameters, σφ0ˉ and, more remarkably, μ significantly affect the dating result. In general, D˙ and D0 have little effect on the exposure age and erosion rate; therefore, the differences in D˙ between the surface and interior of rocks may be ignored. The growth rate of depth of half saturation of granite gneiss is significantly higher than that of sandstone for the same exposure time increment. Therefore, light-colored rocks such as granite should be prioritized for collection during field work. The ranges of dating and obtaining erosion rate using this method are 10-3~102 ka and 10-2~103 mm?ka-1, respectively.
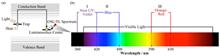
BackgroundLuminescence dating technology has made significant advancements in determining the chronology of archaeological materials subjected to low firing temperatures. However, the luminescence dating of archaeological materials subjected to high firing temperatures remains challenging.PurposeThis study aims to explore the luminescence emission spectrum characteristics and luminescence properties of high-firing temperature quartz to verify the feasibility of thermoluminescence (TL) signals from different bands in luminescence dating.MethodsFirstly, the high-firing temperature (about 950 °C) quartz extracted from pottery unearthed at the Lingjiatan archaeological site was taken as a case study, spectral measurement platform was established using a Ris? DA-20 luminescence dating instrument coupled with an Andor spectrometer and a charge-coupled device camera to analyze the luminescence spectral properties of archaeological quartz with high firing temperatures. Then, five filter combinations and two photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) were used to compare the TL and isothermal thermoluminescence (ITL) sensitivities of blue and red emissions. Kinetic parameters for Blue TL and Red TL were determined by deconvolving the glow curves with the general-order equation. Finally, exposure experiments were conducted on the Blue and Red TL using a solar simulator. The single aliquot regenerative dose (SAR) protocol was implemented to assess the applicability of the Blue TL-SAR, Blue ITL-SAR, Red TL-SAR, Red ITL-SAR, and optically stimulated luminescence (OSL)-SAR methods for dating archaeological quartz exposed to high temperatures during production or use.ConclusionsThe spectral analysis reveals that the archaeological quartz subjected to high firing temperature exhibits significant Red TL emissions at approximately 620 nm, which is correlated with the TL peak at 375 °C. This Red TL at 375 °C exhibits a marked insensitivity to light. The multi-wavelength TL, multiwavelength ITL, and conventional OSL dating results are consistent with the known radiocarbon age within the error range. This study demonstrates the potential feasibility of using luminescence signals of different wavelengths for chronological studies of archaeological materials subjected to high firing temperatures.
BackgroundCultural relics are precious and nonrenewable resources. Scientific dating is the key to research on cultural relics, and luminescence technology is an important method for dating ceramic cultural relics. Currently, the methods for dating ceramic cultural relics include the conventional thermoluminescence (TL) method and the TL predose method. Few reports on the use of optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) to determine the age of cultural relics are available.PurposeThis study aims to verify the reliability of the dating of porcelain cultural relics by luminescence method, and expand the method of dating porcelain cultural relics.MethodsThe conventional TL, TL predose, and OSL single-aliquot regenerative-dose (SAR) methods were employed to date an celadon glazed porcelain piece unearthed from the Qinglong Town ruins in Shanghai. Then, the dating results of three method were compared for applicability analysis.ResultsThe results indicate that the signal for the porcelain obtained using the conventional TL method is almost zero when the temperature is between 300 ℃ and 450 ℃, making it difficult to accurately calculate the equivalent dose. The ages of the TL predose and SAR methods are (1.16±0.05) ka and (1.35±0.05) ka, respectively, which are consistent within the error range.ConclusionsThe results of this study indicate that the OSL technique can be used to date porcelain cultural relics. For the celadon glazed porcelain piece examined in this study, the dating results of TL pre-dose and SAR methods are kept consistent.
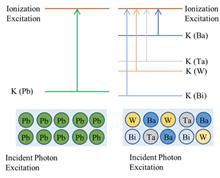
BackgroundLead-free/lead-composite nuclear radiation protection materials are becoming increasingly prevalent in military applications to safeguard the health and safety of military personnel. Currently, accurate measurement and tracing of the shielding performance of military nuclear radiation protective clothing is difficult.PurposeThis study aims to measure lead equivalent in nuclear radiation protection materials for satisfying the radiation performance evaluation requirements of international mainstream military radiation protective clothing.MethodsFirstly, a device to measure lead equivalence in protective clothing was developed. Then, the reference radiation mass for lead equivalence at a photon energy of 130 keV was determined using a combination of Monte Carlo simulation and experimental measurements. Finally, the shielding performances of a standard lead sheet were assessed using developed device under narrow beam conditions, and shielding performances of military nuclear radiation protective clothing materials produced by a few manufacturers were tested in the same conditions.ResultsEvaluation results show the relative expanded uncertainty of lead equivalent measurement results for standard lead sheet and military nuclear radiation protective clothing samples correspond to 4.2% (k=2).ConclusionsThis study identifies measurement conditions for subsequent performance tests of additional military nuclear radiation protective materials prior to delivery.
BackgroundIn thorium-based molten salt reactors (TMSRs), 233Pa is an important intermediate nuclide in the conversion chain of 232Th to 233U, and 233PaF5 can be effectively separated from carrier salt by low-pressure distillation. However, some of the metal fluoride is vaporized along with 233PaF5 simultaneously, and the evaporated fluoride may condense at different temperatures.PurposeThis study aims to investigate the condensation behavior of 233PaF5 and other key metal fluorides in the FLiBeZr molten salt during the low-pressure distillation process.MethodThe FLiBeZr molten salt containing PaF5 and various metal fluorides was low-pressure distillated to examine the condensation behavior of 233PaF5 and key metal fluorides at different temperatures. Then, the optimal temperature of key metal fluorides was evaluated and the separation characteristics between them and 233PaF5 were figured out. Finally, the separation factors of 233PaF5 and the other metal fluorides were calculated and compared with those of the entire low-pressure distillation process at the optimum condensation temperature of 233PaF5.ResultsThe results show that the optimal condensation temperature for 233PaF5 and 95NbF5 is within the range of 600~700 ℃, whilst it is within the range of 400~500 ℃ for 237UF4 and 95ZrF4. The comparison results show that there is no significant difference in the separation factors of 95NbF5 and 233PaF5, but the separation factors of 233UF4 and 95ZrF4 are increased by a factor of two to 20 times.ConclusionIt is confirmed that the separation coefficient is determined primarily by volatilization, but can be further improved by varying the condensation temperature.
BackgroundThe separation and removal of fission products and the recovery of carrier molten salt during nuclear fuel reprocessing in molten salt reactors reduces waste and facilitates useful substance recycling.PurposeThis study aims to separate and remove the rare earth (RE) fission products and recovery of carrier molten salts.MethodsFirstly, high temperature precipitation reactions of rare earth (RE = Ce, Nd, Sm, Eu, Y, Yb) and thorium fluorides were studied in LiF-BeF2 melt using sodium sulfide hydate (Na2S·5H2O) as the precipitant. Their removal ratios were subsequently compared under different conditions. Then, a combined precipitation distillation method was employed to further heat the precipitated mixed salt to 950 °C and distilled under vacuum conditions at a pressure of 10 Pa for 20 min. The content and removal ratio of rare earth Nd, as well as contents of oxygen and sulfur, in condensed collected salts were investigated after using above improved precipitation-distillation processing. Finally, further analysis of the composition of sediment was conducted using X-ray Diffraction (XRD), X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) and Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS).ResultsThe results demonstrate that RE removal ratios are less than 90% when the RE to precipitant ratio is 1:2 at 600 ℃ whilst the RE Nd content in the salt collected by condensation is reduced to 1.39×10-4 g?g-1, and its removal ratio is increased to 99.6% with further improved precipitation-distillation processing. Simultaneously, the oxygen and sulfur contents are 8.5×10-5 g?g-1 and 1.50×10-4 g?g-1, respectively. Analysis results of XRD, XPS and EDS indicate that the sediment mainly consists of RE sulfide and sulfur oxide.ConclusionsThis study confirms the feasibility of separating RE from waste salt using the sulfide precipitation method and that over 99% RE separation efficiency can be achieved using precipitation-distillation combined treatment. Therefore, this provides a reference method for purifying waste salt and realizing molten salt reuse.
BackgroundThe unfolding-synthesis technique is commonly used in digital pulse processing systems for nuclear radiation measurements.PurposeThis study aims to propose a novel flat-topped widened peak-shaping algorithm based on the pulse unfolding-synthesis technique is proposed.MethodsFirstly, the repetition and polynomials were utilizes to shape the digital pulses, and the nuclear pulse signal was unfolded into unit pulses series. Then, an impulse response system was employed to synthesize these unit pulses series to achieve the desired peak shape. Finally, the improved flat-topped peak-shaping algorithm was compared and analyzed against traditional filter shaping algorithms in terms of accuracy in amplitude extraction, interference resistance, and pile-up recognition.ResultsExperimental results demonstrate that, under the same shaping time, the energy resolution of the flat-topped peak-shaping algorithm for the γ characteristic peak of 137Cs is 7.2%, outperforming the trapezoidal, triangular, and Gaussian shaping algorithms. Additionally, it exhibits high counting rate performance.ConclusionsThe flat-topped peak-shaping algorithm of this study can effectively replace traditional pulse-shaping methods and be utilized for high-precision, high-count-rate γ spectroscopy measurements.
BackgroundWith the rapid development of nuclear energy and the wide application of nuclear technology, the radioactivity level of bodies of water has become a highly concerning issue for the public and governments, especially after the Fukushima nuclear accident in Japan.PurposeThis study aims to develop an online γ radioactivitymonitoring system based on 4G Remote Terminal Unit (4G-RTU) to meet the needs of online and emergency monitoring of water radioactivity.MethodsFirst, the γ-ray monitoring device based on sodium iodide detector, 4G-RTU, an integrated power supply waterproof and compression resistant floating device and corresponding software were employed to compose an online monitoring. Second, Qt programming control software was used to realize the remote control of the system, real-time radioactivity monitoring, and data upload. Finally, the original data obtained by the system were used to test the performance indicators, applicability, accuracy, and software functions to verify the practicability of the system.ResultsWithin the coverage of the 4G network, the system realizes remote control of equipment, real-time online monitoring, and data upload throughout the day. The detectable energy range of the system is 30~3 000 keV, and the energy resolution of the system for 137Cs at 662 keV is 7.3% with minimum detectable activity of 0.75 Bq?L-1. The spectral drift for 208Tl at 2 614 keV is 0.33%, and the linearity of the spectral energy is 0.999 970. The maximum value of energy spectrum stability is 2.28% for 7 h continuous operating, and the minimum value is -2.36%. The operating temperature range of the system is in the range of -5 ℃ to +50 ℃.ConclusionsThe on-line monitoring system meets the application demand and achieves the expected function. It has important popularization value and application prospects in the field of online radioactive monitoring of bodies of water such as oceans, lakes, and rivers.
BackgroundGaussian signals have symmetry and completeness, hence, the Gaussian filtering method is widely used in nuclear signal processing and radiation energy spectrum analysis. The mathematical description of Gaussian signals is relatively complex, which makes it difficult to construct digital Gaussian pulse shaping filters for nuclear pulse signal real-time processing. The commonly used digital quasi-Gaussian shaping algorithm in radiation measurement systems is derived from the differential equations of Sallen-Key and CR-(RC)n filters in analog nuclear electronics. However, its output shaping pulse signals have poor symmetry and problems such as undershoot occur when used in a single stage.PurposeThis study aims to explore the convolutional quasi-Gaussian pulse shaping filter algorithm and apply it to the processing of X-ray fluorescence measurement system experimental platform to obtain measured nuclear pulse data.MethodsFirstly, a convolutional quasi-Gaussian pulse shaping algorithm was implemented based on trapezoidal pulse signals, and bipolar pulse shaping was achieved after the initial convolution. Then, the second convolution was accumulated and summed to obtain left and right symmetric quasi-Gaussian shaping pulses. The digital recursive formula of the quasi-Gaussian pulse shaping algorithm was obtained using the Z-transform method, and the effectiveness of the algorithm and the influence of shaping parameters on the amplitude frequency characteristics were studied through simulation. Finally, quasi-gaussian shaping algorithm and trapezoidal shaping algorithm were applied separately to the offline process of measured nuclear pulse data from the X-ray fluorescence measurement system experimental platform.ResultsThe quasi-Gaussian pulse shaping filter has better high-frequency noise suppression performance compared to trapezoidal pulse shaping filters. With the increase of the values of shaping parameters na and nc, the filter passband decreases whilst the low-frequency amplitude relatively increases, and the high-frequency noise suppression effect is enhanced. However, this also leads to shaping pulse broadening and increases the probability of pulse pile-up.ConclusionsThe experimental results demonstrate that the quasi-Gaussian pulse shaping algorithm has better pile-up pulse separation ability. Under identical X-ray tube voltage and current conditions and peaking time, the energy resolution of the energy spectra obtained by both algorithms is fundamentally equivalent. However, the energy spectrum with quasi-Gaussian pulse shaping has a higher characteristic peak area.
BackgroundThe physical quantity concerned in the clinical application of 125I particle source brachytherapy is the 1 cm water absorbed dose rate D˙w,1 cm. However, there is no corresponding standard for this physical quantity in China. It is planned to develop an ionization chamber for the absolute measurement of the water absorbed dose rate of the 125I particle source as a standard device, hence the internal electric field of the ionization chamber must first be analyzed to obtain the most reasonable design scheme to satisfy the condition that the electric field intensity is uniformly distributed in the ionization chamber.PurposeThis study aims to simulate the internal electric field of the ionization chamber for the design of particle source water absorbed dose absolute measurement device.MethodsFirstly, the internal model of the ionization chamber was established by Maxwell software to simulate the distribution of electric field intensity under the six variables of the ionization chamber: with or without a protective electrode, different protective electrode ring width, different insulation ring width, different grid number, different grid shape and different grid thickness. Then, qualitative and quantitative analysis were carried out using finite element method. Finally, the influence of different variables on the distribution of electric field intensity in the ionization chamber of the absolute measurement of water absorbed dose of 125I particle source was obtained.ResultsAnalysis results show the ratio of the width of the guard electrode to the radius of the collector electrode must be not less than 2 for design of the ionization chamber. The edge effect at the edge of the collector is increased with width increment of the insulator ring, hence the width of the insulator ring should be reduced as much as possible. When the number of grid electrodes is 15, the variation of the electric field intensity can be reduced to about 1%. When the grid section is rectangular, the variation in electric field intensity is small compared with the circular and triangular grid sections. The larger the thickness of the grid, the more severe the edge effect at the edge of the grid, and the thickness of the grid should be reduced as much as possible.ConclusionsThe uniformity of the electric field can be effectively improved by increasing the number of grid electrodes. Results of this study is helpful to optimal design of the standard device for measuring the absolute water absorbed dose of 125I particle source.
BackgroundA heat pipe reactor is ideal for underwater unmanned vehicles (UUV) because it is simple, is compact, and has high inherent safety.PurposeA passive residual heat removal system that uses natural circulation to cool the adiabatic section of heat pipes was designed based on the characteristics of a new type of megawatt compact nuclear power plant with a heat pipe reactor.MethodsFirstly, based on the characteristics of 3.5 megawatt compact nuclear power plant for UUV, natural circulation of water was utilized to cool the adiabatic section of heat pipes. Then, the computational fluid dynamics software STAR-CCM+ was used to simulate and analyze the heat removal capacity of the passive residual heat removal system with different geometric parameters, made it conservatively meeting the demand of maximum residual heat removal power.Results & ConclusionsThe results show that a baffle around the adiabatic section of heat pipe bundle is beneficial to reduce the maximum temperature of the fluid. The widths of the inlet and outlet of the baffle have almost no effect on the heat removal capacity, while extending the lower part of the baffle is unfavorable to natural circulation. When the axial length of the emergency cooling chamber is 160 mm, it can conservatively meet the maximum residual heat power of 0.14 MW. The maximum fluid temperature is 288 ℃, which is lower than the boiling point under working pressure, and normal operation is possible in ambient temperatures ranging from 5 ℃ to 25 ℃.
BackgroundThe accuracy of transient thermal hydraulic parameter prediction of reactor cores under various working conditions directly affects reactor safety. Mass flow rate and temperature are important parameters of core thermal hydraulics, which are often modeled as time-series prediction problems.PurposeThis study aims to solve the accuracy problem of continuous prediction of core thermal hydraulic parameters under instantaneous conditions and to test the feasibility of a gated cycle unit based on the attention mechanism in core parameter prediction.MethodsThe 1/2 full core model of China Experimental Fast Reactor (CEFR) core was taken as the research object. The subchannel SUBCHANFLOW program was employed to generate the time series of transient core thermal hydraulic parameters. The gated recurrent unit (GRU) model based on soft attention was used to predict the mass flow and temperature time series of the core.ResultsThe results show that, compared with the adaptive radial basis function (RBF) neural network, the GRU network model with soft attention offers better prediction results. The average relative error of temperature is <0.5% when the step size is 3, and the prediction effect is quite good within 15 s. The average relative error of mass flow rate is <5% when the step size is 10, and fairly good prediction effect is achieved in the subsequent 12 s.ConclusionsThe model constructed in this study not only exhibits higher prediction accuracy in the continuous prediction process but also captures the trend characteristics in the dynamic time series, which is of considerable value for maintaining reactor safety and effectively preventing nuclear power plant accidents. The GRU model based on soft attention can provide continuous prediction for a period of time under transient reactor conditions, providing a reference value in engineering applications and improving reactor safety.
BackgroundIn thermal pipelines of nuclear power systems, thermal stratification is a common phenomenon that can cause stress concentration and deformation of pipeline structures, thereby leading to safety hazards. A stagnant branch pipe is connected to the main coolant pipe, and a large temperature difference exists between the fluid in the pipe and the coolant in the main pipe of the primary circuit. Due to factors such as turbulent flow penetration and valve leakage, thermal stratification is prone to occur in the branch pipe.PurposeThis study aims to analyze the temperature change characteristics and flow characteristics of thermal stratification in stagnant branch pipes and provide a theoretical basis for subsequent experimental research and stress analysis.MethodsFirstly, a stagnant branch pipe model was established, and numerical simulation of thermal stratification phenomenon in stagnant branch pipes was conducted using FLUENT 2022 to analyze the temperature variation characteristics of the pipe wall and the distribution characteristics of the flow field inside the pipe. Then, the SST k-ω model was used to perform three-dimensional numerical simulation of the thermal stratification of stagnant branch pipes, with a leakage flow rate of 0.062 kg·s-1, leakage temperature of 488.15 K, and leakage pressure of 6 MPa.ResultsThermal stratification is prone to occur in horizontal pipe sections. Without insulation measures and a large pipe diameter, thermal stratification can be exacerbated, while the curved section can effectively reduce the temperature difference of the cross-section. A backflow phenomenon occurs in the horizontal section of the stagnant branch pipe, while the structure of the large and small end pipe sections causes secondary backflow in the flow field inside the pipe. The backflow phenomenon is not conducive to the mixing of cold and hot fluids in the pipe; consequently, the influence time of thermal stratification is longer.ConclusionsA significant difference in the thermal stratification phenomenon exists between the stagnant branch pipe and equal cross-section pipes.
BackgroundThe conversion of UF6, which is a primary nuclear product, to UF4 in fluoride molten salt phase is expected to be used in the preparation or reconstitution of nuclear fuel salt for molten salt reactors, thus simplifying the process of molten salt reactor fuel production. Determination of the concentration of the key intermediate UF3 plays an important role in obtaining the reaction parameters.PurposeThis study aims to establish a method for measuring UF3 concentration in solid fluoride molten salts.MethodsThe X-ray diffraction (XRD) was employed to test the homemade standards and obtain the internal standard curve of UF3. Firstly, the α-Al2O3 was taken as the internal standard to obtain the XRD peak height internal standard curve (R=0.986) and peak area internal standard curve of LiF-BeF2-UF3 molten salt. Then, these two internal standard curves were applied to measuring the known content of LiUF5 and UF3 solid mixed samples to compare their accuracies. Finally, measurements were conducted on rapidly cooled LiF-BeF2-UF3 solid molten salt samples and naturally cooled LiF-BeF2-UF3-LiUF5 solid molten salt samples to evaluate the stability and accuracy of the curve, and the relative error was obtained.ResultsIn the UF3 concentration range of 1.00~10.00 wt%, the correlation coefficient of the internal standard curve based on the peak area determined for of LiF-BeF2-UF3 molten salt is 0.995. Measuring results of solid mixed samples of LiUF5 and UF3 with known concentrations indicate that the peak area internal standard curve achieves better accuracy with a relative measurement error of no more than 8.7%. In addition, the results of the same content samples with different cooling methods confirm the good stability and accuracy of the proposed method with less than 5.4% relative standard deviation.ConclusionsThe established method can be used for the quantitative analysis of solid LiF-BeF2-UF3 and LiF-BeF2-UF3-LiUF5 molten salts with good measurement accuracy and repeatability.