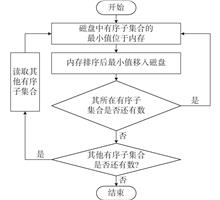
In order to measure the particle size in the medium using near-infrared light source, a particle size measurement method based on light extinction method combined with database technology is proposed. The extinction spectrum database related to different particle size and distribution is first calculated and generated by the total scattering extinction Lambert-Beer law. The database processing algorithm is employed to compare the data in the database with the measured particle extinction spectrum data. Then the particle size and distribution parameters of the measured samples are determined from the calculated values of the best match in the database. Next, numerical simulations of both the unimodal and bimodal particle size distribution are carried out, and the relative root mean square error of the volume frequency distribution of the simulation results is less than 10%. Three kinds of national standard particles with different particle sizes are used for experimental verification, and the relative errors of the measured particle size D50 are all less than 10%. Thus the validity of the proposed method and algorithm is demonstrated through simulations and experiments with satisfactory results. The research in this paper shows that the application of database technology and algorithm to the measurement of particle size by near-infrared narrow-band extinction method is feasible and effective.
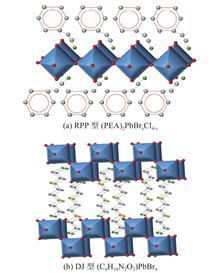
Broadband emission of two-dimensional perovskite has aroused interest in single-component white-light-emitting diodes. In this paper, we use the soft lattice properties of two-dimensional perovskite (PEA)2PbBr2Cl2 and (C6H18N2O2)PbBr4, which have strong photoacoustic coupling effect. The photo-excited electron-hole pair (exciton) is easy to cause lattice distortion and thus be captured by the lattice, forming self-trapping excitons (STEs), which can emit full spectrum white light. The results show that the half-height and full width of the two materials can reach 232 nm and 194 nm, the stokes shift is 182 nm and 198 nm respectively, and the fluorescence lifetime is 9.812 ns and 13.465 ns. Their coordinates on chrominance diagrams (CIE) are (0.36, 0.40) and (0.40, 0.44), color rendering indexes (CRI) are 86.93 and 82.23. Based on these two kinds of perovskites, combined with commercial UV LED, the composite LED color temperature is about 5000 K, providing a new understanding and perspective for the design of single-component white-light-emitting diodes.
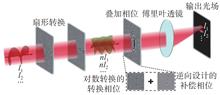
Vortex beams with orbital angular momentum (OAM) have attracted much attention in classical and quantum optics due to their infinite spatial states. In recent years, fractional OAM vortex beams have been introduced to increase the multiplexing ability of OAM mode dimensions. However, how to efficiently detect fractional OAM patterns is still a problem to be solved. This paper uses reverse design combined with coordinate transformation to identify fractional OAM patterns. Firstly, the fractional OAM mode is modulated by sector conversion to obtain a light field with a spiral phase gradient that increases exponentially. Secondly, the light field is re modulated by a logarithmically converted converted conversion phase superimposed on a reversely designed compensation phase. Finally, the recognition of a 21 order OAM pattern with a topological charge interval of 0.1 is realized. Moreover, it was found that after two multiplexed fractional OAM beams pass through the system, the minimum spacing at which the light spots can be separated is 0.6. At the same time, the system can still maintain a high diffraction efficiency of 83%. This provides an effective solution for solving the field of high efficiency and ultra high dimensional optical processing.
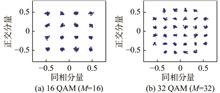
In communication systems, the modulation classification of high order quadrature amplitude modulation signals is a difficult problem. An improved Transformer deep learning modulation classification method is proposed in this paper. The network parallelizes two Transformer encoders. In the additive Gaussian white noise channel, the automatic modulation classification effect of 10 modulation formats ranging from 4 QAM to 4 096 QAM with SNR ranging from -10 dB to 30 dB was analyzed. First, the quadrature and in-phase components of the QAM signal were extracted and preprocessed. Then the preprocessed in-phase component and quadrature component pass through two Transformer encoders to extract component features. Finally, the two extracted component features were combined to judge the modulation format of the QAM signal. The experimental results prove that the network can accurately identify 10 kinds of QAM modulation formats when there is no influence of carrier frequency offset and the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 20 dB. When the carrier frequency offset is 500 Hz and the signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 26 dB, the classification accuracy of the 10 kinds of QAM modulation formats is higher than 98.6%.
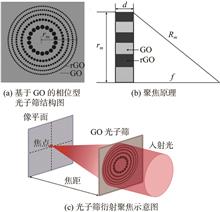
Photon sieve is a new type of diffraction element, which is not limited by diffraction limit and has flexible design structure. Compared with amplitude-type photon sieve, phase-type photon sieve has higher energy transmittance and sharper imaging contrast, which has application advantages. However, common diffractive optical devices face limitations of complex processing and difficulty in tuning. Graphene and its derivatives have good photoelectric tuning properties and are widely used in the preparation of diffractive optical devices. Laser direct writing technology can realize the induced reduction of graphene oxide, which is a simple and efficient micro-nano processing technology. In this paper, the diffraction characteristics of the photon sieve is studied by using the finite-difference time-domain method, and the graphene oxide photon sieve is prepared based on the laser direct writing technology. The refractive index modulation of the material can be obtained by processing with different laser power, and the device can achieve obvious focal length modulation (1.62 mm) and focus efficiency improvement (13.6%). This method is expected to provide a simple and flexible design and preparation method for realizing tunable diffractive optical elements.
In order to further study how to improve the quality factor of terahertz metamaterials and improve the detection sensitivity of metamaterials, we carried out the needle point design of a terahertz metamaterials sensor structure. In this paper, taking the double-opening square ring as an example, the double opening slit was designed with a double-needle structure. Through theoretical simulation, the influence of the angle of the double-sided open needle point on the resonant frequency, current distribution, and half-peak width of the resonant peak of the terahertz metamaterial sensor were studied. Furthermore, the Q value was calculated according to the formula, and the enhancement effect of the double-needle design on the detection sensitivity of the double-open square ring was analyzed. The simulation results show that when the needle angle is 150°, the Q value of the sensor can be increased to 5 times of the model without needle pointing. The needle point design proposed in this paper can also be applied to other resonator unit structures. Introducing it into the existing terahertz metamaterial sensor design will help to further improve the sensor detection sensitivity.
In recent years, object detection in scenarios with fewer samples has attracted widespread attention. Due to the limited information provided by the few samples, most of few-shot object detection models are studied using the improved Faster RCNN detection framework. However, due to the potential module contradiction problem in the Faster RCNN framework, the feature capture and classification capabilities of the existing few-shot object detection models need to be improved. In order to solve the above problems, this paper adds a gradient decoupling mechanism based on the Faster RCNN framework to alleviate the negative impact of the conflict between RPN and RCNN on the backbone network during the backpropagation process. In order to improve the feature detection ability of the object detection model, this paper adopts meta-learning framework, integrates the distillation module based on attention mechanism and the multi-scale attention module, and makes full use of the information of the query set and support set to capture more global feature information. A large number of experiments have proved that under the setting of randomly sampled shot amount k=1, 2, 3, 5, 10, the improved model can reach 21.8%, 34.7%, 40.9%, 44.5%, 51.7% mAP (AP50) on the new class of Pascal VOC dataset, respectively. Under the k=10, 30 setting, the improved model achieves 25.1% and 27.6% mAP (AP50) on the new class of the COCO dataset, respectively.
Despite the rising popularity of tattoos, demand for their removal has also increased. Tattoo removal is mostly treated by laser. But it requires repeated treatment, and the single curative effect is not accurate enough by visual examination. This article mainly studies the quantitative evaluation of treatment effect based on image technology. Tattoos were made on the pigskin with different colors, then we used a picosecond laser set at various energy parameters to remove the tattoos. The images of the treated area and normal skin tissue were collected, and the extracted area was standardized. After extracting features, the area ratio of tattoos before and after irradiation was quantified, and then the removal rate was obtained. In order to verify the reliability of the quantization algorithm, standard images with different contrast are designed to calculate the proportion of pigment, and the errors obtained are all less than 0.01%, which proves that the algorithm is reliable. The quantitative evaluation of pigment removal can objectively reflect the effect of laser pigment removal, and avoid the deviation of curative effect caused by subjective judgment. This study provides great help in selecting laser treatment parameters and improving the efficacy.
Superlens is an imaging device based on metasurface photoregulation. Due to its advantages of miniaturization and process, it has a good application prospect in the aspects of lightweight and portability. In order to meet the demand of lens volume in the current market, a new type of superlens is simulated by using the finite-difference time-domain method. It is a flat plate superlens based on photonic crystal. The size is 2 μm×1 μm, and its working wavelength is in the visible light band of 717 nm. In this design, TiO2 waveguide was used as the substrate for the plate superlens design. Two groups of Au and GaP photonic crystals with the same period are etched on the TiO2 waveguide, and the imaging performance of the lens is simulated and studied. In addition, by introducing a series of defects with different shapes, the imaging performance of the plate lens is analyzed. The results show that when the defect structure is a rectangular size of Lx=0.5 μm, Ly=0.8 μm, the plate superlens presents the best imaging performance and reaches the value of 0.556λ super-resolution, which greatly improves the imaging quality. The flat superlens has great potential in portable imaging devices, AR, VR, and small medical devices in the future.
Accurate and rapid diagnosis of parasitic infection is of significant importance in preventing the spread of parasitic diseases that cause millions of deaths worldwide. However, the lack of conventional microscope in low- and middle-income countries is one of the obstacles in effective control of parasitic diseases, which results in the rising demand for low-cost diagnostic devices. Smartphone-based microscope is a low-cost alternative to expensive conventional microscope because smartphone can capture and process images and so on. In this review, we summarize recent 15 years development of smartphone-based microscopy, applied in specific for the diagnosis of parasitic diseases, and classify researchers' work based on optical design. We also discuss strengths and challenges and offers considerations for a way forward in implementation of smartphone-based microscope in future.