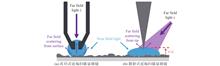
Near-field optics primarily investigates optical phenomena that occur in the near-field region, defined as being within the wavelength of light. This discipline explores the interaction between light and matter at the nanoscale. Unique physical phenomena, such as spin-orbit coupling, emerge in this region, making it a significant area of research in optics. Accurate characterization of these phenomena is crucial for further exploration. However, challenges arise due to the strong confinement and the complex vector nature of near fields. Traditional near-field scanning optical microscopy employs a near-field probe to access this region and collect information about near-field light. While this approach partially addresses the confinement issue, the intricate vector nature of the near fields necessitates specially designed probes to detect various components of near fields. These probes require nanoscale structural designs and complex, expensive semiconductor fabrication processes. This paper focuses on a series of studies utilizing nanoparticles as near-field probes for multi-component characterization of optical near fields. Being spherically symmetric structures, nanoparticles can theoretically respond to all near-field components. Mie scattering theory enables us to characterize the desired near-field components, including in-plane and out-of-plane electric and magnetic fields, by choosing appropriate materials and sizes for the particles. Furthermore, precise measurements of these components allow for accurate characterization of spin components, orbital-spin coupling, and optical topological structures in the near-field region. The probes developed in this approach are easy to fabricate, cost-effective, and do not require complex control systems, providing an efficient method for research in near-field optics.
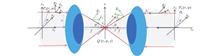
In optics, precise transverse energy flow modulation is critical for applications such as optical trapping and optical communications. Although the importance of transverse energy flow modulation techniques has been widely recognized, it is still challenging to achieve pure transverse energy flow modulation in a 4π tight focus system (4π-TFS). In this study, a method is proposed to generate pure transverse energy flow in 4π-TFS. The core of this method is the use of a vectorial vortex beam to achieve pure transverse energy flow by modulating its spatial parameters, such as polarization distribution and topological charge, which in turn leads to the interferential cancellation of longitudinal energy flow in the focal field. The results of this study not only provide an innovative technical way to realize the modulation of pure transverse energy flow, but also have important scientific significance and application prospects for promoting the development of the field of optical field modulation.
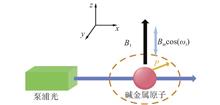
Atomic magnetic field measurement technology is gradually developing into a new generation of ultra-sensitive magnetic field measurement technology with the progress of quantum sensing, information and instrumentation technology. The spin-exchange relaxation free (SERF) atomic magnetometer is a kind of magnetometer with extremely high sensitivity. A single beam atomic magnetometer based on magnetic field modulation is proposed in this paper. The transmitted light intensity of alkali metal atom gas chamber was detected to obtain the corresponding external magnetic field. The rubidium atoms are pumped by near-infrared light with a wavelength of 795 nm. The maximum sensitivity of the system is 175.4 fT/Hz1/2 with the modulation frequency of 1.1 kHz, the modulation amplitude of 82 nT, and the modulation index of 0.887. Experiments show that the designed structure is reasonable and easy to miniaturize, and has practical value in many fields such as weak magnetic field and biological magnetic field measurement.
In view of the stress birefringence of silicon carbide wafers, it is necessary to rotate the silicon carbide wafers with an appropriate angle along the cutting direction to highlight the position of microtubules and dislocations during real-time stress detection. However, the depth of field of the high-power microscopic inspection system is small, and when the silicon carbide wafer is tilted, the large-size wafer may not be fully within the depth of field, resulting in diffusion of focus. Virtual focus has little effect on the stress value, but it can reduce the clarity of microtubules and dislocations, and even cause smaller microtubules to disappear in the virtual focus measurement results. In order to solve this problem, this paper proposes to use the ultra depth field synthesis algorithm to merge the measured results. At the same time, a mobile platform is used to combine different measurement results to synthesize the globally focused measurement results, so as to measure the stress value. Experimental results show that this method can effectively improve the visualization effect of measurement results.
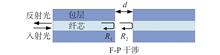
Optical fiber temperature-strain sensors have been widely used in health detection in the fields such as electric power and buildings because of their outstanding performance. This paper proposes a temperature-strain integrated sensor with fiber Bragg grating (FBG) combined with Fabry-Perot (F-P) structure. The F-P sensor is made of fused silica optical fiber. FBG can measure temperature and strain, while the fiber optic FP sensor is only sensitive to strain. By demodulating the two sensor wavelengths, the simultaneous measurement of temperature and strain can be realized by using the transfer matrix. The experimental results showed that the temperature and strain sensitivities of the FBG were 8.4 pm/℃ and 0.62 pm/με, respectively, and the strain sensitivity of the F-P sensor was 1.9 μm/ε, with linearity better than 99%. The sensor has the characteristics of simple structure, low cost, easy fabrication, etc., and has broad application prospects.
Aiming at the problems of inaccurate discriminative feature acquisition and insufficient use of training data in fine-grained image classification tasks, a fine-grained image classification algorithm combining significance and non-local modules is proposed. By clipping the significance region of four training images and stitching them into one training image, the training data could be enriched and enhanced. Moreover, the non-local module was embedded into the bottleneck module in the high-dimensional feature layer of the ResNet-50 model to connect the four salience regions of the enhanced image, which strengthened the model's attention to the global context information. On the Stanford Cars and CUB-200-2011 data sets, the accuracy of Top-1 classification was 94.01% and 85.97%, respectively. This method performs better than compared data augmentation methods and fine-grained image classification algorithms.
To solve the problem of speck noise and artifacts in optical coherence tomography (OCT) image acquisition, a PSRGAN model is proposed and a transfer learning method is combined to improve the reconstruction quality of OCT retinal images. The PSRGAN model was based on the super-resolution generative adversary network (SRGAN) composed of generator and discriminator, and the improved PECA module is added to the discriminator, which can fully capture the spatial information of multi-scale feature maps and realize the cross-dimensional channel feature interaction of images. As for the peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR), structural similarity index (SSIM) and edge retention index (EPI), the proposed method had better results in comparison with the best performance PSRGAN–TL–X-ray network by 2.19% and 4.07%, 10.64%, respectively. The results show that the proposed method significantly improves the image quality and automatic segmentation effect compared with other methods.
Solar cells using perovskite materials as absorption layers have attracted widespread attention due to their low cost and low loss. The working mechanism of perovskite solar cells is the generation and transmission of photo generated carriers. However, the internal defects and the defects at the interface of the material would promote carrier recombination, thus reducing the efficiency of the battery. In this work, daminozide (DA) was introduced as an interlayer and additive into perovskite solar cells, greatly passivating defects and significantly improving battery efficiency. The carrier relaxation dynamics was studied by ultrafast transient absorption spectrum. It is confirmed that the introduction of DA can significantly passivate defects in perovskite films, and led to excellent photovoltaic performance. The study provides theoretical guidance for the preparation of high-performance perovskite solar cells.
The signal transmission delay of the optical fiber time-frequency transfer link fluctuates with the change of temperature, and its fluctuation amplitude increases with the increase of optical fiber link length and temperature change range. For noise with reciprocating fluctuation characteristics in time-frequency transfer links, the weighted average method of the total noise of inter-station clock difference of remote atomic clocks shows good calibration effect in satellite systems. The amplitude of temperature delay fluctuations in ultra-long distance optical fiber time-frequency transfer links far exceeds that of the space-ground communication link of satellite system. The calibration effect of this method on the reciprocating fluctuation noise at the level of optical fiber temperature delay fluctuation is still uncertain. The simulation results based on the hydrogen atomic clock show that this method has good calibration effect on the temperature delay fluctuation of optical fiber. Under the simulated temperature delay fluctuation of 1,000 kilometers, when the time keeping stations at both ends of the optical fiber have 12 hydrogen atomic clocks each, the calibration residual is around 1ns. The difference in frequency stability between the cross-station clock after calibration and the atomic clock is two orders of magnitude lower than the frequency stability of the atomic clock.When the time keeping stations at both ends of the optical fiber have 400 cesium atomic clocks each, the calibration residual is around 10ns. Due to the significant difference in noise between hydrogen atomic clocks and cesium atomic clocks, it’s difficult to achieve joint calculation of hydrogen and cesium atomic clocks.
Filters are core optical elements in various optical instruments. The performance of these filters directly determines the accuracy and reliability of these instruments. Focusing on filters used in fluorescence detection and analysis instruments, their working principle was discussed, and the principles that should be followed when designing these filters were analyzed; the optical coating technology used for filter design and the types of main coating equipment were introduced. Suggestions were given for the selection of coating equipment by comparing and analyzing the advantages and disadvantages of different types of coating equipment. Based on the development and changes of fluorescence detection and analysis instruments, new requirements for these filters were summarized, such as coating on one substrate, more complex spectra, lower wave front distortion, deeper blocking and sharper steepness.
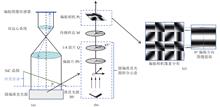
Femtosecond lasers enable high-precision, truly three-dimensional micro- and nanoscale fine processing. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS) is a significant research focus in the field of femtosecond laser micro-nano fabrication. During the LIPSS induction process, the parameters of the pump pulses affect both the morphological characteristics and the periodicity of the structures. Therefore, research on processing techniques under various experimental conditions, along with analysis of transient phenomena during the process, has become essential in this field. In this study, a femtosecond processing-imaging system is developed to investigate the formation characteristics of LIPSS on SiC surfaces. We analyzed the effects of pulse number, laser fluence, and laser polarization state on the final morphology of LIPSS on SiC surfaces. Additionally, using femtosecond pump-probe technology, we imaged the spatiotemporal dynamics of LIPSS formation on SiC surfaces. The results showed that, at a single pulse fluence of 1.01 J/cm², the LIPSS structure began to emerge 5 ps after the third pulse impact and progressively deepened with increasing pulse numbers. This study on SiC contributes to a deeper understanding of the physical mechanisms involved in LIPSS formation, optimizes processing parameters, and advances SiC-related application research.