View fulltext
View fulltext
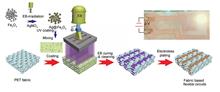
This study focuses on the preparation of fabric-based flexible circuits using polyester fabric (PET) as a substrate via radiation curing and chemical copper plating methods. The microstructures, elemental distributions, durabilities, and stabilities of the flexible circuits were investigated. In this experiment, an industrial electron accelerator was utilized in conjunction with a steel plate "film" mold containing circuit structures to achieve selective irradiation by electron beams. Consequently, cured coating areas corresponding precisely to the designed circuit diagram (containing Ag/Fe3O4 catalyst) were formed on the fabric. Subsequently, metal layers were deposited in situ via chemical plating to construct fabric-based flexible circuits. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) results demonstrated that the fabricated flexible circuit exhibited a well-defined structure and a highly crystalline conductive copper layer. During a bending test comprising 15 000 cycles, the resistance change rate of the fabric-based flexible circuit remained below 16%, whereas during a temperature variation test ranging from 15 ℃ to 55 ℃, it remained below 5%. These results suggest that the circuit exhibits exceptional durability and stability. The fabrication method for fabric-based flexible circuits presented herin offers novel insights into the development of smart textile products.
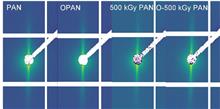
Pre-oxidation is one of the key steps in the preparation of carbon fibers, and most of the defects generated in this process are inherited by the carbon fibers. Therefore, the structural optimization of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) pre-oxidized fibers is particularly important for enhancing the mechanical properties of carbon fibers. Irradiation is a modification method for optimizing the structure of pre-oxidized PAN fibers and effectively improving their mechanical properties. In this study, the microstructural evolution of high-dose electron beam irradiated PAN fibers during the pre-oxidation is investigated. Synchrotron radiation in situsmall angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) and wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) were used to characterize the heat treatment process of high-dose irradiated and unirradiated PAN fibers. Additionally, the characterization of PAN pre-oxidized fibers was analytically investigated by combining differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR).The results showed that high-dose irradiation (500 kGy) promoted the cross-linking and cyclization of the PAN fibers during heat treatment, thus effectively alleviating the intense exotherms caused by the cyclization and reducing the initial cyclization temperature. Additionally, high-dose irradiation significantly affected the molecular structure of the PAN fibers, whereas high-dose irradiation of the PAN fibers during the heat treatment reduced the transverse microporous (D) size, orientation angle (Beq), and crystal-layer spacing d002 to 7.61 nm, 8.58°, and 0.352 nm, respectively. In summary, high-dose irradiation improves the microstructure of the PAN fibers after heat treatment, which facilitates improvements to the structure and the properties of the corresponding carbon fibers.
This study uses the MATLAB App Designer software based on the principles of point kernel integration and the Monte Carlo method to design an interface program for the cobalt source layout effect of gamma irradiation equipment. The interface program can simulate the manual and automatic layout calculation processes of cobalt sources, display real-time changes in the cobalt source position of the operation module and the entire source intensity effect map, and rapidly calculate the surface dose distribution of the source rack and the spatial dose distribution map of the product. Under the expected parameter conditions, the interface program can automatically calculate and select the optimal source discharge scheme by importing information such as the cobalt source activity and position. The layout scheme exported by the interface program can be used to execute the GEANT4 Monte Carlo program directly, thereby verifying the accuracy of the layout scheme. By comparing the concentration and dispersion of different cobalt source activities, the results show that the interface program agrees well with the GEANT4 calculations. Adding cobalt sources or adjusting the layout plan is important for selecting the optimal plan, improving the utilization rate of cobalt sources, and increasing the production capacity of irradiation equipment.
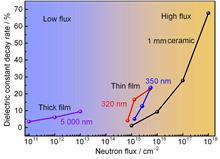
In this paper, we focus on the neutron irradiation effect on lead zirconate titanate (PZT) piezoelectric thick film with a thickness of 5 μm. The selected fluxes are at relatively low fluxes, including 4 kinds of 0 cm-2, 1011 cm-2, 1012 cm-2, 1013 cm-2. The key properties of the samples have been systematically characterized, especially the interface defect (energy level, concentration, and capture cross-section) using deep level transient spectroscopy (DLTS). It benefits the throughout understanding of the role of interface defects on the overall properties of PZT a lot. The results showed that neutron irradiation at 1011 cm-2 increased the activation energy of interface defects in the PZT thick film from 0.9 eV to 1.6 eV. This is a significant factor leading to an 11.2% reduction in polarization intensity, a decrease in dielectric constant, and an increase in leakage current. The degree of impact is positively correlated with the irradiation fluence. The results of this study have important reference significance for the application of piezoelectric materials and devices in irradiated environments.
Radio frequency anti-theft devices employ radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to identify and track objects. An anti-theft system based on the identification of information legitimacy judgment realizes an anti-theft alarm function. In this study, we effectively evaluated the safety of a 13.56 MHz RF anti-theft device in terms of electromagnetic exposure of pedestrians using the RF module in the COMSOL Multiphysics software. To this end, we designed an electromagnetic environment model to study the public electromagnetic exposure of pedestrians when such an RF anti-theft device is used. In particular, four exposure scenarios were analyzed in which the antenna system of the RF antitheft device was operating at 100 mW and 1 W and a pedestrian was located at the center (location A) and 25 cm away in front of the center (location B) of the anti-theft device. The results showed that when the pedestrian was at location A, for the aforementioned antenna feed power of 100 mW and 1 W, the maximum electric field strength of the whole body tissue was 0.26 V/m and 0.84 V/m, and the maximum magnetic field strength was 0.05 A/m and 0.16 A/m, respectively. The maximum values of the specific absorption rate (SAR) were 1.55×10-5 W/kg and 1.5×10-4 W/kg, respectively. When the pedestrian was at location B, for the aforementioned antenna feeding power of 100 mW and 1 W, the maximum electric field strength of the whole body tissue was 0.1 V/m and 0.36 V/m, and the maximum magnetic field strength was 2.08×10-3 A/m and 6.56×10-3 A/m, respectively. In this case, the maximum SAR values were 2.29×10-6 W/kg and 2.92×10-5 W/kg, respectively. These values obtained from simulation are lower than the public electromagnetic exposure limit established by the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP). This indicates that pedestrians passing through the RF electromagnetic environment analyzed in this study are within a safe range of public electromagnetic exposure. Therefore, the proposed anti-theft device does not pose a threat to public health.
This study investigated the gross radioactive background levels in paddy, vegetables, and cultivated soils around major agricultural production bases and key nuclear and radiation facilities in Guangdong Province. From 2018 to 2022, continuous sampling and follow-up monitoring were conducted on paddy, vegetables, and their respective soils. The collected data were statistically analyzed by area and city to explore the α/β ratio in soils across different locations. The gross α, gross β and 40K specific activities in paddy are (13.8±11.5) Bq/kg, (105±13) Bq/kg, (114±16) Bq/kg, respectively. The gross α, gross β and 40K specific activities in vegetables are (4.7±4.9) Bq/kg, (93±33) Bq/kg, (109±47) Bq/kg, respectively. The gross α specific activities of paddy soil and vegetable soil are (2.18±0.94)×103Bq/kg and (1.81±0.83)×103 Bq/kg, respectively. The gross β specific activities of paddy soil and vegetable soil are (1.09±0.49)×103Bq/kg and (0.91±0.39)×103 Bq/kg, respectively. These findings contribute to the enrichment of the background database for natural radioactivity surveys in China, providing essential data for environmental impact assessments post-operation of nuclear facilities, emergency responses to nuclear and radiation accidents, and food safety evaluations in Guangdong Province. The α/β ratio in soil obtained in this study can serve as an early warning indicator, where deviations from the established range may signal the presence of artificial radioactive contamination.
We propose an information management platform that combines software and hardware in response to problems in the production management processes of irradiation enterprises. The proposed platform combines automatic recognition technology to achieve dynamic data collection and the effective storage of irradiated materials during processing as well as the information processing of business data throughout the processing and production processes. First, we analyze the overall structure of the system and the various components of the software and hardware environments. Second, we explore the design and application of a hardware environment based on IoT technology in the irradiation process, including key hardware selection, production line applications, data acquisition, and processing. Finally, by analyzing the system requirements and designing business processes and functional modules, we implement the management system and successfully apply it in practice. The application of this platform can effectively improve the quality of product irradiation processing and provide a useful reference for production information management in irradiation processing enterprises.
In this study, the operation process of a γ-irradiation device, including loading, unloading, and irradiation, was simulated by the state transfer method. The effects of absorbed dose, cargo weight, loading and unloading speeds, and the dose rate of a radiation source on the whole irradiation process were studied. To enhance the irradiation efficiency and shorten the irradiation time required for combined cargo, the irradiation sequence of cargo was optimized using the genetic algorithm-traveling salesman problem (GA-TSP) algorithm. Our results showed that the proposed procedure can simulate the whole irradiation process; the radiation time can be shortened by increasing the dose rate of the radiation source in a reasonable irradiation sequence. At a source irradiation dose rate of 12 Gy/min, the simulation of 10 real incoming batches produced six dynamically optimized irradiation sequences. The time required for the sequential irradiation procedure was reduced from 13 193 min to 12 137 min, representing a reduction of approximately 8%, owing to the optimization of the irradiation sequence. This optimization significantly increases the availability of radioactive sources and improves customer satisfaction.
Cetuximab is commonly used to treat patients with advanced gastric cancer and the overall level of tumor epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression critically impacts the efficacy of cetuximab. This study was performed to select the most clinically relevant probes targeting EGFR via comparative research. Cetuximab was fragmented by enzymatic cleavage to produce Cet-F(ab')2 and Cet-Fab, which were then conjugated with CY3 NHS ester to obtain CY3-Cetuximab, CY3-Cet-F(ab')2, and CY3-Cet-Fab for cell fluorescence experiments to verify their affinity. Three 124I-labeled molecular probes, namely 124I-Cetuximab, 124I-Cet-F(ab')2, and 124I-Cet-Fab, were prepared using the Iodogen method. Micro-PET/CT imaging was performed 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, and 12 h after probe injection for comparative studies. Further, biological distribution experiments were conducted to explore the in vivo distributions of the three probes at different time points. Independent sample t-tests were used for intergroup comparisons. Fragmentation did not significantly decrease cetuximab affinity. The respective molecular weights of Cetuximab, Cet-F(ab')2, and Cet-Fab were approximately 150 kDa, 100 kDa, and 50 kDa, respectively. After 124I labeling and purification, the radiochemical purity of 124I-Cetuximab, 124I-Cet-F(ab')2, and 124I-Cet-Fab exceeded 94%, and the specific activity was approximately 2×104 MBq/μmol. Stability tests in saline and fetal bovine serum (FBS) showed that radiochemical purity remained above 90% after 24 h of incubation. Micro-PET/CT imaging demonstrated significant accumulation of 124I-Cet-Fab at the tumor site 3 h after intravenous injection, whereas 124I-Cet-F(ab')2 exhibited pronounced accumulation at the tumor site 12 h after injection. However, no evident distribution of the imaging agent was observed at the tumor site 12 h after intravenous injection of 124I-Cetuximab. The biological distribution results are consistent with the micro-PET/CT findings. Among the three positron probes, 124I-Cet-Fab exhibited the fastest metabolism, earliest tumor imaging, and the lowest cumulative radiation dose, indicating its potential for clinical translation.
To investigate the beneficial effect of NLRP3 inflammasome specific inhibitor MCC950 on radiation induced lung injury (RILI) and its potential mechanism in mice. A total of 36 female C57BL/6J mice aged 7 weeks were randomly assigned to the control group, the irradiation group, and the irradiation plus MCC950 group. The irradiation group and irradiation plus MCC950 group mice were exposed to whole-thorax radiation at a single 20 Gy dose. The control group mice were provided with an irradiation dose of 0 Gy. The irradiation plus MCC950 group mice were treated with MCC950 following irradiation. The mice in control group and irradiation group were treated with the same amount of normal saline. After 12 weeks, the body weight and the dry and wet lung weight of the three groups mice were measured to assess the lung coefficient (the ratio of the lung wet weigh to the body weight of each mouse) and the wet-to-dry lung weight ratio (weight of the wet lung/weight of the dry lung). The degree of lung tissue injury was assessed using hematoxylin eosin staining. Western blotting was performed to evaluate the expression of macrophage polarization markers, NLRP3 inflammasome, and inflammatory factors. The experimental results indicated that compared with the control group mice, the lung coefficient, wet-to-dry lung weight ratio, the lung tissue injury score, and the protein expression of M1 macrophage markers (CD86), NLRP3 inflammasome (NLRP3, ASC, and Caspase-1), and inflammatory cytokines (Pro-IL-1β, IL-1β, IL-18, and TNF-a) of the irradiation group mice were dramatically enhanced, whereas the protein expression of M2 macrophage markers (CD163) was significantly decreased. Compared with the irradiation group mice, irradiation plus MCC950 group mice had higher protein expression of CD163, and remarkably reduced the lung coefficient, wet-to-dry lung weight ratio, the lung tissue injury score, and the protein expression of CD86, NLRP3, ASC, Caspase-1, Pro-IL-1β, IL-1β, IL-18, and TNF-?a. The above results demonstrated that MCC950 ameliorates RILI through modulating macrophage polarization, and it promises to be an intervention agent against RILI.
为开发高效铀吸附材料,实现从水相中快速高效提取铀酰离子,本工作通过在辐照接枝马来酸酐的聚丙烯纤维基体上原位生长ZIF-8,制备了ZIF-8复合膜(ZIF-8/PP-g-MAH),并研究了pH值、接触时间和初始铀浓度对ZIF-8/PP-g-MAH吸附性能的影响。吸附等温线和动力学分析结果表明,ZIF-8/PP-g-MAH的铀吸附容量高达478.5 mg/g,是ZIF-8粉末的1.26倍,并且其吸附平衡时间为120 min,缩短到ZIF-8粉末用时的1/3。吸附过程与Langmuir等温线和准二阶动力学模型一致。ZIF-8/PP-g-MAH对模拟海水中的铀也表现出良好的选择性。ZIF-8/PP-g-MAH表现出的高吸附性能归因于其膜结构提高了配位位点的利用率,包括Zn-OH、C?-?N和C=N。此外,通过将ZIF-8与聚合物膜复合解决了MOF粉末回收再利用难题。本工作制备了一种可用于快速提铀的高效吸附材料,这将有助于推动提铀技术的进一步发展。
Wound hydrogel dressings are a novel type of medical material known for their hemostatic and antibacterial effects, which expedite wound healing and alleviate patient discomfort. Radiation technology plays an indispensable role in their preparation. Unlike other methods, radiation does not require additional crosslinking agents, simplifying the process and minimizing pollution. Moreover, product stability and consistency can be ensured by controlling absorbed radiation dose and conditions. Using radiation technology for hydrogel dressing preparation integrates sterilization into production, reducing costs and enhancing safety. This review categorizes, outlines characteristics, and surveys recent advances in radiation-prepared hydrogel wound dressings. Additionally, it summarizes their applications and forecasts their future development and expanded clinical utilization.