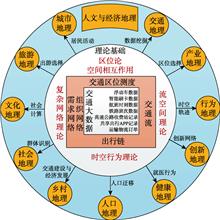
Transport big data can reflect movement and trajectories of human socio-economic activities, and facilitate studies in a wide range of areas using high-resolution data. Various types of continuous observations from different perspectives can provide new ideas and promote the technological development of human and economic geography. Based on the frontier of transport studies, this paper reviewed the development of location theory, time and space behavior, complex network, and space of flow. Also, this paper outlined a research framework of human and economic geography in the era of big data, discussed the possibilities of combining traditional methods and new technologies, and summarized influences of related branches. Then we proposed the major direction and tendency of applying transport big data, including transport planning with 'Mobility as a Service', urban management with artificial intelligence, simulation of traffic flow migration at a large scale, and investigationof space of flow and space at multiple scales, etc. Finally, this paper pointed out emerging issues in the application such as data access and data bias.
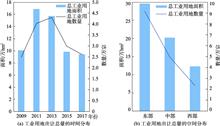
In the context of fiscal decentralization and local competition, local government in China usually adopts means of supplying excessive industrial land and lowering the transfer price of industrial land, in order to attract more investment from enterprises. These measures could directly lead to lots of problems, such as inefficient use of industrial land and even serious waste. Regulating the scale of industrial land supply and giving play to the market's guiding role in the transfer price of industrial land are important ways to promote the intensive and efficient use of industrial land. This paper takes the transfer price of industrial land as the research object, and uses the national industrial land transfer data in 2009, 2011, 2013, 2015, and 2017. Considering that the sample contains both macro and micro level information, this paper uses a hierarchical regression model to empirically analyze the spatial pattern of the transfer price of industrial land and its key affecting factors. The empirical research finds that: (1) Industrial land price in different regions of China have large differences and the government's ability to intervene can significantly affect the transfer price of urban industrial land. By controlling other factors, the stronger the local government's intervention ability, the lower the transfer price of industrial land in the region; (2) At the parcel level, the closer the industrial land is to the city center, the more developed the transport on this plot, or the closer the industrial land is to the water source, the higher the transfer price of the industrial land tends to be; (3) At the city level, the larger population of the city where the industrial land is located often means a higher level of economic development. Thus, the transfer price of the industrial land tends to be higher. This study introduces a layered model into the econometric model for the first time, and uses the premium rate of industrial land transfer (that is, the comparison of the price of industrial land transfer with the "lowest price standard") to characterize the behavior of local government industrial land transfer. At the same time, this article verifies the macro and micro factors that affect the price of industrial land transfer at the national level rather than at the city or province level. Therefore, this study supplements and extends the existing literature from multiple aspects.
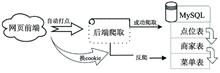
As the most important element with local characteristics in regional culture, dietary geographical culture presents a new diversified situation under the background of large scale population movement. However, up to now, the domestic research on the distribution characteristics of sweet diet based on traditional cognition is still lack of objective data. Based on the web crawler technology, this paper obtained about 20 million pieces of gourmet consumption data in 31 provincial capitals in mainland China. The degree of sweetness in our diets in urban areas was calculated for traditional dishes, main food dishes, drinks, and dessert dishes. Based on ArcGIS and MySQL softwares, spatial analysis and mathematical statistics were used to understand the spatial distribution characteristics of the modern Chinese sweet diet and identify its affecting factors. The results show that there were dramatically regional differences in the spatial distribution of sweet diet in China, especially in the southeastern coastal areas and the central inland areas, with the evaluation parameter (R2) of spatial grouping analysis reaching 0.88. The distribution of modern sweet diet generally presented a surrounding pattern of "High East, Middle North, Micro-low West and Low Inside". From either the overall or local point of view, the Moran indexes were positive at 1% significance level, and there was a significant positive spatial autocorrelation for sweet diet habits at different areas in China rather than an obvious trend of dispersion. There were three distinct geographical agglomeration areas: the high-sweetness agglomeration areas along the southeast coast of Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shanghai, and Fujian, the low-sweetness agglomeration areas in southwest areas of Chongqing, Guizhou, and Sichuan, and the northwest inland low-sweetness agglomeration areas in Shanxi and Ningxia. The accuracy of the stepwise regression model of sweet diet habit distribution was 0.82, and results suggest that meteorological elements such as precipitation, humidity, temperature, and geographical location were important factors that influence the spatial distribution of sweet diet habit in modern China. Moreover, we found that geographical location had a regulating effect on the influence of sunshine duration on sweet diet habit. Specifically, the sweetness of inland cities generally increased with the increase of sunshine duration, while the sweetness of coastal cities usually decreased with the decrease of sunshine duration. This study aims to reveal the regional disparity of sweet culture in modern China, which provides reference for the planning of the category structure in urban catering industry and better understanding of the new trend of the development of modern sweet food consumption.
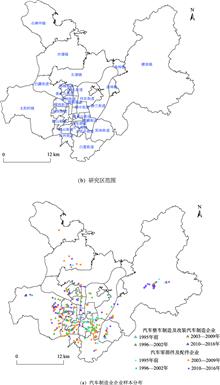
China is a world leader in automobile production, and its production and sales has ranked first in the world for nine consecutive years. However, research on the automobile industry is more concentrated on the regional scale, and research on the urban scale is relatively rare. This paper takes Liuzhou City as a case, and analyzes the spatial distribution and influencing factors of Liuzhou automobile manufacturing enterprises by using micro-enterprise data, nuclear density estimation and negative binomial regression model. The results show that: (1) The automobile manufacturing enterprises are mainly concentrated in Hexi, Luowei, Hedong and Yanghe groups in Liuzhou City. The scope of corporate agglomeration gradually spreads to the east and west sides. The eastward diffusion is mainly in Liudong new district and the westward diffusion is mainly in the Hexihigh-tech industrial development area in Liuzhou City. (2) The automobile manufacturing enterprises in Liuzhou City have a significant agglomeration in the spatial distribution within the range of 0~11 km, and the intensity of spatial agglomeration first increases and then decreases. (3) Land price and traffic conditions, localization economy and policy factors have significant impacts on the spatial distribution of automobile manufacturing enterprises in Liuzhou City. At the same Time, JIT (Just in Time) production mode of automobile manufacturing also has an important influence. On this basis, the circular accumulation mechanism, location proximity mechanism and price transmission mechanism of location selection and spatial distribution of automobile manufacturing enterprises are proposed.
Exploration of the spatial differentiation of the retail industry based on large-scale geospatial data is of great significance for urban development. In the recent years, POI data has become an important data source for studying urban dynamics. POI data abstracts retail stores as a point on the map, and the data are of wide coverage and high fineness. These advantages make the POI data an ideal dataset for micro- analysis of urban retail commercial structure and their spatial distribution mechanism. Based on the data of 47 026 retail outlets in Guangzhou, we explored the driving mechanism of the spatial differentiation of the retail formats. By building an indicator system, we investigated the factors potentially affecting the spatial differentiation of the retail industry, which include population density, business conditions, public transportation convenience, format richness, and rent. Based on information entropy, kernel density function, and spatial regression, we analyzed the main influencing factors of the retail differentiation. Further, we divided the retail outlets by different urban areas and different retail formats, and conducted spatial regression analysis based on the same influencing factors to compare the main driving factors of different retail formats. Results shows that: (1) Demand, location, competition, and cost were the main driving force of the spatial differentiation of retail industry. Furthermore, because of the heterogeneity of the retail formats and the spatial heterogeneity of the city, there was also heterogeneity in the driving mechanism of the spatial differentiation in the retail industry. (2) There were significant spatial differences of the influencing factors. The inner circle of the city had higher population density, better accessibility, better business conditions, and higher format richness, and also higher land rent. There was a significant spatial differentiation between the old city area and the suburbs. (3) Compared with the traditional OLS regression method, the spatial regression method revealed the spatial distribution mechanism of the retail industry more accurately. The spatial error model revealed significant heterogeneity in the factors that influence the spatial agglomeration of the retail industry. Population density was the core driving force of retail spatial differentiation. Public transport convenience, business conditions, and format richness also had a positive effect on retail agglomeration, while the impact of rent was weak. The main driving factors of different retail formats and outlets located in different urban circle were different. Population density was the core factor, while the influence of other factors showed significant differences.
Intercity travel is a time-dependent behavior, which has different spatial characteristics with different time constraints or during different time periods. The patterns of intercity travel and geographical spatial connections revealed by intercity travel could be different with time. However, intercity travel with varying travel time has been studied little so far, in particular for holiday travel. With the booming of holiday tourism, analyzing intercity travel during holidays is of great significance to uncover the spatial movement rules and travel patterns among urban agglomerations. In the era of big data, real-time records of population movement provide a possibility to examine the characteristics of intercity travel in detail. Hence, this paper explores the characteristics, patterns, and structure of intercity travel in 19 urban agglomerations of China during the National Day holiday period (October 1-7) in 2016. The intercity travel data derived from the Tencent Location Big Data and network analysis methods are employed to evaluate intercity travel patterns between urban agglomerations. Using the community detection method, we identify 24 city communities during the National Day holiday, and the directions of intercity travel in urban agglomerations are explored. Results show that intercity travel during this golden week has an obvious timing feature, which is observed as leave period, return period, and journey period receptively. There have formed three intercity travel patterns, namely, hub-and-spoke, polycentric, and monocentric patterns. Meanwhile, the features of intercity travel in the leave period and return period are similar to the Spring Festival, which is characterized by space-time symmetry of population flow. Intercity travel in main urban agglomerations presents a typical long-holiday travel feature, which is characterized by short- and medium- distance travel between core cities and neighboring peripheral cities. While the intercity travel in urban agglomerations in the central and west of China has a typical tidal feature. Based on the population movement records from the Tencent Location Platform, this study has investigated intercity travel features and travel patterns during the National Day holiday in three time periods mentioned above. In addition, our results can provide useful support for intercity traffic management, road resource optimization, and allocation plan in long holidays in China.
Public transportation in large cities is a typical complex giant system. The use of complex network methods to analyze large city public transport network systems is of great significance for urban transport development. Most of current studies take public transport stations as nodes and routes as connecting edges to construct an abstract network adjacency matrix, so to analyze the complexity characteristics of public transport networks according to indicators such as average (shortest) path length, clustering coefficient, degree distribution, node proximity or median centrality. However, the complexity of urban public transport network is not a static topology network composed of bus stops, routes, and their interconnections, but also the dynamic traffic information, which is seldom considered in existing studies. Distinguishing the characteristics of the passenger flow network in different time periods is of great value for formulating time-sharing public transport management policies. Meanwhile, the widely used big data recently provide high-precision traffic information for the study of dynamic traffic network structures. In this paper, we constructed the bidirectional adjacency matrix of passenger flows in different time periods based on swipe card data of Beijing buses, then compared and analyzed the within-day variation of the bus passenger flow network through complex network indexes. In terms of the structural characteristics, the bus passenger flow network in each time period had a small average shortest path and a large clustering coefficient, meaning a small-world network; the distribution of accumulation degree was fitted as an exponential distribution, which indicates that the bus passenger flow network did not have scale-free characteristics. The bus passenger flow distribution in each time period had an obvious distance attenuation rule, and it was mainly for short-distance travels below 10km, which suggests the bus line and operation management should focus on the distance range below 10 km. Degrees centricity and weighted degree centrality of the spatial pattern in different times presented an obvious core-edge character but changing over time; the weighted degree centrality in the top 10 nodes changed a lot, according to which dynamic public transport hubs should be considered in a precious and accurate traffic planning and management. Our findings provide a reference for public transport planning and management policies. In the future, more comprehensive passenger flow data should be used to explore the structural characteristics from a multi-scale perspective.
In the era of big data, traffic flows play an important role in understanding our socioeconomic environment. In recent years, two types of traffic flows, smart card transactions and taxi GPS trajectories, have been widely but usually separately utilized to understand human mobility in big cities. To date, although numerous research achievements have been made, the relationship between these two types of traffic flows that occur in the same area and in the same time period is still poorly understood. Thus, the pattern of urban human mobility may be biased by using a single type of traffic flow. In this study, we aimed to compare the urban human mobility patterns derived from the two traffic flows, i.e., smart card transactions and taxi GPS trajectories. Taking the area within the Sixth Ring Road of Beijing as study area, we collected the smart card transactions and taxi GPS trajectories data from May 9th to May 15th in 2016. Specifically, we compared: ① the spatio-temporal distributions of public transit and taxi usage; ② the travel distance of public transition and taxi usage and the distance-decay effects, and ③ the spatial community structures discovered from the two traffic flows. Our results show that: ① the spatial distributions of travel demand revealed by two traffic flows are highly correlated. However, the correlations between origin and destination time series extracted from the two traffic flows were very weak; ② the usages of public transit and taxi had spatial heterogeneity, and the spatial difference between the usages of public transit and taxi cannot be fully explained by the number of intersections, the number of points of interest, and the average distance to the nearest city center, shopping center, hospital and subway; ③ the travel distances extracted from taxi GPS trajectories decayed faster than that extracted from public transit, indicating that public transit was more important in facilitating long-distance travel, and ④ spatial communities discovered from the two traffic flows both reflected the polycentric spatial structure of the city. However, the differences in spatial community structures indicated that the two traffic flows played different roles in spatial interactions in the city. The quantitative comparison between smart card transactions and taxi GPS trajectories could improve our understanding of human mobility in Beijing, which also demonstrates the potential biases by using a single traffic flow to study urban system dynamic. Our results suggest integrating multi-source traffic flows to understand urban human mobility patterns in future.
The potential bicycle travel demand indicates the travel demand that could potentially be served by bicycles. Assessing the potential bicycle travel demand can help to optimize the allocation of the related infrastructure (e.g., bike parking areas and bike lanes) in cities. Mobile phone location data have the advantage of providing low-cost and large-scale sample sizes that contain rich human mobility information. The data can be used to estimate the potential bicycle travel demand. Based on the spatiotemporal characteristics of daily bicycle travel, we proposed a method for assessing the potential bicycle travel demand from large-scale mobile phone location data. Specifically, each individual instance of travel was taken as a sample for the analysis. First, we used the Stops and Moves of a Trajectory (SMoT) model to extract the movement trajectory segments of the users. Second, we identified a "tour" pattern for the trajectory segments, where the start location and the end location were the same. Then, the location that was at the furthest point from the start location was used to divide the movement trajectory segment into two segments. Finally, the movement trajectory segments that were characterized by short distances and those in which the "last mile" of the travels was served by the public transport system were extracted for further assessment of the potential bicycle travel demand. In this study, Shanghai was chosen as the example city. Through our proposed method, we assessed and analyzed the spatiotemporal characteristics of daily bicycle travel in Shanghai to determine the potential bicycle travel demand. From a spatial perspective, we found the following: (1) the potential bicycle travel demand in Shanghai was mainly concentrated in the downtown areas and commercial centers in the suburb areas; (2) the potential bicycle travel demand in the downtown areas and commercial central urban areas was stable, while the potential bicycle travel demand in the suburban areas tended to be variable; and (3) most of the “last mile” demands were located in the suburb areas, which showed that the characteristics of the “last mile” demands at different public transport stations varied. From a temporal perspective, several patterns could be observed during the morning and evening rush hours: (1) the potential bicycle travel demand in the central urban area continued to remain relatively high; (2) the potential bicycle travel demand in the suburbs in the Songjiang and Qingpu districts had relatively large differences; (3) the potential bicycle travel demand was concentrated in the direction of the central urban area from the noncentral urban areas in the morning, while the potential bicycle travel demand spread from the central urban areas to the noncentral urban areas in the evening; and (4) the potential bicycle travel demand of Shanghai showed a double-peak characteristic (at 11:00—12:00 and 16:00—17:00). The “last mile” type demand also had two peaks (at 7:00—9:00 and 17:00—18:00).
With the development of information and communication technology, such as mobile internet, cloud computing, and big data, smart city has gradually become the important development tendency of urban construction. During the period of the 13 th five-year plan, cities have formulated their smart city construction (or development) plans and regarded these plans as key part of their medium- and long-term urban development strategies. Because smart city involves various context and massive indexes, the assessment of smart cities is undergoing continuous development and improvement. Thus, so far, an unified assessment standard is still lacking. Based on this, we compare the domestic and international index systems to assess smart city development. With the objectives including improving cities' capability of sustainable development, implementing efficient and fair management, and ensuring urban residents' wellbeing, this paper proposes an assessment index system with multiple layers and five sub-systems including smart economy, smart transport, smart healthcare, smart education, and smart management. This paper employs text, webpage, and statistic data and conducts a comprehensive, uniform, and multi-layer assessment to evaluate smart city development status for Chinese cities. finally, we offer constructive suggestion on smart city development from the perspective of sub-system coordination. Main findings are shown here. First, except 8 cities, namely Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Wuhan, Chengdu, Hangzhou, Tianjin, and Nanjing, most cities are at a relatively low level of smart city development. Second, based on the spatial pattern, cities in the coastland are at a relatively higher level of smart city development than those in the inland. Municipalities and provincial capitals are at an obviously higher smart development level than the other cities. Third, from the coordination perspective, five sub-systems are not coordinated well with more than 70% cities showing moderate- to low-level coordination. Overall, the average development level of smart education and smart healthcare are the lowest among all sub-systems. More than 80% of cities have disadvantages in the two sub-systems. Based on these findings, this paper provides some policy implications for the future development of cities. The government should pay more attention to the coordination of sub-systems, such as smart education and smart healthcare. For smart transport, most cities have already had a high level of development, and the efficiency and fairness of transport development will be more important in the future. Innovation and global development have become the key factors restricting the development of smart economy and should be considered in future policy-making. In addition, government and the relevant departments should strengthen the top-level design, module construction, and index statistics of the smart management.
With the development of the new type of urbanization, urban agglomeration plays a key role in modern social-economical development. To date, big data has been considered as a technological breakthrough and applied in many fields in recent years. Spatiotemporal big data mining and data fusion analysis can improve the efficiency of the administration and construction of cities/urban agglomeration in the new era of smart city. In this study, we aimed to review the types, acquisition methods, and analysis techniques of spatiotemporal big data. We investigated researches on urban agglomeration using spatiotemporal big data in order to identify the application of big data. We collected conference and journal articles as well as academic dissertations published in big data and data mining areas between 2004 and 2019. In total, wesummarized ten types of big data which were classified into traditionaltype and newtype categories, five big data acquisition methods including downloading, crawling, purchasing, and data processing, as well as seven most common big data analysis techniques. Five application fields on administration and construction of city/urban agglomeration using big data were concluded through literature review, including demarcation and spatial development monitoring, traffic network monitoring, association and function analysis, industrial coordination analysis, and environment assessment. Moreover, we summarized the bottlenecks of future big data applications, including: (1) difficulties in data management; (2) low-level data sharing; (3) high complexity of data analysis; (4) limitations of research ideas and application fields. In response to the above issues, some suggestions are listed: (1) government should strengthen policy support for more extensive information sharing and efficient information security assurance to create a favorable environment for the development of big data application; (2) constructing adaptable modern network infrastructure to create an all-in-one system which integrates network coordination, simulation, calculation, and administration; (3) building a big data management standard for urban agglomeration to solve the problems triggered by its characteristic of variability and multiformity; (4) promoting the establishment of big data platform to enforce an integrated information sharing mode from regional to national level; (5) adopting the international advanced technologies and methods with some new ideas from the studies on smart cities to build a technical system that is suitable in China. This study finally put forward that the construction of network infrastructure and spatiotemporal big data resources sharing platform could make new patterns of integrated analysis of big data possible, leading to highly effective supervision and strategical development of the city/urban agglomerations in the future.
Rapid development and application of urban space-time big data have provided a new data environment and technical means for identifying urban functional areas. However, the literature regarding mixed urban functional areas detection in the field of urban public service facilities is still lacking. Using spatial point-level data of nine categories of urban public service facilities in Beijing with consideration of their rank and quality, this paper employed cumulative opportunity method to measure urban public service facilities' accessibility in Beijing at 1 km×1 km grid scale, and further emphatically analyzed the mixed functions and influencing factors of urban public service facilities. The results show that the spatial distribution of urban public service facilities' cumulative opportunity accessibility in Beijing presented a similar characteristic of central agglomeration. While the specific spatial patterns and coverage areas of urban public service facilities varied by their categories. In addition, functional areas of urban public service facilities in Beijing were divided into the five types: single functional areas, mixed functional areas with single facility oriented, mixed functional areas with two types of oriented facilities, mixed functional areas with three types of oriented facilities, and balanced mixed functional areas. Finally, population density, distance to the city center, land price, and cumulative opportunity accessibility of several commercial-oriented facilities were important factors affecting the existence of mixed function of urban public service facilities in Beijing. Our findings provide insights for both urban functional studies and spatial optimization of urban public service facilities in Beijing.
Street View Imagery (SVI) is one of the important data sources for the quantitative research of urban built environment. However, it is difficult to fully represent all the information with one type of feature in the SVI due to its complexity and diversity. In this paper, we proposed an effective multi-feature fusion method to evaluate the street space quality based on SVI. Taking Yuexiu district in Guangzhou city as the study area, the Baidu SVIs in the four orientations (front, behind, left, right) at the sample points were obtained. Speeded Up Robust Feature (SURF) and Histogram of Oriented Gradient (HOG) were derived from SVIs as handcrafted features. Semantic features were also derived from SVIs using ENet convolution neural network as features based on deep learning. Based on single feature and multi-feature fusion, Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Random Forest (RF) were used to train the street space quality evaluation model for the four orientations on the training set. The optimal model and the combination of features were selected according to the classification accuracy and Kappa coefficient on the test set. Results showed that: (1) The optimal classification accuracy of models based on SVM was 82.8% (front), 81.7% (behind), 76.6% (left), 76.6% (right), respectively. In the models based on single feature, the average accuracy of the models based on HOG feature (73.03%) or semantic feature (72.28%) was better than the SURF feature (56.00%). The optimal classification accuracy of the models based on RF algorithm was 82.8% (front), 85.0% (behind), 78.1% (left), 70.3% (right). (2) The accuracy of front and behind orientation model was slightly better than that of left and right orientation. The optimal models of each orientation all are multi-feature fusion models. The average classification accuracy and Kappa coefficient of these optimal evaluation models was 80.6% and 0.62, respectively. These results showed that the proposed method could achieve a high recognition performance. (3) The selection and fusion of features were more determined to the model performance when the SVI were used to evaluate the street space quality, while the performance difference between the two algorithms was small. (4) There were obvious spatial differences in the street space quality of Yuexiu district. The street space quality in the southeast of Yuexiu district needed to be improved. A large scale and high precision street space quality evaluation method was proposed based on multi-feature fusion of SVI and achieved a high recognition performance in this study. And the street space quality score in Yuexiu district was obtained. These results could provide valuable clues for local authorities to conduct comprehensive renovations of urban built environment.
As the carrier of human activity and social development, buildings are the most important geographical entities that constitute the spatial structure of a city. It is one of the urgent tasks in the construction of smart cities in China to build elaborate digital models of urban buildings. Classifying a large amount of buildings by their functions facilitates urban functional area division and urban spatial cognition, thus assisting the government in population estimation, land management, urban planning, and smart city construction. In this paper, POI (Point of Interest) with rich semantic information including name, address, and types was used as the main data source, because it was more accessible and updated more frequently than the traditional geographic information data. The process of finding out the functional type of a building was similar with identifying urban functional areas by using POI data, but there existed the problem of low classification rate due to the sparsity of POI. Therefore, to improve the traditional quantitative identification of urban functional areas, this study attempted to calculate the weighted frequency density ratio of each type of POIs inside and within a certain range around a building. Experimenting on more than 5000 buildings near South Shawo Bridge in the west of Beijing, the study found that 93.04 percent of the buildings were effectively classified into different functional types: residential, commercial, public service, and other three mixed types. The classification rate has been greatly improved compared with that of the traditional method. These classified buildings showed the spatial distribution of functional areas more clearly and precisely than blocks used in identifying urban functional areas, since too many multi-functional blocks with very limited practical meaning were identified by using the traditional method. In order to calculate the classification accuracy, more than 2000 randomly selected buildings were manually divided into functional classes with the assistance of POI and AOI data. The overall classification accuracy reached 91.18 percent compared with the manually classified result. The classification error was mainly caused by the shortage of POI and the poor data quality, which could be avoided by merging multi-source POI to improve the data quality or applying various Internet location information, such as the social media data and the real estate transaction data. However, by using easily accessible web POI data, the proposed method, which can replace manual classification in an automated way, has greatly improved the effectiveness of classifying large number of buildings into different functional types, and shown higher accuracy than existing researches.
Urban wind environment is an important research field of urban climate, which is of great significance to the analysis of urban heat island effect and ventilation. Taking the central area of Zhengzhou city as an example, this paper used meteorological observation data in 1971-2018, the data from ZY-3 satellite in 2016, and then combined with the Open Street Map (OSM) data in 2018 to explore potential ventilation corridors and scientifically quantify the impact of urban form on the wind environment through the combination of meteorology and GIS technology. In this study, the wind environment in urban background was firstly simulated and analyzed with the help of WindNinja software, which improved the accuracy of potential ventilation corridors of the city. The Digital Surface Model (DSM) was made based on the data from ZY-3 satellite in 2016, and then combined with the OSM data in 2018 to calculate the surface roughness of the underlying surface. Then ArcGIS software was used to locate and analyze the location of the potential ventilation corridors in the city by means of the Least Cost Path analysis (LCP). The results were as follows: (1) Average wind speed in Zhengzhou declined slowly with an average rate of 0.26 m/s per decade; The prevailing wind throughout the year was northeast wind, which changed in wind speed and direction after entering the city due to the influence of urban form. In particular, the northeast wind gradually changed to northeast easterly wind in the west of the Beijing-Guangzhou Railway. And the wind speed in the east of the Beijing-Guangzhou Railway was relatively higher than in the west of the Beijing-Guangzhou Railway. (2) The surface roughness of Zhongyuan District, Erqi District, Guancheng District and the western part of Jinshui District was high. The wind speed decreased and the wind direction changed greatly after the prevailing wind entering these study areas, and the overall ventilation environment of those four districts was poor. The surface roughness of the eastern part of Jinshui District and Huiji District was relatively low, with relatively good ventilation conditions. After the prevailing wind entered these areas, the wind speed increased and the wind direction changed less. (3) The common feature of the potential ventilation corridors, which were simulated according to the prevailing wind direction, was that the location tended to be low roughness areas. In these areas, the concentration of ventilation paths was lower and there were more potential ventilation corridors.
Earth System Science (ESS) is a comprehensive interdisciplinary discipline, which originates from the study of global climate change and benefits from the progress of remote sensing technology. Now, ESS has entered the era of big data and artificial intelligence technology has played a key role in solving the frontier problems of ESS. Scientific data sharing is essential for the prosperity of science development and utilization of data value. After long-term exploration and practice, sound data management policies and mechanisms, continuous data sharing service system, and diversified scientific data integration modes have been established around the world. Innovative development of data sharing is going on thanks to the progress of sharing theory and ideas, such as the popular "findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable" FAIR principle and data publishing. China has promulgated policies and regulations at the national level, focusing on promoting the development of national scientific data center, collection and management of scientific data resource from national science projects, as well as data publishing and protection. Combing the experience abroad and the actual situation in China, researchers have built the distinctive classification scheme for ESS data resources and major breakthroughs continuously appear in metadata management, distributed interoperability, big data analysis, scientific data sharing services, and other professional technologies, covering the whole life cycle from data collection, integration, analysis to open and sharing. Taking the National Earth System Science Data Center as an example, we summarize the progress of data sharing services and key technologies, and introduce the practice and achievements in China. At present, the national data sharing work in the field of ESS has contributed towards the formation of mature and stable operation mechanism, established a formal standard framework for multi-source distributed scientific data integration, developed multi-scale geoscience database covering diverse disciplines and themes, and built up distributed service networks and systems suitable for massive heterogeneous data sharing. This work not only promotes the development of Geoscience, but also fastens the dissemination and promotion of data sharing theory. However, issues such as isolated data islands, low-level generalization of service systems, and weak accords with international standards still hinder the advance of data sharing. In the future, with personalized needs for data sharing activated, customized "data + knowledge" services are expected to become the prevailing modes, which will bring new opportunities and challenges to data sharing.
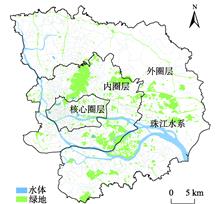
Cities with different land use types influenced by rapid urbanization and urban expansion support various human activities, such as shopping, eating, living, working, and recreation. The mixed use of land can stimulate the vitality of the city, enable the city togather enough people at different points in time, thus producing more interaction, promoting diversified consumption, and improving the economic and social benefits of the city.Mixed characteristics of land use types in cities gain more popularity in many researches due to the huge practical meanings. However, previous researches on mixed characteristics calculation mainly focused on POI data,and there is a lack of consideration for detecting urban topics. Human activities usually take place in different types of points of interest, the potential relationships and spatial interactions between the different types of adjacent POIs can work together to express the potential semantics of locations. In this paper, from an urban topic perspective, a method for the consideration of the relationship between POIs was proposed, and the Hill Numbers Diversity Index was applied to calculate the mixed degree of topics at the block level. Specifically,LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation) topic model was firstly used to generate topic vectors of the block and the co-occurrence patterns of POIs. Secondly, the diversity index was introduced to measure the mixed degree of blocks. Then, according to the Goodness of Variance Fit (GVF) and the nature break method, the blocks wereclassified into three groups: (1) high mixed blocks, (2) medium mixed blocks, and (3) low mixed blocks. Finally, multiple linear regression was applied based on mixed degree and topics in the blocksto uncover the significant topics and mixed pattern.Results show that different mixed blocks haddifferent mixed patterns.For high mixed blocks, the topic of teahouse restaurant was significant; the topics of company, enterprise, and residence weresignificant in medium mixed blocks; and the most typical two patterns in low mixed blocks werethe existence of landscape and famous scenery topic and teahouse restaurant topic. To sum up,starting from the urban topic, this paper reveals the mixed pattern of block, and the results show thatdifferent mixed patterns reflect the characteristics of different mixed areas and present certain rules in spatial distribution, which is conducive to the deep understanding of the cityareas, so as to provide a reference for the construction of Beijing mixed city, and also provide suggestions for other mixed cities.
Augmented Reality (AR) for geographic data is an important development direction of geographic information visualization. In recent years, some geographic studies have begun to use head-wear AR devices to visualize geographic data, making geographic spatial information more fully expressed. However, due to the limited computing power of head-wear AR devices, most of existing geographic information AR studies focus on the visualization of geographic information, yet do not provide complex spatial analysis and computation functions. This paper presents a framework for spatial analysis on AR devices by edge-cloud integration. In order to achieve efficient and end-to-end collaborative computation, the AR device is responsible for spatial data visualization, human-computer interaction, and data preprocessing; while the cloud server is responsible for complex spatial analysis tasks and persistent storage of spatial data. The binary storage method of edge-cloud and the coordinate conversion module between the 3D visualization model and the 3D geographic model provide efficient links between AR end and cloud end. Specifically, the framework divides three-dimensional geospatial data into three-dimensional AR visualization model data and three-dimensional geographic model data with attribute information, which are stored in AR and the server, respectively. The coordinates of the three-dimensional AR visualization model and geospatial coordinates are mapped using Bursa-wolf seven-parameter coordinate transformation method. Finally, HTTP protocol is used to transmit data to achieve high efficiency and end-to-end collaborative computing. Based on this framework, this paper used Hololens, a head-mounted AR device, and based on three-dimensional building data in Wuhan and a sky visibility factor algorithm, to realize complex spatial computation in the meantime of AR visualization. The findings suggest that our framework can provide smooth and stable 3D visualization (FPS was about 35) while guaranteeing the efficiency and accuracy of the complex sky-view factor computation. In conclusion, the edge-cloud integration technology can enable AR devices to perform complex spatial analysis and computation.
Most of the existing OD flow clustering methods adopt the strategy of dividing the OD flow into O point and D point or considering flow as the four-dimensional point to implement flow clustering, which ignores the effects caused by the length, direction and time information on the clustering process. In this paper, we proposedabrand-new spatio-temporal flow clustering method based on the similarity between flows with a strategy of merging flow clusters under different grading. Firstly, a reasonablespatio-temporal similarity measurement formula of OD flow was constructed to quantify the spatio-temporal similarity between OD flows on the basis of full stydy of OD flow's spatial information and temporal information. Then, with the purpose of optimizing the order of merging flow clusters, reducing the time consumption of clustering process, a strategy of merging flow clusters under different grading was used to complete flow clustering. In this method, both of time information and spatial information weretaken into consideration. By modifying the parameters of the spatio-temporal similarity measurement formula, our method can obtain clustering results for different time scales and spatial scales, which makes it possible to analyze the movement patterns from a multi-scale perspective. To verify the effective of our method, a series of experiments on real dataset was executed. The clustering results demonstrate that: ①flow clusters discovered by our method not only hadspatial characteristic but also hadtemporal characteristic; ② our method can discover different spatio-temporal OD flow cluster under different spatio-temporal parameters; ③ by comparingthe clustering results of our method with previous work of advanced technology level, it turnedout that our method hada better clustering performance, which was reflected in the fact that flows within the same flow cluster satisfied the similarity relationship and our method can not only find the obvious movements patterns but also capture inconspicuous movements patterns between non-hot zones. Thespatio-temporal joint OD flow clustering method proposed in this paper obtains new insights into motion from the perspective of joint temporal and spatial information, which is conducive to a reasonable and comprehensive study of residents' movement patterns, spatial linkage between regions, the determination of the known travel structure, and the exploration of the purpose of travel. The process of OD flow clutsering is the beginning of a series of subsequent analysis.