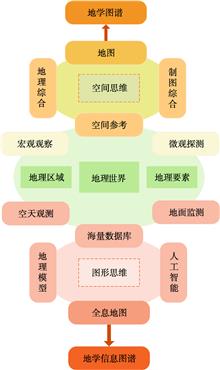
Geo-information Tupu is an important theoretical exploration field advocated by academician Chen Shupeng in the late of 1990s. Tupu is a Chinese word in Pinyin. It could be understood as map series, graph-spectrum, including the meaning of map, chart, graph, spectrum, plan etc., but we could not find a proper term for it in terminology yet. According to Chen's related literature, this paper discusses the connotation of his thought of geo-information Tupu, and holds that Tupu is the methodology of expression and analysis adopted in many fields, while geo-science tupu is a map series of geo-phenomena and processes in the field of geo-science. Geo-information tupu emphasizes quantitative geo-information (geo-database) and geo-computation, supported by geographic information system, it is expected to use geo-graphic language to visualize and analyze geographical phenomena in space and time, and to simulate the law of relationships between man and environment, reconstructing its past, evaluating its present situation and even predicting its future. The idea of geo-information Tupu is closely related to academician Chen's scientific career. Under the guidance of many famous Chinese profesosors, he laid a solid geographical foundation in his youth. In the early stage of career, he participated in a large number of practice of integrated geography and map design. These experiences promoted him to combine the comprehensive thinking of geography with the graphic representation. The development of remote sensing and GIS expanded his vision on geo-technology. In his later years, he put his passion and led China's development in these fields. Geo-information Tupu was developed, which was a collection of rich theories, methods and technical achievements accumulated in the study of geographical science all his life. Geo-information Tupu is a scientific problem that academician Chen Shupeng left to the later generations. Therefore, the authors puts forward some further reserch directions according to the newest related study progress in order to inherit Chen's scientific question. The development of Holographic map is an important basis for the visualization of geo-information Tupu. It is helpful to discover new geographical phenomena and new geographical laws. The "spectrum" detection of land surface information by remote sensing should be supported by the thought of "map" analysis in geography. It fanally come back to answer the core questions of geography, such as the distribution of complex surface and its mechanism. The cognition of geo-information Tupu takes the relationship between man and environment as the center to construct a new cognition theory from real to vitual geographical space. The goal of geo-information Tupu is to assist in the discovery and utilization of new geo-knowledge, and to lay a theoretical and methodological foundation for realizing automatic and intelligent geo-knowledge Tupu.
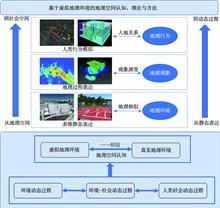
Since the beginning of 1960s, Geographic Information System (GIS) has been advanced in the analysis of geographic information and the services generated from it. Yet the rate of demands from geographers and large engineering projects continues to accelerate in the multi-dimensional geographic process simulation and the assessment of simulation results before those projects carried out. The set of increasing demands gives the Chinese scholars a sense of direction to explore the emerging concept Virtual Geographic Environments (VGEs) over the subsequent decades. In a broad sense, the VGEs is a collective term for all geographic environments except the real geographic environment while in the narrow sense, the virtual geographic environment can be considered as a computer-generated digital geographic environment in which the complex geographic systems are perceived and cognized by means of multi-channel human-computer interaction, distributed geographic modeling and simulation, and cyberspace geographic collaboration. From the very beginning, this paper elaborates on the transformation from the understanding of GIS to VGEs. In the second place, the evolution process of VGEs is analyzed including its current developing stage and a series of challenges it faced with. Aimed at facilitating the research on geoscience in the context of advanced technologies and accumulated geospatial information, this paper describes the new perspectives of VGEs research as followed: geographic space based on VGEs cognitive research, VGEs and experimental geography, virtual geographic cognitive experimental methods, and VGEs and geographic knowledge engineering in the context of big data. It can be foreseen that the study of VGEs is gradually moving towards an open, group-participated, collaborative scientific research paradigm. This is also a true reflection of the development trend of scientific research in the field of geography.
Laws, in expressing the relationships that existed in the world, are powerful ways for people to understand and communicate human understandings. In this paper through the comparison of laws in geography and those well accepted laws in physics (namely Newton's Laws), we concluded that the laws in geography also fit the definition of "law" albeit the laws in geography are different from the laws in physics in how they are generated and how they are expressed. We further compared the geographic similarity principle or the Third Law of Geography as suggested by Zhu et al (Annals of GIS, 2018,24(4):225-240) with the existing laws of geography from the perspectives of broadness, independence and applicability and found that the geographic similarity principle has the similar broad implications in geography as the other two laws but it is fundamentally different from the other two. It solves problems in geographic analysis that the other two were found to be insufficient. We thus believe that geographic similarity principle would serve a great candidate of the Third Law of Geography.
The rapid industrialization and urbanization along with the economic development of China since the 1980s have been profoundly altering land use pattern in China and subsequently affecting regional and national ecological and environmental conditions. Under the guidance of Shupeng Chen, since 1992 the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has established a complete framework for remote sensing-based land use change monitoring and data analyses, as well as a unique classification system, which has laid the foundation for China's Land Use and Land Cover Change (LUCC) information platform. Firstly, this paper systematically described the history of the LUCC studies in CAS, which include three phases: (1) 1992-1995: Establishment of remote sensing platform for National LUCC Monitoring System. In this phase, CAS designed a land classification system, and built the national-scalemonitoring platform for land use interpretation, by using 30 m optical remote sensing data as inputs. (2) 1996-2005: Standardization and operation of National LUCC Monitoring System. The three national satellite image and landuse map databases in the late 1980s, 1995 and 2000 covering the country were built with the National LUCC Monitoring System. (3) 2005-present: Multidisciplinary applications of land use changes results according to the National LUCC Monitoring System. In this phase, the multiple serial land use maps were widely used in various fields, e.g., the driving mechanism of agricultural reclamation and ecological conversion of farmland, and the system provided scientific support for the national ecological protection and sustainable development. Secondly, we proposed key scientific questions in the field of China's LUCC studies: What is the major spatiotemporal process of LUCC in China and even the world since the era of industrialization? What are the combined effects of LUCC and climate change on the structure and function of terrestrial ecosystems? How to treat the land system science as a multidisciplinary solution for sustainability? Thirdly, we also summarized the achievements of recent LUCC researches in the past 10 years, including different topics ranging from land use dynamic models, process and driving mechanism of land use/cover changes, improved land use change detection based on integration of big earth data and cloud computingtechnology, regional climatic and ecological consequences of urban, agricultural and forest land use changes. Finally, potential new directions of LUCC research are discussed from the perspectives of the scientific and technological frontiers. The LUCC research expect to provide important scientific supports for China to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in the future.
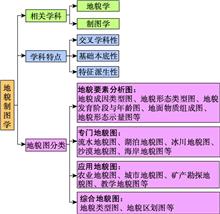
Mr Chen Shupeng, a famous Chinese geographer, remote sensing scientist, and geographic information system scientist, is the banner of modern cartography, remote sensing and Earth information science in China. Mr. Chen adhered to a scientific spirit of being down-to-earth, pioneering and brave. His spirit has influenced generations of scientists and students. Landform is the main element of Earth surface. The subject of geomorphology is to study the characteristics of Earth surface morphology and Earth surface processes. As the main element of Earth surface, landform types and cartography have been heated research topics in a long term in geography and other related disciplines. Researches related to geomorphologic cartography can provide basic and useful data for national economic construction. In commemoration of the 100 th anniversary of Mr. Chen's birth, we reviewed his enormous contribution in geomorphologic cartography in China, such as the topographic mapping based on bird's-eye view, the classification of landform types in Tengchong using remote sensing, and the large-scale landscape mapping in Huang-Huai-Hai Plain. Meanwhile, Mr. Chen firstly put forward the idea of using geographic information to study geoscientific issues. The development of Geo-info-TUPU was resulted from the organic integration of number, shape and philosophy. Through review, the development history of modern geomorphologic cartography in China was summarized, as well as the compilation of the geomorphologic type map and the geomorphologic regionalization map. To date, Chinese researchers have made great progress in application of geomorphologic regionalization theory and methodology, e.g., the publication of Geomorphological Atlas of People's Republic of China. By reviewing the development of modern geomorphological cartography, we will continue to explore new areas, including refining regional topography, refining China's geomorphologic types and geomorphologic regionalization, mapping global geomorphologic types and regionalization, mapping planetary topography, numerical simulation of geomorphologic processes, and etc. We will carry forward the achievements made by Mr. Chen and devote ourselves to future development of geomorphologic cartography.
The idea of geo-information Tupu is reviewed and summarized by reading and analyzing the theses published by Academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Prof. Chen Shupeng in this paper, which come from his scientific probe into geo-system. Geo-information Tupu is the result of combination of Geo-Tupu and information technology, which aims at discovering spatial and temporal knowledge and rule of geo-science, and can provide service to social and economic construction. Geo-information Tupu is classified into different types for each branch of geo-science and each industry according to its research object, and it is also classified into symptom Tupu, diagnosisTupu and realization Tupu according to its function. Prof. Chen developed the technology method for generating geo-information Tupu, proposed the workflow of geo-information Tupu, promoted the application of geo-information Tupu to the economic and social development. Prof. Chen indicated innovation directions of geo-information Tupu development which include innovation of technology and method of obtaining geo-science big data, improvement of intelligent and automatic level of generating geo-information Tupu, and enhancement of the wide and deep application of geo-information Tupu in social and economic construction. Prof. Chen pointed out grid map is important base of geo-information Tupu. The idea of geo-information Tupu proposed by Prof. Chen still has important guidance value in promoting the advance of geo-information science and meeting the major strategic needs of our country. The exploratory practice and results under the guidance of the idea of geo-information Tupu proposed by Prof. Chen were concluded here. The thematic information extraction technology based on knowledge discovery and the fine geo-surface element acquisition technology based on multi-data and multi-knowledge cooperation have been developed in recent years, which improves the automation level and efficiency of obtaining geo-science elements such as waterbody, settlements, green vegetation cover, snow cover, vegetation and landuse types in detail. The study and application of spatio-temporal change information Tupu have been broaden. The intelligent level and efficiency of generating the spatio-temporal change Tupu have been improved. The application of Geo-information Tupuin in social and economic development, ecological construction, environmental protection and disaster risk prevention and control has shown great prospects in recent years. Finally, in order to meet the major strategic needs of jointly building a global community with a shared future for mankind and the internationalization of geo-science in the new era, this paper puts forward the research on the key technologies and its applications of the global geo-science information Tupu, so that the large knowledge are intelligently and automatically discovered from big data of the geo-system through big observation, and the large knowledge is broadly applied to every aspect and every place through internet, which will support the modernization of the governance system and ability of the geo-surface system, and enhance the level and ability of geo-sciences to serve economic and social development, and highlight the characteristics and advantages of the geoscience.
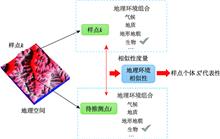
Ecology and environment are the foundation of human society's survival and development, and main part of the construction of national ecological civilization and receives unprecedented attention. In the past 40 years, research and application of remote sensing in China ecological environment have great achievements, and satellite remote sensing technology is playing more and more important role in the processing ecology, atmosphere, water, soil and other environment protection. According to the published documents, through typical or important study cases, this paper expounds development process of remote sensing technology in ecology and environment, including earth observation ability, supporting ecological civilization construction. The development of remote sensing monitoring capacity is mainly reflected in the expansion of application fields, improvement of monitoring accuracy and enhancement of monitoring effectiveness. The development of earth observation capacity is mainly divided into three stages: the period-based on foreign satellites, the development period of environmental satellites, and the application period of GF series satellites. Major events supporting the construction of national ecological civilization mainly include periodic investigation and assessment of national ecosystem, and environmental pollution management and control, emergency response and supervision of law enforcement. Combined with the national strategy and technology development, some thoughts on the future development of remote sensing of ecology and environment are put forward.
Digital Terrain Analysis (DTA), which can derives all kinds of topographic information widely used in diverse terrain-related geographic modeling and simulation, has been one of basic components of geo-spatial analysis, as well as one of fundamental functionalities of GIS. Researches on DTA methods have been continuously conducted in both width and depth. This paper tries to summarize the DTA researches from a new perspective, i.e., the dimensions of methodologic research on DTA. Three dimensions which successively emerged in methodologic researches on DTA are discussed, i.e., accurate, efficient, and easy-to-use. The dimension of "accurate" is of those researches on how to make DTA results more accurate. The dimension of "efficient" is of those researches on how to make DTA execution more efficient, or faster. And the new-emerging dimension of "easy-to-use" is on how to make DTA more easy-to-use in real applications as well as for users (especially those non-experts of DTA). The key study issue to be settled in the dimension of "easy-to-use" is how to formalize the knowledge on building DTA workflow properly and use it to conduct DTA during diverse real applications in an intelligent way. The proposed summarization on the dimensions of methodologic researches on DTA, as well as the corresponding methodologic researches, should be transferable for other domains in geo-spatial analysis, which often face the study issues similar to those in DTA domain.
High-resolution remote-sensing earth observation provide us with effective technical support for objectively inverting the surface patterns-process from the dimensions of space and time. This paper follows the research idea of space-temporal collaboration, and based on the high-resolution remote sensing images, we explored two typical problems in the agricultural remote sensing field: (1) proposed a division control and stratified extraction method for geo-parcel based on visual characteristics of images. Based on the division of DEM, we have designed different geo-parcel extraction models based on the differences in geometric and texture features in the division regions; (2) proposed a method for crop growth parameters inversing at the geo-parcel scale. Geo-parcel is the basic unit to perform physical parameter inversion under the constraints of space-time-attribute combination. The study taking geo-parcels extraction in in Xixiu District of Anshun City in Guizhou Province and Fusui County in Guangxi as examples for the division control and stratified extraction method, and taking inversion of sugarcane leaf area index in Fusui County of Guangxi Province as examples for the method of crop growth parameters inversing at the geo-parcel scale. For the extraction of cultivated land in Xixiu District, The number of geo-parcels with morphological accuracy (IoU) greater than 0.7 accounts for more than 60%, and the accuracy of the types of regular geo-parcels, terraces, forests and grasslands exceeded 80%; also, for the inversion results of sugarcane leaf area index in Fusui County, the results can accurately reflect the difference between base sugarcane and non-base sugarcane, and the base sugarcane is superior in quality to non-base sugarcane. It shows that Spatial-temporal collaboration use of multi-source high-resolution data is an effective way to achieve accurate agricultural remote sensing research.
In April 2012, a resolution was adopted for establishing "Intergovernmental science-policy Platform for Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES)" as an independent intergovernmental body of United Nations (UN) according to the UN Office of Legal Affairs with the seat of the secretariat located in Bonn of Germany.IPBES has 136 members now and is continuously growing. China has formally joined IPBES after State Council of the People's Republic of China gave its stamp of approval in December of 2012. In order to guide the use of scenario analysis and modelling in all work under IPBES to ensure the policy relevance of its deliverables, 'the methodological assessment report on scenarios and models of biodiversity and ecosystem services' was firstly started up in early 2014, which was carried out by experts from all regions of the world. Its summary for policy-makers was approved by the fourth session of the Plenary of IPBES in February 2016 and has been launched in August 2016 in France. Nature, nature's contribution to people and driving forces of nature change are core concepts of the methodological assessment report. Nature includes biodiversity and ecosystems as well as earth system. Nature's contribution to people consists of ecosystem services and nature's gifts. Driving forces of nature change was classified into direct driving forces and indirect driving forces. Advanced work on scenarios and models of biodiversity and ecosystem services is one of deliverables of the work program up to 2030. We review background, history and contents of the scenarios and models of biodiversity and ecosystem services, describe the conceptual framework of IPBES scenarios include exploratory scenarios/attribution scenarios, policy-screening scenarios, target-seeking scenarios and retrospective policy evaluation, and discuss existing problems and perspectives for developing the models and scenarios. To find a solution for these existing problems on global level, a conceptual model is proposed for integrating dynamics of nature, changes of nature's contribution to people, and driving forces of the changes in terms of the fundamental theorem for Earth's surface system modeling. In the meanwhile, interactive mechanisms among nature, nature's contribution and driving forces are considered, along with combination of macro-pattern information and micro-process information.
With the continuous development of modern information technology, GIS has been widely used in tourism fields, especially on all aspects research of tourism resources, including the tourism resources spatial classification, tourism resource monomers evaluation, tourism resource planning mapping, tourism resources management, tourism resources development and utilization, which have obtained the significant achievements. The analysis of the current situation and trend of GIS in the research and application of tourism resources in China is of great significance to understand the theoretical technology system and guide the application of tourism resources. Firstly, this paper reviews the literature in which GIS is used in the research of tourism resources for recent years. According to the study, we found that the GIS theory and method have made substantial progress on the mapping and evaluation of tourism resources. However, the cognition, classification and evaluation of tourism resources remain unsolved problems which included spatial scale and dimension, types of recognition and switching, spatial coupling, the transformation relationship between resources and products, development sequence, etc. However, there are still some unsolved problems in the fields, such as tourism resources cognition, classification and evaluation. Secondly, through summarizes the predecessors' research achievements and group for many years, tourism resources survey, evaluation, planning experience, the paper systematically discusses the tourism resources cognition, tourism resources classification, tourism resources standardization and tourism resources evaluation. At the same time, the paper also discusses the GIS spatial analysis method applies to the regional difference of tourism resources, tourism traffic location, spatial combination analysis, trend prediction and the spatial correlation analysis. Through combing GIS modeling and spatial analysis methods in the tourism resources information extraction and analysis, evaluation of tourism resources, tourism resources development planning and other relevant studies,we found that tourism resources research methods changed from qualitative description to quantitative model, and the application results continued to increase, involved in the comprehensive evaluation, spatial structure optimization, spatial layout and site selection, space development trend forecast, space utilization planning, etc. Finally, we put forward the trend of tourism resources in the future, regarding the knowledge model, knowledge mapping, multidimensional simulation and big data of the tourism resources. The trend of the integrated development of GIS and tourism resource research focuses on the innovation of spatial thinking mode and technological method. The new research includes that increasing GIS scholar invested in the research of tourism resources, building a case for the development of tourism resources and the knowledge model, an intelligent dynamic 3d visualization, increasing the immersion, experience and spatial decision making of tourism researchers and tourists.
Map is intelligent product of human civilization. The rapid development of science and technology increased the diversity and readability of map. Based on the existing concepts and forms of map, this paper developed a concept of pan-information-based high precision navigation map.This new map concept was a kind of intelligent navigation map which was oriented to vehicle mobile operation and integrated more functions, such as environment perception, pan-features fusion, high-precision positioning and planning decision-making. It can collect and fuse different information based on unified data model for different application fields, and it was a brand-new map form. Key innovation of this map was capturing and fusing pan-information of road from multi-source sensors, especially electromagnetic sensors, sound sensors, thermal infrared instruments and the others, in order to provide information for navigation from more aspects. Based on this concept, a theoretical model framework of pan-information-based high precision navigation map with multi-source data fusion was proposed. This framework consisted of four parts: (1) Pan-information road data collection. Data acquisition vehicles and other external sensors were used to collect multi-source data such as LiDAR system point cloud data, remote sensing images, oblique photogrammetric data, high-definition camera images, thermal infrared images, sound signal and electromagnetic signal. (2) Road static information extraction. Static information was basis for route planning and vehicle locating, which was obtained through the multi-source data mentioned above. The main road static information included lane lines, curbs, railings, road signs, road lamps, tunnels. (3) Road dynamic information extraction. Dynamic information was basis for real-time detecting surroundings and adjusting route of auto-vehicle, which was also obtained by extracting and marking the above collected data. The main road dynamic information included the distances between the vehicle and near objects, such as other cars, pedestrians and construction guardrails. Road dynamic information also included some ubiquitous information such as meteorological data, dynamic traffic conditions, POI data. (4) Fusion of dynamic and static information. Integrating road static information and road dynamic information can enrich road information, increase the accuracy of lane line, improve the updating efficiency of pan-information-based high precision navigation map,and provide map services for auto-driving vehiclesand its navigation. Compared with the existing map concepts and technologies, the map proposed in this paper has two characteristics: more detailed road information and more efficient data update, and both of the characteristics were based on our richer data sources, more diverse data collection methods and more efficient information extraction algorithms.
Agricultural lands account for nearly half of the global land area, and changes in agricultural land use directly affect food security, water security, ecological security, and climate change. Remote sensing is the main means for acquiring agricultural land use information. In recent years, the free opening of medium-resolution remote sensing data such as Landsat, Sentinel, and China's GaoFen satellites has opened unprecedented opportunities for extraction of agricultural land use information. A series of promising research progress has been made. This review paper analyzes the state of the art of agricultural land use information extraction from four aspects:cropland, crop type, agricultural planting system, and agricultural land management. We found that: (1) The products of cropland mapping have been improved from the past coarse resolution (500~1000 m) to a higher spatial resolution of 10~30 m in the past decade. The global and regional cropland layers have been well established; but there is a need to track historical cropland changes, especially to identify the key turning points, by making full use of the existing remote sensing data (data fusion and satellite constellation approaches). (2) Existing crop type mapping efforts have been mostly carried out by combining ground survey data with satellite remote sensing (mainly Landsat and Sentinel-2). It has been operationalized in North America and Europe, but the ability to monitor crop planting areas needs to be strengthened in other countries including China. Also, the early season monitoring capacity of crop type mapping needs to be improved; (3) Existing studies on tracking agricultural planting systems are mainly concentrated in Eastern Europe (e.g., the abandonment after the breakup of the Soviet Union). In China, cropland abandonment, rotation, and fallow are also common in the recent decade, due to economic and policy factors; however, existing studies are lacking on this issue. (4) in terms of the agricultural land management, encouraging progress has been made on the regional products of irrigation, but the reliability and accuracy of the products need to be improved. New technologies, including the emerging multiple sources of remote sensing data so-called remote sensing big data, deep learning algorithms, and cloud computing platforms (e.g., Google Earth Engineand Amazon Web Services) provide unprecedented opportunities for future agricultural land use information extraction, which will rely on (1) the fusion of multi-source data to form remote sensing big data with higher spatial, spectral, and temporal resolutions, (2) coupling of intelligent methods such as machine learning and deep learning algorithms with expert knowledge-based methods considering geographical and phenological information, and (3) the application of cutting-edge technologies such as remote sensing cloud computing platforms.
Geopolitical environment security is an important part of national security. Accurate, refined and timely updated information of various types of geopolitical conflicts is the basis of global geopolitical risk assessment and early warning. Based on the armed conflict datasets, this paper comprehensively reviewed the development of the global geopolitical conflict data system, and analyzed the application progress of geo-spatial and temporal positioning, big data mining and other technologies. Under the support of Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, the understanding of the connotation of armed conflict and the general framework of the data system of armed conflict events has been deepened, a large number of high-quality datasets or data products have been produced. Geopolitical conflicts are gradually refined in the theme, the spatial positioning accuracy of conflict events developed from country to smaller scale geographical location (longitude and latitude). Supported by network information search and big data mining technology, the update frequency of armed conflict events increased from annually update to hourly update, the construction of global armed conflict data system has achieved initial results. The deep integration of geo-environmental system science and geographical science, the wide application of geographic big data and artificial intelligence technology will be the important driving forces for the development of this discipline.
The coordinated development of urban transport and land use is of great practical significance to optimize urban spatial structure, reduce traffic congestion, and improve transport level. The integration of land use and transport systems is important for smart growth and sustainable development of cities. The integrated model of urban transport and land use is a key scientific support to analyze and simulate the interaction between urban transport and land use. Over the years, scholars in different countries have developed operational models that can be used for urban spatial policy formulation. However, the core algorithm of these models still need to be further improved. In this paper, the theoretical characteristics of existing mainstream models were analyzed. Based on the theoretical basis and the core algorithms, the advantages and disadvantages of six models were discussed, including spatial interaction model, urban economics and mathematical planning model, spatial input-output model, discrete choice model, micro-simulation model, and cellular automata model. A new comprehensive equilibrium model was proposed to overcome the shortcomings of the existing models. On the one hand, endogenous variable processing and dynamic feedback of the key algorithms need to be improved. On the other hand, the existing models do not fully consider the impacts of exogenous variables such as technological innovation, urban management, and urban planning policies. Therefore, new thinking was put forward for the core algorithm incorporating three key variables: Accessibility, land use characteristics, and travel cost. The equilibrium model adopts land use intensity and diversity to represent land use characteristics, and uses the improved algorithm of accessibility that takes into account the repulsive force caused by housing price and the opportunity scale of land use characteristics. In the generalized travel cost, attributes at the individual level and characteristics at the urban environment level are considered comprehensively. New algorithms were also proposed for the three modules of the integrated model, which include the residence and employment location decision module that considers incremental discrete selection process, the land supply and real estate development module that subdivides real estate types and dynamically feeds back land development results to urban land use evolution, and the comprehensive transport model that adopts improved impedance function, dynamic travel cost, and car ownership. It has important theoretical value for quantitative simulation of urban spatial evolution, prediction of trip distribution, and evaluation of urban management and planning policies. At the same time, it is of practical significance to develop the integrated model of urban transport and land use in China, so as to optimize the distribution of population and trip demand, and ease urban traffic congestion.
Transportation is an important tool and carrier for people to realize their trip purposes. Thus, it's a vital measurement for studying spatio-temporal pattern of individuals. Trip chain refers that a series of displacements completed by an individual in order to do one or more activities using a transportation. The time period of trip chain is one day. There are lots of information on individuals' trip purpose contained in trip chains. Extract this information from trip chains help to explore individuals travel behavior, which help understand the urban space. In previous studies, researchers have been focused on inferring and exploring the dynamic characteristics of commuting behavior, go to school activities, go home activities, entertainment, and leisure activities in urban space with the help of smart card data and taxi trajectory data. But limited studies have been carried on detecting hospital-seeking behavior with the assistance of trip record. With this in mind, this paper attempted to extend the application of trip records on hospital-seeking behavior. Specifically, we proposed a theoretical framework used to detecting hospital-seeking behavior from trip record. It consists of six principle, such as proximity principle, ring-closure principle, single-purpose principle, infrequency principle, time-coherence principle, and accompany principle. Also, a methodology for detecting hospital-seeking behavior was put forward based on the theoretical framework. Taking Beijing as an example, we found the key parameters of detecting hospital-seeking behavior and calibrated their thresholds. Finally, spatial and temporal patterns of hospital-seeking behavior were explored to reveal the accuracy of our results. On the one hand, the spatial patterns of hospital-seeking behavior showed that patients were mainly concentrated in tertiary hospitals. Tertiary hospitals have better professional skills and a larger service area than secondary and primary hospitals. Thus, they attracted and served more patients. On the other hand, patients' arrival time shows a high peak during 8:00 am and 10:00 am and a low peak during 13:00 pm and 15:00 pm, which closed to start time of registration and treatment. Two aspects above both supported the accuracy of results and rationality of the theoretical framework. The application of trip chains on detecting hospital-seeking behavior could make up for the shortages of traditional data, which is a small sample and difficult to access. This paper provided a new perspective, methodology, and data source for researching hospital-seeking behavior. Moreover, it could provide methodology references for other activities based on trip records.
Loess gully should be the most dynamic and changeable landform unit among the loess landforms in the Loess Plateau of China. In this plateau, the surface morphology presents thousands of gullies with a severe soil erosion pattern. This specific environment makes the area to a research focus both in the studies of geomorphology and soil erosion, especially the frontier questions of the formation and evolution of the gully landform. In the recent years, methods of geochronological dating, geomorphological feature expression, and monitoring simulation have been used by many scholars for better understanding of loess gully formation from the perspective of "past", "now", and "future". These advances have enriched our knowledge of loess gully formation and evolutionary processes. In this research, we systematically analyzed the research status quo and progresses of related studies on loess gully evolution in the Loess Plateau. These related studies include the landform evolution in the Loess Plateau, the loess gully formation, and the gully information extraction and expression using the DEM data. We argued that existing studies of loess gully formation and evolution should be further improved, with especially the help of theories and methods of the modern geographical information science. To this end, we proposed the concept of loess gully profile combination, trying to understand loess gully formation and evolutionary processes from a new perspective. The profile of gully transfers matter energy and accumulates terrain power during loess gully evolution. In addition, with the connection of runoff nodes, different gully profiles are connected and combined with each other, forming a specific pattern of gully profile combination. This combination should be a comprehensive information integration which integrates features and processes of loess gully landform. The three-dimensional spatial structure of the gully profile combination is an abstraction and mapping of loess gully landform evolution. The quantitative expression model of gully profile combination is expected to build, which should be oriented to loess gully landform evolution. This gully profile combination will help to achieve a new understanding of the loess gully formation mechanism during loess gully evolutionary processes, and to refine the gully evolution rules and patterns in the Loess Plateau. The gully profile combination is expected to further enrich digital terrain analysis methods.
The city is an accumulation of human civilization. It is also a highly complex system where a large number of agents interact, leading to a form and dynamics seemingly difficult to understand. Many studies in geography, ecology, sociology, economy and physics have been carried out to explore the general rules or regularities beneath the large number and the diverse agents operating in a city. It is widespread accepted that cities are an emergent phenomenon ruled by self-organization. As the language of nature and the fourth generation language of geography, fractal geometry has been a very powerful tool to capture the self-organized properties of cities. Most of the current studies are limited to the geometric fractal, i.e., based on fractal geometry: a shape made of parts similar to the whole in certain ways. Fractal geometry offers the significant advantages of capturing the spatial distribution, expansion, and filling properties of geographical objects in a city, and also describes the relationships between ranks and sizes of cities in an urban system. However, certain information—such as the efficiency of structural organization and the variance of levels of linkage—is ignored. As increasingly noticed by researchers, to better understand the ways a system of cities actually functions, we need to pay more attention to urban networks because current rapid developments of information and technology enable people to connect ever more easily and closely and in many new ways. This article reviews the advances of fractal cities from three aspects, which are geometric fractal, network fractal and evolutionary fractal. The significance and great potentials of fractal theory in urban studies are presented. The main research progress including fractal dimensions, fractal models, empirical studies and fractal cities and fractal urban systems are briefly reviewed, both for geometric and network fractals. As cities keep evolving, we also briefly review the evolutionary fractal cities, that is, the allometric scaling of cities. Based on current limitations on fractal cities, we propose a research agenda for fractal cities including (1) the development of measures and empirical studies on the third type of geographic fractals; (2) the spatial dependence and scale effects of fractal urban networks; (3) the coupling mechanics and influencing factors of fractal urban networks representing physical and non-physical urban spaces;(4) the DNA of a city from the perspective of fractals; and (5) the evolution simulation and policy intervention in fractal cities.
A semantic trajectory is a combination of a spatiotemporal trajectory and semantic information. Besides spatiotemporal information, a semantic trajectory comprises movement states (e.g. speed, direction), external contextual information (e.g. temperature, spatial topological relationships), and social relationships (e.g. friend relationships, social activities) of moving objects. We can derive from semantic trajectories intentions, habits, emotions, and other high order semantic information, thus further discover the patterns, relationships, and rules of individual or collective mobility behaviors. Therefore, compared with spatiotemporal trajectories, semantic trajectories are more in line with the practical requirements of decision-making applications in terms of semantics, interpretation, feasibility, and so on. This paper reviews the key technologies of semantic trajectory mining. First, we introduce the concept of semantic trajectories, and summarize four classic types of semantic trajectory definitions according to semantic elements. Then, we introduce the main phases of semantic trajectory modeling, including preprocessing, trajectory segmentation, and semantic enrichment. Since semantic trajectories cannot be acquired from location-acquisition devices as spatiotemporal trajectories, semantic trajectories need to be obtained through modeling techniques. Thus, the basic idea is to combine spatiotemporal trajectories with semantic information to generate corresponding semantic trajectories. Next, we introduce the main tasks of semantic trajectory mining, including semantic trajectory pattern mining, semantic trajectory clustering, semantic trajectory classification, anomaly detection of semantic trajectories, and so on. For each mining task, this paper introduces the basic principles and related algorithms, and summarizes the main key technologies and challenges. Finally, this paper concludes with the existing challenges and promising research directions of semantic trajectory mining. Specifically, this paper discusses the important research issues of semantic trajectory modeling in aspects including modeling definition, semantic annotation technologies, and multi-source data modeling. This paper also discusses the promising research issues of semantic trajectory mining such as semantic trajectory data management, classification and prediction, trajectory stream mining, privacy protection, multi-granularity mining, and evaluation methods.
Geographic national condition monitoring can comprehensively and dynamically grasp the changes of national information. They can also provide the data for economic and social development. Geographic national condition census generates the vector data according to unified standards, visual interpretation and field verification. The extraction of change information and updating of land cover maps based on geographic national condition census and multi-temporal remote sensing images is the key to geographic national condition monitoring. According to the characteristics of the geographic national condition census and monitoring demand, a change detection framework for geographic national condition monitoring based on multi-temporal remote sensing images is constructed. Multi-temporal image change detection methods and statistical analysis of object entities are proposed. The proposed method realizes the change detection and updating of geographic national condition census with the combination of the previous census outcomes and bi-temporal remote sensing images. The change detection method based on pixel-object combination first extracts the pixel-based change according to the traditional change vector analysis. Taking the vectors of the geographic national census as the statistical unit, this method then calculates the proportion of the changing pixel within the objects to determine whether they have changed and their change intensities. While the change detection method based on statistical analysis of object entities directly considers the geographic national census vectors as the objects for feature extraction and difference image construction. The resulting difference image is then segmented by an automated threshold to achieve the geographic national condition object-based change detection map. According to the change detection results, the pixels in changed areas are segmented by object-based segmentation, and the training samples are selected from the unchanged areas in the previous temporal image and census map to train the classifier model. Finally, the updated geographical condition vectors are achieved based on the combination of the original unchanged pixels and supervised classification results of the changed areas. The geographic national condition census of Jiangyin County and two high-resolution remote sensing images are used in the experiments. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method with accurate results and low cost for change detection and geographic national condition information updating, which provides potential means for geographic national condition monitoring.
The Belt and Road initiative was a globalization cooperation initiative put forward by China to strengthen the opening-up in the new era. With the development of globalization, it is of great significance to optimize the allocation of resources and environment. As an important reference dataset and input factor, the result of temperature interpolation is the basis for optimal allocation of regional resources and environment in large scale study area. Here, taking the Belt and Road (BR) regions as the study area, the monthly and annual mean temperature data in 2679 meteorological stations from 1980 to 2017 were interpolated based on Geographic Information Technology (GIS), using Inverse Distance Squared (IDS), CoKriging (CK), Regression-IDS (RIDS) and Regression-CK (RCK) interpolation methods. The 10 km map of spatial interpolation were generated using aforementioned four methods. The results showed: (1) In the BR regions, the geographical distribution of temperature were better displayed by IDS, CK, RIDS and RCK. The Mean Square Root Error (RMSE) of monthly mean temperature were 1.93~2.43 ℃, 1.78~2.14 ℃, 1.31~2.23 ℃ and 1.23~1.92 ℃, IDS, CK, RIDS and RCK, respectively. And the RMSE of annual mean temperature were 1.94 ℃, 1.83 ℃, 1.37 ℃ and 1.27 ℃, IDS, CK, RIDS and RCK, respectively. (2) The accuracy of CK interpolation with covariates was better than that of IDS, and the peak values produced by IDS were corrected. (3) After considering the impact of terrain, the accuracy of interpolation in temperature based on Residual correction were improved by 29.4% and 30.6%, RIDS compared to IDS and RCK compared to CK, respectively. In summary, The Regression-CK performed better than other three methods in this study area and it can be considered as temperature and climate data interpolation methods in the BR regions.
In the context of global climate change, vulnerability of farmland ecosystems in countries along the "Belt and Road" can directly affect regional food security. In this paper, we quantitatively analyzed the spatial distribution characteristics of farmland ecosystem vulnerability in countries along the "Belt and Road", as well as the responses to climate change. Results show: (1) Farmland ecosystems in countries along the “Belt and Road” generally had higher vulnerability, wherein 77.1% farmland ecosystems were found moderately and severely vulnerable. There was significant spatial variation of the farmland ecosystem vulnerability—higher in Central Asia, West Asia, and Mongolia; moderate in China, Southeast Asia, and South Asia; and lower in Russia, the Commonwealth of the Independent States, and Central and Eastern Europe. (2) Since 1980, farmland ecosystems along the "Belt and Road" have become notably warmer and drier, with the warming and drying area accounts for 64.06% and distributed mainly in central and southern China, the Commonwealth of the Independent States, southwestern Russia, Central Asia, Western Asia, western and southern India, Myanmar, Cambodia, and Indonesia. Warming and drying was the main feature of climate change in the farmland ecosystems of countries along the "Belt and Road". (3) Areas of climate change arranged per farmland ecosystem vulnerability from the lowest to the highest were: warm-wet areas, cold-wet areas, warm-dry areas, and cold-dry areas. The farmland ecosystem in the warm-wet areas was the least vulnerable and that in the cold-dry areas the most; the area of highly vulnerable farmland ecosystem in the warm-wet areas accounted for 43.09%, and that of highly vulnerable farmland ecosystem in the cold-dry areas accounted for 56.01%. Temperature and precipitation variations and their coupling relation controlled the vulnerability of farmland ecosystems, of which the trend of precipitation variation was an important factor influencing farmland ecological coordination and vulnerability. Our findings could serve as a useful reference to address the issue of food security in countries along the "Belt and Road", and to promote the sustainable agricultural development and enhance international cooperation with countries along the “Belt and Road” in agriculture.
Street contact crime refers to violations of the law committed by offenders through directly contact with victims in the street such as pickpocketing, robbery and snatch, etc, which is one of the common crimes in China. It is assumed that street contact crime is the result of interaction among motivated offenders, potential targets and absence of capable guardians. Different types of big data are employed in previous studies as ambient population to represent the potential targets which is one of the essential elements in the routine activity theory. However, these types of big data can not be applied in a micro-scale study of street contact crime because of their limitations. This study aims to fill this gap by using a new type of big data, WeChat heat map, an internet application which shows demographic distribution and changes dynamically with high spatial-temporal resolution to study the street contact crime in XT, ZG city, based on dynamic spatio-temporal distribution of potential Targets. The spatio-temporal pattern of street contact crime in XT, ZG city and their influencing factors were revealed. Street contact crime data, Points of Interest (POI) and data of house prices in XT, ZG city were used in this study as well. The whole day is divided into three intervals (wee hours: 00:00-06:59, daytime:07:00-17:59, night:18:00-23:59) and negative binomial regression models are built for the three intervals accordingly. It is demonstrated that the spatio-temporal distribution of street contact crime in XT, ZG city aggregates obviously. Street contact crime in XT, ZG city mainly concentrate in urban village and night is the peak period while daytime is the low period. The count of street contact crime in XT, ZG city reach its maximum between 22:00 and 22:59. Factors have different impacts on street contact crime from interval to interval. During the wee hours, WeChat population,KTV and leisure Club have significant positive impact on street contact crime. In the daytime, WeChat population and gym have significant positive impact on street contact crime. At night, WeChat population, restaurants, Leisure Club, bus station and distance to the nearest security department have significant positive impact on street contact crime. Others factors such as internet café, shopping mall, house prices and length of road have no significant impact on street contact crime in the whole day. WeChat population as an ambient population represent the potential targets well in routine activity theory as it has significant positive impact on street contact crime in the whole day.
With the continuous development of LiDAR technology, the research of LIDAR point cloud data processing is also in-depth. Point cloud filtering is one of the key steps in airborne LiDAR point cloud processing. The existing point cloud filtering algorithms often work well on some specific terrains, however, their filtering results are not satisfying in the cases of undulating terrains or mixed terrains, some post-processing measures are always needed. Based on relative coefficient of variation and regularized thin-plate-spline interpolation, a new terrain adaptive point cloud filtering method is proposed in this paper. The initial seed points are obtained by two-dimensional and 8-directional region-growing method, and then optimized by extracting line features from the point clouds, the points with low reliability are removed from the sets of reference points. After that the reference points are mostly reliable and scattered in the whole test area, and could be used to generate classifying surface. Finally, the classifying surface between ground points and non-ground points is fitted using thin-plate-spline interpolation. Classifying surface is used to absorb more ground points from point cloud, which could provide reference information for the next round of interpolation. In this process we use regularization item of adaptive coefficient to control the bending extent of classifying surface, in order to make the filtering algorithm adaptive to different types of terrains. Ground points are totally filtered after several iterations. The experimental results on point clouds from multiple devices show that the total errors of our proposed method were 4.14% and 4.17% in Guangzhou and ISPRS datasets, respectively. The result of the proposed filtering method is not the best, but it is more stable and has better terrain adaptability compared to state-of-the-art popular algorithms such as progressive TIN filter, cloth simulation filter, semi-global filter, etc. The proposed method outperforms other comparison methods in both error rate and overall performance in several complex or special terrains, as well as high computational efficiency. Additionally, the promising experimental results demonstrate that the proposed adaptive terrain filtering method is an accurate and efficient solution for airborne LiDAR point cloud filtering in complex terrains, such as slopes, ridges, and mixed terrains including vegetation and buildings.