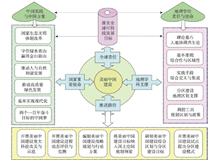
Beautiful China Initiative (BCI) aims at sustainable development with blue sky and green land, lucid waters and lush mountains, prosperous society and rich people, and harmony between humans and nature. The BCI is a Chinese practice to implement the SDGs 2030 of the United Nations, and an important method to promote the harmonious development between humans and nature and to win the gold and silver mountains by maintaining clear waters and green mountains. Geography, an applied cross-discipline serving the country's socio-economic development, has comprehensive and regional characteristics. Geographers shoulder the historical mission of building a beautiful China, and are duty-bound to take the lead in becoming pioneers and practitioners of the BCI. The theory of pericoupling and telecoupling between humans and nature is the theoretical foundation of the BCI. The interdisciplinary and comprehensive integration of geography is the practical means for the BCI. The complex system simulation and optimization of geography provide a scientific tool for coupling ways between humans and nature of the BCI. The main coupling ways for geography to promote the BCI include: carry out major scientific and technological projects and coupling demonstrations; perform dynamic assessment and monitoring of the coupled human and natural systems for the BCI; draw up the strategic coupling roadmap and the action plan of the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) for the BCI; build a concept of beautiful land to comply with the objectives of the National Territorial Space Plan of China; develop a comprehensive regionalization of coupled human and natural systems in accordance with local conditions, and build a group of beautiful urban agglomerations and national parks; undertake pilot projects for the construction of Beautiful China and summarize the regional coupling models for the BCI. These coupling paths will ensure that the whole country and each of its provincial-level region are getting closer to the target according to the schedule and roadmap for building a beautiful China, and diverse regions will achieve the overall goals in the competition.
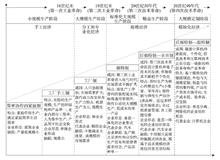
Agricultural and rural modernization is the general goal of the implementation of the rural revitalization strategy. The scientific formulation of the rural revitalization planning is related to the implementation effect of the national rural revitalization strategy. How to establish the basic theory of rural revitalization and develop the methods of rural revitalization planning have become important tasks of academic research and government decision-making. This paper constructed the theoretical model and method system of rural revitalization planning, tried to carry out the main function-oriented zoning, dominant type classification and principal purpose classification of rural regional system, and established the spatial system of rural revitalization planning and its optimal adjustment scheme. This system was applied to the overall rural revitalization planning in Yanchi County of Ningxia. By establishing the principle of rural revitalization planning that sticks to ecological priority, adaptation to local condition, industrial support and urban-rural integration, it put forward that the priority should be given to the development of rural professional cooperation organizations and the mixed economy of villages and towns, and the acceleration of the construction of advantageous industrial system characterized by the industrialization of tan-sheep, day lily, and minor cereals, and highlighted by the wisdom of eco-cultural tourism. Moreover, it was encouraged to give prominence to the position of the central town in space, and form the village organism and housing industry coordination body with the county seat and three key towns as the center of integrated industry development. The typical case study of Yanchi County has shown that the main contents and technical points of rural revitalization planning were embodied in the following four aspects: (1) determining the overall orientation of rural revitalization planning, and clarifying the phased development mode, key areas; (2) developing the county area based on the main function-oriented zoning, leading type classification and main purpose classification system, and exploring the territorial pattern and differentiation rules; (3) establishing the county development mode and industrial system, formulating coordination schemes of different main function-oriented zones, and revealing the spatial configuration and structural relationship of different dominant types; (4) exploring the local association and hierarchical system of each dominant type in its scale and level. The main task of implementing the rural revitalization planning is to promote the formation of a new pattern of urban-rural development with factors gathering, reasonable structure and orderly space in accordance with the objective requirements of "industrial prosperity, ecological livability, rural civilization, effective governance and prosperous life". China is facing great differences in rural development and many problems in transformation. Regional disparities and urban-rural differences determine the complexity, diversity and differences of rural governance and rural revitalization planning. China's rural transformation-urban and rural integration-rural revitalization-high quality development will become the major development logic and new normal in the future. The research on rural revitalization planning in the new era should focus on the overall situation of regional coordination and urban-rural integration, and solve the practical problems of "rural disease", so as to serve the national rural revitalization planning and scientific decision-making.
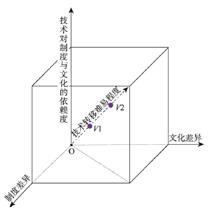
Promoting the construction of the Belt and Road initiative (BRI) towards a new stage of high-quality development raises new subjects for academic research, which demands in-depth study of existing BRI projects, summarizing experiences and lessons and theorizing construction models to guide future development. Research in the field of economic geography focused on outward foreign direct investment (FDI) of Chinese firms, but BRI construction is much broader in scope, consisting of not only FDI projects but also China-financed projects and emerging mixed projects. Case studies of BRI projects have shown that significant cultural and institutional difference between China and host country is the factor that tends to be ignored by Chinese firms in the "going global" efforts. Thus, revisiting the institutional and cultural turn in economic geography and employing its research framework to analyze BRI projects and summarize their construction models may contribute to the development of both economic geography and BRI. This article will first briefly review the background and research trends of the institutional and cultural turn; then summarize three major construction models of BRI projects, namely EPC (Engineering Procurement Construction)-based, concession-based and FDI models; finally draw on the institutional and cultural turn to classify BRI projects according to two indicators of "Breadth and Depth of Territorial Embeddedness" and "Destructive Effects of Technology and Project" into four types, i.e. transformative, supportive and ordinary projects as well as industrial parks. Different institutional and cultural sensitivity can be identified for each type of projects. The preliminary theorization proposed in this article may offer a potential framework for future research on BRI construction.
Since the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) was proposed, the pace of projects investment and construction has been accelerated, which accumulated much experience in the going-out strategy in the context of BRI. Modern railway projects are characterized by "natural monopoly", as well as huge investment and extensive geographical coverage. Moreover, their construction is a typical transformative project, which embedded the necessary institution and culture. The countries along the Silk Road are characterized by weak institutional construction, lack of regulatory system, and underdeveloped industrial civilization, therefore they cannot operate and manage the railway system. In this context, all links, including financing, design, construction, and operation, should be considered in the going-out process of China's railway system. The transfer subject is the technology-institution-culture nexus which takes railway technology as the core. In other words, to achieve railway technology transfer successfully, the host countries should offer rational institutional guarantee and cultural adaptation. Besides, the technical standard of railway construction, management mode, and industry chain in the process of railway operation and maintenance need to be localized. Mombasa-Nairobi standard gauge railway is a successful going-out case of China's railway technology. Learning from the case, this paper proposed the concept of "embedded technology transfer" and constructed the theoretical model of technology-institution-culture nexus transfer. The results can provide references for the transfer of transformative projects or technologies between countries with different institutions and cultures.
The implementation of the Belt and Road Initiative and the increasing frequency of the China-Europe Express have brought new changes to the production system of enterprises along the Belt and Road regions. On the basis of summarizing the evolution of production system of enterprises, this paper takes TCL Poland Plant as an example to conduct an in-depth study on the characteristics of the plant's current production system and its differences from the original production organization mode, and analyzes the impact of the China-Europe Express on its current production system. Some conclusions can be drawn as follows. (1) China-Europe Express had a great impact on the production system of TCL Poland Plant, which is mainly manifested in the following aspects. First, the transportation of raw materials by China-Europe Express Train improves the time efficiency and shortens the whole supply chain. Second, China-Europe Express acts as a "moving inventory", which realizes the flexibility of raw material inventory and "zero inventory" effect based on the punctual transportation. Third, the time and inventory benefits brought by China-Europe Express speed up the response to European market. The comprehensive benefits brought by China-Europe Express lead to a more punctual and lean production system, meet the diversified needs of consumers on account of product quality and diversification, and improve ability to expand European market. (2) On the basis of abandoning the original "Rigid Mass Production" system, we argue that TCL Poland Plant formed a unique production system—"Global Fluid Just-in-Time" which absorbed the essence of Toyota Production System based on the punctual global transportation of China-Europe Express Train. (3) The differences between the current and the original production systems of TCL Poland Plant are mainly focused on the following aspects: the difference of transportation and storage mode of raw materials, and the changes of production line, production mode and quality inspection organization, etc.
The development of a country at a certain stage is an outcome of a long-term historical accumulation process, which forms a mutually adaptive state of development among the main national factors such as institution, economic, cultural and technological systems. And the technology transfer breaking through the original level will cause a disorder among the institutional-economic-cultural-technological systems (IECT system), and produce the frictional effect of technology-environment. This paper constructed a conceptual model on the complex system among the institution, economy, culture and technology, and analyzed its major features. Then, we simplified the above model into railway-institution-economic-cultural model (RIEC system) and probed the adaptive mechanism between railway and institutional-economic-cultural system. Furthermore, we explored the institutional-economic-cultural adaptability of the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway. This article insists that Ethiopia and Djibouti had not experienced the large-scale industrialization. As an electrified railway, the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway is a "spanning transfer" of the technology and there is a misplacement between this railway and the developing stage of Ethiopia and Djibouti. And the construction and operation of this railway brought out an obvious challenge for the institutional-economic-cultural development of these two countries, which resulted in the inadaptability of local institutional, economic and cultural system, and the unbalance of RIEC system. This study can provide a scientific guidance for China's enterprises to construct railways and spread China's railway standard in the world especially in the less-developed countries.
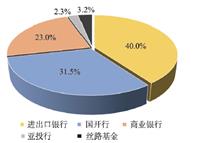
Since the launch of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) in 2013, China's overseas industrial parks have become an important platform for Chinese enterprises to "go global in groups", and also for promoting economic and trade cooperation between China and other countries involved in the BRI. The high-profile intergovernmental industrial parks are at the highest cooperation level, large in investment scale, and rapid in construction progress. Moreover, they are expected by Chinese government to play a demonstration role for the joint construction of the BRI. Against the backdrop, intergovernmental industrial parks have attracted increasing attention from policymakers and academics at home and abroad. However, existing research on overseas parks tends to be policy-oriented, and did not make distinction between the intergovernmental industrial parks from the overseas parks established by private enterprises. Few studies have been conducted so far on construction mechanism of overseas industrial parks from a perspective of multi-scale coupling. This article tries to fill this gap to examine the multi-scale coupling mechanisms of intergovernmental cooperative parks in the framework of the BRI, taking the China-Belarus Industrial Park as an example. This industrial park was launched in 2010 jointly by the presidents of the two countries as a flagship project of the BRI. Now it becomes a new growth pole of the Minsk city. The research shows that the construction of the high-profile overseas industrial parks is a dynamic process, through which the two governments, park developers and park enterprises coordinate, mediate, and arbitrage strategic interests in the global economy, and also pursue common goals. This process involves multi-actors (government, corporations) from various scales (global, intergovernmental, industrial park, corporations). Specifically, the governments of the two countries launched the projects for their respective strategic interests. The intergovernmental cooperation frameworks and mechanisms provide an institutional framework for coordinating the strategic interests of both sides, and also mobilizing the political and economic resources from the two countries and beyond to promote the high-end project. But the top-level cooperation mechanisms cannot automatically guarantee the project's success. The keys are reasonable equity structure of the park development company and its strengths of networking with the global partners. At the same time, the economic performance of the enterprises inside the industrial parks is the fundamental to parks' sustainable development. Therefore, only when the strategic interests of the two countries are properly handled and the economic benefits of the development company and the companies related with the project, the industrial park can survive and develop smoothly. Hopefully, this research can provide a scientific basis for promoting the high-quality development of China's overseas parks.
Policy mobility research has become an important subfield in political geography. Overseas industrial zones serve as burgeoning case areas to testify the theoretical framework of policy mobility, whose development is a key component of the Belt and Road Initiative and an expected experimental way to promote inclusive globalization. The highlight of this paper is the role that the partnership plays for multi-scalar actors in the process of policy mobility when it comes to the overseas industrial zones. In this paper, we interpret Thai-Chinese Rayong Industrial Zone's evolving strategies and development trajectory through two interrelated conceptual lenses, namely, policy mobility and partnership. It is emphasized that the policy mobility of overseas industrial zones is a multi-scalar process of gradual advancement, and the partnership plays an important role in policy mobility. This paper systematically analyzes the institutional background and main partners of Thai-Chinese Rayong Industrial Zone. Policy mobility in terms of tax, land, talent and other elements are shaped and accelerated by the interactions and partnership between Thai and Chinese central governments, local governments, and leading enterprises. Finally, the policy recommendations are proposed for the sustainable development of China's overseas industrial zones in the context of Belt and Road Initiative.
At present, overseas industrial parks have become an important platform for economic and trade cooperation between China and other countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and they are playing an increasingly important role in the construction of the BRI. Most existing studies on overseas industrial parks of China focus on the economic function, while the institutional and cultural platform function need to be further explored. Based on the perspective of the institution and culture, the paper takes Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone in Cambodia as a case to analyze the operating mechanism and construction model of overseas industrial parks, and reveals the role of overseas industrial parks in promoting the outward foreign direct investment of Chinese small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The results show that the Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone has provided a high-quality institutional environment and sufficient transnational development space for the enterprises entering the zone by constructing a multi-level coordination mechanism, creating an excellent investment environment, promoting information and resource sharing, and releasing the agglomeration economic effects. It assists enterprises in the zone to better adapt to the host country's investment, and provides more possibilities for a large number of small and medium-sized enterprises to make path breakthrough and path innovation in their overseas investments. On the basis of the case study, we believe that overseas industrial parks have played an important role in promoting Chinese small and medium-sized enterprises' overseas investment, providing buffer space and growth environment for overcoming institutional and cultural differences in Chinese enterprises' overseas investment, and played a role as an "Investor Garden".
With the rapid increase of productivity, the intense conflict between human and environment has given birth to the discipline of spatial planning. As an indispensable tool for reconciling man-land relationship, high-quality spatial planning is essential for the reasonable utilization of space resources and the promotion of sustainable socio-economic development. Adapting to the rules of man-land interaction is the premise of conducting high-quality spatial planning, which is unachievable without the support of geography. Using bibliometric and typical case analysis method, this study conducts an in-depth analysis of researches and practices on foreign spatial planning from the perspective of geography. The main findings were demonstrated as follows: (1) as a science focusing on "space", geographical theories and methods are indispensable in the reform of spatial planning. Traditional geographical theories still play a pivotal role in spatial planning, while the post-structuralist geographical theories such as relational geography are increasingly applied. Currently, the traditional spatial planning based on an isolated perspective and linear growth can hardly meet the requirements of socio-economic development, while the geographical perspective based on the relationship network combined with multiple developmental trajectories may be conducive to promoting the rationalization of spatial planning. (2) A country's geographical research will greatly affect its spatial planning. For example, the central place theory has made Germany one of the countries with the most balanced spatial development, while the geographical research achievements in Japan have supported the formation of the territorial development pattern dominated by three urban agglomerations. Thus, improving the geographical research level is a cornerstone to promote the healthy development of spatial planning. For China, in the process of promoting the localization of foreign theories, geographers should proceed from the perspective of man-land relationship areal system, in order to provide scientific guidance for resolving unprecedented fierce conflicts between human and environment. (3) Because of the regionality, comprehensiveness, complexity and multi-scale characteristics of the man-land relationship areal system, the construction of a spatial planning system with distinct levels and complementary functions is the guarantee for the operability of spatial planning. Overall, as a science of humanistic pragmatism, geography ought to propose scientific and reasonable policy suggestions aimed at the major national need—the reform of spatial planning, through innovative theories, methods and technological approaches that root in real-world situations, thus contributing to the harmonious development of man-land relationship.
After the release of the Sixth Census Data, more research results have been achieved about the socio-spatial structure in urban China based on the method of factor ecology analysis. However, methodological innovation needs to be promoted. In this paper, combining census data with big data, with the aid of the methods of grid processing and calculation of accessibility of public service facilities, the authors try to interpret the quality of life of urban residents from both the internal and the external environments of residence, and to reveal the relationship between the spatial structure of quality of life and the socio-economic status of urban residents. Taking Changzhou City of Jiangsu province as a case study, first of all, the authors extract the housing data from the Sixth Census, and the data of facilities from the urban POI data of Baidu maps. And then, factor analysis, cluster analysis, accessibility analysis and other methods are used to identify the spatial structure of urban residents' quality of life and reveal some characteristics of urban social space from the viewpoint of socio-spatial dialectic. The results suggest that the spatial structure of the quality of life of residents in Changzhou based on residential environment shows a clear pattern of overlap between the circular structure and the fan-shaped one. In addition, there is a spatial coupling between the spatial structure of urban residents' quality of life and their socioeconomic attributes, that is, residents with different social and economic attributes have some differences in their quality of life. The formation of an interactive relationship between these two aspects is the result of a combination of administrative, market and spatial factors, which may lead to overcrowding in the old city, fire safety problems in living and production buildings, traffic congestion problems caused by tidal commuting, social isolation, unreasonable distribution of public service facilities, and other socio-spatial effects. Its enlightenment for urban planning and management lies in the following aspects including the dispersal of the old city, focusing on fire safety in certain areas, perfecting the transportation links between central and peripheral areas, preventing the emergence of social isolation in the high-tech zones, and improving the public service facilities in rural areas.
Walking, as both a major mode of transport and the most common form of every-day physical activity, deserves further attention in urban geography and public health studies. The control of self-selection has not attracted enough attention in the empirical studies in China, and there is insufficient research on the behavior of distinguishing different walking purposes. Based on the micro survey data of the built environment and residents' travel behavior in Xi'an city in 2014, the quasi-experimental study design of matching case control was adopted. By controlling the self-selection effect brought by travel attitude, this paper explored and distinguished the impact of urban rail transit itself and built environment on walking behavior. Research findings are listed as follows. (1) Self-selection factors such as travel attitude and preference have a critical influence on individual walking behavior. (2) After controlling of individual socio-economic attributes and self-selection factors, the respondents' perception of built environment greatly affected the walking frequency. (3) There is a certain difference of the impact of objective built environment variables on walking behavior between China and developed countries. No significant effect of density was found in walking frequency models of transport or leisure walking. The number of shopping stores and the number of bus stations in the objective built environment variables has a significant positive effect on the transport walking frequency. However, for leisure walking, these built environment variables do not have significant impact. (4) Subway has a significant independent influence on the transport walking frequency. These conclusions can help to further understand the influencing factors and mechanism behind urban residents' pedestrian travel behavior and provide enlightenment for urban transportation and urban planning policies that guide urban residents to green and healthy travel by optimizing urban land use planning.
The construction of the modern rural governance system becomes an important part in promoting the urban-rural integration development and rural vitalization. Solving systemic problems such as limited development space, unclear ownership relationship and inefficient organization in the process of using rural space has become the primary task of rural spatial governance. Based on the breakthrough of the comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space, this paper attempts to analyze the mechanism of rural space governance in promoting rural space restructuring, ownership reshaping and organizational system reconstruction, and further explores the feasible path of rural space governance to optimize the urban-rural pattern, improve the urban-rural interaction, and promote the urban-rural integration development. The conclusions are as follows: (1) Physical space governance facilitates the optimization of rural spatial structure, the space ownership governance safeguards the development rights of different stakeholders, and the space organization governance enhances rural organizational capabilities. The comprehensive governance of "matter-ownership-organization" in rural space helps to impel the restructuring of rural space, the reshaping of ownership relations and the reconstructing of organizational system, to achieve the goals of the modern rural space governance system with clear rural space ownership. (2) The "population-land-industry" transformation path guided by rural space governance creates conditions for the analysis of "deepening space governance-activating rural space-optimizing human-land relationship-improving the urban-rural pattern". (3) Rural space governance promotes the continuous evolution of urban-rural development, and the improvement of urban-rural interaction becomes an important basis for upgrading urban-rural integration development and solving the dilemma of rural development. Finally, this paper constructs an analytical framework and feasible path for the interaction between rural space governance and the urban-rural integration development, and explores the internal relationship and research trends of rural space governance and territory spatial planning.
Based on the objective-weight value-assigning method, by means of establishing one comprehensive index system from four dimensions, namely natural endowment, flow input, output capacity and facilities' mechanism, this paper makes a series of experimental tests on the actual agricultural competitiveness within the 29 provincial-level areas of China from 2000 to 2016. And with application of spatial measurement model, it also makes a profound analysis upon spatio-temporal evolving rules and factors influencing China's agricultural competitiveness in hope for offering certain theoretical supports for formulating a series of targeted and differentiated agricultural competitiveness upgrading policies in the near future. The results of analysis show that: (1) China's agricultural competitiveness, featured by obvious spatial auto-correlation, is on the rise. The spatial spillover intensity presents an inverted "U-shaped" pattern. And the two sub-competitiveness indexes, namely flow input and output capacity, still keep on the upside. The overall resource endowment is relatively stable and the facilities' mechanism is witnessing a fluctuant increasing process. (2) The agricultural competitiveness in the central and western provinces continues to decline as that in the eastern provinces rises rapidly, which presents an apparent polarization. And the local-spatial clustering pattern is dominated by HH clustering mode and LL clustering mode with the characteristics of stronger stability and serious path dependency. (3) Multiple factors, including farmers' income, household-consuming level, economic basis, R&D input, planting structure and grain-variety selection, have direct effects on the spatio-temporal evolution of provincial agricultural competitiveness. At the same time, the above factors have indirect spillover effects on other provinces. (4) We should give full play of the current demonstration effect and diffusion effect brought by the agricultural competitiveness and related influencing factors to push future optimal allocation of agricultural resources, promote subsequent rational flow of the existing agricultural producing factors and plan finally-balanced development of agricultural competitiveness.
China is experiencing rapid urbanization. It is of great significance to clarify the characteristics of urban spatial expansion and its evolution law for regional coordinated development. Urbanization involves many aspects such as economy and population. However, current researches still face challenges in comprehensively reflecting the spatial pattern, evolution process, and intrinsic mechanism of regional urbanization, and they cannot effectively reveal and quantify the spatial correlation and evolution process of regional urbanization. Based on the data of economy, population and urban space in the Yangtze River Delta region from 1995 to 2015, this paper used spatial polarization and diffusion theory to quantitatively analyze the spatial evolution process and characteristics of urbanization. The results showed that: (1) The characteristics of urbanization level in the study area were obvious. Shanghai was at the first level, Nanjing, Hangzhou and Suzhou were at the second level, and the rest of the cities were at the third, fourth and fifth levels. The spatial correlation intensity of urbanization shows that the high-value level was concentrated in the eastern part of the region and 10 cities, such as Shanghai, Suzhou and Hangzhou, constituted the most intensive urbanization development spatial network. (2) During the study period, the spatial polarization and spatial diffusion characteristics existed simultaneously in the Yangtze River Delta region. During the study period, a diffused region always rapidly presented a patttern of polarization in space, then the polarization weakened and turned into a new diffusion phase. It is most obvious in Nanjing and Hangzhou among all the 41 cities. Our findings completely demonstrate that the spatial correlation among cities is changing over time. This study also explored the driving mechanism of regional urbanization, indicating that industrial upgrading and transfer within the study area is the main endogenous driving force for spatial polarization or diffusion. Our study has important theoretical and practical value for future regional development planning.
Climate change caused by CO2 emissions has become an environmental issue globally in recent years, and improving carbon emission performance is an important way to reduce carbon emissions. Although some scholars have discussed the carbon emission performance at the national scale and industry level, literature lacks studies at the city- level due to a limited availability of statistics on energy consumptions. In this study, based on China's city-level remote sensing carbon emissions from 1992 to 2013, we used the super-efficiency SBM model to measure the urban carbon emission performance, and the traditional Markov probability transfer matrix and spatial Markov probability transfer matrix are constructed to explore the spatio-temporal dynamic evolution characteristics of urban carbon emission performance in China for the first time and to predict its long-term evolution trend. The study shows that urban carbon emission performance in China presents a trend of steady increase in the fluctuation, but the overall level is still at a low level, so there is still a great improvement space in urban carbon emission performance, with huge potential for energy conservation and emission reduction. The spatial pattern of national urban carbon emission performance shows the characteristics of "high in the south and low in the north", and there is a significant difference in the level of carbon emission performance between cities. The spatial Markov probabilistic transfer matrix results show that the transfer of carbon emission performance type in Chinese cities is stable, thus it forms the "club convergence" phenomenon, and the geographical background plays an important role in the process of the transfer. From the perspective of long-term trend prediction, the future evolution of urban carbon emission performance in China is relatively optimistic. The carbon emission performance will gradually improve over time, and the distribution of carbon emission performance presents a trend of high concentration. Therefore, in the future, China should continue to strengthen research and development to improve the performance level of urban carbon emissions and achieve the national target of energy conservation and emission reduction. At the same time, neighboring cities with different geographical backgrounds should establish a sound linkage mechanism of economic cooperation to pursue coordinated development between economic growth, energy conservation and emission reduction, so as to realize low-carbon city construction and sustainable development.