View fulltext
View fulltext
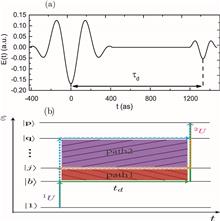
We propose a scheme that utilizes weak-field-induced quantum beats to investigate the electronic coherences of atoms driven by a strong attosecond extreme ultraviolet (XUV) pulse. The technique involves using a strong XUV pump pulse to excite and ionize atoms and a time-delayed weak short pulse to probe the photoelectron signal. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates that the information regarding the bound states, initiated by the strong pump pulse, can be precisely reconstructed from the weak-field-induced quantum beat spectrum. To examine this scheme, we apply it to the attosecond XUV laser-induced ionization of hydrogen atoms by solving a three-dimensional time-dependent Schrödinger equation. This work provides an essential reference for reconstructing the ultrafast dynamics of bound states induced by strong XUV attosecond pulses.
In this work, we compare different methods for implementing a triplicator, a phase grating that generates three equi-intense diffraction orders. The design with optimal efficiency features a continuous phase profile, which cannot be easily reproduced, and is typically affected by quantization. We compare its performance with binary and sinusoidal phase profiles. We also analyze the effect of quantizing the phase levels. Finally, a random approach is adopted to eliminate the additional harmonic orders. In all cases, a liquid-crystal-on-silicon spatial light modulator is employed to experimentally verify and compare the different approaches.
In order to alleviate the impact of turbulence on the performance of underwater wireless optical communication (UWOC) in real time, and achieve high-speed real-time transmission and low cost and miniaturization of equipment, a 2×2 real-time multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) high-speed miniaturized UWOC system based on a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and a high-power light-emitting diode (LED) array is designed in this Letter. In terms of multiplexing gain, the imaging MIMO spatial multiplexing and high-order modulation for the first time are combined and the real-time high-speed transmission of PAM-4 signal based on the LED array light source in 12 m underwater channel at 100 Mbps rate is implemented, which effectively improves the throughput of the UWOC system with a high-power commercial LED light source. In light of diversity gain, the system employs the diversity of repeated coding scheme to receive two identical non-return-to-zero on-off keying (NRZ-OOK) signals, which can compensate the fading or flickering sublinks in real time under the bubble-like simulated turbulence condition, and has high robustness. To our knowledge, this is the first instance of a high rate and long-distance implementation of a turbulence-resistant real-time MIMO miniaturized UWOC system based on FPGA and high-power LED arrays. With spatial diversity or spatial multiplexing capabilities, its low cost, integrity, and high robustness provide the system with important practical prospects.
We introduce an all-optical approach, optical parametric amplification (OPA) processor to suppress the impact of Sun outage in laser satellite communication systems, which is implemented by only one nonlinear semiconductor optical amplifier driven by both electrical and optical pumps. The optimized OPA processor, with a current of 539 mA and a pump-to-signal ratio of 16 dB, could significantly improve the signal quality by 3.5 dB in experiments for the elevation angle of Sun radiation of 0 rad. The signal quality improvement is observed in the whole range of the elevation angle, confirming the effectiveness of the proposed OPA processor in the field of Sun radiation mitigation.
In this Letter, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a lens-free wavefront shaping method that utilizes synchronized signal block beam alignment and a genetic algorithm (SSBGA) for a diffuse non-line-of-sight (NLOS) visible light communication (VLC) system. The proposed method effectively controls the position and mobility of visible light beams by partitioning spatial light modulator pixels and manipulating beams to converge at distinct spatial positions, thereby enhancing wavefront shaping efficiency, which achieves a significant 23.9 dB optical power enhancement at +2 mm offset, surpassing the lens-based continuous sequence (CS) scheme by 21.7 dB. At +40° angle, the improvement reaches up to 11.8 dB and 16.8 dB compared to the results with and without lens-based CS, respectively. A maximum rate of 5.16 Gbps is successfully achieved using bit-power loading discrete multi-tone (DMT) modulation and the proposed SSBGA in an NLOS VLC system, which outperforms the lens-based CS by 1.07 Gbps and obtains a power saving of 55.6% during the transmission at 4 Gbps. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that high-speed communication has been realized in an NLOS VLC system without a lens.
In this paper, we present a fast mode decomposition method for few-mode fibers, utilizing a lightweight neural network called MobileNetV3-Light. This method can quickly and accurately predict the amplitude and phase information of different modes, enabling us to fully characterize the optical field without the need for expensive experimental equipment. We train the MobileNetV3-Light using simulated near-field optical field maps, and evaluate its performance using both simulated and reconstructed near-field optical field maps. To validate the effectiveness of this method, we conduct mode decomposition experiments on a few-mode fiber supporting six linear polarization (LP) modes (LP01, LP11e, LP11o, LP21e, LP21o, LP02). The results demonstrate a remarkable average correlation of 0.9995 between our simulated and reconstructed near-field light-field maps. And the mode decomposition speed is about 6 ms per frame, indicating its powerful real-time processing capability. In addition, the proposed network model is compact, with a size of only 6.5 MB, making it well suited for deployment on portable mobile devices.
Lens-free on-chip microscopy with RGB LEDs (LFOCM-RGB) provides a portable, cost-effective, and high-throughput imaging tool for resource-limited environments. However, the weak coherence of LEDs limits the high-resolution imaging, and the luminous surfaces of the LED chips on the RGB LED do not overlap, making the coherence-enhanced executions tend to undermine the portable and cost-effective implementation. Here, we propose a specially designed pinhole array to enhance coherence in a portable and cost-effective implementation. It modulates the three-color beams from the RGB LED separately so that the three-color beams effectively overlap on the sample plane while reducing the effective light-emitting area for better spatial coherence. The separate modulation of the spatial coherence allows the temporal coherence to be modulated separately by single spectral filters rather than by expensive triple spectral filters. Based on the pinhole array, the LFOCM-RGB simply and effectively realizes the high-resolution imaging in a portable and cost-effective implementation, offering much flexibility for various applications in resource-limited environments.
The pandemic of respiratory diseases enlightened people that monitoring respiration has promising prospects in averting many fatalities by tracking the development of diseases. However, the response speed of current optical fiber sensors is still insufficient to meet the requirements of high-frequency respiratory detection during respiratory failure. Here, a scheme for a fast and stable tachypnea monitor is proposed utilizing a water-soluble C60-Lys ion compound as functional material for the tracking of humidity change in the progression of breath. The polarization of C60-Lys can be tuned by the ambient relative humidity change, and an apparent refractive index alteration can be detected due to the small size effect. In our experiments, C60-Lys is conformally and uniformly deposited on the surface of a tilted fiber Bragg grating (TFBG) to fabricate an ultra-fast-response, high-sensitivity, and long-term stable optical fiber humidity sensor. A relative humidity (RH) detecting sensitivity of 0.080 dB/% RH and the equilibrium response time and recovery time of 1.85 s and 1.58 s are observed, respectively. Also, a linear relation is detected between the resonance intensity of the TFBG and the environment RH. In a practical breath monitoring experiment, the instantaneous response time and recovery time are measured as 40 ms and 41 ms, respectively, during a 1.5 Hz fast breath process. Furthermore, an excellent time stability and high repeatability are exhibited in experiments conducted over a range of 7 days.
The compact, sensitive, and multidimensional displacement measurement device plays a crucial role in semiconductor manufacture and high-resolution optical imaging. The metasurface offers a promising solution to develop high-precision displacement metrology. In this work, we proposed and experimentally demonstrated a two-dimensional displacement (XZ) measurement device by a dielectric metasurface. Both transversal and longitudinal displacements of the metasurface can be obtained by the analysis of the interference optical intensity that is generated by the deflected light beams while the metasurface is under linearly polarized incidence. We experimentally demonstrated that displacements down to 5.4 nm along the x-axis and 0.12 µm along the z-axis can be resolved with a 900 µm × 900 µm metasurface. Our work opens up new possibilities to develop a compact high-precision multidimensional displacement sensor.
We demonstrate a high power, Er:LuAG single-longitudinal-mode laser in an anti-misaligned resonator. Based on the Faraday effect, a 1.61 W single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) laser is obtained with the double corner-cube-retroreflector (CCR) structure, and the tunable wavelength is 1649.2–1650.3 nm. Additionally, we investigate the anti-misalignment characteristics when the CCR moves and rotates along the optical axis. Furthermore, by utilizing the Er:LuAG amplifier, the maximum 2.32 W single-longitudinal-mode laser at 1649.6 nm is achieved. The beam quality factors M2 of the 2.32 W Er:LuAG single-longitudinal-mode laser are 1.23 and 1.25 along the horizontal (x) and vertical (y) directions, respectively.
The high-power mode-programmable orbital angular momentum (OAM) beam has attracted significant attention in a wide range of applications, such as long-distance optical communication, nonlinear frequency conversion, and beam shaping. Coherent beam combining (CBC) of an optical phased array (OPA) can offer a promising solution for both generating the high-power OAM beam and rapidly switching the OAM modes. However, achieving real-time phase noise locking and formation of desired phase structures in a high-power CBC system faces significant challenges. Here, an internal phase-sensing technique was utilized to generate the high-power OAM beam, which effectively mitigated thermal effects and eliminated the need for large optical devices. An OPA with six elements was employed for experimental demonstration. The first effective generation of over 1.5 kW mode-programmable OAM beam in a continuous-wave domain was presented. Moreover, the results demonstrated that the generated OAM beam could be modulated with multiple dimensions. The topological charge can be switched in real time from -1 to -2. Notably, this OAM beam emitter could function as an OAM beam copier by easily transforming a single OAM beam into an OAM beam array. More importantly, a comprehensive analysis was conducted on power scaling, mode switching speed, and expansion of OAM modes. Additionally, the system’s compact design enabled it to function as a packageable OAM beam emitter. Owing to the advantages of having high power and programmable modes with multiple dimension modulation in phase structures and intensity distribution, this work can pave the way for producing high-power structured light beams and advancing their applications.
The dynamic gain of a few-mode erbium-doped fiber amplifier (FM-EDFA) is vital for the long-haul mode division multiplexing (MDM) transmission. Here, we investigate the mode-dependent dynamic gain of an FM-EDFA under various manipulations of the pump mode. First, we numerically calculate the gain variation with respect to the input signal power, where a mode-dependent saturation input power occurs under different pump modes. Even under the fixed intensity profile of the pump laser, the saturation input power of each spatial mode is different. Moreover, high-order mode pumping leads to a compression of the linear amplification region, even though it is beneficial for the mitigation of the differential modal gain (DMG) arising in all guided modes. Then, we develop an all-fiber 3-mode EDFA, where the fundamental mode of the pump laser can be efficiently converted to the LP11 mode using the all-fiber mode-selective coupler (MSC). In comparison with the traditional LP01 pumping scheme, the DMG at 1550 nm can be mitigated from 1.61 dB to 0.97 dB under the LP11 mode pumping, while both an average gain of 19.93 dB and a DMG of less than 1 dB can be achieved from 1530 nm to 1560 nm. However, the corresponding signal input saturation powers are reduced by 0.3 dB for the LP01 mode and 1.6 dB for the LP11 mode, respectively. Both theoretical and experimental results indicate that a trade-off occurs between the DMG mitigation and the extension of the linear amplification range when the intensity profile of pump laser is manipulated.
We propose and experimentally demonstrate the programmable photonic radio frequency (RF) filters based on an integrated Fabry–Pérot laser with a saturable absorber (FP-SA). Owing to the high output power and the relative flatness spectrum of the FP-SA laser, only a waveshaper and an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) were needed, which can greatly reduce the complexity of the system. The sinc filter employed 87 taps, representing a record-high tap number and resulting in a 3-dB bandwidth of 0.27 GHz and a quality factor of 148. Furthermore, Gaussian apodization enabled the out-of-band rejection of the filter to reach 34 dB and the center frequency to be finely tuned over a wide range, spanning from 4 to 14 GHz. These results indicate that the proposed scheme could provide a promising guideline for the photonic RF filters that demand both high reconfigurability and greatly reduced size and complexity.
Electromagnetic topological chiral edge states mimicking the quantum Hall effect have attracted a great deal of attention due to their unique features of free backscattering and immunity against sharp bends and defects. However, the matching techniques between classical waveguides and the topological one-way waveguide deserve more attention for real-world applications. In this paper, a highly efficient conversion structure between a classical rectangular waveguide and a topological one-way waveguide is proposed and demonstrated at the microwave frequency, which efficiently converts classical guided waves to topological one-way edge states. A tapered transition is designed to match both the momentum and impedance of the classical guided waves and the topological one-way edge states. With the conversion structure, the waves generated by a point excitation source can be coupled to the topological one-way waveguide with very high coupling efficiency, which can ensure high transmission of the whole system (i.e., from the source and the receiver). Simulation and measurement results demonstrate the proposed method. This investigation is beneficial to the applications of topological one-way waveguides and opens up a new avenue for advanced topological and classical integrated functional devices and systems.
Polarizers have always been an important optical component for optical engineering and have played an indispensable part of polarization imaging systems. Metasurface polarizers provide an excellent platform to achieve miniaturization, high resolution, and low cost of polarization imaging systems. Here, we proposed freeform metasurface polarizers derived by adjoint-based inverse design of a full-Jones matrix with gradient-descent optimization. We designed multiple freeform polarizers with different filtered states of polarization (SOPs), including circular polarizers, elliptical polarizers, and linear polarizers that could cover the full Poincaré sphere. Note that near-unitary polarization dichroism and the ultrahigh polarization extinction ratio (ER) reaching 50 dB were achieved for optimized circular polarizers. The multiple freeform polarizers with filtered polarization state locating at four vertices of an inscribed regular tetrahedron of the Poincaré sphere are designed to form a full-Stokes parameters micropolarizer array. Our work provides a novel approach, we believe, for the design of meta-polarizers that may have potential applications in polarization imaging, polarization detection, and communication.
We demonstrate a high-Q perfect light absorber based on all-dielectric doubly-resonant metasurface. Leveraging bound states in the continuum (BICs) protected by different symmetries, we manage to independently manipulate the Q factors of the two degenerate quasi-BICs through dual-symmetry perturbations, achieving precise matching of the radiative and nonradiative Q factors for degenerate critical coupling. We achieve a narrowband light absorption with a >600 Q factor and a > 99% absorptance at λ0 = 1550 nm on an asymmetric germanium metasurface with a 0.2λ0 thickness. Our work provides a new strategy for engineering multiresonant metasurfaces for narrowband light absorption and nonlinear applications.
Optical tweezers have proved to be a powerful tool with a wide range of applications. The gradient force plays a vital role in the stable optical trapping of nano-objects. The scalar method is convenient and effective for analyzing the gradient force in traditional optical trapping. However, when the third-order nonlinear effect of the nano-object is stimulated, the scalar method cannot adequately present the optical response of the metal nanoparticle to the external optical field. Here, we propose a theoretical model to interpret the nonlinear gradient force using the vector method. By combining the optical Kerr effect, the polarizability vector of the metallic nanoparticle is derived. A quantitative analysis is obtained for the gradient force as well as for the optical potential well. The vector method yields better agreement with reported experimental observations. We suggest that this method could lead to a deeper understanding of the physics relevant to nonlinear optical trapping and binding phenomena.
Entangled photon pairs are crucial resources for quantum information processing protocols. Via the process of spontaneous parametric downconversion (SPDC), we can generate these photon pairs using bulk nonlinear crystals. Traditionally, the crystal is designed to satisfy a specific type of phase-matching condition. Here, we report controllable transitions among different types of phase matching in a single periodically poled potassium titanyl phosphate crystal. By carefully selecting pump conditions, we can satisfy different phase-matching conditions. This allows us to observe first-order Type-II, fifth-order Type-I, third-order Type-0, and fifth-order Type-II SPDCs. The temperature-dependent spectra of our source were also analyzed in detail. Finally, we discussed the possibility of observing more than nine SPDCs in this crystal. Our work not only deepens the understanding of the physics behind phase-matching conditions, but also offers the potential for a highly versatile entangled biphoton source for quantum information research.
Curvature sensing plays an important role in structural health monitoring, damage detection, real-time shape control, modification, etc. Developing curvature sensors with large measurement ranges, high sensitivity, and linearity remains a major challenge. In this study, a curvature sensor based on flexible one-dimensional photonic crystal (1D-PC) films was proposed. The flexible 1D-PC films composed of dense chalcogenide glass and water-soluble polymer materials were fabricated by solution processing. The flexible 1D-PC film curvature sensor has a wide measurement range of 33–133 m-1 and a maximum sensitivity of 0.26 nm/m-1. The shift of the transmission peak varies approximately linearly with the curvature in the entire measurement range. This kind of 1D-PC film curvature sensor provides a new idea for curvature sensing and measurement.
AlGaN-based light-emitting diodes (LEDs) on offcut substrates enhance radiative emission via forming carrier localization centers in multiple quantum wells (MQWs). This study introduces the carrier transport barrier concept, accessing its impact on the quantum efficiency of LEDs grown on different offcut sapphire substrates. A significantly enhanced internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of 83.1% is obtained from MQWs on the 1° offcut sapphire, almost twice that of the controlled 0.2° offcut sample. Yet, 1° offcut LEDs have higher turn-on voltage and weaker electroluminescence than 0.2° ones. Theoretical calculations demonstrate the existence of a potential barrier on the current path around the step-induced Ga-rich stripes. Ga-rich stripes reduce the turn-on voltage but restrict sufficient driving current, impacting LED performance.
Organic–inorganic hybrid perovskite formamidinium lead bromide nanosheet (FAPbBr3 NS) is regarded as a superior substance used to construct optoelectronic devices. However, its uncontrollable stability seriously affects its application in the field of photodetectors. In this paper, FAPbBr3 is combined with cadmium sulfide nanobelt (CdS NB) to construct a hybrid device that greatly improves the stability and performance of the photodetector. The response of the FAPbBr3 NS/CdS NB detector under 490 nm light illumination reaches 5712 A/W, while the response of the FAPbBr3 photodetector under equivalent conditions is only 25.45 A/W. The photocurrent of the FAPbBr3 NS/CdS NB photodetector is nearly 80.25% of the initial device after exposure to air for 60 days. The difference in electric field distribution between the single material device and the composite device is simulated by the finite-difference time-domain method. It shows the advantages of composite devices in photoconductive gain and directly promotes the hybrid device performance. This paper presents a new possibility for high stability, fast response photodetectors.
Based on the transverse-longitudinal mapping of Bessel beams, we propose a simple method to construct a self-similar Bessel-like beam whose transverse profile maintains a stretched form during propagation. Specifically, the propagating-variant width of this beam can be flexibly predesigned. We experimentally demonstrate three types of self-similar Bessel-like beams whose width variations are linear, piecewise, and period functions of propagation distance, respectively. The experimental results match well with the theoretical predictions. We also demonstrate that our approach enables the generation of self-similar higher-order vortex Bessel-like beams.
Recently, there has been increased attention toward 3D imaging using single-pixel single-photon detection (also known as temporal data) due to its potential advantages in terms of cost and power efficiency. However, to eliminate the symmetry blur in the reconstructed images, a fixed background is required. This paper proposes a fusion-data-based 3D imaging method that utilizes a single-pixel single-photon detector and millimeter-wave radar to capture temporal histograms of a scene from multiple perspectives. Subsequently, the 3D information can be reconstructed from the one-dimensional fusion temporal data by using an artificial neural network. Both the simulation and experimental results demonstrate that our fusion method effectively eliminates symmetry blur and improves the quality of the reconstructed images.
Phase-coherent multi-tone lasers play a critical role in atomic, molecular, and optical physics. Among them, the Raman opeartion laser for manipulating atomic hyperfine qubits requires gigahertz bandwidth and low phase noise to retain long-term coherence. Raman operation lasers generated by directly modulated and frequency-multipled infrared lasers are compact and stable but lack feedback control to actively suppress the phase noise, which limits their performance in practical applications. In this work, we employ a fiber electro-optical modulator driven by a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) to modulate a monochromatic laser and employ a second-harmonic generation process to convert it to the visible domain, where the beat note of the Raman operation laser is stabilized by controlling the output frequency of VCO with a digital phase-locked loop (PLL). The low-frequency phase noise is effectively suppressed compared to the scheme without active feedback and it reaches -80 dBc/Hz@5 kHz with a 20 kHz loop bandwidth. Furthermore, this compact and robust scheme effectively reduces the system’s complexity and cost, which is promising for extensive application in atomic, molecular, and optical physics.
We demonstrate a high-performance acousto-optic modulator-based bi-frequency interferometer, which can realize either beating or beating free interference for a single-photon level quantum state. Visibility and optical efficiency of the interferometer are (99.5±0.2)% and (95±1)%, respectively. The phase of the interferometer is actively stabilized by using a dithering phase-locking scheme, where the phase dithering is realized by directly driving the acousto-optic modulators with a specially designed electronic signal. We further demonstrate applications of the interferometer in quantum technology, including bi-frequency coherent combination, frequency tuning, and optical switching. These results show the interferometer is a versatile device for multiple quantum technologies.
Optical vortex arrays, with their unique wavefront structures, find extensive applications in fields such as optical communications, trapping, imaging, metrology, and quantum. The methods used to generate these vortex beam arrays are crucial for their applications. In this review, we begin with introducing the fundamental concepts of optical vortex beams. Subsequently, we present three methods for generating them, including diffractive optical elements, metasurfaces, and integrated optical devices. We then explore the applications of optical vortex beam arrays in five different domains. Finally, we conclude with a summary and outlook for the research on optical vortex beam arrays.
Modern scintillator-based radiation detectors require silicon photomultipliers (SiPMs) with photon detection efficiency higher than 40% at 420 nm, possibly extended to the vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) region, single-photon time resolution (SPTR) < 100 ps, and dark count rate (DCR) < 150 kcps/mm2. To enable single-photon time stamping, digital electronics and sensitive microcells need to be integrated in the same CMOS substrate, with a readout frame rate higher than 5 MHz for arrays extending over a total area up to 4 mm × 4 mm. This is challenging due to the increasing doping concentrations at low CMOS scales, deep-level carrier generation in shallow trench isolation fabrication, and power consumption, among others. The advances at 350 and 110 nm CMOS nodes are benchmarked against available SiPMs obtained in CMOS and commercial customized technologies. The concept of digital multithreshold SiPMs with a single microcell readout is finally reported, proposing a possible direction toward fully digital scintillator-based radiation detectors.
On-chip stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) has attracted extensive attention by introducing acousto-optic coupling interactions in all-optical signal processing systems. A series of chip-level applications such as Brillouin lasers, amplifiers, gyroscopes, filters, and nonreciprocal devices are realized based on Brillouin acousto-optic interaction. Here, we first introduce the fundamental principle of SBS in integrated photonics and a method for calculating Brillouin gain; then we illustrate the Brillouin effect on different material platforms with diverse applications. Finally, we make a concise conclusion and offer prospects on the future developments of on-chip SBS.
In recent years, optical phased arrays (OPAs) have attracted great interest for their potential applications in light detection and ranging (LiDAR), free-space optical communications (FSOs), holography, and so on. Photonic integrated circuits (PICs) provide solutions for further reducing the size, weight, power, and cost of OPAs. In this paper, we review the recent development of photonic integrated OPAs. We summarize the typical architecture of the integrated OPAs and their performance. We analyze the key components of OPAs and evaluate the figure of merit for OPAs. Various applications in LiDAR, FSO, imaging, biomedical sensing, and specialized beam generation are introduced.