View fulltext
View fulltext
Emission spectrum and CIE chromaticity coordinates of the as-prepared Sr2LaTaO6:0.2Eu3+ red phosphors.
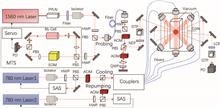
An ultranarrow bandwidth Faraday atomic filter is realized based on cold Rb87 atoms. The atomic filter operates at 780 nm on the 52S1/2, F=2 to 52P3/2, F′=3 transition with a bandwidth of 7.1(8) MHz, which is approaching the natural linewidth of the transition. The peak transmission achieves 2.6(3)% by the multi-pass probe method. This atomic filter based on cold atoms may find potential applications in self-stabilizing lasers in the future.
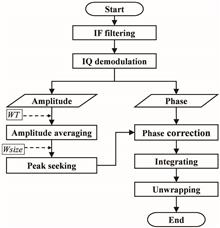
A simple and effective interference-fading tolerant method for phase-sensitive optical time-domain reflectometry (Φ-OTDR) using optimal peak-seeking is proposed. This method can reconstruct the vibration signal with high fidelity under the premise of using only an ordinary single-mode sensing fiber without changing the structure of the traditional Φ-OTDR system. Based on the data after interference suppression, we applied different machine learning models to recognize the invasive events category. The promising results show potential applications of Φ-OTDR equipment and future implementation with machine learning algorithms.
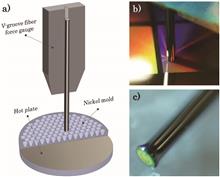
A phase-shifted fiber Bragg grating (PS-FBG) based on a microchannel was proposed and realized by combining the point-by-point scanning method with chemical etching. The PS-FBG is composed of a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) and a microchannel through the fiber core. The microchannel can introduce phase shift into the FBG. What is more important is that it exposes the fiber core to the external environment. The phase shift peak is sensitive to the liquid refractive index, and it shows a linear refractive index response wavelength and intensity sensitivity of 2.526 nm/RIU and -111 dB/RIU, respectively. Therefore, such gratings can be used as sensors or tunable filters.
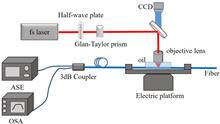
Thermal nanoimprinting is a fast and versatile method for transferring the anti-reflective properties of subwavelength nanostructures onto the surface of highly reflective substrates, such as chalcogenide glass optical fiber end faces. In this paper, the technique is explored experimentally on a range of different types of commercial and custom-drawn optical fibers to evaluate the influence of geometric design, core/cladding material, and thermo-mechanical properties. Up to 32.4% increased transmission and 88.3% total transmission are demonstrated in the 2–4.3 μm band using a mid-infrared (IR) supercontinuum laser.
This paper reports a detection method of two-dimensional (2D) enhancement and three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction for subtle traces with reflectance transformation imaging, which can effectively locate the trace area of interest and extract the normal data of this area directly. In millimeter- and micron-scale traces, during 3D construction, we presented a method of data screening, conversion, and amplification, which can successfully suppress noise, improve surface and edge quality, and enhance 3D effect and contrast. The method not only captures 2D and 3D morphologies of traces clearly but also obtains the sizes of these traces.
Natural logarithm wavelength modulation spectroscopy (ln-WMS) is demonstrated in this Letter. Unlike the conventional wavelength modulation spectroscopy (WMS)-2f technique, it is a linear method even for large absorbance, which is the core advantage of ln-WMS. The treating method used in ln-WMS is to take the natural logarithm of the transmitted intensity. In order to determine the proper demodulation phase, the η-seeking algorithm is introduced, which minimizes the absolute value of the first harmonic within the non-absorbing region. Subsequently, the second harmonic of the absorption signal is extracted by setting the demodulating phase as 2η. To illustrate the validity of ln-WMS, it was applied to water vapor experimentally. The result shows that even if the absorbance (base-e) is between 1.60 and 6.26, the linearity between ln-WMS-2f and volume fraction is still established. For comparison, measurement with conventional WMS-2f was also done, whose response no longer kept linearity. The η values retrieved in continuous measurements and the residuals were shown so as to evaluate the performance of the η-seeking algorithm. Time consumed by this algorithm was roughly 0.28 s per measurement. As an alternative WMS strategy, ln-WMS has a wide range of potential applications, especially where the absorbance is large or varies over a wide area.
Two-dimensional (2D) Te nanosheets were successfully fabricated through the liquid-phase exfoliation (LPE) method. The nonlinear optical properties of 2D Te nanosheets were studied by the open-aperture Z-scan technique. Furthermore, the continuous wave mode-locked Nd:YVO4 laser was successfully realized by using 2D Te as a saturable absorber (SA) for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. Ultrashort pulses as short as 5.8 ps were obtained at 1064.3 nm with an output power of 851 mW. This primary investigation indicates that the 2D Te SA is a promising photonic device in the fields of ultrafast solid-state lasers.
On the basis of a home-made femtosecond Yb-doped fiber laser, we designed a compact and efficient third harmonic generation scheme by a simple compensation plate of β-BaB2O4 crystal. The compensation plate is optimized through its thickness and cutting angle to reverse both spatial and temporal walk-off. By optimizing the parameters of the compensation plate and incident light intensity, a maximum output of 2.23 W with a repetition rate of 1 MHz at 345 nm is obtained, which implies a conversion efficiency of 23% from the infrared to ultraviolet.
At the surfaces of crystals, linear susceptibility tensors would differ from their counterparts in the interior of the bulk crystal. However, this phenomenon has not been shown in a visible way yet. In previous researches, numerous types of nonlinear Cherenkov radiation based on different materials have been studied, while linear Cherenkov radiation is barely reported. We experimentally prove the generation of linear Cherenkov radiation on the potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP) crystal surface and theoretically analyze its phase-matching scheme. In our study, o-polarized light and e-polarized light can mutually convert through the linear Cherenkov process. According to this result, we figure out new nonzero elements at off-diagonal positions in the linear susceptibility tensor matrix at crystal surfaces, compared with the normal form of a bulk KDP.
We demonstrate a configuration optimization process of an off-axis parabolic mirror to maximize the focused peak intensity based on a precise knowledge of the tight focusing properties by using a full vector-diffraction theory and obtain an optimum configuration scaling rule, which makes it possible to achieve the maximum peak intensity. In addition, we also carry out an assessment analysis of the offset and off-axis angle tolerances corresponding to a 5% drop of the maximum focused peak intensity and present scaling laws for the tolerances of the offset and off-axis angle. Understanding these scaling laws is important to enhance the focusability of a laser beam by an off-axis parabolic mirror in the optimum configuration, in particular, which is valuable for structural design and selection of an off-axis parabolic mirror in ultrashort and ultraintense laser–matter interaction experiments.
We develop a method for completely shaping optical vector beams with controllable amplitude, phase, and polarization gradients along three-dimensional freestyle trajectories. We design theoretically and demonstrate experimentally curvilinear Poincaré vector beams that exhibit high intensity gradients and accurate state of polarization prescribed along the beam trajectory.
Halide perovskites have attracted great attention due to their high color purity, high luminance yield, low non-radiative recombination rate, and solution processability. Although the external quantum efficiency of perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) is comparable with that of the organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) and quantum-dots light-emitting diodes (QLEDs), the brightness is still low compared with the traditional OLEDs and QLEDs. Herein, we demonstrate high brightness and high-efficiency CsPbBr3-based PeLEDs using interface and bulk controlled nanocrystal growth of the perovskite emission layer. The interface engineering by ethanolamine and bulk engineering by polyethylene glycol led to highly crystallized and cubic-shaped perovskite nanocrystals with smooth and compact morphology. As a result, PeLEDs with a high brightness of 64756 cd/m2 and an external quantum efficiency of 13.4% have been achieved.
The instability of lead halide perovskites in various application-related conditions is a key challenge to be resolved. We investigated the formation of metal nanoparticles during transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging of perovskite-related metal halide compounds. The metal nanoparticle formation on these materials originates from stimulated desorption of halogen under electron beams and subsequent aggregation of metal atoms. Based on shared mechanisms, the TEM-based degradation test can help to evaluate the material stability against light irradiation.
Bright Eu3+-activated double-perovskite Sr2LaTaO6 red-emitting phosphors were successfully synthesized by a high-temperature solid-state method. Under near-ultraviolet excitation at 394 nm, optimal Sr2LaTaO6:0.2Eu3+ phosphors emitted high-brightness red light around 613 nm with the International Commission on Illumination chromaticity coordinates (0.650, 0.349). Notably, the color purity can reach 92%. Impressively, the favorable thermal stability of the Sr2LaTaO6:0.2Eu3+ phosphors was characterized by temperature-dependent emission spectra at different temperatures from 303 to 463 K, and the emission intensity at 423 K remained 73% of its value at 303 K. All of the results suggested that the as-prepared Sr2LaTaO6:0.2Eu3+ phosphors can be used in near-ultraviolet-excitable white light-emitting diodes as a red-emitting color converter.
Structural geometry, electronic band gaps, density of states, optical and mechanical properties of double perovskite halides Cs2InBiX6 (X = F, Cl, Br, I) are investigated using the density functional theory. These compounds possess genuine perovskite stoichiometry, evaluated using various geometry-based indices like tolerance factor, octahedral factor, and formation energy. The fundamental electronic band gaps are direct and valued in the range 0.80–2.79 eV. These compounds have narrow band gaps (except Cs2InBiF6) due to strong orbital coupling of the cations. The valence band maximum and conduction band minimum are confirmed to be essentially of In 5s and Bi 6p characters, respectively. The splitting of Bi 6p bands due to strong spin-orbit coupling causes reduction in the band gaps. These compounds have large dispersion in their bands and very low carrier effective masses. The substitution of halogen atoms has great influence on the optical properties. The mechanical properties reveal that Cs2InBiX6 (X = F, Cl, Br, I) satisfy the stability criteria in cubic structures.
Optoelectronic applications based on the perovskites always face challenges due to the inherent chemical composition volatility of perovskite precursors. The efficiency of perovskite-based light-emitting diodes (Pe-LEDs) can be enhanced by improving the perovskite film via solvent engineering. A dual solvent post-treatment strategy was applied to the perovskite film, which provides a synchronous effect of passivating surface imperfections and reduces exciton quenching, as evidenced by improved surface morphology and photoluminance. Thus, the optimized Pe-LEDs reach 17,866 cd·m-2 maximum brightness, 45.8 cd·A-1 current efficiency, 8.3% external quantum efficiency, and relatively low turn-on voltage of 2.0 V. Herein, we present a simple technique for the fabrication of stable and efficient Pe-LEDs.