View fulltext
View fulltext
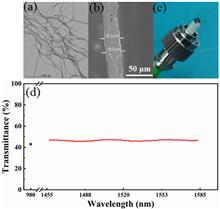
Experimental setup of all-optical inverter based on CNT-PVA thin film.
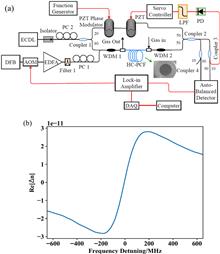
We report the first demonstration of group delay tuning with stimulated Raman scattering-induced dispersion in a hydrogen-filled hollow-core optical fiber. A pump laser induces a sharp refractive index change near the S0(0) Raman transition of hydrogen molecules, enabling the control of the group velocity of signal pulses around the Stokes wavelength. Experiments with an 80-m-long hollow-core fiber filled with 2.5 bar hydrogen achieved continuous tuning of the pulse delay up to 1.42 ns by varying the Raman amplification from 0 to 10 dB. The tunable pulse delay is realized by changing the pump power as well as the hydrogen pressure. This work provides a new technique for controlling the pulse propagation in optical fibers with high flexibility.
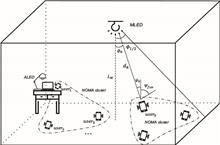
This Letter proposes a model of indoor visible light communication (VLC) heterogeneous networks entirely based on LEDs with different specifications and applies non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) to it because of the narrow modulation bandwidth of LEDs. Moreover, a user-grouping scheme that is based on matching theory is proposed to improve the network achievable sum rate. Simulation results indicate that when each NOMA cluster contains 6 users, the proposed scheme has a 49.54% sum-rate enhancement compared with the traditional user-grouping scheme. As the number of users in each NOMA cluster increases, the proposed scheme performs better at the cost of computational complexity.
All-optical light control plays an important role in optical signal processing and communications. In this Letter, we demonstrate an all-optical inverter using carbon nanotube (CNT)-polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) thin film and obtain a long-time stable output due to the environmental insensitivity of the device. The thermo-optic effect in the CNT-PVA thin film generates a thermal lens and modifies the beam propagation in the thin film. The obtained all-optical inverter has a front (trailing) time constant of ~55 μs (44 μs) for 1550 nm signal pulses and ~7 kHz response bandwidth.
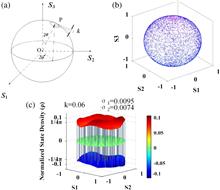
We report a new method to deeply analyze the scrambling characteristic of polarization scramblers based on density of polarization states (DPS) statistics that makes it possible to describe the DPS distribution in detail on the whole Poincaré sphere, thus easy to locate accurately the nonuniform areas of defective polarization scramblers, which cannot be realized by existing methods. We have built a polarization scrambling system to demonstrate the advantages of our method compared with others by experiments and suggested effective evaluation indexes whose validity is well confirmed by applying to a commercial scrambler. Our conclusions are valuable for accurately analyzing and diagnosing the performance of any polarization scrambler, and quality evaluation of polarization controllers or other polarization devices.
In this Letter, a method for shape visualization of small objects (microscopic) in the form of a hologram is presented. It consists of a standard optical set-up for small object registration (i.e., stereoscopic or biological microscope). The focus stacking technique is used to obtain a series of images with increased depth of field and on them a shape reconstruction procedure (structure from motion, SfM) is made. With use of a dense cloud of points, a sequence of parallax-related images suitable for Geola’s digital holographic printing is generated. The holographic printer produces single-parallax holographic (full three-dimensional) images of real or virtual objects.
To fully describe the structure information of the point cloud when the LIDAR-object distance is long, a joint global and local feature (JGLF) descriptor is constructed. Compared with five typical descriptors, the object recognition rate of JGLF is higher when the LIDAR-object distances change. Under the situation that airborne LIDAR is getting close to the object, the particle filtering (PF) algorithm is used as the tracking frame. Particle weight is updated by comparing the difference between JGLFs to track the object. It is verified that the proposed algorithm performs 13.95% more accurately and stably than the basic PF algorithm.
An aberration-free imaging technique was used to design a double-spherically bent crystal spectrometer with high energy and spatial resolutions to ensure that the individual spectral lines are represented as perfectly straight lines on the detector. After obtaining the matched parameters of the two crystals via geometry-based optimization, an alignment method was employed to allow the spacing between the crystals and the detector to be coupled with the source. The working principle of this spectrum-measuring scheme was evaluated using a Cu X-ray tube. High-quality spectra with energy resolutions (E/ΔE) of approximately 3577 were obtained for a relatively large source size.
An equivalent circuit model including multi-section distributed parameters is proposed to analyze wideband photodiodes (PDs) with coplanar waveguide (CPW) electrodes. The model helps extract CPW parameters as well as intrinsic bandwidth parameters so that the influence of the CPW structure can be investigated, making it valuable for the design of high-performance PDs. PDs with an inductive 115 Ω impedance CPW are fabricated, and the 3 dB bandwidth is improved from 28 GHz to 37.5 GHz compared with PDs with a conventional 50 Ω impedance CPW.
We experimentally demonstrated that the distributed feedback (DFB) lasers with the active distributed reflector achieved a 25.8 Gb/s operation over a wide temperature range of ?40 to 85°C. The DFB lasers can achieve additional feedback from an active distributed reflector with accurately controlled phase, and single-mode yields are not related to the position of cleave. The threshold currents of the fabricated laser are 6 mA and 20 mA at ?40°C and 85°C, respectively. The side mode suppression ratio of the fabricated laser is above 50 dB at all temperatures. Transmissions of 25.8 Gb/s after 10 km single-mode fibers with clear eye openings and less than 0.8 dB power penalty over a wide temperature range have been demonstrated as well.
A 21.2 kW, 1.94 times the diffraction-limit quasi-continuous-wave laser is presented in this Letter based on a multi-stage, power-scalable Yb:YAG master-oscillator-power-amplifier (MOPA) system under adaptive optics (AO) control. The output laser of the MOPA system is a rectangular beam with a length-width ratio of 2:1, a 200 μs pulse duration, and a 1000 Hz repetition rate. With the AO control system, the beam quality of the laser is improved from 4.20 to 1.94 times the diffraction limit. To our knowledge, this is the best quality laser in the 20 kW class except for combined lasers.
Rotating elliptical nanowire arrays as two-dimensional photonic crystals has been proposed and studied in this Letter. The analysis of the four lowest energy bands and the first bandgap width of some examples illustrates that the rotation and configuration of the primitive cell can have effects on the reducibility of the Brillouin zone. As the central element’s orientation changes, the irreducible Brillouin zone could be expanded to the whole first Brillouin zone. Special attention has been paid to the nanowire arrays with adjacent elements perpendicular to each other, and the irreducible Brillouin zone unexpectedly retracted back to the 1/8 of the first Brillouin zone though the symmetry of elements is lower than that of the square lattice. Meanwhile, the first bandgap width of the perpendicular array can be adjusted by the rotation of each primitive element.
Broadband transverse displacement sensing by exploiting the interaction of a focused radially polarized beam with a silicon hollow nanodisk is proposed. The multipolar decomposition analysis indicates that the interference between a longitudinal total electric dipole (TED) moment and a lateral magnetic dipole (MD) moment is dominant in the far-field transverse scattering in the near-infrared region. Within a broadband wavelength range with the width of 155 nm, the longitudinal TED is almost in phase with the lateral MD, and then broadband position sensing based on the sensitivity of scattering directivity to transverse displacement can be achieved.
Planar photonic crystal (PPC) cavities with high quality (Q) factors were currently designed by missing or moving air holes. Here, we propose that cutting air holes in PPC into semicircles could be considered as another strategy to realize and optimize cavities, presenting superiorities over cavities with missed or moved air holes in a higher Q factor and a smaller mode volume (Vmode). Examples are demonstrated: (1) in a PPC lattice, cutting two adjacent air holes promises a cavity mode with a Q exceeding 200,500 and an ultrasmall mode volume Vmode λ/2 n)3; (2) in a PPC waveguide, cutting two air holes on opposite sides of the waveguide supports a cavity mode with a Q exceeding 104,600 and a Vmode λ/2 n)3; (3) cutting the two air holes at the edges of an L3-type PPC cavity, the Q factor is optimized from 5500 to 124,700, with an almost constant Vmode. The concept of cutting air holes to introduce defects in PPC also promises the design of PPC also waveguides with an engineered transmission loss and dispersion.
Polarization aberration caused by material birefringence can be partially compensated by lens clocking. In this Letter, we propose a fast and efficient clocking optimization method. First, the material birefringence distribution is fitted by the orientation Zernike polynomials. On this basis, the birefringence sensitivity matrix of each lens element can be calculated. Then we derive the rotation matrix of the orientation Zernike polynomials and establish a mathematical model for clocking optimization. Finally, an optimization example is given to illustrate the efficiency of the new method. The result shows that the maximum RMS of retardation is reduced by 64% using only 48.99 s.
An asymmetrical tapered singlemode–multimode–singlemode (SMS) fiber coupler based on two parallel physical contact SMS fiber structures was proposed. Since the coupler includes modes both from fiber core and cladding, two dips of the transmission spectrum exhibit different sensing characteristics to the surrounding temperature and refractive index (RI) change, which allows the use of the standard matrix inversion method to determine temperature and RI simultaneously. The temperature sensitivities of 0.0498 and 0.0324 nm/°C and RI sensitivities of 1151.76 and 1325.66 nm/RIU have been achieved, respectively. For biosensing application, with the functionalized fiber coupler sensor, a human chorionic gonadotropin concentration of 0.05 mIU/mL has been detected for a wavelength shift of 0.2 nm with good stability and excellent selectivity. The developed tapered SMS fiber coupler structure has advantages of simultaneous measurement of two independent parameters, simple configuration, low cost, and good repeatability that offer a great potential for medical diagnostics.
We propose and numerically demonstrate a dynamic beam deflector based on plasmonic resonator loaded thermoresponsive freestanding hydrogel that swells and collapses in water by temperature. For this purpose, we utilize four-step phase gradients mounted on freestanding hydrated hydrogel. For normal incidence, linearly orthogonal light deflects to 19.44° in the collapsed state and 14.40° in the swollen state of hydrogel. Furthermore, the light deflects at a third angle of 12.29° when the solvent changes from water to ethanol. It is expected that our metadesign will provide a platform for dynamic holography, active lensing, data storage, and anticounterfeiting.
In this Letter, we find that Morse potential (proposed about 90 years ago) could be connected to Coulomb potential (or Newton potential) and harmonic potential (or Hooke potential) by conformal mappings. We thereby design a new conformal lens from Morse potential, Eaton lens, and Luneburg lens and propose a series of generalized Eaton/Luneburg lenses. We find that this Morse lens is a perfect self-focusing asymmetric lens that differs from a Mikaelian lens. Our theory provides a new insight to Morse potential and other traditional potentials, and revisits their classical applications on designing lenses.
Refractive index enhancement is crucial in the fields of lithography, imaging, optical communications, solar devices, and many more. We present a review of advancements in the process of designing high refractive index metamaterials, starting from quantum coupling and photonic bandgap materials to metamaterials utilizing deep subwavelength coupling to achieve ever-high values of refractive index. A particular attention is given to experimentally verified schemes in engineering a high index of refraction. The understanding of the evolution of material design from intrinsic electronic states manipulation to meta-atoms design is not only fascinating but also a prerequisite to developing successful devices and applications.