View fulltext
View fulltext
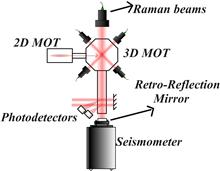
For most atom interferometers, the vibration isolation unit is applied to reduce vibration noise. In our experiment, instead of isolation, the vibration signals are monitored, and combining with the sensitive function, the compensation phase shift for the atom interferometer is obtained. We focus on the correction over a wide spectrum rather than on “monochromatic” frequencies. The sensitivity of the atom gravimeter can be upgraded by a factor of more than two. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the atom interferometer can still produce a good measurement result without passive vibration isolation in extremely noisy environments by using vibration compensation.
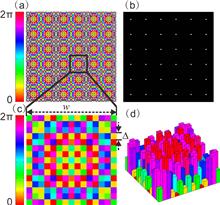
In this Letter, we propose a simple and effective approach for transforming a conventional Talbot array illuminator (TAI) with multilevel phase steps into a binary-phase TAI (BP-TAI) through detour phase encoding. The BP-TAI is a binary (0 π) phase-only diffractive optical element, which can be utilized to generate a large-scale focal spots array with a high compression ratio. As an example, we design a square BP-TAI with the fraction parameter β = 15 for achieving a square multifocal lattice with a high compression ratio β2. Theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate that the detour phase encoding is efficient for designing the BP-TAI, especially with the high compression ratio. Such results may be exploited in practical large-scale optical trapping and X-ray imaging.
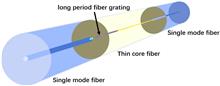
A refractive index intensity detecting sensor with long-period grating written in the single-mode–thin-core–single-mode fiber (STS) structure is proposed and optimized theoretically. The sensor is composed of two single-mode fibers connected by a section of long-period fiber grating fabricated on thin-core fiber. After optimization and benefitting from the phase matching point, the loss peak of the structure can reach 62.8 dB theoretically. The wavelength of the characteristic peak is fixed at the phase matching point, so intensity detection can be achieved. The sensitivity can reach 272.5 dB/RIU. The structural optimization in this Letter provides a reference for the fabrication of an easy-made all-fiber sensor without extra cladding.
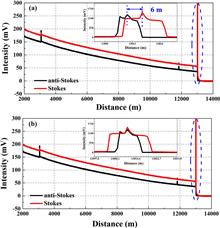
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a novel Raman-based distributed fiber-optics temperature sensor (RDTS) for improving the temperature measurement accuracy and engineering applicability. The proposed method is based on double-ended demodulation with a reference temperature and dynamic dispersion difference compensation method, which can suppress the effect of local external physics perturbation and intermodal dispersion on temperature demodulation results. Moreover, the system can omit the pre-calibration process by using the reference temperature before the temperature measurement. The experimental results of dispersion compensation indicate that the temperature accuracy optimizes from 5.6°C to 1.2°C, and the temperature uncertainty decreases from 16.8°C to 2.4°C. Moreover, the double-ended configuration can automatically compensate the local external physics perturbation of the sensing fiber, which exhibits a distinctive improvement.
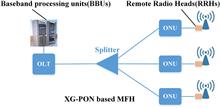
A novel predictive dynamic bandwidth allocation (DBA) method based on the long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network is proposed for a 10-gigabit-capable passive optical network in mobile front-haul (MFH) links. By predicting the number of packets that arrive at the optical network unit buffer based on LSTM, the round-trip time delay in traditional DBAs can be eliminated to meet the strict latency requirement for MFH links. Our study shows that the LSTM neural network has better performance than feed-forward neural networks. Based on extensive simulations, the proposed scheme is found to be able to achieve the latency requirement for MFH and outperforms the traditional DBAs in terms of delay, jitter, and packet loss ratio.
All-optical ultrasound probes that contain a photoacoustically-based ultrasound generator paired with a photonic acoustic sensor provide a promising imaging modality for diagnostic and MRI-compatible applications. Here, we demonstrate the fabrication of a fiber-based all-optical ultrasound probe and its applications in pulse-echo ultrasound imaging. The ultrasound generator is fabricated on a 125 μm multimode optical fiber by forming a light-absorbing multiwalled carbon nanotube (MWCNT)-polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) composite coating on its distal end. A peak-to-peak acoustic pressure of 0.95 MPa was achieved with laser irradiation at 2.46 μJ by chemically functionalizing the fiber surface to enable a strong adsorption. Ultrasound reception was performed by a fiber-laser ultrasound sensor that translates ultrasound pressure into differential lasing-frequency changes. By linearly scanning the probe, ex vivo two- and three-dimensional imaging of a segment of swine trachea was demonstrated by detecting the echo ultrasound signals and reconstructing the acoustic scatterers. The probe presents axial and lateral resolutions at 150 and 62 μm, respectively. The small-sized, side-looking all-fiber ultrasound probe presents a promising approach for assembling an interventional endoscopy.
A method is proposed to optimize the recording structure of the photorefractive volume grating to compensate high spatial frequency in the distorted wavefront by optical phase conjugation. Based on the coupled-wave equation, the diffraction efficiency of the recorded grating formed by the scattered beams in different recording structures is simulated. The theoretical results show that the recorded modulations with high spatial frequency can be significantly improved in the small recording angle. In the experiment, three recording structures with the recording angles of 7.5°, 30°, and 45° are chosen to verify the compensation effect. Compared with the reconstructed image in the large recording angle of 45°, the signal to noise ratio of the image recorded at 7.5° increases to 3.2 times of that at 45°.
In this Letter, we propose an advanced framework of ghost edge imaging, named compressed ghost edge imaging (CGEI). In the scheme, a set of structured speckle patterns with pixel shifting illuminate on an unknown object. The output is collected by a bucket detector without any spatial resolution. By using a compressed sensing algorithm, we obtain horizontal and vertical edge information of the unknown object with the bucket detector detection results and the known structured speckle patterns. The edge is finally constructed via two-dimensional edge information. The experimental and numerical simulations results show that the proposed scheme has a higher quality and reduces the number of measurements, in comparison with the existing edge detection schemes based on ghost imaging.
Praseodymium-ion-doped gain materials have the superiority of lasing at various visible wavelengths directly. Simple and compact visible lasers are booming with the development of blue laser diodes in recent years. In this Letter, we demonstrate the watt-level red laser with a single blue laser diode and Pr:YLiF4 crystal. On this basis, the passively Q-switched pulse lasers are obtained with monolayer graphene and Co:ZnO thin film as the Q-switchers in the visible range.
We demonstrate the frequency stabilization of a 1.55 μm erbium-doped fiber laser by locking it to a 5-km-long optical fiber delay line (FDL). The stabilized laser is characterized via comparison with a second identical laser system. We obtain a fractional frequency stability of better than 3 × 10 15 over time scales of 1–10 s and a laser linewidth of 0.2 Hz, which is the narrowest linewidth of an FDL-stabilized laser observed to date.
A large-mode-area (LMA) ytterbium-doped photonic crystal fiber (PCF) with core NA of 0.034 and core diameter of 50 μm was made by the stack-and-draw technique. The core is formed by Yb3+/Al3+/F /P5+ co-doped silica glass containing 0.09 mol% Yb2O3 with an absorption coefficient at 976 nm up to 3.2 dB/m. The core glass with homogeneous distribution of Yb3+ ions and refractive index difference of 4 × 10 4 compared with pure silica was prepared by the sol-gel method and heat homogenization at 2000°C. Laser power amplification of this LMA PCF was studied using a seed source of 21 ps pulse duration and 48.7 MHz repetition rate at 1030 nm wavelength. With pump power of 520 W, a maximum 272 W (266 kW peak power) quasi-single-mode laser output with M2 of 2.2 was achieved in a 4.7 m fiber length bent at a diameter of 47 cm with slope efficiency of 52%, and no obvious mode instability, stimulated Raman scattering, or thermal damage on the end facet of the fiber were observed.
In this work, a soliton mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) with a high-quality molecular beam epitaxy (MBE)-grown topological insulator (TI) Bi2Se3 saturable absorber (SA) is reported. To fabricate the SA device, a 16-layer Bi2Se3 film was grown successfully on a 100 μm thick SiO2 substrate and sandwiched directly between two fiber ferrules. The TI-SA had a saturable absorption of 1.12% and a saturable influence of 160 MW/cm2. After inserting the TI-SA into the unidirectional ring-cavity EDFL, self-starting mode-locked soliton pulse trains were obtained at a fundamental repetition rate of 19.352 MHz. The output central wavelength, pulse energy, pulse duration, and signal to noise ratio of the radio frequency spectrum were 1530 nm,18.5 pJ, 1.08 ps, and 60 dBm, respectively. These results demonstrate that the MBE technique could provide a controllable and repeatable method for the fabrication of identical high-quality TI-SAs, which is critically important for ultra-fast pulse generation.
We demonstrate a strain compensated long lifetime semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) with a high modulation depth for fiber lasers. The SESAM was measured to have a damage threshold of 9.5 mJ/cm2, a modulation depth of 11.5%, a saturation fluence of 39.3 μJ/cm2, and an inversed saturable absorption coefficient of 630 mJ/cm2. The SESAM has been applied to a linear cavity mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser, which has been working for more than a year without damage of the SESAM.
We present an Er-doped fiber (Er:fiber)-based femtosecond laser at 780 nm with 256 MHz repetition rate, 191 fs pulse duration, and over 1 W average power. Apart from the careful third-order dispersion management, we introduce moderate self-phase modulation to broaden the output spectrum of the Er:fiber amplifier and achieve 193 fs pulse duration and 2.43 W average power. Over 40% frequency doubling efficiency is obtained by a periodically poled lithium niobate crystal. Delivering through a hollow-core photonic bandgap fiber, this robust laser becomes an ideal and convenient light source for two-photon autofluorescence imaging.
We report here a single-pass 1.56 μm fiber gas Raman laser in a deuterium-filled hollow-core fiber and a 2.86 μm cascade fiber gas Raman laser with methane in the second stage. The maximum output powers at 1.56 and 2.86 μm are 27 and 8.5 mW with Raman conversion efficiency of 30% and 42%, respectively. The results offer a new method to produce a 1.5 μm fiber source and prove the potential of the cascade fiber gas Raman laser in extending the available wavelength.
All-optical logic gates including AND, XOR, and NOT gates, as well as a half-adder, are realized based on two-dimensional lithium niobate photonic crystal (PhC) circuits with PhC micro-cavities. The proposed all-optical devices have an extinction ratio as high as 23 dB due to the effective all-optical switch function induced by two-missing-hole micro-cavities. These proposed devices can have potential implementation of complex integrated optical functionalities including all-optical computing in a lithium niobate slab or thin film.
In this Letter, we propose the electronic manipulation of localized surface plasmon resonance for active tuning in near-field nanofocusing. We theoretically studied the excited graphene tuning of the nanofocusing field in few-layer graphene (FLG)-based hybrid nanotips. It is revealed that the normalized enhanced electric field can be significantly promoted to more than 300 times. It is also observed that resonant peaks can be unprecedently modified by the electron state of excited graphene that is embedded in the substrate. It shows the possibility of flexible tuning of plasmon resonances via controlling the electron excitation state of graphene for specific advanced near-field nanofocusing applications.
Squeezed states belong to the most prominent non-classical resources. They have compelling applications in precise measurement, quantum computation, and detection. Here, we report on the direct measurement of 13.8 dB squeezed vacuum states by improving the interference efficiency and gain of balanced homodyne detection. By employing an auxiliary laser beam, the homodyne visibility is increased to 99.8%. The equivalent loss of the electronic noise is reduced to 0.05% by integrating a junction field-effect transistor (JFET) buffering input and another JFET bootstrap structure in the balanced homodyne detector.
High-resolution frequency-domain spectroscopy (FDS) is set up using a coherent and continuous wave terahertz (THz) emitter and receiver. THz waves are generated and detected by two photomixers with two distributed feedback (DFB) lasers. Atmospheric water vapor with different relative humidity is systematically investigated by the FDS. A high-frequency resolution of ~14 MHz is obtained with the help of Hilbert transformation, leading to a well resolved and distinct transmittance characterization of water vapor. Compared with conventional THz time-domain spectroscopy, the high-resolution continuous wave THz spectrometer is one of the most practical systems in gas-phase molecular sensing, identification, and monitoring.