View fulltext
View fulltext
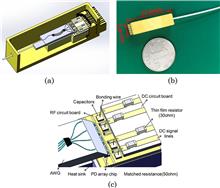
An ultra-compact hybrid-integration receiver optical subassembly (ROSA) with four channels is demonstrated in our laboratory with the size of 23.3 mm × 6.0 mm × 6.5 mm. The ROSA is comprised of a planar lightwave circuit (PLC) arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) chip, a top-illuminated positive-intrinsic-negative photodetector array chip, and a three-dimensional microwave circuit that is specially designed for compact packaging. For each transmission lane, the 3 dB bandwidth of the ROSA is up to 20 GHz, and the maximum responsivity is up to 0.53 A/W. The proposed package structure can be used for smaller package sizes and would be an easy assembling solution for 100 GbE optical communication devices.
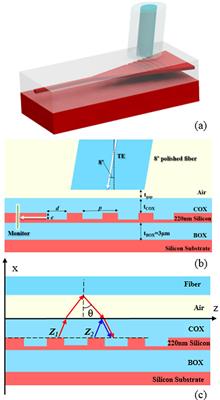
A simple method for improving grating couplers’ coupling efficiency without any extra microfabrication processes is proposed. This method can improve the coupling efficiency with 1.69 dB by utilizing the combined interference in the cladding layer and air gap between the cladding surface and the paralleled angle polished fiber facet. The proposed method can be applied to various kinds of on-chip grating couplers. Back reflection, 1 dB bandwidth, and fiber alignment tolerance have also been improved at the same time.
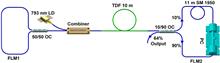
We demonstrate a 2080 nm long-wavelength mode-locked thulium (Tm)-doped fiber laser operating in the dissipative soliton resonance (DSR) regime. The compact all-fiber dumbbell-shaped laser is simply constructed by a 50/50 fiber loop mirror (FLM), a 10/90 FLM, and a piece of large-gain Tm-doped double-clad fiber pumped by a 793 nm laser diode. The 10/90 FLM is not only used as an output mirror, but also acts as a periodical saturable absorber for initiating DSR mode locking. The stable DSR pulses are generated at the center wavelength as long as 2080.4 nm, and the pulse duration can be tunable from 780 to 3240 ps as the pump power is increased. The maximum average output power is 1.27 W, corresponding to a pulse energy of 290 nJ and a nearly constant peak power of 93 W. This is, to the best of our knowledge, the longest wavelength for DSR operation in a mode-locked fiber laser.
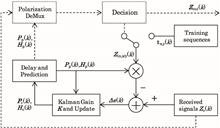
We propose the modified Kalman filter (MKF) using the received signal for observation and constructing an inverse process of the conventional Kalman filter (CKF) for polarization de-multiplexing in coherent optical (CO) orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) transmissions. The MKF can avoid the convergence error problem in CKF without matrix inverse operation and has a faster converging speed and a much larger tolerance to the process and measurement noise covariance, about two orders of magnitude more than those of CKF. We experimentally demonstrate the 12 Gbaud OFDM signal transmission over 480 km standard single-mode fiber. The performance of MKF and CKF outperforms pilot-aided polarization de-multiplexing with better accuracy and nonlinearity tolerance.
By improving the long-term correlation tracking (LCT) algorithm, an effective object tracking method, improved LCT (ILCT), is proposed to address the issue of occlusion. If the object is judged being occluded by the designed criterion, which is based on the characteristic of response value curve, an added re-detector will perform re-detection, and the tracker is ordered to stop. Besides, a filtering and adoption strategy of re-detection results is given to choose the most reliable one for the re-initialization of the tracker. Extensive experiments are carried out under the conditions of occlusion, and the results demonstrate that ILCT outperforms some state-of-the-art methods in terms of accuracy and robustness.
A frequency-degenerate cavity (FDC) is the resonator that the ratio of transverse and longitudinal mode frequency spacings is a simple rational number. When an optical resonator is close to the FDC, transverse-mode-locking (TML) takes place with drastic changes of laser mode. We report for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, the multi-frequency emission and spectral modulation effects coupled with TML in FDC. The Yb:CaGdAlO4 (Yb:CALGO) crystal with large gain bandwidth was used as a gain medium in an off-axis-pumped hemispherical FDC for realizing broadband emission. Interestingly, the spectrum can transform from a single smooth packet shape to a multi-peak structure; meanwhile, the transverse pattern accordingly transforms into some exotic wave-packet profiles through controlling off-axis displacement in a special degenerate state.
Wide-range optical sensors based on a single ring resonator are investigated theoretically and experimentally. The sensor worked at the TE and TM modes simultaneously. Because the sensitivities of the TE mode and TM mode are different, the TE mode is used for the large measurement range, and the TM mode is used for the high sensitivity measurement. The experimental results showed that the measurement range for the TE mode was almost three times larger than that of the TM mode. A sensitivity of 233 nm/RIU was achieved for the wavelength interrogation of the TM mode.
In this work, non-isothermal bleaching of Yb–Li co-doped fiber was investigated. The Yb–Li co-doped fiber was beneficial to reduce the photodarkening-induced excess loss and had no bad effect on the temperature of thermal bleaching (TB). Photodarkened fibers were bleached with different temperature ramp rates. The higher the ramp rate, the higher the complete bleaching temperature. The activation energy of the bleaching of Yb/Al/Li fiber was calculated by fitting, which was similar to that of an Yb-doped fiber. These observations are helpful in revealing the relationship between the mechanism of Li ion co-doping and TB.
A novel 1 kHz single-frequency, Q-switched Er-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Er:YAG) laser pumped by a 1470 nm laser diode is demonstrated. The 500 ns, 5.52 mJ single-frequency, diffraction-limited pulses are obtained by using a ‘ramp-fire’ injection-seeding technique and an optical feedback architecture. The full width at half-maximum of the pulse spectrum is measured to be 1.47 MHz by using the heterodyne technique. The beam quality M2 factors are measured to be 1.18 and 1.24 in the x and y directions, respectively.
The spatial resolved method, which measures the laser-induced damage fluence by identifying the location of the damage point in the Gaussian beam three-dimensional direction, is demonstrated. The advantages and practicality of this method have been explained. Taking a triple frequency beam splitter as an example, the defect damage fluence can be accurately calculated by the spatial resolved method. The different defect damage performance of the triple frequency splitter is distinguished under irradiations of only the 355 and 532 nm lasers. The spatial resolved method provides a way to obtain precise information of optical film defect information.
The photoelectric properties of In0.3Ga0.7As solar cells applied in laser wireless power transmission (LWPT) were studied when they were irradiated by 1070 nm continuous wave (CW) laser of various intensities. The influences of laser intensity on solar cell parameters extracted by the pollination algorithm were analyzed quantitatively. Results show that the conversion efficiency of the cell rose to the maximum and then decreased rapidly in the laser intensity range of 50–900 mW/cm2. With higher energy laser irradiation, the rise of ideality factor and reverse saturation current would lead to the degradation of voltage at the maximum power point, which was the main reason for the decrease of conversion efficiency. The results provide the basis for choosing the appropriate input energy in the case of different transmission systems.
We report the observation of ultralow-power absorption saturation in a tapered optical fiber (TOF) mounted in a hot cesium (Cs) vapor in a vacuum chamber. The small optical mode area of TOF produces a great influence on optical properties, allowing optical interactions with nanowatt-level power. The comparison of transmission characteristics for the TOF system and free-space vapor is investigated at different input power and atomic density. The unique performance of the Cs-TOF system makes it a promising candidate in resonant nonlinear optical applications with ultralow power.
We report a universal approach based on the surface plasmon resonances (SPRs) attained in filamentation in water doped with gold nanoparticles for enhancing the nonlinear refractive index. The filament-induced supercontinuum spectrum in water overlaps with SPRs of gold nanospheres, which further leads to a modification on the Kerr nonlinear refractive index. In our experiment, the measured nonlinear refractive index (n2) in water doped with gold nanoparticles increases by six times, as compared with that in pure water. Such enhancement may be useful for filament-induced nonlinear applications with modest incident intensity.
We report a theoretical demonstration for the creation of space–time holes based on birefringence of reflection, transmission, and the Goos–H chen (GH) shifts from a chiral medium. We observed space–time holes in the reflection, transmission, and their corresponding GH-shifted beams. Two space–time holes are clearly detected in the regions of 0<t≤5τ0 and 5w≤y≤5w, as well as in the regions of 5τ0≤t≤0 and 5w≤y≤5w. These space–time holes hide objects and information contents from observers and hackers. The objects and information contents are completely undetectable, and thus events can be cloaked. The results of this paper have potential applications in the invisibility of drone technology and secure communication of information in telecom industries.
Enhancing light–matter interaction in cavity quantum electrodynamics has aroused widespread interests in on-chip quantum information processing. Here, we propose a hybrid nanotoroid–nanowire system to enhance photon–exciton interaction. A nanoscale gap is formed by placing a dielectric nanowire close to a dielectric nanotoroid, where the coupling coefficient between photon and emitter can achieve 5.55 times of that without nanogap. Meanwhile, the cavity loss and spontaneous emission of the emitter will remain at a small value to guarantee the realization of strong coupling. The method might hold promise for the research of nanophotonics, quantum optics, and novel optical devices.
A λ/4–λ/4 broadband antireflective (AR) coating is developed with a sol-gel dip-coating method. By adding SAR-5 organosilicon resin into a base-catalyzed silica sol top layer and treating at 300°C, a broadband AR coating used for blast shields with a high average transmission of 99.34% (450–950 nm) and good hydrophobicity (with a water-contact angle of 119°) was obtained. After being subjected to rubbing 50 times and being maintained at a relative humidity of around 95% for 50 days, the average transmission of the coating decreased by 0.29% and 0.04%, respectively. This indicates that the organically modified silica (ORMOSIL) broadband AR coating has good abrasion resistance and humidity stability.
As a key figure-of-merit for high-performance microwave filters, the out-of-band noise rejection is of critical importance in a wide range of applications. This paper overviews the significant advances in photonic microwave filters (PMFs) having ultra-high rejection ratios for out-of-band noise suppression over the last ten years. Typically, two types of PMFs, the bandpass and bandstop ones, are introduced with fundamental principles, detailed approaches, and then cutting-edge results for noise rejection. Ultra-high noise rejection ratios of ~80 dB and >60 dB have been demonstrated for single-passband and single-stopband PMFs, respectively, which are comparable with the state-of-the-art electronic filters operating in stringent conditions. These PMFs are also characterized by wide frequency coverage, low frequency-dependent loss, and strong immunity to electromagnetic interference due to the intrinsic features from the advanced photonics technology.
The global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is a well-established outdoor positioning system with industry-wide impact due to the multifaceted applications of navigation, tracking, and automation. At large, however, is the indoor equivalent. One hierarchy of solutions, visible light positioning (VLP) with its promise of centimeter-scale accuracy and widespread coverage indoors, has emerged as a viable, easy to configure, and inexpensive candidate. We investigate how the state-of-the-art VLP systems fare against two hard barriers in indoor positioning: the need for high accuracy and the need to position in the three-dimensions (3D). We find that although most schemes claim centimeter-level accuracy for some proposed space or plane, those accuracies do not translate into a realistic 3D space due to diminishing field-of-view in 3D and assumptions made on the operating space. We do find two favorable solutions in ray–surface positioning and gain differentials. Both schemes show good positioning errors, low-cost potential, and single-luminaire positioning functionality.