View fulltext
View fulltext
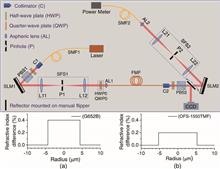
In free-space or in optical fibers, orbital angular momentum (OAM) multiplexing for information transmission has been greatly developed. The light sources used were well coherent communication bands, and the fibers used were customized. Here, we use an 810 nm femtosecond laser to generate optical vortices carrying OAM and then feed them into two kinds of commercial step-index few-mode fibers to explore the transmission characteristics of OAM modes. We also propose a method without multiple-input multiple-output digital signal processing to identify the input OAMs. It is of great guiding significance for high-dimensional quantum information experiments via the OAMs as a degree of freedom, using the light generated by the spontaneous parametric down-conversion as the source and the commercial fibers for information transmission.
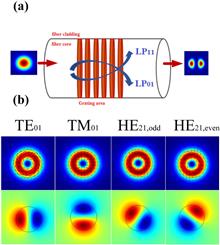
We report here an ultra-broadband linearly polarized (LP) LP01 LP11 mode converter operating at 1 μm based on a long period fiber grating (LPFG) fabricated in a conventional two-mode fiber (TMF) by a line-focused CO2 laser. The measured 3 dB bandwidth is about 240 nm, which is the broadest bandwidth for such fiber mode converters. The maximum conversion efficiency between the LP01 and LP11 modes is >99% over the range of 1000 nm to 1085 nm, almost covering the whole emission band of Yb3+, which is useful for further power scaling of high-power fiber lasers operating at the 1 μm band.
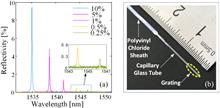
A weak fiber Bragg grating (WFBG) is an ideal quasi-distributed optical fiber sensor. Special attention should be paid to the spectrum and sensing performance of the WFBG at extreme temperatures due to its poor reflection intensity. In this Letter, the temperature characteristics of the WFBG from 252.75°C to 200.94°C are experimentally investigated. Five WFBGs with reflectivity from ~0.25% to ~10% are used in the experiments. The reflectivity variations and wavelength shifts at different temperatures are studied. Experimental results show that the WFBG can survive and work at extreme temperatures, but the performance is affected significantly. The reflectivity is affected significantly by both cryogenic temperature and high temperature. The temperature responses of Bragg wavelengths in the wide temperature range are also obtained.
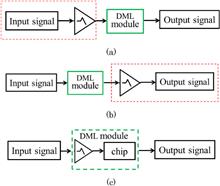
We demonstrate a package-level passive equalization technology in which the wire-bonding-induced resonance effect is used to compensate for the limited gain strength within the Nyquist frequency. The corresponding gain strength under various inductance and capacitance combinations could be quantitatively determined using a numerical simulation. With the increase in the Nyquist frequency, the capacitance shows a greater effect on the gain strength than the inductance. Therefore, the parasitic capacitance should be decreased to realize the desired gain strength at a higher Nyquist frequency. With this equalization technology, gain strength of 5.8 dB is obtained at 22 GHz, which can compensate for the limited bandwidth for the 112 Gbps pulse amplitude modulation (PAM4) signal. The experimental results show that 112 Gbps/λ PAM4 transmission based on a directly modulated laser (DML) module can be realized with a bit error rate of 1 × 10 3 at a received optical power of 3 dBm.
A sunlight communication system is proposed that uses Sr2Si5N8:Eu2+ phosphors to concentrate sunlight signals in strong background light noise; thus, a wide spectrum sunlight communication system is converted into a narrow spectrum one. A communication method is proposed to enable compression to the dark line H-α (656.28 nm) spectrum. A 50% solar energy conversion efficiency is achieved with a 0.3 μs code delay, a 0.2 μs code rise time (20%–80%), and a 96% optical transmittance. Experimental results show that phosphors enhance the sunlight intensity 1.5 times with the same distance. This method has immense potential in future long-distance sunlight communication.
Dispersed fringe sensors are a promising approach for sensing the large-scale physical step between adjacent segments with acceptable accuracy. However, the nature of dispersion in a dispersed fringe sensor leads to the ideal dispersed fringe pattern becoming vulnerable to noise, particularly at low light levels. A reliable merit-function-based algorithm with an active actuation is introduced here. The feasibility of our algorithm is numerically demonstrated, and Monte Carlo experiments for different signal-to-noise ratios are conducted to assess its robustness. The results show that the method is valid even when the signal-to-noise ratio is as low as 1.
We develop a source and mask co-optimization framework incorporating the minimization of edge placement error (EPE) and process variability band (PV Band) into the cost function to compensate simultaneously for the image distortion and the increasingly pronounced lithographic process conditions. Explicit differentiable functions of the EPE and the PV Band are presented, and adaptive gradient methods are applied to break symmetry to escape suboptimal local minima. Dependence on the initial mask conditions is also investigated. Simulation results demonstrate the efficacy of the proposed source and mask optimization approach in pattern fidelity improvement, process robustness enhancement, and almost unaffected performance with random initial masks.
Subtractive imaging is used to suppress the axial sidelobes and improve the axial resolution of 4pi microscopy with a higher-order radially polarized (RP) Laguerre–Gaussian (LG) beam. A solid-shaped point spread function (PSF) and a doughnut-shaped PSF with a dark spot along the optical axis are generated by tightly focusing a higher-order RP-LG beam and a modulated circularly polarized beam, respectively. By subtracting the two images obtained with those two different PSFs, the axial sidelobes of the subtracted PSF are reduced from 37% to about 10% of the main lobe, and the axial resolution is increased from 0.21λ to 0.15λ.
We demonstrate an effective approach of mode suppression by simply using a tungsten probe to destroy the external neck surface of polymer microbottle resonators. The higher-order bottle modes with large axial orders, spatially located around the neck surface of the microresonator, will suffer large optical losses. Thus, excitation just with an ordinary free-space light beam will ensure direct generation of single fundamental bottle mode lasers. This method is with very low cost and convenient and can obtain high side-mode suppression factors. Our work demonstrated here may have promising applications such as in lasing and sensing devices.
We report an efficient mid-infrared extracavity optical parametric oscillator (OPO) based on the nonlinear crystal BaGa4Se7 pumped by a diode-side-pumped Q-switched Nd:Y3Al5O12 (Nd:YAG) laser. The maximum pulse energy of 1.03 mJ at 4.25 μm is obtained with the repetition rate of 10 Hz and pulse width of 12.6 ns when the pump energy was 13.5 mJ, corresponding to an optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 7.6% from 1.064 μm to 4.25 μm. The idler wave slope conversion efficiency was 12%. To the best of our knowledge, it is the highest reported conversion efficiency for the compact BaGa4Se7 OPO driven by the Nd:YAG laser.
Fifth harmonic generation (5th HG) of a Nd:glass laser is an effective way to acquire high-energy coherent deep-ultraviolet radiation near 200 nm. In this work, cascade generation of the fifth harmonic of a Nd:glass laser in a 5 mm ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP) crystal was investigated, and maximum conversion efficiency of 14% and large angular acceptance of 45 mrad were demonstrated at a noncritical phase-matching temperature of 75.1°C. However, as the results reveal, the temperature sensitivity and nonlinear absorption would hinder its high-energy application. As for that, based on the complementary relationship of the angle and temperature in the phase-matching condition, an upgraded focusing 5th HG design coupled with the cylindrical temperature distribution scheme was proposed. By this upgraded focusing design, more than the improvement of the conversion efficiency, the output 5ω near-field intensity distribution turns out to be insensitive to the temperature gradient. Potentially, this idea can be applied for many other frequency conversion schemes such as high-repetition frequency lasers, which have similar temperature gradient problems.
Due to the composition-dependent properties of two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), alloying of existing dissimilar TMDs architecture is a novel and controllable route to tailor crystal structures with superior optical and optoelectronic properties. Here, we reported the hexagonal-phase WSe1.4Te0.6 alloy can enable great promise for enhanced saturable absorption response exceeding the parent component WSe2 and WTe2, with larger modulation depth and lower saturable intensity. These advantages allowed the 1064 nm passively Q-switched lasers based on WSe1.4Te0.6 to be more efficient, with pulse duration narrowed to 45%, and slope efficiency increased by 232%. Our findings highlighted the appropriate alloying of TMDs as an effective strategy for development of saturable absorbers.
Experimental generation of stable mode-locked pulses and cylindrical vector beams (CVBs), from an all few-mode fiber (FMF) ring laser is first reported, to the best of our knowledge. In this laser, a section of few-mode erbium-doped fiber (FM-EDF) is used as the gain medium. The FM-EDF is pumped by 976 nm laser with LP11 mode, which is simultaneously converted and multiplexed through a homemade hybrid device, i.e., wavelength division multiplexing-mode selection coupler (WDM-MSC). All the components in our experiment are connected using FMF. The resulted CVB pulses have a spectral width of 0.33 nm with a repetition rate of 30.58 MHz under the pump power of 340 mW. Moreover, both azimuthally and radially polarized CVBs were achieved with a high purity of >95%. This mode-locked CVB fiber laser with an all FMF configuration opens the way to manipulate the transverse mode in mode-locked fiber lasers.
The tilted energy band in the multiple quantum wells (MQWs) arising from the polarization effect causes the quantum confined Stark effect (QCSE) for [0001] oriented III-nitride-based near ultraviolet light-emitting diodes (NUV LEDs). Here, we prove that the polarization effect in the MQWs for NUV LEDs can be self-screened once the polarization-induced bulk charges are employed by using the alloy-gradient InxGa1-xN quantum barriers. The numerical calculations demonstrate that the electric field in the quantum wells becomes weak and thereby flattens the energy band in the quantum wells, which accordingly increases the spatial overlap for the electron-hole wave functions. The polarization self-screening effect is further proven by observing the blueshift for the peak emission wavelength in the calculated and the measured emission spectra. Our results also indicate that for NUV LEDs with a small conduction band offset between the quantum well and the quantum barrier, the electron injection efficiency for the proposed structure becomes low. Therefore, we suggest doping the proposed quantum barrier structures with Mg dopants.
Extraordinary optical transmission (EOT) in subwavelength metal structures has been studied widely. Herein, we propose a strategy for tuning the EOT of the bullseye structure. Specifically, the bullseye structure was immersed in a nonlinear medium, and a controlling light was employed to change the refractive index of the medium. At different intensities and distributions of controlling light, the transmission property of signal light in the bullseye structure was simulated. The results show that a variable transmission spectrum in the bullseye structure can be realized. Moreover, the position of the central transmission peak shifts linearly with the increasing intensity of controlling light.
A gradient-index Reuleaux-triangle-shaped hole array was fabricated on germanium (Ge) by nanoimprint lithography and inductively coupled plasma processing as a broadband mid-infrared (IR) antireflective surface. The interaction between the {111} planes of cubic crystalline Ge and a circular mold successfully produced an orderly and periodically distributed Reuleaux-triangle-shaped hole array. As a result, the average transmittance increased 15.67% over the waveband at 3–12 μm and remained stable at the incidence angle of up to 60°. The vertices of the Reuleaux triangle showed local enhancement of the electric field intensities due to interference of the incident and reflected radiation fields. It was also found that nonuniform hole depths acted to modulate the transmittance over the 3–12 μm waveband.
In the context of nonlinear plasmonics, we review the recently introduced concept of plasmonic parametric resonance (PPR) and discuss potential applications of such phenomena. PPR arises from the temporal modulation of one or more of the parameters governing the dynamics of a plasmonic system and can lead to the amplification of high-order sub-radiant plasmonic modes. The theory of PPR is reviewed, possible schemes of implementation are proposed, and applications in optical limiting are discussed.
We demonstrate a novel type of miniature spectrometer based on a Fourier transform spectrometer (FTS) chip with a dense output array and a commercial photodetector (PD) array. The FTS chip has an output array cycle of 20 μm and consists of 51 Mach–Zehnder interferometers (MZIs), and the PD array is a commercial linear charged coupled device (CCD). An achromatic triplet lens is used to image the MZI output interferogram onto the CCD with a small aberration. Our experiment result shows that a free spectral range (FSR) from 489 nm to 584 nm and a retrieved spectral resolution of 3.5 nm at 532 nm are obtained. The achieved properties show that our spectrometer has the potential to outperform the best commercial compact one in terms of most performance indices.
Spontaneous optical emission properties of laser-produced plasma during laser damage events at input and exit surfaces of fused silica were retrieved and compared. We show that plasma at the input surface is much larger in size and exhibits significantly higher electron number density and excitation temperature, even when smaller laser energy was used. This effect was attributed to the stronger laser–plasma coupling at the input surface. In addition, a strong continuum background containing three peaks at 1.3 eV, 1.9 eV, and 2.2 eV was observed at the exit surface, and possible origins for this effect are also discussed.
We show the intensity control of filamentation in fused silica by temporally shaping the femtosecond laser pulse. The arbitrary control of filamentation intensity has been obtained by the feedback control based on the genetic algorithm, and the peak intensity of filament has changed from about 670 to around 2100 (charge-coupled device counts). This modulation is in qualitative agreement with the simulation results. It is shown that the control of the intensity is realized by modulating the peak power of the shaped pulse.