View fulltext
View fulltext
A Ti:Sapphire crystal with a diameter of 235 mm and a thickness of 72 mm was grown by heat exchange method.
A single-groove grating for five-port TE-polarization beam splitting under normal incidence at the wavelength of 1550 nm is presented. The transmitted diffraction efficiency of the gratings is over 94.5% with uniformity better than 2%. A physical view of diffraction inside the grating is presented by the simplified modal method (SMM). Initial parameters of the grating profiles are obtained by use of SMM and then optimized by employing rigorous coupled-wave analysis and the simulated annealing algorithm.
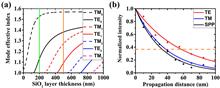
We design and demonstrate a type of multiplexed hologram by nanoscatterers inside a dielectric-loaded plasmonic waveguide with guided-wave illuminations. The mode division multiplexed hologram (MDMH) is fulfilled by the scattering of guided waves to free space with respect to different modes. According to different mode numbers, these guided modes have different responses to the multiplexed hologram, and then give rise to different holographic images in reconstructions. In experiments, we show two kinds of MDMHs based on TM0/TE0 and TE0/TE1 modes as examples. Our approach could enrich the holography method that favors on-chip integration.
Detecting and tracking multiple targets simultaneously for space-based surveillance requires multiple cameras, which leads to a large system volume and weight. To address this problem, we propose a wide-field detection and tracking system using the segmented planar imaging detector for electro-optical reconnaissance. This study realizes two operating modes by changing the working paired lenslets and corresponding waveguide arrays: a detection mode and a tracking mode. A model system was simulated and evaluated using the peak signal-to-noise ratio method. The simulation results indicate that the detection and tracking system can realize wide-field detection and narrow-field, multi-target, high-resolution tracking without moving parts.
Electronic speckle pattern interferometry (ESPI) and digital speckle pattern interferometry are well-established non-contact measurement methods. They have been widely used to carry out precise deformation mapping. However, the simultaneous two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) deformation measurements using ESPI with phase shifting usually involve complicated and slow equipment. In this Letter, we solve these issues by proposing a modified ESPI system based on double phase modulations with only one laser and one camera. In-plane normal and shear strains are obtained with good quality. This system can also be developed to measure 3D deformation, and it has the potential to carry out faster measurements with a high-speed camera.
Real-time single-shot measurement of the femtosecond electron beam duration in laser wakefield accelerators is discussed for both experimental design and theoretical analysis that combines polarimetry and interferometry. The probe pulse polarization is rotated by the azimuthal magnetic field of the electron beam and then introduced into a Michelson-type interferometer for self-interference. The electron beam duration is obtained from the region size of the interference fringes, which is independent of the pulse width of the probe laser. Using a larger magnification system or incident angle, the measurement resolution can be less than 1 fs.
A Ti:sapphire crystal with a diameter of 235 mm and thickness of 72 mm was grown by the heat exchange method (HEM). The absorption intensity of the crystal at 532 nm averaged at 91%. The figures of merit (FOMs) at different positions of the crystal were measured and the FOM value in the central region was found to reach 90. The transmittance laser beam was intact with no obvious distortions and had only a small deformation compared with the incident laser beam. A small-signal amplification experiment was performed on the Ti:sapphire crystal and a gain of more than 6 times was achieved with a pump energy density of 1.98 J/cm2. These tests indicate that the 235 mm Ti:sapphire crystal has excellent optical qualities and will further improve the energy output of a 10 PW laser system.
We proposed a novel wavelength-spread compression technique for spectral beam combining of a diode laser array. A reflector, which is parallel to the grating, is introduced to achieve a double pass with a single grating. This facilitated the reduction of the wavelength spread by half and doubled the number of combined elements in the gain range of the diode laser. We achieved a power of 26.1 W under continuous wave operation using a 19 element single bar with a wavelength spread of 6.3 nm, which is nearly half of the original wavelength spread of 14.2 nm, demonstrating the double-compressed spectrum capability of this structure. The spectral beam combining efficiency was 63.7%. The grating efficiency and reflector reflectance were both over 95%; hence, the efficiency loss of the double-pass grating with a reflector is acceptable. In contrast to double-grating methods, the proposed method introduces a reflector that efficiently uses the single grating and shows significant potential for a more efficient spectral beam combining of diode laser arrays.
Blood oxygenation and flow are both important parameters in a living body. In this Letter, we introduce a simple configuration to simultaneously measure blood flow and oxygenation using an off-the-shelf spectrometer. With the integration time of 10 ms, flow phantom measurements, a liquid blood phantom test, and an arm cuff occlusion paradigm were performed to validate the feasibility of the system. We expect this proof-of-concept study would be widely adopted by other researchers for acquiring both blood flow and oxygenation changes due to its straightforward configuration and the possibility of multimodal measurement.
Myopia has become a noteworthy issue due to the increasing use of our eyes. We propose a continuous power variation vision-training device based on Alvarez lenses with the power ranging from 10 D to +2 D. First, we introduce the principle of Alvarez lenses and the evaluation method of dioptric power and astigmatism. Then, we optimize the optical system described by Zernike polynomials. Finally, we analyze the distributions of dioptric power and astigmatism with the overall surface analysis and fields of view (FOVs) analysis. The results show that the optical performance of an optimized system can meet the requirement within a 40° FOV.
We report on a systematic study of the laser polarization effect on a femtosecond laser filamentation in air. By changing the laser’s ellipticity from linear polarization to circular polarization, the onset position of laser filament formation becomes farther from the focusing optics, the filament length is shorter, and less laser energy is deposited. The laser polarization effect on air filaments is supported by a simulation and analysis of the polarization-dependent critical power and ionization rates in air.
The effect of material surface morphology on the periodic subwavelength of nano-structures induced by a femtosecond (fs) laser was investigated systematically from the initial surface roughness, the different scratches, the pre-formed ripples, and the “layer-carving” technology experiments. The results of the comparative experiments indicate that the initial surface conditions of the target surface have no obvious effects on the spatial structured periods (SSPs) and the ripple orientation of the periodic nano-structures induced by a fs laser, which agreed well with the foretold present surface two-plasmon resonance (STPR) model. Furthermore, different shapes of nano-grids with high regularity and uniformity were obtained by fs-laser fabrication.
In recent years, the nanostructure for solar cells have attracted considerable attention from scientists as a result of a promising candidate for low cost devices. In this work, quantum dots sensitized solar cells with effective performance based on a co-sensitized CdS/CdSe:Mn2+ (or Cu2+) nanocrystal, which was made by successive ionic layer absorption and reaction, are discussed. The optical, physical, chemical, and photovoltaic properties of quantum dots sensitized solar cells were sensitized to Mn2+ and Cu2+ dopants. Therefore, the short current (JSC) of the quantum dot sensitized solar cells is boosted dramatically from 12.351 mA/cm2 for pure CdSe nanoparticles to 18.990 mA/cm2 for Mn2+ ions and 19.915 mA/cm2 for Cu2+ ions. Actually, metal dopant extended the band gap of pure CdSe nanoparticles, reduced recombination, enhanced the efficiency of devices, and improved the charge transfer and collection. In addition, Mn2+ and Cu2+ dopants rose to the level of the conduction band of pure CdSe nanoparticles, which leads to the reduction of the charge recombination, enhances the light-harvesting efficiency, and improves the charge diffusion and collection. The results also were confirmed by the obtained experimental data of photoluminescence decay and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy.
The optical saturation characteristics in the germanium-on-silicon (Ge-on-Si) photodetector are studied for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. The relationship between the optical saturation characteristics and the optical field distribution in the Ge layer is illustrated by the simulation. This theory is verified by comparative experiments with single-injection and dual-injection structures. The dual-injection photodetector with a more balanced and uniform optical field distribution has a 13% higher responsivity at low optical power and 74.4% higher saturation current at 1550 nm. At higher optical power, the bandwidth of the dual-injection photodetector is five times larger than that of the single-injection photodetector.