View fulltext
View fulltext
A schematic (left) and photo (right) image of carbon-nanotube mode-locked 550 -MHz femtosecond Cr:YAG laser. The compact Cr:YAG laser delivers 147- mW output power and 110- fs pulses at 550 MHz repetition rate near 1.5 μm.
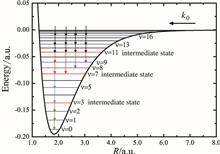
Photoassociation via reverse ladder transition controlled by two and four laser pulses is investigated using the time-dependent quantum wave packet method. The calculated results show that the amplitudes of the pulses have an enormous effect on the target population and total yield of association. For the target state with a high energy level, the population of background states can reduce the state-selectivity. Although, the total yield of association is decreased, the four pulses can induce the population transferring to low vibrational levels, and the state-selectivity of the target state is high.
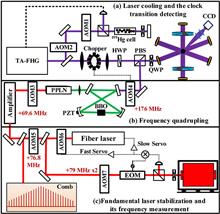
We report on the observation of the highly forbidden S10–P30 optical clock transition in laser-cooled Hg199 atoms. More than 95% depletion of cold Hg199 atoms is detected in the magneto-optical trap. Using the free-of-field detection method, the AC Stark shift from the cooling laser is removed from the in-field spectroscopy. At low-power clock laser pumping, the linewidth of the clock spectroscopy is approximately 450 kHz (full width at half-maximum), which corresponds to a Doppler broadening at the atom temperature of 60 μK. We determine the S10–P30 transition frequency to be 1,128,575,290.819(14) MHz by referencing with a hydrogen maser and measuring with a fiber optical frequency comb. Moreover, a weak Doppler-free signal is observed.
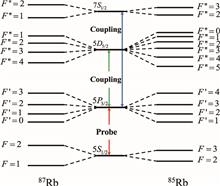
We present a method to precisely determine the hyperfine structure constants of the rubidium 5D5/2 and 7S1/2 states in a cascade atomic system. The probe laser is coupled to the 5S1/2→5P3/2 hyperfine transition, while the coupling laser is scanned over the 5P3/2→5D5/2(7S1/2) transition. The high-resolution double-resonance optical pumping spectra are obtained with two counter-propagating laser beams acting on rubidium vapor. The hyperfine splitting structures are accurately measured by an optical frequency ruler based on the acousto-optic modulator, thus, the magnetic dipole hyperfine coupling constant A and quadrupole coupling constant B are determined. It is of great significance for the atomic hyperfine structure and fundamental physics research.
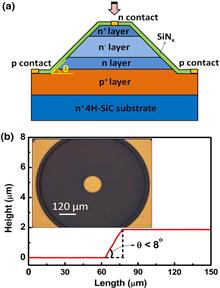
In this Letter, we report large-area (600 μm diameter) 4H-SiC avalanche photodiodes (APDs) with high gain and low dark current for visible-blind ultraviolet detection. Based on the separate absorption and multiplication structure, 4H-SiC APDs passivated with SiNx instead of SiO2 are demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge. Benefitting from the SiNx passivation, the surface leakage current is effectively suppressed. At room temperature, high multiplication gain of 6.5×105 and low dark current density of 0.88 μA/cm2 at the gain of 1000 are achieved for our devices, which are comparable to the previously reported small-area SiC APDs.
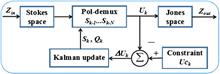
A flexible polarization demultiplexing method based on an adaptive Kalman filter (AKF) is proposed in which the process noise covariance has been estimated adaptively. The proposed method may significantly improve the adaptive capability of an extended Kalman filter (EKF) by adaptively estimating the unknown process noise covariance. Compared to the conventional EKF, the proposed method can avoid the tedious and time consuming parameter-by-parameter tuning operations. The effectiveness of this method is confirmed experimentally in 128 Gb/s 16QAM polarization-division-multiplexing (PDM) coherent optical transmission systems. The results illustrate that our proposed AKF has a better tracking accuracy and a faster convergence (about 4 times quicker) compared to a conventional algorithm with optimal process noise covariance.
A novel distributed feedback (DFB) fiber laser sensor, which can measure acoustic and magnetic fields simultaneously, is proposed. The magnetic field can be measured by detecting the change of resonant frequency of the fiber laser, and the acoustic pressure can be measured by detecting the phase shift of the fiber laser. Both of the signals can be simultaneously demodulated in the frequency domain without affecting each other. Experimental studies show that the acoustic pressure sensitivity of this sensor is about 130 dB (0 dB re 1 pm/μPa) and the sensor has a good linearity with a magnetic field sensitivity of 0.57 Hz/mT.
Both the 4×20 GHz coarse wavelength division multiplexing and LAN-WDM receiver optical sub-assemblies (ROSAs) were developed. The ROSA package was hybrid integrated with a planar lightwave circuit arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) with 2% refractive index difference and a four-channel top-illuminated positive-intrinsic-negative photodetector (PD) array. The output waveguides of the AWG were designed in a multimode structure to provide flat-top optical spectra, and their end facet was angle-polished to form a total internal reflection interface to realize vertical coupling with a PD array. The maximum responsivity of ROSA was about 0.4 A/W, and its 3 dB bandwidth of frequency response was up to 20 GHz for each transmission lane. The hybrid integrated ROSA would be a cost-effective and easy-assembling solution for 100 GbE data center interconnections.
In this Letter, we propose a modified hybrid linear and nonlinear post-equalizer to aid pre-convergence of space–time block coding (STBC) decoding in the formulated multiple-input-single-output (MISO) visible light communication (VLC) model. Meanwhile, we present a channel estimation algorithm, as the existing method is suboptimal. Experiments demonstrate that a data rate of 1 Gbit/s is easily achieved in 1.3 m indoor free space transmission with the bit error rate (BER) limited to 3.8×10 3. Correspondingly, the Q factor can be improved to 3.13 dB compared to the pure linear equalizer case.
A broadband photonic analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for X-band radar applications is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. An X-band signal with arbitrary waveform and a bandwidth up to 2 GHz can be synchronously sampled and processed due to the optical sampling structure. In the experiment, the chirp signal centered at 9 GHz with a bandwidth of 1.6 GHz is sampled and down-converted with a signal-to-noise ratio of 7.20 dB and an improved noise figure. Adopting the photonic ADC in the radar receiver and the above signal as the transmitted radar signal, an X-band inverse synthetic aperture radar system is set up, and the range and cross-range resolutions of 9.4 and 8.3 cm are obtained, respectively.
It is rare for a conventional direct detection method to measure the transmittance uniformity of mirrors with rigorous standards, especially to meet the requirement of transmittance/reflectance and phase detection simultaneously. In this study, a new method of self-calibrated balanced heterodyne detection (SCBHD) is proposed. It can be self-calibrated by a two-channel structure to overcome the environmental effects in large optics scanning detection by employing highly accurate heterodyne interference. A typical transmittance measurement experiment was performed at 1053 nm wavelength via SCBHD. A standard deviation (SD) of 0.038% was achieved in the preliminary experiment. The experimental results prove to reduce the SD by approximately two orders of magnitude compared with the conventional direct detection method in the same condition. The proposed method was verified as being promising not only for its wider dynamic measurement range and its higher accuracy but also for its simultaneous transmittance and phase detection ability.
Dissimilar metal joining of magnesium to aluminum was investigated using the latest generation nanosecond pulsed fiber laser. The tensile shear test shows that the average tensile shear strength of a joint was 86 MPa, which was 75% of the aluminum substrate. The weld interface exhibited a mixture phase (Mg solid solution and Mg17Al12) that improves the strength and toughness of the joint. A thin Mg–Al intermetallic compound layer was formed on both sides of the weld seam toward the Al side. Fracture occurred toward the Al substrate side rather than the Mg–Al interface, indicating a high joining strength at the weld interface.
A high power linearly polarized tunable Raman random fiber laser (RFL) was studied theoretically and experimentally. The parameters required for the system design were obtained through numerical simulation, based on which a hundred-watt-level linearly polarized tunable RFL was successfully demonstrated. The central wavelength can be continuously tuned from 1113.76 to 1137.44 nm, and the output power exceeds 100 W for all of the lasing wavelengths with the polarization extinction ratio (PER) exceeding 20 dB at the maximum output power. Besides, the linewidth, spectral evolution, and temporal dynamics of a specified wavelength (1124.72 nm) were investigated in detail. Moreover, the theoretical results and the experimental results fit well. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time for a hundred-watt-level linearly polarized tunable RFL ever reported.
Sub-picosecond chirped laser pulse-induced airflow and water condensation were investigated in a cloud chamber. The results indicate that the positively chirped sub-picosecond laser pulses generate a more uniform intensity distribution inside the plasma column, leading to a weaker airflow and an elliptic-shaped snow pile. The negatively chirped sub-picosecond laser pulses generate a spark-like intensity distribution inside the plasma column, which produces a wider range of airflow and a round snow pile. The amount of snow weight and the concentration of NO3 are found to be dependent on the intensity distribution inside the plasma column. The visibly stronger plasma column generates much more snow and a higher concentration of NO3 . These experimental results provide a reference for sub-picosecond laser-induced water condensation in realistic atmospheric conditions.
We demonstrate a femtosecond Cr:YAG laser mode-locked by a carbon nanotube saturable absorber mirror (CNT-SAM) at a repetition rate of 550 MHz. By employing the CNT-SAM, which exhibits a modulation depth of 0.51% and a saturation fluence of 28 μJ/cm2 at 1.5 μm, we achieved a compact bulk Cr:YAG laser with self-starting mode-locked operation near 1.5 μm, delivering an average output power of up to 147 mW and a pulse duration of 110 fs. To our knowledge, this system provides the highest repetition rate among reported CNT-SAM mode-locked Cr:YAG lasers and the shortest pulse duration among saturable absorber mode-locked Cr:YAG lasers with repetition rates above 500 MHz.
A 0.1 mol.% CoF2-doped Na5Lu9F32 single crystal with high quality in the size of ~ 10 mm×100 mm was grown by the Bridgman method. Three peaks located at 504, 544, and 688 nm and a broad band in the range of 1200–1600 nm centered at 1472 nm were observed in the absorption spectra. The absorption peak position suggests cobalt ions in the divalent state in the grown crystal. Moreover, the cobalt ions are confirmed to locate in the distorted cubic crystal structure. Upon excitation of 500 nm light, a sharp emission peak at 747 nm ascribed to the T22(H1)→4A2(F) transition was observed for the crystal. The Co2+-doped Na5Lu9F32 crystal shows a potentially promising material for the application of a passively Q-switched laser operating in the near-infrared range.
We studied Goos–H nchen (GH) shifts on a reflective phase-gradient-produced metasurface. Their analytical solutions were achieved for both TE and TM polarizations utilizing the generalized Snell’s law. The calculated results show that the GH shifts are evidently affected by phase gradients and incident angles, which means that a certain range of GH shifts can be realized as long as an incident angle, phase gradient, and frequency are properly chosen. This offers an effective method for the control of GH shifts.
A liquid crystal Pancharatnam–Berry (PB) axilens is proposed and fabricated via a digital micro-mirror-device-based photo-patterning system. The polarization-dependent device behaves as an axilens for a left-handed circularly polarized incident beam, for which an optical ring is focused with a long focal depth in the transverse direction at the output, and an anti-axilens for a right-handed circularly polarized incident beam, for which an optical ring gradually expands at the output. The modification of the size and the sharpness of the diffracted ring beam is demonstrated by encoding a positive (negative) PB lens term into the director expression of a PB (anti-)axicon.
We experimentally demonstrate the ultra-high range resolution of a photonics-based microwave radar using a high repetition rate actively mode-locked laser (AMLL). The transmitted signal and sampling clock in the radar originate from the same AMLL to achieve a large instantaneous bandwidth. A Ka band linearly frequency modulated signal with a bandwidth up to 8 GHz is successfully generated and processed with the electro-optical upconversion and direct photonic sampling. The minor lobe suppression (MLS) algorithm is adopted to enhance the dynamic range at a cost of the range resolution. Two-target discrimination with the MLS algorithm proves the range resolution reaches 2.8 cm. The AMLL-based microwave-photonics radar shows promising applications in high-resolution imaging radars having the features of high-frequency band and large bandwidth.
A classical ensemble method is used to investigate nonsequential double ionization (NSDI) of Ar atoms irradiated by linearly polarized few-cycle laser pulses. The correlated-electron momentum distribution (CMD) exhibits a strong dependence on the carrier-envelope phase (CEP). When the pulse duration is four cycles, the CMD shows a cross-like structure, which is consistent with experimental results. The CEP dependence is more notable when the laser pulse duration is decreased to two cycles and a special L-shaped structure appears in CMD. Recollision time of returning electrons greatly depends on CEP, which plays a significant role in accounting for the appearance of this structure.
Based on the hybrid integration technology, an ultra-compact and low cost transmitter optical subassembly module is proposed. Four directly modulated lasers are combined with a coarse wavelength division multiplexer operated at the O-band. The bandwidth for all channels is measured to be approximately 3 GHz. The 112 Gb/s transmission is experimentally demonstrated for a 10 km standard single mode fiber (SSMF), in which an optical isolator is used for avoiding the back-reflected and scattered light to improve the bit error rate (BER) performance. A low BER and clear eye opening are achieved for 10 km transmission.