View fulltext
View fulltext
The interferometer of geostationary interferometric infrared sounder.
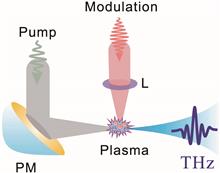
We report the terahertz (THz) wave generation from a single-color scheme modulated by pre-ionized air plasma via an orthogonal pumping geometry. It is found that the amplitude of the THz signal generated by the pump beam tends to decrease gradually with the increase of the modulation power. We believe that the ponderomotive force plays an important role in the process of the interaction between the pump beam and the pre-ionization beam. The hydrostatic state of the electrostatic separation field caused by the modulation beam will directly affect the generation efficiency of the THz wave. Our results contribute to further understanding of the theoretical mechanism and expanding of the practical applications of THz wave generation and modulation.
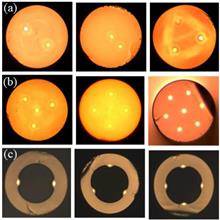
An all-fiber femtosecond vortex laser based on common fiber components is constructed. It can produce femtosecond orbital angular momentum modes whose time pulse width is 398 fs. The topological charge of output orbital angular momentum (OAM) modes from this laser can be adjusted among 0, +1, and 1 easily while it is also easy to convert between continuous OAM modes and pulse OAM modes.
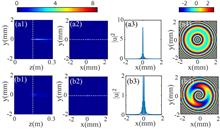
We numerically investigate the propagation properties of ring Airy Gaussian beams (RAGBs) with cosine modulated optical vortices (CMOV). In comparison to the common RAGBs without any modulation, the dynamic propagation of RAGBs with CMOV exhibits a unique feature: the rings of RAGBs with CMOV will gradually shrink into several main lobes with the increase of the propagation distance. The number of lobes and the peak intensity of each lobe are determined by the factors of cosine modulated function. By designing the initial phase, we can easily change the transversal location of the peak intensity. Our results may find potential applications in optical manipulations.
In-fiber integrated optics is an attempt to use silica fiber as a substrate, integrating various optical paths or optical components into a single fiber, to build a functional optical device or component, and to realize a micro optical system, achieving various functions. In-fiber integrated optics is expected to be a new branch of photonics integration. This integration technique enables convenient light beams control and manipulation inside in one fiber. It also provides a research platform with micro and nano scale for interaction between light wave and microfluidic materials. In this review, we briefly summarize the main ideas and key technologies of the in-fiber integrated optics by series integration examples.
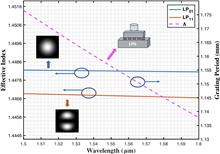
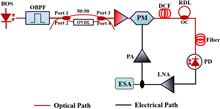
A wideband tunable optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) based on a tunable single-bandpass microwave photonic filter (MPF) and a recirculating delay line is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The MPF is formed by cascading a finite impulse response filter and an infinite impulse response filter, which can enhance the quality factor of the MPF and suppress the side modes of the OEO. The frequency response of the tunable MPF is theoretically analyzed. By placing the MPF into the OEO, tunable microwave signals from 10.3 GHz to 26.7 GHz and a 100 MHz step tunability are experimentally demonstrated. The phase noise is 113 dBc/Hz@10 kHz. The results agree well with the theory.
In this paper, an inclinometer based on a vertical pendulum and a fiber Bragg grating Fabry–Perot cavity (FBG-FP) is proposed. A low-damping rotation structure is used to reduce the mechanical frictions of the pendulum system and induce a wavelength shift of FBG-FPs. We find that the sensitivity can be maximized by optimizing the parameters of the inclinometer. Using a high-resolution demodulation system, a sensitivity of 179.9 pm/(°), and a resolution better than 0.02″ can be achieved. Experiments also show that the proposed inclinometer has good linearity and repeatability.
Novel composite materials are synthesized by incorporating N-acryloylmorpholine (ACMO) in highly concentrated phenanthrenequinone (PQ) doped poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). The photosensitizer concentration of PQ was increased from 0.7 wt. % to 1.8 wt. %. The doping of ACMO component results in a higher diffraction efficiency and photosensitivity than a typical PQ/PMMA system. The enhanced performance of the material may stem from the ACMO molecules, which might open a new route for improving the holographic performance of the PQ/PMMA photopolymer.
We introduce a Casimir force in a conventional optomechanical system to study the high-order sideband generation. In this system, a nanosphere is placed near the moveable mirror of the conventional optomechanical system. The moveable mirror is coupled to the cavity field and the nanosphere by the optomechanical interaction and the Casimir interaction, respectively. We find that the amplitude and cutoff order of the high-order sideband can be enhanced by decreasing the sphere–mirror separation (increasing the Casimir force) and increasing the optomechanical coupling strength. Our proposal provides an alternative method for generating the high-order sidebands and for measuring the Casimir force.
Digital speckle pattern interferometry (DSPI) is a high-precision deformation measurement technique for planar objects. However, for curved objects, the three-dimensional (3D) shape information is needed in order to obtain correct deformation measurement in DSPI. Thus, combined shape and deformation measurement techniques of DSPI have been proposed. However, the current techniques are either complex in setup or complicated in operation. Furthermore, the operations of some techniques are too slow for real-time measurement. In this work, we propose a DSPI technique for both 3D shape and out-of-plane deformation measurement. Compared with current techniques, the proposed technique is simple in both setup and operation and is capable of fast deformation measurement. Theoretical analysis and experiments are performed. For a cylinder surface with an arch height of 9 mm, the error of out-of-plane deformation measurement is less than 0.15 μm. The effectiveness of the proposed scheme is verified.
To measure the global atmospheric three-dimensional distribution and change of temperature and humidity is one of the key areas in atmospheric remote sensing detection; it is also a new research and development direction in the field of meteorological satellite application. As a main element of China second generation of geostationary meteorological satellite Fengyun 4 (FY-4), which was launched on Dec. 11, 2016, the Geostationary Interferometric Infrared Sounder (GIIRS) is the first interferometric infrared sounder working on geostationary orbit internationally. It is used for vertical atmospheric sounding and gains atmospheric temperature, humidity, and disturbances. The combination of Fourier transform spectrometer technology and infrared detectors makes GIIRS have high spectral resolution and large coverage over spatial areas. With this kind of instrument, meteorological satellites can improve the capabilities for severe weather event monitoring and numerical weather prediction. Here a concise review of the GIIRS development project, including its history, missions and functions, technical design, key technologies, system integration, calibration and in-orbit operation status, etc., is presented.
44.6 fs pulses from a 257 MHz, mode-locked non-polarization maintaining Er-doped fiber laser based on a biased nonlinear amplifying loop mirror are reported. The output power is 104 mW and the single-pulse energy is 0.4 nJ. The minimum pulse duration of the direct output is 44.6 fs, which is the shortest in this kind of laser.
The fluorescence from the out-of-focus region excited by the sidelobes of a Bessel beam is the major concern for light-sheet fluorescence microscopy (LSFM) with Bessel beam plane illumination. Here, we propose a method of applying the subtractive imaging to overcome the limitation of the conventional LSFM with Bessel beam plane illumination. In the proposed method, the sample is imaged twice by line scanning using the extended solid Bessel beam and the ring-like Bessel beam. By subtracting between the two images with similar out-of-focus blur, the improved image quality with the suppression of the Bessel beam sidelobes and enhanced sectioning ability with improved contrast are demonstrated.
We propose a high-gain and frequency-selective amplifier for a weak optical signal based on stimulated Brillouin scattering in a single mode fiber. To be able to satisfy the needs of high gain and high signal-to-noise ratio laser pulse amplification, different fiber lengths and core diameters are used to fulfill this experiment. In the experiment, a 430 nW (peak power) pulsed signal is amplified by 70 dB with a signal-to-noise ratio of 14 dB. The small size, high gain, low cost, and low noise of the fiber Brillouin amplifier make it a promising weak signal amplification method for practical applications such as lidar.
A simple and straightforward method to objectively measure the transverse chromatic aberration (TCA) at horizontal field angles out to ±10° from the visual axis of the human eye was proposed. Longitudinal chromatic aberration (LCA) was also measured across the visual field. The TCA of a human eye was obtained by deviation of the point spread function (PSF) images. LCA was calculated from the Zernike defocus. The average TCA changing with eccentricity was 0.162 arcmin/degree between 639 nm and 795 nm wavelengths. Near the optic axis of the eye, the average LCA was 0.37 ± 0.02 D, and it increased slightly with eccentricity (up to 0.54 ± 0.02 D).
Astigmatism is inevitable and inherent to progressive addition lenses (PALs), which are typically distributed in the lateral areas on both sides of the progressive corridor. In this study, we took into account the spectacle frame for the customized freeform PAL design with the variational-difference numerical approach. The PAL surface with minimized astigmatism, approximately equal to 84% of the added power, was numerically resolved without expending the zone for clear vision. We validated our approach by experimentally demonstrating the procedure from tool path generation to surface power measurement, thus providing an efficient solution to the personalization of astigmatism-minimized PAL design and manufacture.