View fulltext
View fulltext
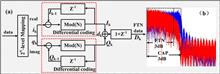
With the rapid development of the light-emitting diode (LED) industry, interest in visible light communication (VLC) is growing. The limited bandwidth of commercial LEDs is one of the main challenges to achieve high-speed VLC. In this Letter, a kind of bandwidth-efficient VLC system based on carrierless amplitude and phase (CAP) modulation is proposed, where a simple differential faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) pre-coding scheme is employed to compress the spectrum and further improve the overall system baud rate. The system is experimentally demonstrated with a data rate of 1.47-Gb/s over 1.5 m free space transmission. The results indicate that an improvement of 80 Mbaud is achieved by FTN-CAP4 at 20% subband overlap and 40 Mbaud rate improvement by FTN-CAP16 at 7.5% subband overlap. Compared with traditional CAP, the FTN pre-coded CAP shows a better performance in spectral efficiency (SE) and intercarrier interference resistance. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first time to employ FTN pre-coded CAP in indoor high-data-rate VLC systems.
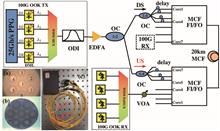
We experimentally demonstrate a real-time quasi-full-duplex 400G/300G optical interconnection over 20 km multicore fibers (MCFs), using 10G-class transponders operated in the C-band. Optical delay interferometer (ODI)-based optical frequency equalization is applied to mitigate chirp and dispersion induced impairments, so that the tolerance to inter-symbol interference (ISI) can be enhanced, thus enabling 4×25 Gb/s on-off keying (OOK) transmission per core over severely limited bandwidth channels. Real-time bit error ratio (BER) performances of the bidirectional 400 Gb/s transmission are measured without using extra digital signal processing (DSP) or electrical equalization, which ensures low complexity and less power consumption.
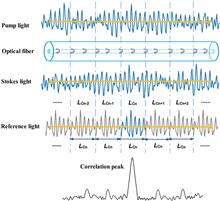
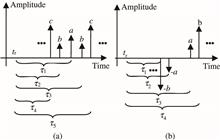
To obtain high spatial resolution over a long sensing distance in Brillouin optical correlation domain reflectometry (BOCDR), a broad laser spectrum and high pump power are used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). In this Letter, we use a noise-modulated laser to study the variation of the Brillouin spectrum bandwidth and its impact on the coherent length of BOCDR quantitatively. The result shows that the best spatial resolution (lowest coherent length) is achieved by the lowest pump power with the highest noise-modulation spectrum. Temperature-induced changes in the Brillouin frequency shift along a 253.1 m fiber are demonstrated with a 19 cm spatial resolution.
Investigation on the group delay performance of microwave photonic filters is presented. Analysis and simulation results show symmetrical distribution on the delayed optical signals in the impulse response is required to obtain a constant group delay performance. Experimental results for both symmetrical and asymmetrical tap distribution microwave photonic notch filters are presented showing the group delay response with <±25 ps and around 1 ns ripples, respectively.
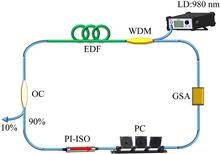
We report a regime of the loose soliton bunch in an erbium-doped passively mode-locked fiber laser. In this state, every soliton bunch consists of multiple pulses. The amount of multiple pulses inside the soliton bunch increase as the pump power rises. Moreover, the temporal average pulse-to-pulse separation decreases in general with the increase of the pump power. Further, the spatial-temporal sequences based on the dispersive Fourier transformation technique show that pulse-to-pulse interactions and time jitter can result in pulse forking inside the soliton bunch. Finally, we theoretically demonstrate the soliton bunch with different pulse-to-pulse separations.
We numerically and experimentally investigate the propagation of deformed 2D vortex Airy beams. Our results show that, for different topological charges, two parabolic trajectories that can be controlled by changing the initial wing angle always dominate the beam propagations. In this case, the main lobes take different propagation distances to restore to the peak intensity. The profiles tend to evolve into 1D or 2D Airy-like patterns to various degrees in the same propagation distance. Furthermore, the whole profiles yield a small change in their acceleration direction, depending on the topological charge and the initial wing angle.
Transporting information is one of the important functions of photons and is also the essential duty of information science. Here, we realize multiple imaging by detecting photons with changeable wavelengths based on time-resolved correlation measurements. In our system, information from multiple objects can be transported. During this process, the wavelength of the photons illuminating the objects is different from the wavelength of the photons detected by the detectors. More importantly, the wavelength of the photons that are utilized to record images can also be changed to match the sensitive range of the used detectors. In our experiment, images of the objects are reconstructed clearly by detecting the photons at wavelengths of 650, 810, and 1064 nm, respectively. These properties should have potential applications in information science.
In this Letter, we propose a three-dimensional (3D) free view reconstruction technique in axially distributed image sensing (ADS). In typical integral imaging, free view reconstructed images can be obtained by tilting all elemental images or tilting the reconstruction plane due to large lateral perspectives for 3D objects. In conventional ADS, the reconstructed images at only a front view can be generated since the sensor is moved along with its optical axis so that it has small lateral perspectives for 3D objects. However, the reconstructed 3D images at any viewing point may be obtained because the virtual viewing camera may capture these slightly different perspectives for 3D objects. Therefore, in this Letter, we employ the virtual viewing camera to visualize the 3D images at the arbitrary viewing point. To support our proposed method, we show the experimental results.
Enhanced quantitative X-ray phase-contrast (QXPC) imaging is implemented with a Foucault knife-edge array filter (FKAF), which is a real differential spatial filter. The intensities of Foucault differential filtering (FDF) are acquired according to the linear translation of the FKAF along the axes. The FDF using the FKAF scheme for obtaining the QXPC images is demonstrated by a stereoscopic rendering of the quantitative phase images of the tail fin of an anchovy containing soft and hard components in specimen. FDF is a noninterferometric quantitative phase-imaging method that depicts quantitative phase images and renders stereoscopic images.
The star tracker, an optical attitude sensor with high accuracy, is widely used in satellites for attitude determination and control. However, it is susceptible to the sunlight and the earthlight for application on satellites in the sun-synchronous orbit. Therefore, the suppression of the sunlight and the earthlight is important for the star tracker. In this Letter, a vector model is proposed to describe the relationship among the Sun, the Earth, and the satellite body, and, based on the equations of the boundary curves, the vector areas free from the sunlight and the earthlight in the body coordinate system of the satellite are derived. Meanwhile, the installation orientation of the star tracker and the corresponding exclusion angle of the earthlight are optimized. The simulation results indicate that the optimization method for the installation orientation and the exclusion angle of the star tracker is accurate and effective.
There exist some shallow scratch defects on the super-smooth optical surface. Their detection has a low efficiency with the existing technologies. So a new detection method, dark-field detection of adaptive smoothing and morphological differencing (DFD-ASMD), is proposed. On one hand, the information of shallow scratches can be kept in dark-field images. On the other hand, their weak characteristics can be separated and protected from being overly reduced during the elimination of noise and background in the image. Experiments show the detection rate of shallow scratches is around 82%, and DFD-ASMD can lay a foundation for quality control of defects on the high-quality optical surface.
The pretilt angle of a twisted nematic (TN) liquid crystal display has a strong effect on viewing angles and response times of the display as well as shifting the light-leaking disclination lines into the black-matrix area within pixels of a thin-film-transistor driven TN panel for a high contrast ratio. In this Letter, we develop an optical method to determine the TN pretilt angle based on heterodyne measurements of the phase versus the incident angle of a thin TN cell subjected to out-of-plane rotations. We believe that our method of measuring phases has advantages of simpler setup and calculations, better stability, and less sensitive to ambient electromagnetic interference than the commonly used method of measuring intensities.
We demonstrate a polarization insensitive arrayed-input spectrometer using echelle diffraction grating (EDG) for hyperspectral imaging. The EDG consists of 65 input waveguides and 129 output waveguides, allowing spectral measurements of 65 image pixels at a time when used in combination with a micro-electromechanical system micro mirror array. The spectral resolution reaches 7.8 nm for wavelengths ranging from 1250 to 1700 nm. The measured loss is 2 dB, and the crosstalk is lower than 20 dB. The 3 μm silicon-on-insulator platform provides the device with polarization insensitive characteristics. The chip size is only 6 mm×10 mm.
The cavity transmission spectrum is experimentally investigated in Λ-type three-level atoms coupled to a standing-wave cavity system. It is shown that the dark-state polariton peak is not generated at resonance but rather at off-resonance. The theoretical analysis reveals that the absence of an on-resonance dark-state polariton peak is mainly caused by the strong absorption of the intracavity medium to the probe cavity mode counterpropagating with the coupling field due to the Doppler shift in the hot atoms. Moreover, the optimal frequency position of the cavity mode for an efficient dark-state polariton peak is also demonstrated.
Broad-area diode lasers usually supply high output power but low lateral beam quality. In this Letter, an on-chip combined angled cavity is proposed to realize narrow lateral far field patterns and high brightness. The influence of included angles, emitting facets on output power, and beam quality are investigated. It demonstrates that this V-junction laser is able to achieve a single-lobe far field at optimal cavity length with a 3.4 times improvement in brightness compared with Fabry–Perot (F-P) cavity lasers. The excited high-order modes at a high injection level reduce the brightness, but it is still 107% higher than that of F-P lasers.
A series of Ce3+, Sm3+-doped Zn2GeO4 phosphors are prepared by the solid-state reaction. A blue photoluminescence (PL) of Zn2GeO4 is observed as the recombination of the electrons trapped on VO and Zni with holes trapped on VGe and VZn′. The energy transfer process between Ce3+ and Sm3+ is confirmed by the PL spectra and decay curves, and the emission colors can be adjusted from blue to orange–red. Furthermore, we verify unambiguously that the energy transfer from Ce3+ to Sm3+ occurs. Besides, Ce3+</inline-
In optical studies on layered structures, quantitative analysis of radiating interfaces is often challenging due to multiple interferences. We present here a general and analytical method for computing the radiation from two-dimensional polarization sheets in multilayer structures of arbitrary compositions. It is based on the standard characteristic matrix formalism of thin films, and incorporates boundary conditions of interfacial polarization sheets. We use the method to evaluate the second harmonic generation from a nonlinear thin film, and the sum-frequency generation from a water/oxide interface, showing that the signal of interest can be strongly enhanced with optimal structural parameters.
The influence of laser temporal contrast on high-order harmonic generation from intense laser interactions with solid-density plasma surfaces is experimentally studied. A switchable plasma mirror system is set up to improve the contrast by two orders of magnitude at 10 ps prior to the main peak. By using the plasma mirror and tuning the prepulse, the dependence of high-order harmonic generation on laser contrast is investigated. Harmonics up to the 21st order via the mechanism of coherent wake emission are observed only when the targets are irradiated by high contrast laser pulses by applying the plasma mirror.
We use the selective area growth (SAG) technique to monolithically integrate InP-based 4-channel arrayed waveguide gratings (AWGs) with uni-traveling carrier photodiode arrays at the O-band. Two kinds of channel spacing demultiplexers of 20 nm and 800 GHz are adopted for potential 100 Gbps coarse wavelength division multiplexing and local area network wavelength division multiplexing systems, with an evanescent coupling plan to facilitate the SAG technique into device fabrication. The monolithic chips in both channel spacings exhibit uniform bandwidths over 25 GHz and a photodiode responsivity of 0.81 A/W for each channel, in agreement with the simulated quantum efficiency of 80%. Cross talk levels are below 20 dB for both channel spacing chips.
In this Letter, the liquid crystal variable phase retarder is applied for the accurate modulation of the laser power in a detection system and the construction of a system that suppresses the influence of laser noise on the gyro’s bias instability. A closed-loop control method for a laser noise suppression system is proposed. We obtain a power stability index of 0.038% in a 3-h continuous test, and the nuclear magnetic resonance gyroscope bias instability reaches 1°/h. The proposed control method effectively improves the signal-to-noise ratio of the gyroscope detection signal, which lays the technical foundation for future research work.
Higher emission rates and controllable emission direction are big concerns when it comes to finding a good single photon source. Recently, surface plasmons are introduced to this application, as they can manipulate and enhance the luminescence of single emitters. Here, we experimentally achieve a wide-area multiple directional enhanced light source through periodic metal grating structures. The surface-plasmon-coupled emission can have multiple precisely emission angles by just changing the period of the grating. Our result indicates that metal plasmonic grating can be used as a productive quantum device for unidirectional quantum light sources in quantum optics.
A specific system structure of down-looking synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) is given, and a far-field experiment over 6 km of down-looking SAIL under this system design is carried out. The down-looking SAIL can overcome the influence of atmospheric turbulence to a great extent. By applying this system design, it also has advantages in self-compensating phase modulation. A fine image is obtained after aligning in the orthogonal direction and phase error compensation in the travel direction based on a dominant scatterer. The achieved imaging resolutions in the two dimensions are both better than 5 cm.
In this Letter, a miniature wearable Raman spectroscopy system is developed. A wearable fiber-optic probe is employed to help the stable and convenient collection of Raman spectra. A nonlinear partial least squares model based on a multivariate dominant factor is employed to predict the glucose level. The mean coefficients of determination are 0.99, 0.893, and 0.844 for the glucose solution, laboratory rats, and human volunteers. The results demonstrate that a miniature wearable Raman spectroscopy system is feasible to achieve the noninvasive detection of human blood glucose and has important clinical application value in disease diagnosis.