View fulltext
View fulltext
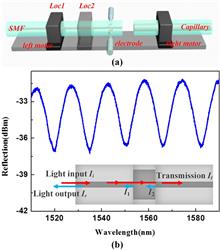
A simple capillary-based extrinsic Fabry–Perot structure is presented and fabricated, using the manual welding method with the strain sensing characteristics investigated in detail. Strain sensitivities of 4.2, 2.8, and 2.4 pm/με are obtained experimentally with the interferometer length around 50 μm and the inner diameter of 75, 50, and 25 μm, respectively. The underlying physics of the strain sensitivity of this device is negatively correlated with the interferometer length and positively correlated with the capillary inner diameter, which provides two simple parameters to tailor the strain sensitivity.
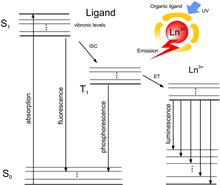
Lanthanide-doped polymers are very attractive, since they can be used for luminescent optical fiber fabrications. This Letter presents the terbium-ions-doped poly(methyl methacrylate) fiber fabrication and spectroscopic characterization. The measured excited state (D45) lifetime of 0.741 ms confirms that a used organometallic can be used to obtain an intense luminescence in a polymeric fiber. The luminescence spectrum shape modification versus the fiber length is also investigated.
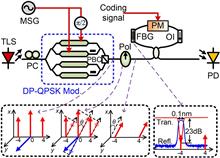
An approach for photonic generation of a frequency-octupled phase-coded signal based on carrier-suppressed high-order double sideband modulation is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The key component of the scheme is an integrated dual-polarization quadrature phase shift keying modulator, which is used to achieve the carrier-suppressed high-order double sideband modulation. At the output of the modulator, two fourth-order optical sidebands are generated with the optical carrier suppressed. After that, a Sagnac loop incorporating a fiber Bragg grating and a phase modulator is employed to separate the two optical sidebands and phase modulate one sideband with a binary coding signal. The approach features large carrier frequency tuning range for the generated phase-coded signal from several megahertz to beyond the W-band. A proof-of-concept experiment is carried out. The 2 Gbit/s phase-coded signals with frequencies of 16.48, 21.92, and 29.76 GHz are generated.
We present a theoretical analysis and an experimental study of the impacts of external optical feedback on dual-frequency fiber lasers. The external optical feedback can effectively suppress the phase noise of the beat notes of dual-frequency fiber lasers, provided some requirements are satisfied. The polarization of the optical feedback is important for the fiber laser’s stability, and it can also tune the beat note frequency. A side effect of external optical feedback, as demonstrated in the experiments, is lowering the sensitivity of the dual-frequency fiber laser-based sensors, although such degradation is not obvious.
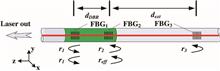
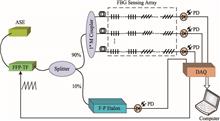
A new wavelength division multiplexing method for fiber Bragg grating (FBG) sensors based on spectrum profile identification is proposed. In this method, FBGs and tilted FBG (TFBG) sensors are cascaded in a single fiber in one sensing channel. The different spectrum profiles enable the cross-correlation method to demodulate the wavelength. Therefore, the different types of sensors can occupy the same central wavelength band. Using this method, the multiplexing capacity is optimized. Experiment results demonstrate the feasibility of this method and it is useful for applications where large numbers of FBGs are needed.
We propose a broadband fiber optic parametric amplifier (FOPA) based on a near-zero ultra-flat dispersion profile with a single zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) by using a selective liquid infiltration technique. The amplifier gain and bandwidth is investigated for a variety of fiber lengths, pump power, and operating wavelengths. It is observed that sufficient peak gains and broader bandwidths can be achieved with a small negative anomalous dispersion (β2≤0) and a positive value of the 4th-order dispersion parameter (+ β4) around the pump. We can optimize an FOPA with a bandwidth of more than 220 nm around the communications wavelength.
A laser interferometry technique is developed to detect water surface capillary waves caused by an impinging acoustic pressure field. The frequency and amplitude of the water surface capillary waves can be estimated from the local signal data at some special points of the phase modulated interference signal, which is called the turning points. Demodulation principles are proposed to explain this method. Experiments are conducted under conditions of different intensity and different frequency driving acoustic signals. The results show the local signal data analysis can effectively estimate the amplitude and frequency of water surface capillary waves.
We experimentally observe that Si micro-ring modulator (MRM) modulation characteristics are strongly influenced by the modulation data rate and the data pattern and determine this influence is due to the temperature increase caused by dynamic power dissipation within the Si MRM device. We also quantitatively determine the amount of Si MRM resonance wavelength shift due to different modulation data rates, data patterns, and modulation voltages. Our results should be of great help for achieving reliable and optimal modulation characteristics for Si MRMs.
We demonstrate a continuous-wave (CW) dual-wavelength Nd:YVO4 laser working at 1064 and 1066 nm simultaneously. The method of Nd:YVO4 crystal angle tuning is used to balance the ratio of the stimulated emission cross sections of the two wavelengths, leading to the realization of a simultaneous dual-wavelength operation from only one laser. The experimental results show that at a 2.85 W pump power, the maximum output powers at wavelengths of 1064 and 1066 nm are 0.55 and 0.54 W, respectively. The linear resonate cavity is as short as 10 mm, which gives the laser the advantages of a miniature configuration and low threshold. Such a dual-wavelength laser can be very attractive for the development of compact THz sources based on difference frequency generation.
Accurate and precise wavelength controlling of narrowband excimer lasers is essential for the lithography of an integrated circuit. High-precision wavelength tuning and calibration of a line-narrowed ArF laser are presented in this work. The laser spectrum is narrowed to a sub-picometer with a line narrowing system. Absolute wavelength calibration of the line-narrowed laser is performed based on the optogalvanic (OG) effect using iron hollow cathode discharge (HCD). An sccuracy of better than 0.1 pm for wavelength tuning and calibration is achieved with our homemade wavemeter.
A fused silica glass micro-channel can be formed by chemical etching after femtosecond laser irradiation, and the successful etching probability is only 48%. In order to improve the micro-channel fabrication success probability, the method of processing a high-temperature lattice by a femtosecond laser pulse train is provided. With the same pulse energy and scanning speed, the success probability can be increased to 98% by optimizing pulse delay. The enhancement is mainly caused by the nanostructure, which changes from a periodic slabs structure to some intensive and loose pore structures. In this Letter, the optimum pulse energy distribution ratio to the etching is also investigated.
Far-field blooming, a serious far-field dependence on driving current, affects the stability of beam quality and applications of broad-area (BA) diode lasers. In this Letter, the lateral ridge waveguide (LRW) is introduced to BA lasers by a simple and cost-effective approach to control the far-field stability and beam divergence. The influences of LRW length on output power, near- and far-field, are investigated and it is found that the optimized LRW length is able to improve both the far-field blooming and output power. The mechanism behind this is analyzed and a 0.13°/A dependence of lateral divergence angle on the injection current is achieved.
We demonstrate the generation of mode-locked pulses in an erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) by using a new manganese-doped cadmium selenide quantum-dots-based saturable absorber. The laser produces a soliton pulse train operating at 1561.1 nm with a repetition rate of 1 MHz, as the pump power is varied from 113 to 250 mW. At the maximum pump power, we obtain the pulse duration of 459 ns with a signal-to-noise ratio of 50 dB.
The laser performance of a new Yb:germanophosphate (Yb:GP) glass is investigated. A maximum output power of 826 mW at 1063 nm is achieved with direct diode pumping at 976 nm. The wavelength is tuned from 1034.47 to 1070.83 nm, corresponding to a tuning range of 36.36 nm. Thermal lens effects are investigated to optimize the optical cavity.
We report a 307 W 1018 nm Yb-doped fiber laser pumped by a single 976 nm laser diode. The cavity slope efficiency is up to 75.9% and the amplified spontaneous emission is suppressed by 54 dB. The beam quality of the output laser has an M2 factor of 1.17. Effective thermal management is considered to ensure the stable operation of our system. The power stability at the maximum output power level is measured during a period of 0.5 h and the power fluctuation is less than 0.8%. This architecture can be an effective high brightness pump source of core-pumping high-power fiber amplifiers.
We experimentally demonstrate a cascaded Raman scattering continuum, utilizing a compact mode-locked Yb-doped fiber laser based on a nonlinear polarization rotation technique in the all normal dispersion regime. There is no physical filter or polarization controller in the oscillator, and a different mode-locked operation is achieved, corresponding to the extra fiber location in the oscillator. The broadband spectrum generation owes to the enhanced stimulated Raman scattering progress. The maximum output average power and peak power are 14.75 nJ and 18.0 W, and the short coherence light is suited for optical coherence tomography.
We theoretically investigate the attosecond pulse generation in an orthogonal multicycle midinfrared two-color laser field. It is demonstrated that multiple continuum-like humps, which consist of about twenty orders of harmonics and an intensity of about one order higher than the adjacent normal harmonics, are generated when longer wavelength driving fields are used. By filtering these humps, intense isolated attosecond pulses (IAPs) are directly generated without any phase compensation. Our proposal provides a simple technique to generate intense IAPs with various central photon energies covering the multi-keV spectral regime by using multicycle midinfrared driving pulses with high pump energy in the experiment.
Photothermal/photoacoustic (PT/PA) spectroscopy provides useful knowledge about optical absorption, as well as the thermal and acoustical properties of a liquid sample. For microfluidic biosensing and bioanalysis where an extremely small volume of liquid sample is encapsulated, simultaneous PT/PA detection remains a challenge. In this work, we present a new optofluidic device based on a liquid-core optical ring resonator (LCORR) for the investigation of PT and PA effects in fluid samples. A focused 532 nm pulsed light optically heats the absorptive fluid in a capillary to locally create a transient temperature rise, as well as acoustic waves. A 1550 nm CW laser light is quadrature-locked to detect the resonance spectrum shift of the LCORR and study thermal diffusion and acoustic wave propagation in the capillary. This modality provides an optofluidic investigative platform for biological/biochemical sensing and spectroscopy.