View fulltext
View fulltext
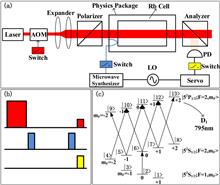
We report the recent progress of our pulsed optically pumped (POP) vapor cell rubidium clock with dispersive detection. A new compact physics package is made. A rubidium cell with a high precision buffer gases mixing ratio is obtained, and the temperature controlling system is renovated to reduce fractional frequency sensitivity to temperature variation. The resolution of the servo control voltage is also optimized. With these improvements, a clock frequency stability of 3.53×10 13 at 1 s is obtained, and a fractional frequency stability of 4.91×10 15 is achieved at an average time of τ=2000 s.
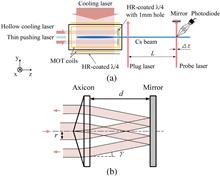
The construction of a two-dimensional magneto–optical trap with hollow cooling and pushing (2D-HP MOT) is reported in detail, and a velocity-tunable cold atomic beam produced by this 2D-HP MOT is demonstrated. The magneto–optical trap system, which is constructed by a transparent quartz tube, is low in price, easy to fabricate and assemble, and convenient for atomic trapping and detection. The mean axial velocity of the cold atomic beam can be tuned from 4.5 to 8 m/s, while the atomic flux remains at a level of 1010 atoms/s. This cold atomic beam source can be applied in the areas of high-precision measurements based on cold atoms.
A flow measurement system consisting of an optical fiber Fabry–Perot (F-P) sensor and an elbow tube is proposed and demonstrated to realize flow measurements and eliminate thermal disturbance. Two F-P sensors are symmetrically mounted on the inner-wall surface of the elbow of 90° in order to eliminate the effect of thermal disturbance to the flow measurement accuracy. Experimental results show that the absolute phase difference is the square root of the fluid flow. It is consistent with the theoretical analysis, which proves that the flow measurement method can measure flow and eliminate the influence of thermal disturbance simultaneously.
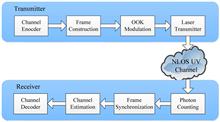
We extend the transmission range of non-line-of-sight ultraviolet communication to 500 m in a real-time system experiment using a 200 mW solid-state 266 nm laser, where the data rate can reach 400 kbps at a frame error rate lower than 10 5 in the real-time system test. The results can beat the best record so far, in terms of both the data rate and transmission distance.
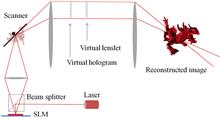
This Letter proposes a scanned holographic display system that takes the advantage of a high-speed resonant scanner to augment a galvanometer and hence improves the opto-mechanical information distribution capabilities, thereby potentially achieving an increased image size and enlarged viewing angles.
Modal analysis of the 1×3 highly efficient reflective triangular grating operating in the 800 nm wavelength under normal incidence for TE polarization is presented in this Letter. The rigorous coupled wave analysis and simulated annealing algorithm are used to design this beam splitter. The reflective grating consists of a highly reflective mirror and a transmission grating on the top. The mechanism of the reflective triangular grating is clarified by the simplified modal method. Then, gratings are fabricated by direct laser writing lithography.
Projection-type recorders of computer-generated Fourier holograms have potential due to the decreased precision requirements of the optical scheme compared to most known holographic data recorders based on two-beam schemes. In the case of optical memory system development, the reduction factor of the projection scheme requires the application of properly developed optical components. The present report is dedicated to the development of special objectives for the projection scheme of computer-generated Fourier holograms.
In this Letter, we report a Golay3 sparse-aperture telescope newly built in the Key Laboratory of Optical Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences and present the experimental results of enhanced resolution. The telescope consisting of 3 collector telescopes of 127 mm diameter can achieve a theoretical resolution corresponding to a monolithic aperture of 245 mm diameter. It is shown by the experimental results that the resolution is improved to 3.33 μrad with respect to the diffraction limit of 6.07 μrad for a single aperture using the Rayleigh criteria at 632 nm. The compact optical configuration and cophasing approach are also described.
In this Letter, we propose an on-line inspection method based on a plenoptic camera to detect and locate flaws of optics. Specifically, due to the extended depth of field of the plenoptic camera, a series of optics can be inspected efficiently and simultaneously. Moreover, the depth estimation capability of the plenoptic camera allows for locating flaws while detecting them. Besides, the detection and location can be implemented with a single snapshot of the plenoptic camera. Consequently, this method provides us with the opportunity to reduce the cost of time and labor of inspection and remove the flaw optics, which may lead to performance degradation of optical systems.
In this Letter, we demonstrate a 1×4 low-crosstalk silicon photonics cascaded arrayed waveguide grating, which is fabricated on a silicon-on-insulator wafer with a 220-nm-thick top silicon layer and a 2 μm buried oxide layer. The measured on-chip transmission loss of this cascaded arrayed waveguide grating is ~4.0 dB, and the fiber-to-waveguide coupling loss is 1.8 dB/facet. The measured channel spacing is 6.4 nm. The adjacent crosstalk by characterization is very low, only 33.2 dB. Compared to the normal single silicon photonics arrayed waveguide grating with a crosstalk of ~ 12.5 dB, the crosstalk of more than 20 dB is dramatically improved in this cascaded device.
A mode-locked (ML) picosecond ytterbium-doped thin disk laser using a monolayer MoS2 as the saturable absorber (SA) is demonstrated. The monolayer MoS2 is fabricated through the method of low-pressure chemical vapor deposition. The laser directly produces stable ML picosecond pulses at a slope efficiency of 9.71%. The maximum output power is approximately 890 mW, while the corresponding repetition, pulse energy, and pulse duration are 48.6 MHz, 18.3 nJ, and 13.1 ps, respectively. Results suggest that the monolayer MoS2 is a promising SA for ultrafast lasers system.
A high power continuous-wave single-frequency green fiber laser by second-harmonic generation of a Yb-doped fiber amplifier (YDFA) is developed. A linearly polarized single-mode fiber amplifier produces a 60 W infrared laser at 1064 nm with a 103 W incident diode pump laser at 976 nm, corresponding to an optical conversion efficiency of 58%. An external bow-tie enhancement cavity incorporating a noncritically phase-matched lithium triborate crystal is employed for second-harmonic generation. A 33.2 W laser at 532 nm is obtained with a 45 W incident 1064 nm fundamental laser, corresponding to a conversion efficiency of 74%.
Employing 0.3 nm diameter single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) as saturable absorbers, we demonstrate a passively mode-locked fiber laser operating at 1950 nm. The 0.3 nm diameter SWCNTs are prepared by pyrolyzing dipropylamine in the channels of zeolite crystals MgAPO-11 (AEL). The laser pumped by a 1550 nm laser source produces 972 fs pulses with a spectral width at half-maximum of 4.2 nm and a repetition rate of 21.05 MHz, an average output power of 2.3 mW corresponding to the maximum pump power of 420 mW with a 10% output coupler.
To further improve the luminous efficiency of LED lightings, this Letter proposes a chip-on-board (COB) device by combining diced staggered V-shaped patterns and remote phosphors. The results show that the V-shaped patterned COB (V-COB) with vertex angles from 120o to 150o can achieve a ~17% output power increase (OPI) compared to the conventional COB. V-COB remote phosphor devices (RPDs) are then manufactured and tested. The luminous efficiency of the proposed RPD represents an 11.6% increase at the correlated color temperature of ~3000 K. Such an improvement can be attributed to both the decreases of total internal reflections and phosphor backscatterings.
The Brillouin gain properties in a double-clad As2Se3 photonic crystal fiber (PCF) are simulated based on the finite-element method (FEM). The results indicate that the Brillouin gain spectrum (BGS) of our proposed chalcogenide PCF exhibits a multipeaked behavior and has a high Brillouin gain coefficient. We also find that a larger size of inner cladding air holes will lead to a more pronounced second peak in the BGS. On the other hand, the size of the outer cladding has nearly no effect on the BGS behavior. Through these results, one can tailor the Stimulated Brillouin scattering effect in PCFs for a wide range of applications.
Calibration of the relationship between the scattering angle and the CCD pixel is a key part of achieving accurate measurements of rainbow refractometry. A novel self-calibrated global rainbow refractometry system based on illumination by two lasers of different wavelengths is proposed. The angular calibration and refractive index measurement of two wavelengths can be completed simultaneously without extra measurement devices. The numerical and experimental results show the feasibility and high precision of the self-calibration method, which enables the rainbow refractometry to be implemented in a more powerful and convenient way. The self-calibrated rainbow system is successfully applied to measure the refractive indices of ethanol-water solutions with volume concentrations of 10% to 60%.
Specimens of PbTe single film are deposited on Ge substrates by vacuum thermal evaporation. During the temperature range of 80–300 K, the transmittance of a PbTe film within 2–15 μm is measured every 20 K by the PerkinElmer Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy cryogenic testing system. Then, the relationship between the refractive index and wavelength within 7–12 μm at different temperatures is received by the full spectrum inversion method fitting. It can be seen that the relationship conforms to the Cauchy formula, which can be fitted. Then, the relationship between the refractive index of the PbTe film and the temperature/wavelength can be expressed as n(λ,T)=5.82840 0.00304T+4.61458×10 6T2+8.00280/λ2+0.21544/λ4, which is obtained by the fitting method based on the Cauchy formula. Finally, the designed value obtained by the formula and the measured spectrum are compared to verify the accuracy of the formula.
A Schwarzschild microscope with a numerical aperture of 0.2 and a magnification of 130 in a 100 μm field of view (FOV) is designed and is working at 13.5 nm. Meanwhile, a CCD is used as a detector with a pixel size of 13 μm×13 μm and imaging area of 13 mm×13 mm. The imaging quality with tolerances of system and errors of mirrors are considered. We obtain that the best on-axes object resolution can be up to about 200 nm, the average value is 230 nm, and the resolution is about 360 nm at 80 μm FOV.
We demonstrate a high-speed silicon carrier-depletion Michelson interferometric (MI) modulator with a low on-chip insertion loss of 3 dB. The modulator features a compact size of <1 mm2 and a static high extinction ratio of >30 dB. The Vπ·Lπ of the MI modulator is 0.95–1.26 V·cm under a reverse bias of 1 to 8 V, indicating a high modulation efficiency. Experimental results show that a 4-level pulse amplitude modulation up to 20 Gbaud is achieved with a bit error rate of 6×10 3, and a 30 Gb/s binary phase-shift-keying modulation is realized with an error vector magnitude of 25.8%.