View fulltext
View fulltext
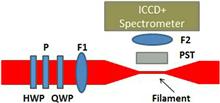
We demonstrate that the filamentation process is strongly influenced by the polarization state of the driver laser. When the laser polarization changes from linear to circular, the critical power for the self-focusing of a Ti:Sapphire laser (800 nm, 40 fs) in air increases from about 9.6±1.0 to 14.9±1.5 GW, while the second nonlinear refractive index n2 of air decreases from 9.9 × 10 20 to 6.4 × 10 20 cm2/W. We also demonstrate that the luminescence from the neutral nitrogen molecules at 337 nm is dependent on both the laser intensity and plasma density inside the filament.
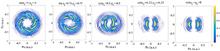
The photoionization by two elliptically polarized, time delayed attosecond pulses is investigated to display a momentum distribution having the helical vortex or ring structures. The results are obtained by the strong field approximation method and analyzed by the pulse decomposition. The ellipticities and time delay of the two attosecond pulses are found to determine the rotational symmetry and the number of vortex arms. For observing these vortex patterns, the energy bandwidth and temporal duration of the attosecond pulses are ideal.
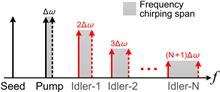
We propose a method to enhance the performance of Brillouin optical correlation domain analysis (BOCDA) with a broad chirp span of optical sources based on the frequency chirp magnification technique. In BOCDA systems, the number of effective sensing points is proportional to the chirp span of the light source, which is normally limited by the characteristics of the laser diode. We demonstrate a chirp span of 126 GHz with the proposed method, to double the effective sensing points of BOCDA. By combining with differential measurement schemes, a spatial resolution of <10 cm over a 1 km range is achieved.
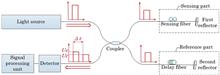
We demonstrate a size sensing technique for nano-particles using optical differential phase measurement by a dual fiber interferometer through phase-generated carrier (PGC) demodulation. Nano-particle diameters are obtained from the differential phase shift as a result of adding an optical scattering perturbation into two-beam interference. Polystyrene nano-particles with diameters from 200 to 900 nm in a microfluidic channel are detected using this technique to acquire real-time particle diameters. Compared with amplitude sensing with over 10 mW of laser irradiance, particle sizing by PGC phase sensing can be achieved at a laser power as low as 1.18 mW. We further analyze major sources of noise in order to improve the limits of detection. This sensing technique may find a broad range of applications from the real-time selection of biological cell samples to rare cell detection in blood samples for early cancer screening.
We propose a compensation technique based on pulse reference for intensity-modulated optical fiber sensors that can compensate the power fluctuation of the light source, the change of optical components transmission loss, and the coupler splitting ratio. The theoretical principle of this compensation technique is analyzed and a temperature sensor based on fiber coating-covered optical microfiber is carried out to demonstrate the compensation effect. The system noise is measured to be 0.0005 dB with the temperature sensitivity reaching 0.063 dB/°C, and the output drift is 0.006 dB in 2 h at room temperature. The output shows a slight variation (0.0061 dB) when the light source and the common light path suffer a 3 dB attenuation fluctuation.
We report efficient power scaling of the laser output with an adaptive beam profile from an Nd:YAG dual-cavity master oscillator using a three-stage end-pumped Nd:YVO4 amplifier. We succeed in the fast switching of an excited laser mode by modulating an acousto-optic modulator loss in a dual-cavity master oscillator, thereby achieving temporal modulation of the output beam profile. The outputs from the master oscillator are amplified via a three-stage power amplifier yielding 36.6, 40.5, and 45.4 W of the maximum output at 116.8 W of incident pump power for the transverse electromagnetic, Laguerre–Gaussian, and quasi-top-hat beam, respectively. The prospects for further power scaling and applications via the dual-cavity master-oscillator power-amplifier (MOPA) system are considered.
A computer generated holographic stereogram based on the wavefront recording plane (WRP) is presented. A WRP closed to the parallax image plane is introduced to record the complex amplitude in a small region for each point in the parallax image. By using three times of fast Fourier transform (FFT) to execute the Fresnel diffraction calculation between the WRP and the holographic stereogram plane, the object wave contributing to the hologram pattern can be achieved. The computation complexity of the proposed approach is dramatically reduced. The results show that the calculation time can be decreased by more than one order of magnitude.
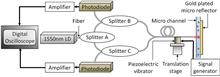
We demonstrate fast time-division color electroholography using a multiple-graphics-processing-unit (GPU) cluster system with a spatial light modulator and a controller to switch the color of the reconstructing light. The controller comprises a universal serial bus module to drive the liquid crystal optical shutters. By using the controller, the computer-generated hologram (CGH) display node of the multiple-GPU cluster system synchronizes the display of the CGH with the color switching of the reconstructing light. Fast time-division color electroholography at 20 fps is realized for a three-dimensional object comprising 21,000 points per color when 13 GPUs are used in a multiple-GPU cluster system.
Single-pixel cameras, which employ either structured illumination or image modulation and compressive sensing algorithms, provide an alternative approach to imaging in scenarios where the use of a detector array is restricted or difficult because of cost or technological constraints. In this work, we present a robust imaging method based on compressive imaging that sets two thresholds to select the measurement data for image reconstruction. The experimental and numerical simulation results show that the proposed double-threshold compressive imaging protocol provides better image quality than previous compressive imaging schemes. Faster imaging speeds can be attained using this scheme because it requires less data storage space and computing time. Thus, this denoising method offers a very effective approach to promote the implementation of compressive imaging in real-time practical applications.
A bimorph deformable mirror (DM) with a large stroke of more than 30 μm using 35 actuators is presented and characterized for an adaptive optics (AO) confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope application. Facilitated with a Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor, the bimorph DM-based AO operates closed-loop AO corrections for human eyes and reduces wavefront aberrations in most eyes to below 0.1 μm rms. Results from living eyes, including one exhibiting ~5D of myopia and ~2D of astigmatism along with notable high-order aberrations, reveal a practical efficient aberration correction and demonstrate a great benefit for retina imaging, including improving resolution, increasing brightness, and enhancing the contrast of images.
A 360° light field 3D display system is presented, which consists of a liquid crystal display, a novel triplet lenses array, and a holographic functional screen (HFS). The mapping relationship among pixels, 3D objects, and viewing positions are investigated. The aberration analysis of the single lens is carried out both in the simulation and the experiment, which shows that it cannot provide an excellent 3D image to the viewers. In order to suppress the aberrations, “the primary aberration theory” and “the damped least-squares method” are used for optical analysis and lens design. A 3D image with aberration correction can be viewed around the proposed display system.
We experimentally demonstrate a Faraday laser at Rb 1529 nm transition by using a performance-improved Rb electrodeless-discharge-lamp-based excited-state Faraday anomalous dispersion optical filter as the frequency-selective element. Neither the electrical locking scheme nor the additional frequency-stabilized pump laser are used. The frequency of the external-cavity diode laser is stabilized to the Rb 1529 nm transition, and the Allan deviation of the Faraday laser is measured by converting the optical intensity into frequency. The Faraday laser can be used as a frequency standard in the telecom C band for further research on metrology, microwave photonics, and optical communication systems.
The pulse characteristics of a laser diode dual-end-pumped electro-optic Q-switched Nd:LuAG ceramic laser at various repetition rates are presented. The largest output pulse energy of 11 mJ is realized at the repetition rate of 100 Hz with pump energy of 84.3 mJ, and the slope efficiency in respect to pump pulse energy is 18.6%. The single pulse peak power reaches up to 1.57 MW. Using Nd:LuAG ceramic as the amplification medium seeded by an Nd:YAG laser of 5.2 mJ, a 10.3 mJ amplified pulse is obtained with pump pulse energy of 42.8 mJ, corresponding to an extraction efficiency of 11.9%.
We experimentally demonstrate the generation of sub-100-fs pulses from a diode-pumped passively mode-locked Yb:Y3ScAl4O12 (Yb:YSAG) ceramic laser. Stable mode-locked pulses as short as 96 fs at the central wavelength of 1052 nm with a repetition rate of ~102 MHz are obtained. The laser has a maximum average output power of 51 mW. To the best of our knowledge, these are so far the shortest pulses and the first demonstration of sub-100-fs pulses obtained from the mode-locked Yb:YSAG ceramic lasers.
Bismuth (Bi)-doped laser glasses and fiber devices have aroused wide attentions due to their unique potential to work in the new spectral range of 1 to 1.8 μm traditional laser ions, such as rare earth, cannot reach. Current Bi-doped silica glass fibers have to be made by modified chemical vapor deposition at a temperature higher than 2000°C. This unavoidably leads to the tremendous loss of Bi by evaporation, since the temperature is several hundred degrees Celsius higher than the Bi boiling temperature, and, therefore, trace Bi (~50 ppm) resides within the final product of silica fiber. So, the gain of such fiber is usually extremely low. One of the solutions is to make the fibers at a temperature much lower than the boiling temperature of Bi. The challenge for this is to find a lower melting point glass, which can stabilize Bi in the near infrared emission center and, meanwhile, does not lose glass transparency during fiber fabrication. None of previously reported Bi-doped multicomponent glasses can meet the prerequisite. Here, we, after hundreds of trials on optimization over glass components, activator content, melting temperature, etc., find a novel Bi-doped gallogermanate glass, which shows good tolerance to thermal impact and can accommodate a higher content of Bi. Consequently, we successfully manufacture the germanate fiber by a rod-in-tube technique at 850°C. The fiber exhibits similar luminescence to the bulk glass, and it shows saturated absorption at 808 nm rather than 980 nm as the incident power becomes higher than 4 W. Amplified spontaneous emissions are observed upon the pumps of either 980 or 1064 nm from germanate fiber.
A series of RE3+ (RE=Eu/Tb/Ce)-activated Sr4La(PO4)3O (SLPO) phosphors are synthesized with a high-temperature solid-state reaction method. The photoluminescence properties, thermal stability, morphology, and CIE values of the SLPO:Eu3+/Tb3+/Ce3+ phosphors are investigated. Under 394 nm excitation, the SLPO:Eu3+ exhibits red emission, and the SLPO:Tb3+ presents a green emission upon 379 nm excitation, while Ce3+-doped SLPO has a broad emission band ranging from 370 to 650 nm under 337 nm excitation. The investigation results indicate that the SLPO:Eu3+/Tb3+/Ce3+ phosphors can be effectively excited by near-ultraviolet light and may have the potential to serve as red-, green-, and blue-emitting phosphors for applications in white light-emitting diodes.
We observe conical sum-frequency generation in a bulk anomalous-like dispersion medium, which is attributed to complete phase-matching of one fundamental wave and the scattering wave of the other fundamental wave. In addition, efficient sum-frequency output is achieved making use of total internal reflection with conversion efficiency of 7.9% by only one reflection. The experiment proposes a new phase-matching mode under an anomalous-like dispersion condition, which suggests potential applications in efficient frequency conversion.
The authors would like to apologize for an error in our paper in Chin. Opt. Lett. 15(10), 100604 (2017).
Generation of a cavity-enhanced nondegenerate narrow-band photon pair source is a potential way to realize a perfect photonic quantum interface for a hybrid quantum network. However, to ensure the high quality of the photon source, the pump laser for the narrow-band photon source should be generated in a special way. Here, we experimentally generate the blue 453 nm laser with a sum frequency generation process in a periodically poled lithium niobate waveguide. A 13 mW laser at 453 nm can be achieved with a low-power 880 nm laser and 935 nm laser input, and the internal conversion efficiency is 21.6% after calculation. The frequency of a 453 nm laser is stabilized by locking two pump lasers on one ultrastable optical cavity. The single pass process without employing cavity enhancement can ensure a good robustness of the whole system.
To simultaneously obtain high-resolution multi-wavelength (from visible to near infrared) tomographic images of the solar atmosphere, a high-performance multi-wavelength optical filter has to be used in solar imaging telescopes. In this Letter, the fabrication of the multi-wavelength filter for solar tomographic imaging is described in detail. For this filter, Ta2O5 and SiO2 are used as high- and low-index materials, respectively, and the multilayer structure is optimized by commercial Optilayer software at a 7.5° angle of incidence. Experimentally, this multi-wavelength optical filter is prepared by a plasma ion-assisted deposition technique with optimized deposition parameters. High transmittance at 393.3, 396.8, 430.5, 525, 532.4, 656.8, 705.8, 854.2, 1083, and 1565.3 nm, as well as high reflectance at 500 and 589 nm are achieved. Excellent environmental durability, demonstrated via temperature and humidity tests, is also established.