View fulltext
View fulltext
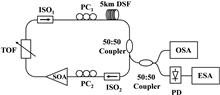
A tunable single-longitudinal-mode (SLM) semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA)-based fiber laser based on a dispersion-shifted fiber (DSF) is proposed and successfully demonstrated. SLM operation is obtained due to the spectral narrowing effect resulting from inverse four-wave mixing in a DSF. A tunable optical filter performs wavelength selection function. By inserting a length of DSF in the laser cavity, SLM lasing can possibly be obtained when laser oscillation is stably established after traveling through the DSF many roundtrips. Stable tunable SLM oscillation with a signal-to-noise ratio as high as 65 dB over a wavelength range of about 35 nm is achieved experimentally, and each spectral linewidth is less than 6.5 kHz.
We demonstrate a femtosecond mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) using a nickel oxide (NiO) as a saturable absorber (SA). NiO nanoparticles are hosted into polyethylene oxide film and attached to fiber ferrule in the laser cavity. The NiO-SA shows a 39% modulation depth with a 0.04 MW/cm2 saturation intensity. Our ring laser cavity based on erbium-doped active fiber with managed intracavity dispersion has the ability to generate ultrashort pulses with a full width at half-maximum (FWHM) of around 2.85 nm centered at 1561.8 nm. The pulses repeat at a frequency of 0.96 MHz and duration of 950 fs.
Photonic generation of radio-frequency (RF) arbitrary microwave waveform with ultra-wide frequency tunable range based on a dispersion compensated optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. Dispersion compensation scheme and specially designed fiber Bragg grating (FBG)-based Fabry–Perot (F-P) filters are employed in the OEO loop to realize a frequency tunable range of 3.5–45.4 GHz. An optimization process provided by the combination of an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) and FBG is employed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of final RF signals. The generation of linear-frequency and phase-coded microwave waveforms, with a tunable carrier frequency ranging from 4 to 45 GHz and tuned chirping bandwidths or code rates, is experimentally demonstrated.
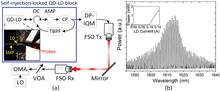
We demonstrate an indoor 5 m free-space optical wireless coherent communication in mid L-band (1606.7 nm) by employing a tunable self-seeded InAs/InGaAlAs/InP quantum-dash (Qdash) laser as a subcarrier generator for 128 Gb/s dual-polarization quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK) modulation signal. The bare Qdash laser diode displays ~6 nm self-locked Fabry–Perot mode tunability with ~30 dB side mode suppression ratio (SMSR) and ~10 dBm mode power across the tuning range, thus encompassing ~10 modes with an achievable capacity of 1.28 Tb/s (10×128 Gb/s) and potentially qualifying the source requirements for future access networks.
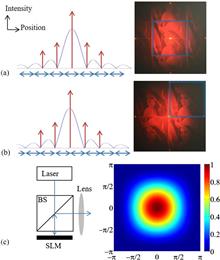
A simple and effective approach is proposed to minimize the effect of unmodulated light and uneven intensity caused by the pixelated structure of the spatial light modulator in a holographic display. A more uniform image is produced by purposely shifting the holographic images of multiple reconstructed lights with different incident angles from the zero-diffraction-order and overlapping those selected different orders. The simulation and optical experimental results show that the influence of the zero-diffraction-order can be reduced, while keeping the good uniformity of the target images by this new approach.
This Letter presents a simple and effective method to improve the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of compressing imaging. The main principles of the proposed method are the correlation of the image signals and the randomness of the noise. Multiple low SNR images are reconstructed firstly by the compressed sensing reconstruction algorithm, and then two-dimensional time delay integration technology is adopted to improve the SNR. Results show that the proposed method can improve the SNR performance efficiently and it is easy to apply the algorithm to the real project.
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) has the unique capability of visualizing optical absorption inside several centimeters-deep biological tissue with a high spatial resolution. However, single linear-array transducer-based PAT suffers from the limited-view challenge, and thus the synthetic aperture configuration is designed that still requires multichannel data acquisition hardware. Herein, a feasible synthetic aperture PAT based on compressed sensing reconstruction is proposed. Both the simulation and experimental results tested the theoretical model and validated that this approach can improve the image resolution and address the limited-view problem while preserving the target information with a fewer number of measurements.
A signal processing method of realizing a large-range displacement measurement in a sinusoidal phase-modulating laser diode interferometer is proposed. The method of obtaining the dynamic value of the effective sinusoidal phase-modulating depth is detailed, and the residual amplitude modulation is also taken into account. Numerical simulations and experiments are carried out to compare this method with the traditional one. We prove that, with this method, the sinusoidal phase-modulating laser diode interferometer can realize a centimeter-level displacement measurement range with high precision, which is much better than the traditional method.
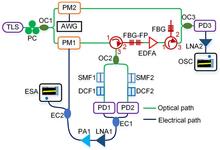
We demonstrate a new synchronization method for the White Rabbit system. Signals are transmitted in a single mode fiber in both directions with the same light wavelength. Without the complex calibration process of the fiber asymmetry parameter, the new method reduces the effect of chromatic dispersion and improves the synchronization accuracy. The experiment achieves timing synchronization accuracy below 200 ps over 50 km fiber constructed by different companies’ fiber spools. The proposed method would make White Rabbit technology immune to the chromatic dispersion of fiber links and can be applied to long distance synchronization.
A grating is an important element of a phase-shifting point diffraction interferometer, and the grating constant and duty cycle have a great impact on the interferometer, so the design of a grating becomes significant. In order to measure the projection objective with a numerical aperture of 0.2, we present a joint optimization method of a pinhole and grating based on scalar diffraction and the finite difference time domain method. The grating constant and the film thickness are selected, and the duty cycle of the grating is optimized. The results show that in the grating processing the material chromium is adopted, the thickness is 200 nm, and the grating constant is 15 μm. When the duty cycle is 55%, the interference fringe contrast is the greatest. The feasibility of the design result is further verified by experiment.
Switchable single and double Brillouin multiwavelength and pulsed laser is successfully demonstrated. Brillouin spacing can be switched from single (0.08 nm) to double spacing (0.16 nm) or vice versa by swapping the ports of the coupler in the proposed configuration. The proposed configuration can also be used to produce pulsed laser by inserting a home-made carbon nanotubes saturable absorber into the laser cavity. The proposed system is very versatile and flexible as it can be used as a multiwavelength laser or pulsed laser to cater for different types of applications.
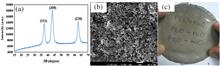
Graphene oxide carboxylic acid (COOH), a novel two-dimensional (2D) layered material with its unique optical and electronic properties, is discovered to exhibit the saturation of optical absorption under laser illumination. Applying the liquid-phase exfoliation method, we prepare graphene oxide-COOH dispersions with deionized water and fabricate graphene oxide-COOH polyvinyl alcohol polymer composite film. We further obtain stable Q-switching pulse and mode-locked laser operation with a 22.7 MHz repetition rate and a 1.5 ps pulse duration by incorporating the graphene oxide-COOH-based saturable absorbers into the all-fiber erbium-doped fiber laser cavity. The experimental results show that the proposed graphene oxide-COOH material can act as an effective absorber for pulsed fiber lasers, which demonstrate potential applications in the area of ultrafast optics.
A polarization-independent nonmechanical laser beam steering scheme is proposed to realize continuous two-dimensional (2D) scanning with high efficiency, where the core components are two polarization-dependent devices, which are called liquid crystal optical phased arrays (LC-OPAs). These two one-dimensional (1D) devices are orthogonally cascaded to work on the state of azimuthal and elevation steering, respectively. Properties of polarization independence as well as 2D beam steering are mathematically and experimentally verified with a good agreement. Based on the experimental setup, linearly polarized beams with different polarization angles are steered with high accuracy. The measured angular deviations are less than 5 μrad, which is on the same order of the accuracy of the measurement system. This polarization-independent 2D laser beam steering scheme has potential application for nonmechanical laser communication, lidar, and other LC-based systems.
We report on a quantum dot quantum cascade detector (QD-QCD), whose structure is derived from a QD cascade laser. In this structure, more ordered InAs QD layers formed in the Stranski–Krastanow growth mode on a thin GaAs buffer layer are incorporated into the active region. This QD-QCD can operate up to room temperature with a peak detection wavelength of 5.8 μm. A responsivity of 3.1 mA/W at 160 K and a detectivity of 3.6 × 108 Jones at 77 K are obtained. The initial performance of the detector is promising, and, by further optimizing the growth of InAs QDs, integrated QD-quantum cascade laser/QCD applications are expected.
This Letter gives the general construction of an enhanced self-heterodyne synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) system, and proposes the principle of image processing. A point target is reconstructed in the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL as well as in down-looking SAIL experiments, and the achieved imaging resolution of the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL is analyzed. The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the point target final image in the enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL is higher than that in the down-looking SAIL. The enhanced self-heterodyne SAIL can improve the SNR of the target image in far-distance imaging, with practicality.
This Letter proposes a coordinate difference homogenization matching method to solve motion influence in three-dimensional (3D) range-intensity correlation laser imaging. Firstly, features and feature pairs of gate images are obtained by speeded-up robust figures and bi-directional feature matching methods. The original mean value of the feature-pair coordinate differences is calculated. Comparing the coordinate differences with the original mean value, the wrong feature pairs are removed, and then an optimized mean value is updated. The final feature-pair coordinates are re-registered based on the updated mean value. Thus, an accurate transformation is established to rectify motion gate images for 3D reconstruction. In the experiment, a 3D image of a tower at 780 m is successfully captured by our laser gated imaging system on a pan–tilt device.
Aiming to overcome the low converging rate and susceptibility to the environment in focusing the coherent light through the turbid medium, four-element division algorithm (FEDA) optimization is proposed. Full levels of comparisons with the currently employed element-based algorithms, stepwise sequential algorithm (SSA), and continuous sequential algorithm (CSA) show that FEDA only takes one third of the measurement time to find the optimized solution, which means that FEDA is promising in practical applications, such as for deep tissue imaging.