View fulltext
View fulltext
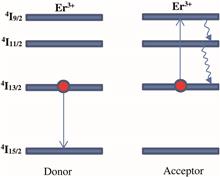
To design a compact erbium-doped fiber laser, a high-concentration erbium-doped fiber (EDF) is needed. However, increasing the erbium ion (Er3+) concentration can reduce the EDF performance via the Er3+-Er3+ interaction. In this Letter, we investigate the Er3+-Er3+ interaction effect by designing a tunable erbium-doped fiber-ring laser (EDFRL). This is the first time (to the best of our knowledge) that someone has considered different numbers of ions per cluster and simulated the EDFRL output power degradation due to ion–ion interaction. If the number of ions in the cluster is increased, the lasing output power will decrease accordingly. The most dominant effect is seen in the 1530 nm wavelength region, where the EDF shows a higher signal absorption compared to the other wavelength region. Moreover, a comparison has been done for lasing performance analysis with different dopant ion concentrations. The comparison results show that a higher dopant concentration is advantageous for longer-wavelength lasing.
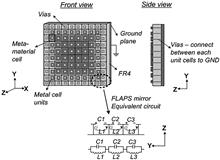
Flat mirrors, also known as flat parabolic surfaces, for millimeter-wave and terahertz imaging systems are demonstrated. This flat mirror is based on the metasurface in which an inexpensive printed circuit board technology is used to realize copper patterns printed on an FR4 substrate. Compared to the conventional reflector antennas used today in diverse applications (for homeland security, medical systems, communication, etc.), the suggested mirror has major advantages in process simplicity, mechanical flexibility, frequency alignment, weight, and cost. The theoretical background, simulation results, experimental results, and proof of concept are given in this Letter.
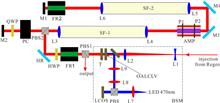
We present a lamp-pumped Nd: phosphate glass laser amplifier delivering up to 1 J of pulse energy at 1053 nm with a repetition rate of 1 Hz and an injected pulse energy of 2.5 mJ. The amplifier system employs a beam-shaping module and a four-pass, lamp-pumped amplifier. The thermally induced wavefront distortion is mitigated and a uniform gain distribution is obtained by a four-lamp-pumped laser head in the amplifier. Thus, an excellent beam quality is obtained.
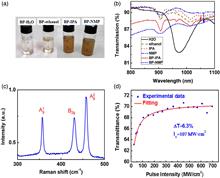
A novel black phosphorus (BP) solution saturable absorber (SA) is fabricated by the liquid-phase-exfoliated method and successfully used for passively Q-switched (QS) Nd:YVO4 laser. Compared with a traditional solid SA, a BP solution SA possesses more excellent optical transparency and higher damage resistance. The shortest pulse duration and highest average output power are measured to be 119 ns and 1.23 W, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, both of them are the best results among QS solid-state lasers with BP-based absorbers so far. The repetition rate is in the range of 533.2 to 722 kHz. The results indicate the potential application of the BP solution SA into high-power solid-state pulse lasers.
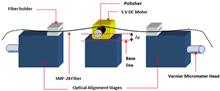
A dual-wavelength fiber laser operating at the 1550 nm region using a side-polished arc-shaped fiber with deposited ZnO nanoparticles is proposed and demonstrated. The arc-polished fiber is fabricated by using a simple but novel approach in which a silicon carbide paper polishes one side of a conventional single-mode fiber. An arc-polished fiber with a length of 2.25 mm and an insertion loss of 0.95 dB is obtained and deposited with ZnO nanoparticles by the drop-cast method. A stable dual-wavelength output is obtained at 1562.5 and 1563.4 nm at peak powers of 9.3 and 10.1 dBm, respectively, as well as a signal-to-noise ratio of 28.4 dB and a channel spacing of 0.9 nm. Both lasing wavelengths also have narrow linewidths of between 0.045 and 0.049 nm and show little to no wavelength or power fluctuations over continued testing.
We demonstrate the electrical beat note analysis and radio frequency (RF) injection locking of a continuous wave (cw) terahertz quantum cascade laser (QCL) emitting around 3 THz (~100 μm). In free running the beat note frequency of the QCL shows a shift of ~180 MHz with increasing drive current. The beat note, modulation response, injection pulling, and terahertz emission spectral characteristics in the different current regimes I, II, and III are investigated. The results show that in the current regime I close to the laser threshold we obtain a narrower beat note and flat response to the RF modulation at the cavity round trip frequency. The pulling effect and spectral modulation measurements verify that in the current regime I the RF injection locking is more efficient and a robust tool to modulate the mode number and mode frequency of terahertz QCLs.
We provide the first demonstration of pure red emission in the visible light region via three-photon excitation in monodisperse Na3ZrF7:Er nanoparticles (NPs) by using a laser operating in the telecommunication band. NPs of ~22 nm in diameter are synthesized at 260°C by the thermal decomposition method. The experimental results reveal that the Na3ZrF7:Er NPs exhibit pure red emission in the visible region under 1480 nm laser excitation, and the emission intensity is significantly influenced by the Er3+ ion concentration. The decay times of the S3/24→F415/2 and F9/24→F415/2 transitions of the Er3+ ions at 540 and 655 nm, respectively, are reduced by increasing the Er3+ ion concentration in the <mml:math display="inline" id="m9" xmlns:mml="http://ww
Microwave photonic components and subsystems can replace or complement their electronic counterparts with a net gain in functionality, bandwidth, size, mass, complexity, and cost, facilitating the innovative implementation of radio frequency (RF) systems due to broad bandwidth, low loss, light weight, flat frequency response, favorable isolation, and immunity to electromagnetic interference (EMI) provided by photonic technologies. Much attention has been recently paid to this area, which results in impressive progresses. Hence, we designed a focus issue intended to introduce the recent advancements in this field, especially the works by some distinguished research groups.
The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres with four different particle diameters of 10, 50, 100, and 200 nm suspended in water are investigated theoretical and experimentally in the spectral range of the entire visible range and part of the near-infrared region. The scattering properties of ZnO nanospheres suspended in water are described by employing three main parameters: the angular distribution of the scattering intensity I, the scattering extinction coefficient αscat, and the scattering cross section σscat. The results indicate that (i) at a certain wavelength, the angular distribution of the scattering intensity appears as an obviously forward-propagating feature, and the forward-scattering intensity is dominant gradually when the particle diameter increases from 10 to 200 nm, and (ii) the scattering extinction coefficient and cross section can be determined by using the measured transmittance changes of a pure water sample and a given ZnO sample; they all are shown to be dependent on the particle size and incident wavelength. The experimental results of four different scattering samples agree well with the theoretical predictions within the given wavelength range.