View fulltext
View fulltext
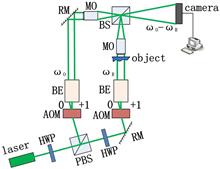
Digital holographic microscopy using multiframe full-field heterodyne technology is discussed in which two acousto-optic modulators are applied to generate low-frequency heterodyne interference and a high-speed camera is applied to acquire multiframe full-field holograms. We use a temporal frequency spectrum analysis algorithm to extract the object’s information. The twin-image problem can be solved and the random noise can be significantly suppressed. The relationship between the frame number and the reconstruction accuracy is discussed. The typical objects of microlenses and biology cells are reconstructed well with 100-frame holograms for illustration.
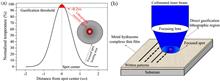
Metal hydrazone complex thin films are used as laser patterning materials, and the patterns with a minimum resolution of about 78 nm are successfully obtained by the laser writing setup (λ=405 nm, NA=0.9). The minimum resolution is only about 1/8 of the writing spot size. In the formation of patterns, there is only a single step for forming patterns by the laser heating-induced clear thermal gasification threshold effect without any other development processes such as wet etching. This work provides an effective method for directly achieving nanoscale-resolved pattern structures with diode-based maskless laser writing lithography at visible light wavelengths.
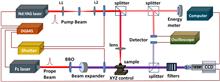
We investigate the dynamic processes of the Nd:YAG pulse laser ablation of fused silica by ultrafast time-resolved optical diagnosis with a nanosecond time resolution. The evolution process of plasma expansion in air and shock waves propagation in the bulk are both obtained with spatial and temporal resolutions. Laser-induced damage in the bulk of fused silica with filaments and shock waves are observed. Thermoelastic wave, mechanical wave, and shock wave dependence on the laser fluence and intensity of the plasma are analyzed. The shock pressure P and temperature T calculated through the measured shock velocity D and the Hugoniot data of fused silica are measured.
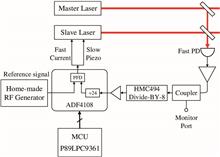
We present a compact, low-noise, and inexpensive optical phase-lock loop (OPLL) system to synchronize the frequency and the phase between two external cavity diode lasers. Based on a direct digital synthesizer technique, a programmable radio-frequency generator is implemented as the reference signal source. The OPLL has a narrow beat note linewidth below 1 Hz and a residual mean-square phase error of 0.06 rad2 in a 10 MHz integration bandwidth. The experimental test results prove the competent performance of the system, which is promising as a low-budget choice in atomic physics applications.
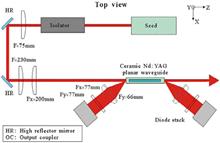
We present a diode-pumped high-energy ceramic Nd:YAG planar waveguide that is demonstrated as a record in output energy for the ceramic planar waveguide fabricated by nonaqueous tape casting and solid-state reactive sintering. Under a repetition rate of 100 Hz and a pulse width of 250 μs, a maximum output pulse energy of 327 mJ is obtained with a beam quality factor of =2.6×7.0. The corresponding peak power is 1308 W. The extraction efficiency of the system is about 56%.
In this work, we report a broadband terahertz wave modulator based on a top-gate graphene field effect transistor with polyimide as the gate dielectric on a PET substrate. The transmission of the terahertz wave is modulated by controlling the Fermi level of graphene via the polyimide as the top-gate dielectric material instead of the traditional dielectric materials. It is found that the terahertz modulator can achieve a modulation depth of ~20.9% with a small operating gate voltage of 3.5 V and a low insertion loss of 2.1 dB.
The tunable multiple plasmon-induced transparency (PIT) effect is investigated numerically in a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) waveguide with three side-coupled rectangular resonators. The system exhibits dual-mode PIT effects in the visible and near-infrared regions. By adjusting the geometrical parameters of the structure, we can manipulate not only each single PIT window, but also the double PIT windows simultaneously. Our structures may have potential applications for optical communication, integrated optics, and optical information processing. The finite element method (FEM) illustrates our theoretical design.
A fiber in-line Fabry–Pérot interferometer is presented. The sensing head consists of a micro ellipsoidal air cavity and a small section of solid-core photonic crystal fiber. The reflective index (RI) and temperature can be interrogated simultaneously through a fast Fourier transform and by tracing the dip wavelength shift of the reflective spectrum. Experimental results show that the RI amplitude and wavelength sensitivities are 5.30/RIU and 8.46×10 1 nm/RIU in the range from 1.34 to 1.43, and the temperature amplitude and wavelength sensitivities are 6.8×10 4/°C and 2.48×10 3 nm/°C in the range from 15°C to 75°C, respectively. Easy fabrication, a simple system, and simultaneous measurement make it appropriate for dual-parameter sensing application.
A dual-frequency laser Doppler velocimeter implemented by a dual-polarization fiber grating laser is proposed, with the two laser frequencies produced by the two orthogonally polarized laser outputs of the fiber grating laser. The reflected laser outputs from a moving target experience the Doppler frequency shift, which is shown to be linearly related to the velocity and the beat note frequency difference between the laser outputs and the reflected light. With a digital frequency demodulation scheme, a high sensitivity of 0.64 MHz/(m/s) and a velocity resolution of less than 0.5% of the velocity for velocity measurement are demonstrated, which shows that the proposed laser Doppler velocimeter is capable of measurement of wide range of velocity.
We experimentally study the combined nonlinear effects, including four-wave mixing, stimulated Raman scattering, soliton dynamics, and cross-phase modulation by coupling femtosecond pulses around 850 nm into the normal dispersion region near the zero-dispersion wavelength in the fundamental mode of a homemade silica photonic crystal fiber. The nonlinear optical dynamics at different stages are demonstrated, and the discrete ultraviolet (UV) to visible wavelengths widely separated from the pump wave are generated by the interaction of several nonlinear effects involved. The UV to visible wavelengths can be used as short pulse sources for multiphoton ionization, fluorescence spectroscopy, and biochemical imaging.
An evanescent field optical fiber sensor based on a short section of polarization maintaining fiber spliced with a tapered single mode fiber is proposed and experimentally investigated. We mainly focus on the refractive index (RI) and temperature sensing characteristics of this compact device. The transmission spectrum of the resonance wavelength, induced by the interference between the excited low order cladding modes and core modes, shows the quadratic function relationships with RI and linear relationships with temperature. Thus, the proposal of this simple-to-fabricate, compact, and low cost sensor shows its possible potential in the sensitive detection field.
In this Letter, an efficient bidirectional differential phase-shift keying (DPSK)—DPSK transmission for a ultra-dense wavelength division-multiplexed passive optical network is proposed. A single distributed feedback laser at the optical network unit (ONU) is used both as the local laser for downlink coherent detection and the optical carrier for uplink. Phase-shift keying is generated using a low-cost reflective semiconductor optical amplifier (RSOA) at the ONU. The RSOA chip has the bandwidth of 4.7 GHz at the maximum input power and bias current. For uplink transmission, the sensitivity of the RSOA chip reaches 48.2 dBm at the level of bit error rate=10 3 for back-to-back, and the penalty for 50 km transmission is less than 1 dB when using polarization diversity.
We report on temperature compensation for beat-frequency-encoded dual-polarization fiber laser sensors based on a cleave-rotate-splice method. By cleaving the laser cavity into two segments with comparable lengths, aligning them with a rotated angle of 90°, and then fusion splicing the two halves, the temperature sensitivity in terms of beat-frequency variation can be greatly reduced from 1.99 to 0.30 MHz/°C (or by 84.9%). In contrast, the sensitivity to point loaded mass hardly changes. We also find that the beat-frequency fluctuation decreases from ±30 to ±25 kHz as a result of the temperature compensation.
This Letter presents a multi-hop relay visible light communication (VLC) system for maritime applications. Maritime VLC systems suffer from limited coverage distance due inherently to the usage of light-emitting diodes and photodetectors. The proposed system employs a multiple of decode-and-forward relays to extend coverage distance in maritime environments. The multi-hop relay based maritime VLC is analyzed under a maritime channel modeled by the JONSWAP spectrum and gamma–gamma distribution. It is found that the use of relays in maritime environments can extend the coverage distance significantly and also improve the performance. In addition, the performance of the system is analyzed using various combining techniques at the receiver to enhance the performance. The maximal ratio combining technique is found to provide superior link quality in maritime environments.
We experimentally demonstrate a direct-detection orthogonal-frequency-division-multiplexing quadrature-phase-shift-keying (OFDM-QPSK) system that is capable of delivering a 32 Gbaud OFDM-QPSK signal over 7 km single-mode fiber-28 (SMF-28). Intra-symbol frequency-domain averaging (ISFA) channel response estimation is applied to suppress in-band noise, while discrete Fourier transform-spread (DFT-spread) is used to reduce the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) of the transmitted OFDM signal. With the aid of ISFA-based channel estimation and PAPR reduction enabled by DFT-spread, the bit-error ratio of the system after 7 km SMF-28 transmission can be improved from 2×10 3 to error-free when the received optical power is 8.5 dBm.
Metasurface is a new kind of 2D metamaterial that is able to manage a variety of light beam modulations through steering the phase of the scattering waves. In this work, we utilize the metasurface to manipulate the light beam in the mid-infrared regime. By using the metallic rod and the plate structure, the metasurface presents a high polarization conversion efficiency and a wide working bandwidth. With specially rotated metallic rods, the metasurface can realize various light beam manipulations, such as negative reflection, beam collimation, and focusing. All of these results show that such a metasurface will have potential applications in future mid-infrared optics.
This Letter is concerned with the influence of polarization on the damage performance of type I doubler potassium dihydrogen phosphate crystals grown by the conventional growth method under 532 nm pulse irradiation. Pinpoint density (ppd) and the size distribution of pinpoints are extracted through light scattering pictures captured by microscope. The results show that the ppd of polarization that parallels the extraordinary axis is around 1.5× less than that of polarization that parallels the ordinary axis under the same fluence, although polarization has no influence on size distribution of pinpoints. We also find that the size distribution is independent of fluence, although the number of pinpoints grows with fluence.
Er ions are implanted into the GaN thick films grown by hydride vapor phase epitaxy. The implantation energy is 200 keV and the implantation doses are 1×1013, 1×1014, 1×1015, and 5×1015 atom/cm2, respectively. The effects of the implantation dose and annealing temperature on the GaN band-edge luminescence are investigated. The cathodoluminescence spectra from 82 to 323 K are measured for 1×1015 atom/cm2-implanted GaN annealed at 1100°C. Luminescence peaks at 356, 362, 376, 390, and 414 nm are observed on the 82 K cathodoluminescence spectrum. When the temperature is increased to 150 K, the intensities of the 356 and 414 nm peaks are nearly unchanged and the 362, 376, and 390 nm peaks disappear. The intensity ratio of 538 nm (H11/22→I15/24) and 559 nm (S3/24→I15/24) is increased with the increase in temperature. We try to shed light on the above interesting phen
Silicon-rich oxide films with controllable optical constants and properties are deposited by the reactive magnetron sputtering method on a Si target. The O/Si atomic ratio x of SiOx is tuned from 0.12 to 1.84 by adjusting the oxygen flow rate, which is found to be a more effective way to obtain SiOx films compared with changing the oxygen content [O2/(Ar+O2) ratio]. The optical properties of SiOx films can be tuned from semiconductor to dielectric as a function of ratio x. The structures and components are also investigated by an x ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of the Si 2p core levels, the results of which exhibit that the structures of SiOx can be thoroughly described by the random bonding model.
A method of multi-beam femtosecond laser irradiation combined with modified HF-HNO3-CH3COOH etching is used for the parallel fabrication of all-silicon plano-concave microlens arrays (MLAs). The laser beam is split by a diffractive optical element and focused by a lens to drill microholes parallely on silicon. An HF-HNO3-H2SO4-CH3COOH solution is used to expand and polish laser-ablated microholes to form microlenses. Compared with the HF-HNO3-CH3COOH solution, the solution with H2SO4 can effectively reduce the etched surface roughness. The morphologies of MLAs at different laser powers and pulse numbers are observed. The image array formed by the silicon microlenses is also demonstrated.
A light purplish red sapphire is heat treated in an airtight crucible. The sample changes little in color after receiving heat treatment at 1100°C, but turns to light blue and blue after being treated at 1200°C and 1300°C, respectively. Before heating, the UV-VIS absorption spectra of the sample are dominated by the 551 nm broad absorption band contributed by the d-electron transition A24→T24 of Cr3+. After heating, the UV-VIS absorption spectra are dominated by the 563 nm broad absorption band contributed by the intervalence charge transfer of Fe2+ Ti4+. The x ray photoelectron spectroscopy test reveals that the Fe2+ and Ti4+ ion contents increase with increasing temperature. The sapphire changing from light purplish red to blue in the heating process is owing to the fact that the Fe2+ and Ti4+ contents grow and the intervalence charge transfer of Fe2+ Ti4+ selectively absorbs UV-VIS light.