View fulltext
View fulltext
We theoretically investigate multiple electron rescatterings in high-order harmonic generation with a wide range of driving laser wavelengths. In order to obtain a clear and intuitive insight, the time-frequency analysis of the dipole acceleration calculated by the numerical solution of the time-dependent Schr dinger equation is performed and compared with the classical electron trajectory calculation. The result shows that in the mid-infrared regime, the high-order electron trajectory associated with multiple rescatterings plays a more important role than the usually referred-to “long and “short” electron trajectories. To provide quantitative evidence, the strong-field approximation is used to calculate the yield ratio of the high-order harmonic generation from the first rescattering and the multiple rescatterings.
We propose a novel small-angle measuring optical method based on the astigmatic effect of two orthogonally placed cylindrical lenses. According to the one-to-one correspondence between the laser spot shape and the angle, the angle is determined. We theoretically analyze the measuring range and demonstrate that a longer distance between the rotating axis and the optical axis leads to a smaller measuring range, but better sensitivity. Also, an associated experimental system is established and a measuring range of 0.94 mrad (cubic fit r=0.9993) as well as a good linear range of 0.37 mrad (linear fit r=0.9994) with a resolution of 8 μrad is achieved.
Two different methods from graphic processing unit (GPU) and central processing unit (CPU) are proposed to suitably optimize look-up table algorithms of computer generated holography (CGH). The numerical simulations and experimental results show that we can reconstruct a good quality object. The computation of CGH for a three-dimensional (3D) dynamic holographic display can also be sped up by programming with our proposed method. It can optimize both file loading and the inline calculation process. The phase-only CGH with gigabyte data for reconstructing 10 MB object samplings is generated. In addition, the proposed method effectively reduced time costs of loading and writing offline tables on a CPU. It is believed the proposed method can provide high speed and huge data CGH for 3D dynamic holographic displays in the near future.
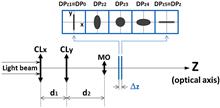
A method to three-dimensional position moving particles with one lens and two cameras is proposed. Two particle images with different degrees of defocusing are adopted to solve the ambiguous problem of particle positions. A single-lens dual-camera system is developed to simultaneously capture these two images for the moving particles. The measurement principles and theoretical analysis are introduced first, and then simulated investigations and experimental research are discussed. The measurement errors in the simulations and experiments are less than 1% and 4%, respectively, in 20 times the depth of field of the system, which validates the feasibility of this method.
We report on the experimental observation of the airflow motion induced by an 800 nm, 1 kHz femtosecond filament in a cloud chamber filled with air and helium. It is found that vortex pairs with opposite rotation directions always form both below and above the filaments. We do not observe that the vortices clearly formed above the filament in air just because of the formation of smaller particles with weaker Mie scattering. Simulations of the airflow motion in helium are conducted by using the laser filament as a heat source, and the simulated pattern of vortices and airflow velocity agree well with the experimental results.
Hybrid octagonal-ring microlasers are investigated for realizing a stable output from a silicon waveguide based on a two-dimensional simulation. The inner radius of the ring is optimized to achieve single-mode and low-threshold operation. Using the divinylsiloxane-benzocyclobutene (DVS-BCB) bonding technique, a hybrid AlGaInAs/Si octagonal-ring microlaser vertically coupled to a silicon waveguide is fabricated with a side length of 21.6 μm and an inner radius of 15 μm. A single transverse-mode operation is achieved with a threshold current density of 0.8 kA/cm2 and a side-mode suppression ratio above 30 dB, and a stable output from the lower silicon waveguide is obtained.
The stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) threshold affected by repetition rate and pulse duration in a single-frequency nanosecond pulsed fiber amplifier is studied. The experimental results demonstrate that the SBS threshold can be improved either by reducing the repetition rate or by narrowing the pulse duration; however, the average power may be limited in some cases. Otherwise, two evaluation methods for the SBS threshold in the fiber amplifier are compared and discussed, aiming to obtain a more accurate description for the SBS threshold in our single-frequency amplifier system.
Diffractive optics is an important technique for beam shaping with high light efficiency and strong diffraction pattern flexibility. Since the diffraction angle is limited by the unit size of the diffractive optical element (DOE), the size of the required diffraction pattern is always rather small. In this Letter, refractive/diffractive hybrid optical elements (RDHOEs) consisting of a DOE and a lens are used to realize beam shaping for a large diffraction pattern. The lens, as the component of the RDHOEs, can not only be concave but also convex, and the double sampling Fresnel diffraction algorithm is developed for the design of these two types of RDHOEs. The simulation and experimental results provide solid evidence to demonstrate the proposed method with the pure phase spatial light modulator.
An improved model-based wavefront sensorless adaptive optics algorithm is proposed for laser beam cleanup. Deformable mirror (DM) eigenmodes are used to replace traditional Lukosz modes in order to avoid DM fitting errors. The traditional method is based on a sophisticated calibration process and solving linear equations. In our method, coefficients of DM eigenmodes are estimated by adding bidirectional modal biases into the system and then solving parabolic equations. The calibration process is omitted in our method, which makes it more feasible. From simulation and experimental results, the corrective accuracy of the improved method is higher than the traditional one.
In this Letter, we demonstrate that by adjusting the thickness of the buffer layer, the optical responses of a guided-mode resonance filter (GMRF) can be improved for sensor applications. The GMRF is fabricated using a replica molding with a plastic substrate and a UV-curable polymer. SiO2 buffer layers of different thicknesses are deposited before the waveguide-layer deposition. The sensitivity of the GMRFs decreases slightly with increasing SiO2 layer thickness. By contrast, the full width at half-maximum reduces substantially with increasing SiO2 layer thickness, resulting in the improvement of the overall figure of merit.
A model for the temperature sensitivity of radiation-induced attenuation (RIA) is investigated. The RIA spectra in a germanium (Ge) and phosphorous (P) co-doped fiber ranging from 825 to 1600 nm at different temperatures are measured and decomposed according to the configurational coordinate model. It is found that there is a linear relationship between the parameters of the color center absorption band and temperature. The model is verified at 850, 1310, and 1550 nm by both simulation and experiment. This work will be useful to research on the applications of optical fiber sensors in a complicated space environment.
This Letter demonstrates the application of dual-output modulation in a photonic analog-to-digital converter (PADC) with a high sampling rate and resolution. The PADC is time-wavelength interleaved and based on an actively mode-locked laser. According to theoretical analysis, the dual-output PADC system shows a better linearity for achieving a higher dynamic range. In the experiment, third-order distortion is significantly suppressed by ~40 dB when the dual-output modulator is used and the effective number of bits of the PADC has reached 9.0 bits below 0.2 GHz and 6.4 bits at 6.1 GHz in our PADC with a sampling rate of 20 GS/s.
A Fourier analysis applied to the Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI) transmission spectrum for simultaneous refractive index (RI) and temperature measurements is proposed and experimentally demonstrated in this Letter. In the fast Fourier transform (FFT) spectrum of the MZI transmission spectrum, several frequency components are generally observed, which means that the transmission spectrum of the MZI is formed by the superposition of some dual-mode interference (DMI) spectra, and each frequency component represents different core-cladding interferences. We can select some dominant frequency components in the FFT spectrum of the MZI transmission spectrum to take the inverse FFT (IFFT). Then, the corresponding DMI patterns can be obtained. Due to the shift of the wavelength of these DMI spectra with changes in the environmental parameters, we can use the coefficient matrix of these DMI spectra for multi-parameter sensing. In this Letter, two DMI patterns are separated from the resultant transmission spectrum of the MZI. As the RI and temperature change, the shifts of the two DMI patterns with respect to the RI and temperature will be observed. The sensitivities of the RI and temperature are 137.1806 nm/RIU (RI unit) and 0.0860 nm/°C, and 22.9955 nm/RIU and 0.0610 nm/°C for the two DMIs. Accordingly, it can be used to simultaneously measure RI and temperature changes. The approach can eliminate the influence of multiple interferences and improve the accuracy of the sensor.
We experimentally demonstrate all-optical clock recovery for 100 Gb/s return-to-zero on–off keying signals based on a monolithic dual-mode distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser, which can realize both mode spacing and wavelength tuning. By using a coherent injection locking scheme, a 100 GHz optical clock can be recovered with a timing jitter of 530 fs, which is derived by an optical sampling oscilloscope from both the phase noise and the power fluctuation. Furthermore, for degraded injection signals with an optical signal-to-noise ratio as low as 4.1 dB and a 25 km long distance transmission, good-quality optical clocks are all successfully recovered.
Since significant ocular differences in both anatomical structure and optical properties exist between rodents and humans, clinical imaging devices for human use are not suitable for use on rodents. In this study, we develop a contact probe with a flexible surface that can closely fit the rodent cornea for fundus imaging with a confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Both Zemax simulation and in vivo fundus imaging demonstrate that this contact probe can significantly improve both the imaging quality and the operational convenience.
Based on the standard angular momentum theory, we create an experiment on preparing maximally path-entangled (|N,0 +|0,N )2 (NOON) states of triphotons. In order to explain the error between the theoretical and experimental data, we consider the background events during the experiment, and observe their effect on the uncertainty in S^1. Afterwards, we calculate the quantum Fisher information (QFI) of the states to evaluate their potential applications in quantum metrology. Our results show that by adding the appropriate background terms, the theoretical data of the produced states matches well with the experimental data. In this case, the QFI of the states is lower than maximally entangled NOON states, but still higher than a classical state.
Efficient second harmonic generation (SHG) in a nonlinear transparent conducting oxide (TCO) stripe waveguide that incorporates an organic polymer is theoretically investigated. The phase match condition between the fundamental photonic mode at the second harmonic and the fundamental long-range plasmonic mode at the fundamental frequency can be satisfied by dynamically or statically tuning the free carrier concentration of the TCO. The theoretically generated signal reaches its maximum up to 56.4 mW at a propagation distance of 34.8 μm for a pumping power of 1 W. The corresponding normalized conversion efficiency of the phase-matched SHG is up to 4.65×103 W 1 cm 2.
We propose and demonstrate an ultrasensitive integrated photonic current sensor that incorporates a silicon-based single-mode-multimode-single-mode waveguide (SMSW) structure. This kind of SMSW structure is placed over a direct current carrying power resistor, which produces Joule’s heat to change the temperature of the SMSW and further results in the change of the effective refractive index between different propagating modes. Interference occurs when the modes recombine at the second single mode waveguide. Finally, the current variation is measured by monitoring the shift in the output spectrum of the multimode interferometer. In low current, the wavelength shift has almost linear dependence: Δλ∝Ic. This effect can be used as a current sensor with a slope efficiency of 4.24 nm/A in the range of 0–200 mA.
Solar-blind ultraviolet detection is of great importance in astronomy and industrial and military applications. Here, we report enhanced solar-blind ultraviolet single-photon detection by a normal silicon avalanche photodiode (Si APD) single-photon detector with a specially designed photon-collecting device. By re-focusing the reflected photon from the Si chip surface on the detection area by the aluminum-coated hemisphere, the detection efficiency of the Si APD at 280 nm can be improved to 4.62%. This system has the potential for high-efficiency photon detection in the solar-blind ultraviolet regime with low noise.