View fulltext
View fulltext
This feature issue is the second Joint Applied Optics (AO) and Chinese Optics Letters (COL) Feature Issue on digital holography and three-dimensional (3D) imaging. The first installment of such a joint feature issue was in 2011. In the present feature issue, there are a total of 24 papers in AO and 9 papers in COL.
One of the most fascinating principles in quantum mechanics must be Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, which can be briefly stated as follows: every physical observation cannot be precisely determined without some degree of error or uncertainty. And it is by no means can one use the principle within the limit of certainty region, as will be shown in this Letter. Two of the most important pillars in modern physics must be Einstein’s relativity theory and Schr dinger’s contribution to quantum mechanics. Yet, there is a profound connection between these discoveries by means of the uncertainty relationship, in which we shown that the observation of a high-speed object is conceivable if the speed of the observer keeps up with object’s speed.
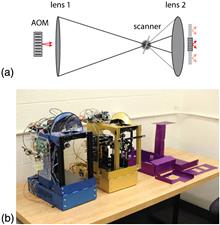
This paper presents progress on the characterization of guided-wave light modulators for use in a low-cost holographic video monitor based on the MIT scanned-aperture architecture. A custom-built characterization apparatus was used to study device bandwidth, RGB operation, and linearity in an effort to identify optimal parameters for high bandwidth, GPU-driven, full-color holographic display.
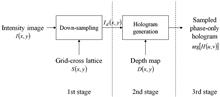
Past research has demonstrated that a phase-only hologram can be obtained by down-sampling the intensity image of the object scene prior to the generation of the hologram. In this Letter, we extend the method to the generation of binary phase-only holograms. A hologram derived with our proposed method is referred to as a binary-sampled phase-only hologram (BSPOH). Being different from the parent scheme, we have adopted an off-axis configuration in the generation of the BSPOH to avoid the quantization noise, the zeroth-order light, and the conjugate lights. An experimental evaluation reveals that the reconstructed image of the BSPOH is of good quality, and only contains slight amount of noise.
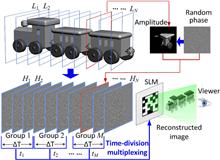
A time-division multiplexing method for computer-generated holograms (CGHs) is proposed to solve the problem of the limited space-bandwidth product. A three-dimensional (3-D) scene is divided into multiple layers at different depths. The CGH corresponding to each layer is calculated by an angular-spectrum algorithm that is effective at a wide range of propagation distances. All of the CGHs are combined into several group-CGHs. These group-CGHs are sequentially uploaded onto one spatial light modulator at a high frame rate. The space-bandwidth product can be benefited by the time-division processing of the CGHs. The proposed method provides a new approach to achieve high quality 3-D display with a fast and accurate CGH computation.
Anisotropic edge enhancement is simulated using a spiral phase plate (SPP) in optical scanning holography (OSH). We propose to use a delta function and an SPP as the pupil functions to realize anisotropic edge enhancement. The interference of these two pupils is used to two-dimensionally scan an object to record its edge-only information. This is done in three ways: first, by shifting the SPP, second, by using two offset SPPs of same charge, and finally, by using two oppositely charged SPPs. Our computer simulations show the capability of selectively enhancing the edges of a given object.
A novel method for a full-parallax three-dimensional (3D) holographic display by means of a lens array and a holographic functional screen is proposed. The process of acquisition, coding, restoration, and display is described in detail. It provides an efficient way to transfer the two-dimensional redundant information for human vision to the identifiable 3D display for human eyes. A holo-video system based on a commercial 4 K flat-panel displayer is demonstrated as the result.
We present a polarization-multiplexing off-axis Mach–Zehnder configuration for dual-wavelength digital holography to achieve phase imaging in one shot. In this configuration, two orthogonal linear-polarized waves with respect to different wavelengths are employed to record respective holograms synchronously, where two recording waves transmit independently through the same optical paths of the interferometer, and by installing two analyzer polarizers each to filter off either of two wavelengths, and filtering through the other, the holograms are acquired, respectively, by a pair of CCDs at the same time. The unwrapped phase image of a grating with groove depth 7.1 μm is retrieved via spatial frequency filtering.
A polarization holographic grating, which integrates the functions of a grating and a wave plate and is called a diffractive wave plate, is recorded by two beams (left and right circularly polarized) of a 532 nm laser in an azo polymer with a liquid-crystal structure. The polarization conversion characteristics of the diffractive wave plates are investigated with a detecting light of 650 nm by metering the polarization state of first-order diffracted light. It is confirmed that the diffractive wave plates convert the incident linear polarization into circular polarization for a linearly polarized probe laser and reverse the sense of rotation of the circular polarization when the detecting light is circularly polarized light.
Because the bottom of the cavity has the shadow and occlusion, the angle between the projection system and imaging system is limited. So the traditional fringe projection technique based on the principle of optical triangulation is inapplicable. This Letter presents a 3D shape measurement method of using the light tube for the cavity. The method can measure an object from two opposite views at the same time, which means it will obtain two different groups of 3D data for the same object in a single measurement. The experimental results show the feasibility and validity of the 3D shape measurement method.
A wavelength-swept laser is constructed using a free space external cavity configuration coupled with a fiber-based ring cavity at the 850 nm region. The external cavity filter employs a galvo-mirror scanner with a diffraction grating for wavelength selection. The filter is connected to a ring cavity through an optical circulator. The ring cavity contains a broadband semiconductor optical amplifier with a high optical output. The performance of this laser is demonstrated with broad bandwidths and narrow linewidths. The 3 dB linewidth and the bandwidth of this source are 0.05 nm (~20 GHz) and 48 nm, respectively. The maximum output power is 26 mW at 160 mA current.
We produce a maximum 1.45 W laser output at 1064 nm using a neodymium-doped silicate glass fiber that has a rectangular core with dimensions of ~6.3 μm×31.5 μm. The measured divergence angles of the output laser in two dimensions are 3.22° and 1.76°, respectively. The output power is stable and limited only by the available pump power.
We observe a nonlinear response of a dual-wavelength Nd:YAG laser when subjected to low-frequency periodic modulations of cavity losses. The modulation frequency is far from the relaxation oscillation frequency. The harmonic resonances of the two laser wavelengths associated with antiphase intensity oscillations are demonstrated and resonances up to the fourth order were observed. For relatively weak modulation, the intensity oscillation frequency of the laser is equal to the modulation frequency. Harmonic resonances occur under a stronger modulation. We find that more harmonic components appear when the modulation frequency is increased. Furthermore, with enhancing the modulation, the dominant frequency of the intensity oscillations of both wavelengths is shifted toward the higher-order harmonic frequency.
During the formation of sub-wavelength ripples, the initial surface plasmon (SP)-laser interference plays an important role. In this Letter, the effects of grating structures on the distribution of the absorbed laser intensity, SP-laser coupling, free electron distributions, and ablation shapes are investigated by the plasma model, taking into consideration both the laser wave-particle duality and the transient localized changes of material properties. The simulation results show that the grating structures can strongly enhance the energy absorption and SP-laser coupling, which makes the fabrication of sub-wavelength ripples more efficient. It is also found that the ablation shapes, in terms of ablation depths and sub-wavelength ripples periods, are strongly related to the grating structures, which can be used to control micro/nanostructures precisely and uniformly.
By investigating the cross-spectral density of partially coherent multi-rotating elliptical Gaussian beams (REGBs) that propagate through a focusing optical system, we obtain the radiation force on a Rayleigh particle. The radiation force distribution is studied under different beam indexes, coherence widths, and elliptical ratios of the partially coherent multi REGBs. The transverse and the longitudinal trapping ranges can increase at the focal plane by increasing the beam index or decreasing the coherence width. The range of the trapped particle radii increases as the elliptical ratio increases. Furthermore, we analyze the trapping stability.
A terahertz excitation source based on a dual-lateral-mode distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) laser working in the 1.5 μm range is experimentally demonstrated. By optimizing the width of the ridge waveguide, the fundamental and the first-order lateral modes are obtained from the laser. The mode spacing between the two modes is 9.68 nm, corresponding to a beat signal of 1.21 THz. By tuning the bias currents of the phase and DBR sections, the wavelengths of the two modes can be tuned by 2 nm, with a small strength difference (<5 dB) and a large side-mode suppression ratio (SMSR>45 dB).
We report on the continuous-wave (CW) and passive Q-switching performance of a miniature Yb:Y3Ga5O12 crystal laser end pumped by a 935-nm diode laser. A maximum CW output power of 12.03 W is produced with an optical-to-optical efficiency of 54.4%, while the slope efficiency is 63%. In the passively Q-switched operation achieved with a Cr4+:YAG saturable absorber, an average output power of 2.12 W at 1025.2 nm is generated with a slope efficiency of 46% at a pulse repetition rate of 5.0 kHz. The pulse’s energy, duration, and peak power are 424 μJ, 2.3 ns, and 184.3 kW, respectively.
Pockel’s effect and optical rectification induced by the built-in electric field in the space charge region of a silicon surface layer are demonstrated in a {001}-cut high-resistance silicon crystal. The half-wave voltage is about 203 V, deduced by Pockel’s effect. The ratio χzxx(2)/χzzz(2) is calculated to be about 0.942 according to optical rectification. Our comparison with the Kerr signal shows that Pockel’s signal is much stronger. This indicates that these effects are so considerable that they should be taken into account when designing silicon-based photonic devices.
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA)-based large-capacity sensing network with ultra-weak fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) is proposed and experimentally studied. The demodulation system is constructed to interrogate 1642 serial time-division-multiplexing FBGs with a peak reflectivity of about 40 dB and equal separations of 2.5 m. Two semiconductor optical amplifiers and an InGaAs linear sensor array controlled by an FPGA are introduced to the demodulation system to achieve fast, precise, and flexible interrogation. The low crosstalk and spectral distortion are investigated through both theoretical analysis and experiments.
The interference of optically induced electric and magnetic resonances in high-refractive-index dielectric nanoparticles provides a new approach to control and shape the scattering patterns of light in the field of nanophotonics. In this Letter, we spectrally tune the electric and magnetic resonances by varying the geometry of a single isolated lead telluride (PbTe) dielectric nanocube. Then, we overlap the electric dipole resonance and magnetic dipole resonance to suppress backward scattering and enhance forward scattering in the resonance region. Furthermore, a broadband unidirectional scattering is achieved by structuring the dielectric nanocuboids as a trimer antenna.
A lateral photovoltaic effect (LPE) is discovered in an LaTiO3+δ film epitaxially grown on a (100) SrTiO3 substrate. Under the illumination of a continuous 808 nm laser beam that is focused on the LaTiO3+δ film through the SrTiO3 substrate, the open-circuit photovoltage depends linearly on the illuminated position. The sensitivity of the LPE can be modified by the bias current. The LaTiO3+δ film shows a stable photoelectric property under the high pressure, up to 9 MPa. These results indicate that the LaTiO3+δ films can give rise to a potentially photoelectronic device for near-infrared position-sensitive detection in high-pressure environments.
A low-threshold Raman effect in a kilowatt ytterbium-doped narrowband fiber amplifier system is reported. The Raman Stokes light at 1120 nm is achieved with the total output power of only ~400 W, indicating that the Raman threshold of this kilowatt codirectional pumped continuous wave fiber amplifier is much lower than the predicted value estimated by the classic formula. To figure out the mechanism of this phenomenon, simulations based on the general stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) model are analyzed indicating that the key factor is the coupling between four-wave mixing (FWM) and SRS. The simulation results are in good agreement with our experiments.