View fulltext
View fulltext
Head-up display (HUD), a primary cockpit display, helps in optimizing a pilot’s attention towards aircraft and outside events. Slight mismatch in the balance may cause missed events; this phenomenon is called attention tunneling and affects the situational awareness of the pilot. This work reports an intuitive approach to detect attention tunneling while use of HUD in aircrafts. Texture analysis of a composite HUD camera video provided three distinguishing parameters, viz., contrast, correlation, and homogeneity. These three texture parameters are used as inputs for a fuzzy inference-based assistive detection system which could be used for distinguishing tunneled and nontunneled HUD operation.
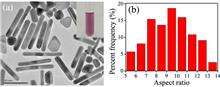
We report on the generation of Q-switched and Q-switched mode-locked (QML) pulses in an erbium-doped fiber ring laser by using a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) -based gold nanorod (GNR) saturable absorber (SA). The PVA-based GNR SA has a modulation depth of ~4.8% and a non-saturable loss of ~26.9% at 1.5 μm. A Q-switched pulse train with a repetition rate varying from 18.70 to 39.85 kHz and a QML pulse train with an envelope repetition rate tuning from 20.31 to 31.50 kHz are obtained. Moreover, the lasing wavelengths of the Q-switched pulses can be flexibly tuned by introducing a narrow bandwidth, tunable filter into the laser cavity. The results demonstrate that the GNRs exhibit good optical performance and can find a wide range of applications in the field of laser technology.
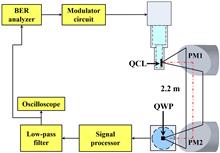
A wireless terahertz (THz) communication link is demonstrated, in which a THz quantum cascade laser and a THz quantum-well photo-detector (QWP) serve as the emitter and receiver, respectively. With the help of the well-matched THz QWP, the optical collection efficiency has greatly been improved. A data signal transmitted over 2.2 m with a low bit error rate (≤1×10 8) and data rate as high as 20 Mbps is achieved, which are almost 1 order of magnitude higher than that previously reported.
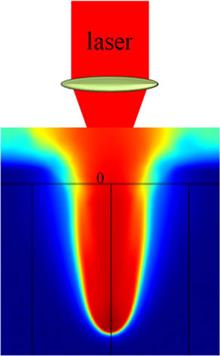
A two-dimensional, transient model is proposed to study the dynamic process of keyhole formation and the material changes during both the laser-on and -off periods. The keyhole shape, temperature field, and velocity field are analyzed. The results indicate that the dynamic changes of the target material in the laser-off period have a great influence on the final structure of the keyhole.
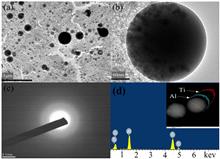
A simple and versatile strategy is designed to successfully fabricate ultrafine TiO2 nano-cages based on the rapid decomposition reaction between amphoteric hydroxide and ammonia solution by pulsed laser ablation of Ti/Al alloy in liquid. With the ammonia concentration (Vammonia:Vwater, where V is volume) increasing from 1∶10 to 1∶4, the diameter and shell thickness of quasi-spherical TiO2 nano-cages substantially decrease from 300 and 60 nm to 9.2 and 2.8 nm, respectively. The obtained results have significant implications for obtaining insight into the properties of the TiO2 porous nano-cages, offering the basis for further fabrication of other nano-cages.
A passively Q-switched mode-locked (QML) Tm:LiLuF4 (LLF) laser with a MoS2 saturable absorber (SA) is demonstrated for the first time, to our best knowledge. For the Q-switching mode, the maximum average output power and Q-switched pulse energy are 583 mW and 41.5 μJ, respectively. When the absorbed power is greater than 7.4 W, the passively QML pulse is formed, corresponding to an 83.3-MHz frequency. The modulation depth in Q-switching envelopes is approximately 50%. Results prove that MoS2 is a promising SA for Q-switched and QML solid-state lasers.
We demonstrate a potassium titanyl phosphate-based optical parametric oscillator (OPO) emitting at 1729 nm. A maximum output power of 1.56 W at 1729.4 nm is obtained with an original fundamental laser power of 5.48 W. The pulse with a pulse duration of 11.22 ns exceeds 3 mJ at a 500 Hz repetition rate. To our knowledge this is the highest energy output of an OPO laser emitting around 1.73 μm operating at a 100 Hz order of magnitude. This laser is primarily used for bond-selective imaging of deep tissue, a promising way for diagnosing vulnerable plaques in live patients.
Temporal properties of random lasing under ultrashort pulse excitation are investigated in a two-dimensional disordered medium. The pumping light is described individually and coupled into the rate equations. The Maxwell equations and rate equations are numerically solved by using the finite-difference time domain method. The time evolution of the emission pulse is studied with the variation of the surface-filling fraction, refractive index, and scatterer radius. Results show that the behavior of random lasing depends strongly on the sample parameters. Our work enriches the knowledge about random lasers in the ultrashort pulse pumping regime and offers some guidance for relevant experiments.
In this Letter, we propose an optical attenuator based on the phase modulation of a spatial light modulator (SLM). In this system, we use two polarized beam splitters (PBSs) to control the polarized light and one SLM to modulate the phase of the polarized light. In the initial state, the light beam is divided into p-light and s-light when it passes through the first PBS. When the light passes through the second PBS, s-light is reflected and p-light is detected by the CCD camera. By loading different grayscales on the SLM, p-light changes its polarized state to s-light. The light power can be attenuated during the loading process. Our experiment shows that the system can obtain a wide optical attenuation from 1–27.2 dB. When loading two grayscales, the SLM has a fast switching time of 25 ms under a low actuated voltage of 5.5 V. The response time of the optical attenuator depends on the switching time of the SLM. Therefore, the system can also have a fast response time. By using the method of spatial multiplexing and adding two mirrors in the system, it can also be extended into a 1×2 optical switch. The results verify its feasibility. The optical attenuator has wide applications in photonic signal processing and fiber-optic communication.
Preparation and characterization of a liquid level sensor based on macro-bending coupling of fibers are demonstrated in this Letter. The sensitive component can be obtained through a twisting and twining structure of transparent cladding plastic fibers. The difference in light power originating from the surrounding media in the fibers is tested. The light power loss for different tested media and the fiber bending magnitude are investigated. The sensing measurements show that the coupling light power in the passive fiber decreases in accordance with increasing liquid level, whereas it exhibits a steady tendency in the case of the active fiber.
Carrierless amplitude and phase (CAP) modulation is generating increasing interest for short-reach optical communications. Polarization multiplexing (PolMux) is a good way to improve the CAP system’s data rate further with the limited bandwidth of electrical devices. In this Letter, we experimentally demonstrate a 56 Gb/s direct-detection PolMux CAP system over a 15 km fiber link for the first time, to our best knowledge. Two-band CAP modulation with different modulated orders for each band is employed. An optical filter at the receiver is utilized to realize the polarization separation. No extra digital signal processing for polarization-dependent distortion is required.
For nonline-of-sight ultraviolet communication links, a simple and concise parametric expression (PE) of channel path loss is valuable for link performance analysis in typical scenarios. It is observed that the light energy in the scattering volume can be approximated using a line integral. Combining curve fitting for the scattering phase function and the mean value theorem of integrals, we propose a simple but highly accurate PE. It matches well with the Monte Carlo simulations for typical LED-based communication with small beam divergence (<45°); when the beam divergence is smaller than 10°, their differences are less than 1 dB in most geometrical conditions. The proposed PE also shows good consistency with our outdoor experimental measurements, and the reported experimental results in the literature.
We propose and demonstrate a scheme to measure the distribution of temperature along an optical fiber based on pseudo-random sequence modulation. In our experimental work, current modulation with a pseudo-random bit sequence (PRBS) is applied to a laser diode that serves as the Brillouin pump light and reference light. Because of the independence of the spatial resolution on the PRBS length, the measurement range can be extended while maintaining high spatial resolution using a long PRBS length. Temperature-induced changes in a Brillouin frequency shift of 250 m fiber sections are clearly observed with 54 cm spatial resolution by this method.
We experimentally demonstrate a high-speed phosphorescent white light emitting diode (LED) visible light communication (VLC) system without utilizing an optical blue filter. Here, the white light response is equalized by using the proposed analog equalizers. The 3 dB bandwidth of the VLC link could be extended from 3 to 132 MHz, which allows 330 Mbit/s non-return-to-zero on–off keying (NRZ-OOK) data transmission with a bit error ratio (BER) of 7.2×10 10 and 672 Mbit/s 64-quadrature amplitude modulation (64-QAM) data transmission with a BER of 3.2×10 3. These resultant BERs are less than the forward error correction (FEC) limit of 3.8×10 3. The VLC link distance is 1 m using a single 1 W LED. The transmitter and receiver modules are integrated to a compact size. Furthermore, the relationships between the signal performance and illumination level or optical power are investigated and analyzed.
A quasi-optical single-sideband (quasi-OSSB) modulation approach with a tunable carrier-to-sideband ratio (CSR) is proposed and demonstrated. By simply tuning the polarizing angle, a continuously tunable CSR can be obtained. Since the upper sideband is highly suppressed during the CSR’s tuning, quasi-OSSB modulation signals with extremely small interference are generated. An experiment is undertaken for verification. It is found that the target CSR can be continuously tuned over a wide range, which can be used to improve the receiver sensitivity of the fiber links.
For manufacturing a fine optical glass lens, it is important to obtain a 3D profile of a semi-finished product with a rough surface. We develop an active binocular 3D scanning setup to measure the 3D profile of a rough surface optical element. Two cameras simultaneously capture the band-pass binary random patterns which are projected on the target object. The highlight of this system is using the temporal correlation technique to determine the stereo correspondence between the pixels of the two cameras. The 3D point cloud can be reconstructed by the triangulation principle. Experiment results confirmed that this method effectively measures the rough surface of an optical element with sufficient accuracy.
We present a method of time coding with ABAB synchronization timing control for real-time 3D super-resolution range-gated imaging (3DSRGI). To meet the high precision of time delay and pulse width in ABAB synchronization time sequencing, phase shift is implemented to achieve ns-scaled delay and width accuracy without restoring to high clock frequencies. Theoretical analysis and experiments prove that 1 ns delay and width precision is obtained by our timing control unit based on a single field-programmable gate array with 5 ns clock cycle. Finally, a prototype experiment of 3DSRGI is demonstrated at a 10 Hz video rate with 696 pixels×520 pixels.
The inclusions in conventionally grown KD2PO4 (DKDP) crystals are investigated. The inclusions are captured by a light-scattering technique. The sizes are determined by an optical microscope and a transmission electron microscope (TEM), and the compositions are analyzed by time of flight secondary ion mass spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) and an energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS). Two kinds of inclusions are observed in the DKDP crystals: a submicron-scale inclusion and a micron-scale inclusion. The typical submicron-scale inclusions contain growth solution, and their sizes range from tens to hundreds of nanometers, whereas the micron-scale inclusions contain growth solution and the metal element Na, and the sizes are tens of microns. The possible formation mechanisms of the inclusions are discussed, and the influence of the inclusions on laser-induced damage behaviors are analyzed and discussed.
We report an Er3+-doped fluorogallate glass with good thermal and chemical stability. The low maximum phonon energy and high mid-infrared (IR) transmittance of the glass are confirmed by Raman and IR spectra, respectively. Based on Judd–Ofelt theory, intensity parameters and radiative properties are determined from the absorption and emission spectra. The proposed glass possesses a large fluorescence branching ratio β (21.71%) and a maximum stimulated emission cross-section σem of Er3+:I11/24→I13/24 transition at 2.71 μm (1.04×10 20 cm2). The results indicate that it can be potentially applied in high-power 2.7 μm fiber lasers.
We demonstrate a soft lithography approach for fabrication of a topographically patterned polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) liquid-crystal (LC) alignment layer. This specific approach employs modified micromolding in capillaries for negative replication of the PVA microstructures on indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates from patterned poly(dimethylsiloxane) molds in a single step, leading to planar alignment on the desired regions. By doping with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane nanoparticles, which can induce vertical alignment on bare ITO surfaces, periodic LC phase gratings based on an alternating vertical-aligned/hybrid-aligned nematic geometry are presented as an application, and a theoretical model was used to simulate and examine the experimental results.
A geometry of transient-grating self-referenced spectral interferometry (TG-SRSI) is proposed for weak femtosecond pulse characterization. By using a reflective microscope objective (RMO), we build a compact, robust, and easy to adjust device with a higher sensitivity to pulse energy in comparison to all previous SRSI methods. A 65 nJ/~40 fs/1 kHz pulse at 800 nm is successfully characterized, which speaks to the capability of our device to characterize a weak pulse. It is expected to extend the TG-SRSI method to the characterization of femtosecond pulses from oscillators in the near future.
A simple method to fabricate vertically coupled micro-ring resonators in amorphous silicon-on-insulator is created by a three-step lithography process. First, the linear loss at 1.55 μm of the a-Si:H film is calculated to be 0.2±0.05 dB/cm. Then, the bottom line waveguide of Su-8 with a flat top surface of 300 nm is created by etching. The thickness of Su-8 can easily be controlled by the etching time. Finally, by opening the window pattern and etching several layers, the first layer marks made by electron beam lithography are found with a 50 nm resolution, and the high quality of the micro-ring resonator is demonstrated.
We report the fabrication details of a monolithically integrated electro-absorption modulated distributed feedback laser (EML) based on the ion-implantation induced quantum well intermixing (QWI) technique. To well-preserve material quality in the laser region, thermal-oxide SiO2 is deposited before implantation and the ion-implantation buffer layer is etched before annealing. Thirteen pairs quantum well and barrier are employed to compensate deterioration of the modulator’s extinction ratio (ER) caused by the QWI process. The fabricated EML exhibits an 18 dB static ER at 5 V reverse bias. The 3 dB small signal modulation bandwidth of modulator is over 13.5 GHz indicating that this EML is a suitable light source for over 16 Gb/s optical transmission links.
We propose a scheme to obtain a low-loss propagation of Airy surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) along the interface between a dielectric and a negative-index metamaterial (NIMM). We show that by using the transverse-magnetic mode and the related destructive interference effect between electric and magnetic absorption responses, the propagation loss of the Airy SPPs can be largely suppressed when the optical frequency is close to the lossless point of the NIMM. As a result, the Airy SPPs obtained in our scheme can propagate more than a 6 times longer distance than that in conventional dielectric–metal interfaces.
We propose a reflection-type infrared biosensor by exploiting localized surface plasmons in graphene ribbon arrays. By enhancing the coupling between the incident light and the resonant system, an asymmetric Fabry–Perot cavity formed by the ribbons and reflective layer is employed to reshape the reflection spectra. Simulation results demonstrate that the reflection spectra can be modified to improve the figure of merit (FOM) significantly by adjusting the electron relaxation time of graphene, the length of the Fabry–Perot cavity, and the Fermi energy level. The FOM of such a biosensor can achieve a high value of up to 36/refractive index unit (36/RIU), which is ~4 times larger than that of the traditional transmission-type one. Our study offers a feasible approach to develop biosensing devices based on graphene plasmonics with high precision.
The average bit error rate (BER) performance of a free-space optical (FOS) system based on the multi-hop parallel decode-and-forward cooperative communication method with an M-ary phase shift keying subcarrier intensity modulation is studied systematically. With the max–min criterion as the best path selection scheme, the probability density function and the cumulative distribution function of the gamma–gamma distribution random variable signal-to-noise ratio are derived. The analytical BER expression is then obtained in terms of the Gauss–Laguerre quadrature rule. Monte Carlo simulation is also provided to confirm the validity of the presented average BER model.