View fulltext
View fulltext
Ablation dynamics of tungsten irradiated with a 70 fs laser pulse is investigated with X-ray interferometry and X-ray imaging using a 13.9 nm soft X-ray laser of 7 ps pulse duration. The evolution of high-density ablation front of tungsten (i.e., W) is presented. The ablation front expands to ~120 nm above the original target surface at 160 ps after femtosecond-laser irradiation with an expansion speed of approximately 750 m/s. These results will provide important data for understanding ablation properties of W, which is a candidate material of the first wall of magnetic confinement fusion reactors.
Investigations are performed to explore high-repetition-rate femtosecond laser ablation effects on the physical and chemical properties of poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA). A scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used to characterize the morphology change in the laser-ablated regions. The infrared and Raman spectroscopy reveals that the fundamental structure of the PMMA is altered after laser ablation. We demonstrate the cumulative heating is much greater during high-repetition-rate femtosecond laser ablation, supporting a photothermal depolymerization mechanism during the ablation process.
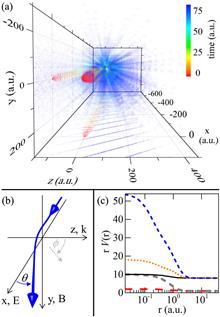
We report photoelectron energy spectra and angular distributions for ionization with elastic scattering in ultrastrong laser fields. Noble gas species with Hartree–Fock scattering potentials show a reduction in elastic rescattering with the increasing energy of ultrastrong fields and when the Lorentz deflection of the photoelectron exceeds its wave function spread. The relativistic extension of a three-step recollision model is well-suited to the ultrastrong intensity regime (>1017 W/cm2) that lies between traditional strong fields and extreme relativistic interactions.
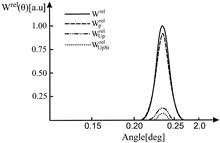
In this Letter, we focus on the theoretical analysis of the relativistic energy and angular distributions of the ejected photoelectrons during the relativistic tunnel ionization of atoms by intense, circularly polarized light. We make a small modification of the general analytical expressions for these distributions. The role of the initial momentum, the ponderomotive potential, and the Stark shift are considered. We also present the maximal angle of electron emission.
Intense-laser-induced above-threshold ionization of a bound electron into continuum states with low energy is investigated in the context of the strong-field approximation that allows for one act of rescattering of the revisiting electron. The quantum orbits for forward and backward scattering are evaluated and generalized to arbitrary scattering angles. The velocity map of the liberated electron exhibits the well-known low-energy structure as well as other features off the polarization axis.
The visible and near-UV emission spectroscopy of methane (CH4) induced by a femtosecond intense laser field (800 nm, 40 fs, 1014 W/cm2) is studied. By measuring the decay profiles of the neutral fragment product CH (A2Δ→X2Π), two reaction pathways, i.e., the electron-ion recombination through e +CH4+ and the direct disintegration of CH4+ are found to be responsible for populating the electronic excited states of the neutral fragment product CH, which gives rise to the photoemissions. Our results provide complementary information on previous understanding of the strong-field-induced photoemission mechanism of CH4 through neutral dissociation of superexcited states.
The influence of air turbulence on the transverse wandering of a single femtosecond laser filament is studied by numerical simulation. The results show that the average transverse displacement of the single filament δr is proportional to the square root of turbulent structure constant and the relations between δr and the propagation distance can be fit by a power function. In addition, by using an axicon as a focusing optics, the wandering of a single filament is suggested to be stronger than the free-propagation case.
In this Letter, temporal self-modifying behavior of amplitude modulation pulse propagation characteristics in multiphoton absorbers is presented by solving the underlying theoretical model coupling the propagation equation with the rate equations. The characteristics of the output temporal shapes are of primary concern and are discussed in detail. Amplitude modulation suppressing effects of multiphoton absorbers are numerically demonstrated; they have not been reported previously, to our knowledge. By taking a time resolved absorption coefficients, the corresponding physical mechanism is explicitly interpreted.
With the rapid development of ultrafast intense laser technologies, the interaction of intense laser radiation with matter has been a frontier for few decades. The International Conference on Multiphoton Processes (ICOMP), initiated in 1977, covers the latest advances in the field every three years. The special issue is based on the spirit of the 13th International Conference on Multi-Photon Processes, ICOMP13, which was held in Shanghai, organized by Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, on Dec. 7-10, 2014.
In this Letter, we propose a novel three-dimensional (3D) color microscopy for microorganisms under photon-starved conditions using photon counting integral imaging and Bayesian estimation with adaptive priori information. In photon counting integral imaging, 3D images can be visualized using maximum likelihood estimation (MLE). However, since MLE does not consider a priori information of objects, the visual quality of 3D images may not be accurate. In addition, the only grayscale image can be reconstructed. Therefore, to enhance the visual quality of 3D images, we propose photon counting microscopy using maximum a posteriori with adaptive priori information. In addition, we consider a wavelength of each basic color channel to reconstruct 3D color images. To verify our proposed method, we carry out optical experiments.
A continuous-wave all-solid-state tunable Ti:sapphire laser with compact configuration is presented. The frequency-tuning range extends from 760 to 825 nm by rotating the birefringent filters. When the intracavity etalon is locked on the oscillating frequency of the laser and the length of the resonator is scanned by the piezoelectric ceramics transducer, a maximal continuous frequency-tuning range of 15.3 GHz is realized. The obtained Ti:sapphire laser is successfully applied to scan the saturation absorption spectroscopy of D1 transitions of Rb87 atoms around the wavelength of 794.97 nm.
The effect of co-doping Y3+ and the doping concentration of Nd3+ on the spectroscopic properties and laser performance of Nd:CaF2 crystals are investigated systematically. For a 0.5% Nd:CaF2 crystal, the emission lifetime at 1.06 μm increases from 18 to 361 μs by co-doping 10 at.% Y3+, while the emission cross section increases to 4.27×10 20 cm2 at 1054 nm. With a 10 at.% doping concentration of Y3+, Nd,Y:CaF2 crystals concentrate emission bands that peak at 1054 nm with shoulders at 1063 nm, and FWHM at about 30 nm. A diode-pumped, highly efficient laser operation is obtained with 0.5% Nd, 10% Y:CaF2 and 0.6% Nd, 10% Y:CaF2 crystals, with slope efficiencies over 30% and 27%, respectively, and a maximum output power up to 901 mW.
We demonstrate a narrow-linewidth linearly polarized 1645 nm Er:YAG laser, directly diode-pumped by a fiber-coupled continuous-wave laser diode at 1532 nm. Passive Q-switching is realized by a few-layer graphene saturable absorber. A maximum polarized average output power of 3.13 W is achieved at 23.28 W incident pump power. A pulse energy of as much as 58.8 μJ and pulse width of 4.21 μs are yielded at a 53.2 kHz pulse repetition rate. The spectrum and linewidth of the output beams are measured to be 1645.34 and 0.05 nm, respectively. This laser can be useful in the detection of atmosphere pollutants.
We propose an adaptive parallel coordinate (APC) algorithm for quickly forming a series of focused spots at a multimode fiber (MMF) output by controlling the MMF input field with a spatial light modulator (SLM). Only passing over the SLM once, we can obtain SLM reflectance to form focused spots on different positions. Compared with the transmission matrix method, our APC does not require iterations and massive calculations. The APC does not require as much access device time as the adaptive sequential coordinate ascent (SCA) algorithm. The experiment results demonstrate that the time taken to form 100 spots with our APC is 1/54th the time with the SCA.
Long-period gratings (LPGs) are fabricated in a photonic crystal fiber (PCF) using the symmetric point-by-point CO2 laser irradiation method to explore the sensitivity characterization of PCF–LPG. Numerical simulation is used to guide the investigation. It is found that the refractive index (RI) sensitivity of PCF–LPG depends on the coupled cladding modes as well as the coupled resonance wavelength (RW) of the LPG. Experimental studies show that the longer the RW, the higher the RI sensitivity for the same cladding mode. At similar RWs, the lower the cladding mode, the higher the RI sensitivity of PCF–LPG.
In this Letter, we propose a color holographic zoom system based on a liquid lens. We use the spatial multiplexing method to realize color reconstruction. By controlling the focal lengths of the liquid lens and the encoded digital lens on the spatial light modulator panel, we can change the magnification of the reconstructed image very quickly, without mechanical parts and keeping the output plane stationary.
In visible light communication, orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) is an effective approach to improve the system speed. However, the nonlinearity of the light-emitting diode (LED) suppresses the transmission performance. The low-frequency part of the transmitted signal from LED suffers more from nonlinearity. Therefore, a pre-equalization scheme which suppresses the low frequency part of the OFDM signal and enhances the high frequency part can decrease the impact of LED nonlinearity. The experimental results show that the bit-error rate performance is largely enhanced by the pre-compensation.
In this Letter the problem of optimization of speckle patterns in a ghost imaging (GI) system is addressed. The mutual coherence between the measuring matrix and the sparsifying dictionary matrix is minimized to obtain the required speckle patterns. Simulation and experimental results are presented, both showing that the quality of the reconstructed results obtained with the optimized speckle patterns is much improved in comparison with that obtained with the general unoptimized ones. We expect this method can be used to design GI systems with high performance.
This Letter proposes a high bit-depth coding method to improve depth map resolution and render it suitable to human-eye observation in 3D range-intensity correlation laser imaging. In this method, a high bit-depth CCD camera with a nanosecond-scaled gated intensifier is used as an image sensor; subsequently two high bit-depth gate images with specific range-intensity profiles are obtained to establish the gray depth map and finally the gray depth map is encoded by an equidensity pseudocolor. With this method, a color depth map is generated with higher range resolution. In our experimental work, the range resolution of the depth map is improved by a factor of 1.67.
We develop a prototype endoscope system that can perform high-dynamic-range structure imaging and hyperspectral imaging. The system is used to successfully acquire the oxyhemoglobin spectrum of blood capillaries and obtain in vivo images of the various vascular pattern structures of the underside of the human tongue with high intrinsic contrast and high dynamic range. The dynamic range of the acquired high-dynamic-range mucosa image is 116.5 dB, which is 68.2 dB higher than that of the mucosa images acquired by a normal low-dynamic-range CCD. Our results demonstrate the system’s tremendous potential for the clinical diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases.
The absorption spectra, excitation spectra, and emission spectra of Tb3+/Eu3+ ions in LiYF4 single crystals synthesized by an improved Bridgman method are measured. The emission spectra of several bands, mainly located at blue ~487 nm (Tb:D45→F76), yellowish green ~542 nm (Tb:D45→F75), and red ~611 nm (Eu:D05→F72) wavelengths, are observed under excitation by UV light. An ideal white light emission as a result of simultaneous combination of these emissions can be obtained from 1.11 mol% <mml:math display=
In this Letter, the effects of the iron (Fe) dopant concentration on the nonlinear optical properties of iron-doped ferroelectric X-cut LiNbO3 crystals plates are studied by using the Z-scan technique with a cw laser at the wavelength of 532 nm. The amount of iron in the compound is varied from 0 to 0.15 mol%. Measurements of nonlinear refractive index n2 and the nonlinear absorption coefficient β are determined. The sign of the nonlinear refractive index is found to be negative and the magnitude is on the order of 10 8 cm2/W. This nonlinear effect increases as the concentration increases from 0 to 0.15 mol%. A good linear relationship is obtained between nonlinear refractive index, nonlinear absorption coefficient, and concentration.
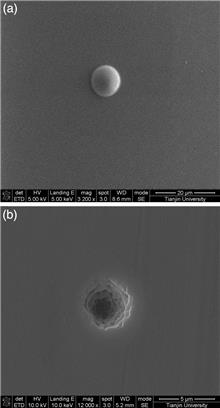
The periodic ripple structures on wolfram and titanium surfaces are induced experimentally by linear polarized femtosecond laser pulses at small incident angles. The structural features show a material difference in the s- and p-polarized laser irradiation. The interspace between the ripples increases significantly for p-polarized laser irradiation when it exceeds a threshold angle, and the ripples’ periodicities are larger than the wavelength of the incident p-polarized femtosecond laser; however, no significant change in the period of the ripples is observed with increasing incident angle for s-polarized laser irradiation. To explain these phenomena we propose a resonant absorption mechanism, by which the experimental observations can be interpreted.
In order to improve the reconstruction accuracy in fluorescence molecular tomography (FMT), a common approach is to increase the number of fluorescence data or projections. However, this approach consumes too much memory space and computational time. In this Letter, a data compression strategy that involves the removal of the redundant information from both intra- and inter-projections is proposed to reduce the dimension of the FMT inverse problem. The performance of this strategy is tested with phantom and in vivo mouse experiments. The results demonstrate that the proposed data compression strategy can accelerate the FMT reconstruction nearly tenfold and almost without any quality degradation.
High-speed cameras are widely used in experimental research and industrial measurement. Although multiple cameras are commonly used, whether the cameras are triggered at the same time is typically overlooked. This study measures the startup time difference between two high-speed cameras employing a proposed measuring system. A series of comparative experiments was conducted to consider the complex factors that can lead to a time difference. The system recorded the startup time differences for different combinations of two cameras at different frame rates, and thus acquired the dependence of the time difference on these factors. Suggestions are made on the basis of the experimental results.
We propose a method for simultaneous 3D temperature and velocity measurement of a micro-flow field. The 3D temperature field is characterized with two-color laser-induced fluorescence particles which are tracked with micro-digital holographic particle tracking velocimetry. A diffraction-based model is applied to analyze defocused particles to determine the intensity ratio of two fluorescent dyes on the particle. The model is validated with experimental images. As the result shows that the intensity ratio nearly remains unchanged with respect to depth positions, defocused particles can be used as 3D temperature sensors. Numerical work is carried out to check the method, and 3D temperature and velocity field in a 120 μm×120 μm×80 μm test volume are retrieved.
We experimentally observe polarization spectroscopy (PS) of the S01-P31 transition of mercury atom gases at 253.7 nm. The PS signal can be observed in all six richly abundant isotopes and the PS signal of six transitions for laser cooling are all clear and of a dispersive line shape. The optimized pump power and probe power are found for the PS of Hg202. We find the linearly polarized component in the pump beam will distort the original PS signal due to the use of linear PS. Consequently, the purity of the pump beam is crucial to laser frequency stabilization by PS.
In this work, a psychophysical experiment is implemented to assess the white sensation of light-emitting diode (LED) lighting in illuminant mode via a categorical judgment method by a panel of 10 observers. The visual data indicates that the higher values of white sensation estimations locate near the Planckian locus within a correlated color temperature (CCT) range of 5000–9000 K. A model of white sensation for LED lighting in illuminant mode is proposed, from which the predicted maximal white sensation locates near the Planckian locus with a CCT of 6622 K, and the 95% white sensation covers a narrow two-dimensional region.