View fulltext
View fulltext
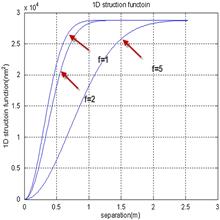
We propose a sub-aperture stitching algorithm based on a frequency domain that can be denoted as a power spectral density (PSD). Our algorithm is verified by the experimental data obtained from measuring a Φ1.23 m mirror at the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics. Then, we apply it to the Great Steering Science Mirror (GSSM) of the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) with the simulated data before the preliminary design phase, and obtain a more objective result on the frequency domain aberrations. Therefore, the sub-aperture stitching-based PSD is expected to be useful for specifying a large aperture mirror surface for mirror vendors.
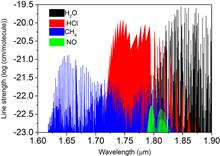
We report a 1.8 μm two-section distributed Bragg reflector laser using butt-jointed InGaAsP bulk material as the waveguide core layer. The threshold current is 17 mA and the output power is 8 mW on average. The threshold current, output power, and emitting wavelength dependences on temperature are measured. The obtained wavelength tuning range is 10 nm. This device has potential applications in simultaneous multiple-gas detection.
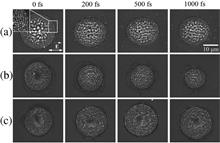
A surprising phenomenon can be discovered by using femtosecond double-pulse ablation of silicon and germanium in ethanol. The ablation areas present an oscillation increase phenomenon when the pulse delay increases from 200 fs to 1 ps in the fluence range of 0.5–0.6 J/cm2. In contrast, the ablation areas exhibit an oscillation decrease phenomenon as the pulse delay increases when the laser fluence F<0.5 J/cm2, which is consistent with the results of the experiment in air. It is considered that the adjustment of the photon–electron coupling efficiency by pulse train technology plays an important role in the ablation process.
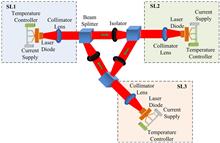
A ring of three unidirectionally coupled semiconductor lasers (RTUC-SLs) is used to generate broadband chaos with no pronounced time-delay (TD) signature. Using the autocorrelation function and permutation entropy as the TD measures, we demonstrate that under suitable coupling strength, the loss of the TD signature of the lasers in the RTUC-SL configuration is achieved both for the intensity and the phase. These findings should prove valuable for developing high-quality optical chaos for potential applications, such as chaos-based communications and random number generation.
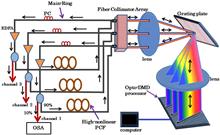
A stable three-channel dual-wavelength fiber ring laser is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The digital micromirror-device (DMD) processor can select and recirculate any dual waveband from the gain spectrum of the erbium-doped fiber at each channel. The uniform and stable dual-wavelength oscillation is obtained by a highly nonlinear photonic crystal fiber, which causes two degenerate the four-wave-mixing processes. By loading different reproducibility diffraction gratings on the optoelectronic DMD processor, the laser can be operated stably in a three-channel dual-wavelength scheme at room temperature. The power fluctuation of each laser channel is less than ~0.02 dB.
A simple and repeatable method to fabricate high-aspect-ratio (HAR) and high-quality microgrooves in silica is reported. The method consists of two steps: (1) formation of laser-modified regions by femtosecond Bessel beam irradiation, and (2) removing laser-modified regions through HF etching. Uniform, straight microgrooves can be fabricated and the highest aspect ratio that can be reached is ~52. The phenomenon is attributed to the uniform energy distribution in the long propagation distance, which leads to the long and uniform laser-modified regions and subsequent HF acid etching of laser-modified regions with high selectivity. This method will have potential applications in fabrication of HAR microgrooves in transparent materials.
The generation and measurement of complex ultraviolet laser pulse shapes is demonstrated in the SG-III laser facility. Relatively high contrast ratio of 300∶1 required by the physics experiment is achieved and successfully measured. Two continuous main shots validate the reproduction and the stability of the pulse shape, which provide solid foundation for precise physics experiment and laser power balance.
The combination of deep wet etching and a magneto-rheological finishing (MRF) process is investigated to simultaneously improve laser damage resistance of a fused-silica surface at 355 nm. The subsequently deposited SiO2 coatings are researched to clarify the impact of substrate finishing technology on the coatings. It is revealed that a deep removal proceeding from the single side or double side had a significant impact on the laser-induced damage threshold (LIDT) of the fused silica, especially for the rear surface. After the deep etching, the MRF process that followed does not actually increase the LIDT, but it does ameliorate the surface qualities without additional LIDT degradation. The combination guarantee both the integrity of the surface’s finish and the laser damage resistance of the fused silica and subsequent SiO2 coatings.
Two kinds of novel blue-emitting materials, anthracene-based derivatives, are synthesized by the Suzuki coupling reaction. It is worth noting that the maximum emission wavelengths of the two materials are 441 and 444 nm in tetrahydrofuran and 456 and 454 nm in film states, which are the typical blue fluorescence and the fluorescence quantum yields of them are 0.87 and 1.12 by using 9,10-diphenylanthracene (Φf=0.90) as a calibration standard. The full width at half maximum of them are 56, 55 nm in solution, respectively, presenting good color purity. Both of them display superior thermal properties and electrochemical properties. Scanning electronic microscope results show that the films of two compounds are continuous, compact, and smooth after 100°C for 3 h. These data indicate their potential to be prepared for high efficiency and long operation lifetime organic light-emitting diodes devices.
The bit error rate performance of non-line-of-sight ultraviolet communication through atmospheric turbulence is studied. The communication performance degradation under different strengths of turbulence is evaluated. Particularly, under strong turbulence conditions, the communication distance can be shortened by 30%, or at a given distance the communication rate can be reduced by half than the counterpart of no turbulence.
The stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm is widely used in wavefront sensor-less adaptive optics (WSAO) systems. However, the convergence is relatively slow. Modal-based algorithms usually provide much faster convergence than SPGD; however, the limited actuator stroke of the deformable mirror (DM) often prohibits the sensing of higher-order modes or renders a closed-loop correction inapplicable. Based on a comparative analysis of SPGD and the DM-modal-based algorithm, a hybrid approach involving both algorithms is proposed for extended image-based WSAO, and is demonstrated in this experiment. The hybrid approach can achieve similar correction results to pure SPGD, but with a dramatically decreased iteration number.
A surface defect evaluation system can combine microscopic scattering dark-field imaging with sub-aperture scanning and stitching. Thousands of sub-apertures are involved; mechanical errors will cause stitching dislocation, leading to defect cracks. In this Letter, we propose standard line coordinate error adjustment dealing with consistency error between coordinates of the scanning and imaging system, and defocus depth estimation leveling method dealing with high-cleanliness fine optics defocuing caused by the surface which is not perpendicular to microscope’s optical axis. Experiments show defect cracks are effectively solved and the defocus of 420 mm×420 mm components can be controlled within depth of field 20 μm.
In this Letter, we present a possible methodology to directly “read” the force on an atom via the photons emitted from the atom. In this methodology, the mean radiative force on an atom exerted by external fields can be expressed as a function of the average number of emitted photons N and its derivatives via the generating function approach developed by us recently.
Refractive indices for crystals ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), 30% deuterated ADP (DADP), 50% DADP, and 70% DADP are measured from 253 to 1529 nm with 5×10 6 accuracy. Numerical fits to modified double-pole Sellmeier equation are made. Second-harmonic generation, third-harmonic generation phase matching (PM) angles, and noncritical PM (NCPM) wavelengths are calculated using the Sellmeier parameters. The deuterated crystals show smaller PM angles than pure crystal. Fourth-harmonic generation process can be realized by DADP in smaller deuterium content than deuterated potassium dihydrogen phosphate (DKDP). The measured NCPM wavelengths are consistent with the calculated value. PM characteristics are compared between DADP and DKDP.
We report on the rich dynamics of two-dimensional fundamental solitons coupled and interacting on the top of an elliptical shaped potential in a two-dimensional Ginzburg–Landau model. Under the elliptical shaped potential, the solitons display unique and dynamic properties, such as the generation of straight-line arrays, emission of either one elliptical shaped soliton or several elliptical ring soliton arrays, and soliton decay. When changing the depth and sharpness of the external potential and fixing other parameters of the potential, various scenarios of soliton dynamics are also revealed. These results suggest some possible applications for all-optical data-processing schemes, such as the routing of light signals in optical communication devices.
Adaptive optics (AO) systems greatly improve the resolution of retinal imaging instruments by actively correcting ocular aberrations. In this Letter, closed-loop correction as well as ocular aberration compensation of a 62-element silicon unimorph deformable mirror (DM) driven by only positive voltage is performed. The experimental results show that the root-mean square (RMS) wavefront of the initial mirror surface is reduced to 0.011 μm in a closed-loop AO system. The DM reproduces Zernike shapes from the third to 35th mode accurately. The simulated compensation of 200 ocular wavefronts shows that the average RMS value after correction is reduced to 0.017 μm.
A transfer method is introduced to derive the normalized radiance for CE318 Sun/sky radiometer using viewing solid angles and extraterrestrial calibration constants. The new transfer method has a good consistency at different parts of the sky scanning. Error analysis suggests that the uncertainty of the transferred method is about 2.0%–2.4%. The normalized radiances are used as input of the aerosol inversion to test the performance of the new transfer method. The residuals of the inversion (e.g., difference between fitted and measured radiance) are chosen as the index of the radiance calibration accuracy. Analyses of one year’s measurements in Beijing suggest an average sky residual of 3.3% for almucantar scanning (while 3.7% for the AERONET method), which suggest a better accuracy of the transfer method when used in aerosol retrieval.
Nonlinear dynamics in an optoelectronic delayed feedback semiconductor laser and its application in sensing are studied. We analyze the theories of stability and period of the laser. A route to quasi-periodic bifurcation or a stochastic state from stability is numerically analyzed by shifting the feedback level. The induced dynamics are found to be in one of four distributions (stable, periodic pulsed, period-three pulsed, and undamping oscillating). An external injection into the laser results in the process being more or less the opposite with the conventional optical injection cases. Based on this process or the dynamic regimes, we present a modeling of the incoherent detection sensor using the nonlinear period-one characteristic of the laser. The sensor discriminates the injection light variation as a sensing signal via detecting the behaviors from the period-one laser.
Signal distortion due to the non-uniform response of the detector degrades the measurement accuracy of most metrology instruments. In this Letter, we report a newly developed calibration source system for reference-based non-uniformity correction using a laser source, a fiber, and a diffusive module. By applying the Monte Carlo simulation, we show that the transmittance of the system highly depends on the cavity reflection of the diffusive module. We also demonstrate the use of this system to achieve a flat field at a very low non-uniformity (less than 0.2%) with proper illumination intensity, which most costly commercial integrating sphere systems traditionally cannot provide.
A static-mode synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) in which the target and carrying platform are kept still during the collection process is proposed and demonstrated. A target point of 0.5 mm×0.5 mm and a two-dimensional (2D) object are reconstructed in the experiments, in which an optical collimator with a focal length of 10 m is used to simulate the far-field condition. The achieved imaging resolution is in agreement with the theoretical design. The static-mode down-looking SAIL has the capability to eliminate the influence from the atmospheric turbulence and can be conveniently operated outdoors.