View fulltext
View fulltext
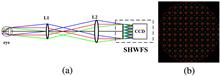
In order to detect the aberration from a wide field of view (FOV) on the retina with adaptive optics, we present a multiple-object Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor (MOSHWFS) design. The simulated results indicate that the wavefront from our MOSHWFS can be reconstructed for multiple objects, and the measurement error can be less than λ/7 with an MOSHWFS with an FOV of 6.7°, for maximum eye aberration. The experimental result with two objects indicates that the measurement error can be less than λ/14, with the root mean square of the reference wavefront as 0.798λ and 0.895λ, respectively.
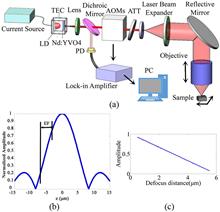
A new optical method based on frequency-shift feedback and laser confocal microscopy is presented to noninvasively measure a microstructure inside a sample. Due to the limit of axial resolution caused by poor signal detection ability, conventional laser feedback cannot precisely measure the microstructure. In this Letter, the light scattered by the sample is frequency shifted before feedback to the laser to obtain a magnification. Weak signals that change with the microstructure can be detected. Together with the tomography ability of laser confocal microscopy, the inner microstructure can be measured with high axial resolution.
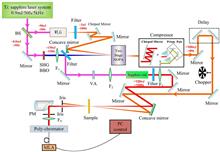
We report the experimental demonstration of transform-limited sub-6 fs pulses at an optimal central wavelength by a tunable noncollinear optical parametric amplification (NOPA) source. Meanwhile, a white light continuum in the near-infrared (NIR) range from 900 to 1100 nm is also successfully generated by focusing the unconverted 800 nm beam during NOPA generation on a sapphire rod. Both visible-pump/visible-probe and visible-pump/NIR-probe experiments are realized using the same laser system. As examples, ultrafast photo-induced exciton dynamics inside two kinds of materials are investigated by the visible-pump/visible-probe and visible-pump/NIR-probe spectroscopy, respectively.
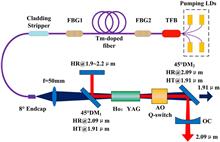
A high-power, high-energy Ho:YAG oscillator resonantly pumped by a Tm-doped fiber laser is presented. A maximum continuous output power of 38 W with a slope efficiency of 51.9% is achieved at the wavelength of 2.09 μm, and M2≈1.48. In the Q-switching regime, the maximum pulse energy of 12.8 mJ, corresponding to a 514.5 kW peak power, is obtained at the pulse repetition frequency of 1 kHz. Furthermore, the thermal lens effect of the system is studied theoretically, and the radius of the transverse electromagnetic (TEM00) mode of the laser crystal under different pump powers is given.
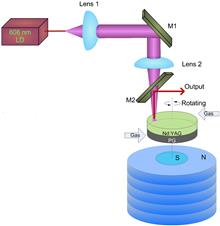
We propose and demonstrate a laser-diode-pumped, maglev rotating Nd:YAG disk laser. The disk of the laser crystal is attached to a maglev pyrolytic graphite disk and is rotated by compressed gas. In this rotating disk laser, the detrimental thermal effects are alleviated and the laser can be operated in the single transverse electromagnetic (TEM)00 mode with high brightness. In our proof-of-concept experiment, we achieve a 17.7 mW laser output at 447 mW of absorbed pump power and a ~4 Hz rotation frequency.
This Letter proposes a brand-new filament diameter measurement method based on what is called “dual diffraction,” in that a grating is added behind the filament to make full use of its subdivision and amplification characteristics. Higher measurement accuracy is achieved by this method compared with the traditional diffraction method. To verify its accuracy, three standard filaments with nominal values of 100.2, 120.1, and 140.8 μm are measured by the dual diffraction method and traditional diffraction method under the same experimental conditions. The relative measurement errors of the new method are less than 0.75%, and its average relative error is reduced by 56% compared with the traditional diffraction method.
In this Letter, we propose a method of fabricating linear variable filters by ion beam etching with masking mechanisms. A triangle-shaped mask is designed and set between the ion source and sample. During the ion etching, the sample is moved back and forth repeatedly with a constant velocity for the purpose of obtaining the linearly varied thickness of the cavity. Combined with ion beam assistant thermal oxidative electron beam evaporation deposition technology, we finish the fabrication of linear variable filters, whose filtering range is from 500 to 580 nm. The measured results indicate that the transmittance and bandwidth at the peak wavelength are around 40% and 3 nm.
A combination of light-emitting diode (LED) identification and a time-division multiplexing scheme is proposed in this Letter for indoor location-based service. With the scheme, the arrangement of white LED lamps and the structure of a data frame are designed to realize high-accuracy indoor positioning and location-based payload data transmission simultaneously. The results of the experiment demonstrate that the indoor positioning accuracy is 10 cm and 2 Mb/s data transmission with high signal quality is realized.
This Letter presents intrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometers in the fiber tapers fabricated by the femtosecond laser micromachining technique. The sensing of temperatures as high as 1000°C based on the fiber device is characterized, with a sensitivity of 15.28 pm/°C. A nearly linear refractive index sensing is also obtained by using the fringe visibility to characterize, with a sensitivity of 73.05 dB/RIU. These intrinsic Fabry–Perot interferometers in fiber tapers may be useful in applications of high-temperature and linear refractive index sensing.
The existing two-dimensional vision measurement methods ignore lens distortion, require the plane to be perpendicular to the optical axis, and demand a complex operation. To address these issues, a new approach based on local sub-plane mapping is presented. The plane calibration is performed by dividing the calibration plane into sub-planes, and there exists an approximate affine invariance between each small sub-plane and the corresponding image plane. Thus, the coordinate transformation can be performed precisely, without lens distortion correction. The real comparative experiments show that the proposed approach is robust and yields a higher accuracy than the traditional methods.
The distribution of a modulated squeezed state over a quantum channel is the basis for quantum key distribution (QKD) with a squeezed state. In this Letter, a modulated squeezed state is distributed over a lossy channel. The Wigner function of the distributed state is measured to observe the evolution of the quantum state over a lossy channel, which shows that the squeezing level and the displacement amplitude of the quantum state are decreased along with the increase of the channel loss. We also measure the squeezing level in the frequency domain by the frequency shift technique. The squeezing of the modulated squeezed state at the modulation frequency is observed in this way. The presented results supply a reference for a QKD with a squeezed state.
In this Letter, new concepts of fluorescence phase-change materials and fluorescence phase-change multilevel recording are proposed. High-contrast fluorescence between the amorphous and crystalline states is achieved in nickel- or bismuth-doped Ge2Sb2Te5 phase-change memory thin films. Opposite phase-selective fluorescence effects are observed when different doping ions are used. The fluorescence intensity is sensitive to the crystallization degree of the films. This characteristic can be applied in reconfigurable multi-state memory and other logic devices. It also has likely applications in display and data visualization.
Research on light scattering from a large chiral sphere shows that the rainbow phenomenon is different from that of an isotropic sphere. A chiral sphere with certain chirality generates three first-order rainbows. In this Letter, we present a geometric optics interpretation for the phenomenon and make a calculation of the rainbow angles. The ray traces inside the sphere are determined by the reflection and refraction laws of light at the achiral–chiral interface and the chiral–achiral interface. The calculated rainbow angles achieve good agreements with those obtained by the analytical solutions. The effects of chirality and the refractive index of the sphere on rainbow angles are analyzed.
In our investigation, lead germanium telluride, which is a pseudo-binary alloy of IV-VI narrow-gap semiconductor compounds of PbTe and GeTe, can be used in the fabrication of mid-wavelength infrared narrow bandpass filters as a high-index coating material, due to its high refractive index, lower absorption, and tunability of fundamental absorption edges. It is demonstrated that a half-width of 160 nm and a better rejection ratio can be obtained for a simple 8-layer double cavity filter with a central wavelength at 4 μm, compared with a half-width of 390 nm for those conveniently fabricated using Ge as high-index material.
The influence of group velocity dispersion (GVD) on the self-focusing of femtosecond laser pulses is investigated by numerically solving the extended nonlinear Schr?dinger equation. By introducing the GVD length LGVD into the semi-empirical, self-focusing formula proposed by Marburger, a revised one is proposed, which can not only well explain the influence of GVD on the collapse distance, but also is in good agreement with the numerical results, making the self-focusing formula applicable for more cases.
In this Letter, we investigate a method for controlling the intensity of a light by another light in a periodically poled MgO-doped lithium niobate (PPMgLN) crystal with a transverse applied external electric field. The power of the emergent light can be modulated by the power ratio of the incident ordinary and extraordinary beams. The light intensity control is experimentally demonstrated by the Mach–Zehnder interference configuration, and the results are in good agreement with the theoretical predictions.
Pulsed collimated blue light at 420.3 nm is generated in hot Rb vapor by upconverting the 778.10 nm pumping beam through four wave mixing process. The energy conversion efficiency exceeds 1% when a 45 cm-long, 170°C heated Rb cell is used. The influence of cell temperature, wavelength, and energy of a pumping laser are fully examined. The efficiency of the photon conversion is found to be more sensitive to the blue detuning of the pump light and less sensitive to the red detuning of the pump light. This phenomenon can be explained by stimulated hyper-Raman scattering involved in the four-wave mixing process.
We propose and demonstrate a pseudo Fabry–Pérot filter in the terahertz frequency range of 0.1–0.5 THz. It consists of alternative liquid crystal layers and metallic slats. Separate sharp resonant peaks are shown in the simulated transmission spectra, and their positions shift toward higher frequencies when the refractive index of liquid crystal decreases. The measured transmission spectra are consistent with corresponding simulations. Via thermally tuning the refractive index of the filled liquid crystal, the resonant transmission frequencies shift accordingly. The work supplies a novel design for tunable terahertz filters, which would play important roles in terahertz imaging, sensing, high speed communication, and security applications.
We investigate the reflected field for few-cycle ultra-short laser pulses propagating through resonant media embedded within wavelength-scale structures. Full-wave Maxwell–Bloch equations are solved numerically by using the finite-difference time-domain method. The results show that the spectral feature of the reflected spectrum is determined by the Bragg reflection condition, and that the periodic structure of a dense atomic system can be regarded as a one-dimensional photonic crystal and even as a highly reflective multilayer film. Our study explains the suppression of the frequency shifts in the reflected spectrum based on the Bragg reflection theory and provides a method to control the frequency and frequency intervals of the spectral spikes in the reflected spectrum.
A second generation solar adaptive optics (AO) system is built and installed at the 1-m New Vacuum Solar Telescope (NVST) of the Fuxian Solar Observatory (FSO) in 2015. The AO high-order correction system consists of a 151-element deformable mirror (DM), a correlating Shack–Hartmann (SH) wavefront sensor (WFS) with a 3500 Hz frame rate, and a real-time controller. The system saw first light on Mar. 16, 2015. The simultaneous high-resolution photosphere and chromosphere images with AO are obtained. The on-sky observational results show that the contrast and resolution of the images are apparently improved after the wavefront correction by AO.