View fulltext
View fulltext
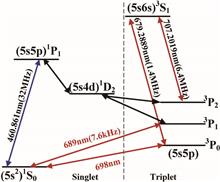
We report experiments on the observation of the S01 P03 transition spectrum of Sr88 in the Lamb-Dicke regime. After going through a two-stage magneto-optical trap (MOT), Sr88 cold atoms with number of about 1×105 and a longitudinal temperature of 8.4 μK are loaded into a one-dimensional (1D) optical lattice, which is realized with a semiconductor laser at 813.4 nm. Using the magnetic field-inducing P13 state mixing into P03 state, the spectroscopy of the S01 P03 transition with a linewidth of 180 Hz is detected.
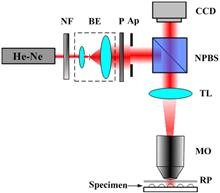
We present a Fizeau interferometer using a microscopic objective as a tool for surface contouring without the need for a numerical lens for reconstruction. The interferometer is associated with a telescope system to feature the object with collimated light. The experiment is conducted on two objects possessing different step heights. The phase maps from the captured off-axis holograms are calculated numerically, which allows us to deduce the contours of the objects. The great advantages of the presented technique are that it can be done in real time and there is no need for numerical lenses for micro-objects reconstruction.
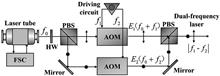
A beam combination setup for a dual-frequency laser with orthogonal linear polarization is proposed. It consists of two polarizing beam splitters (PBSs) whose polarization axes are orthogonal to each other. A theoretical analysis demonstrates that a combined dual-frequency laser beam with this setup strictly meets orthogonal linear relation. The experimental results show that compared with the conventional setup, the ellipticity and nonorthogonality of the combined dual-frequency laser beam are significantly reduced.
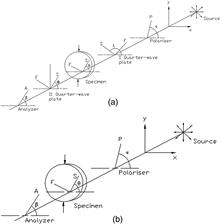
A method for isochromatic determination in three-fringe photoelasticity is presented. It combines the phase-shifting method with cubic polynomial curve-fitting technology to eliminate the errors caused by color repetition. We perform a demonstration of the method on a circular disc subjected to compressive loading and an injection-molded cover with residual stresses. The test results compare well with the theoretical results.
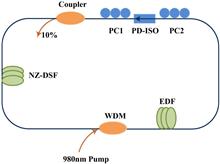
We experimentally and numerically demonstrate the generation of square pulses without any wave-breaking in a fiber ring laser. A segment of nonzero dispersion-shifted fiber is used to increase the laser cavity length and to optimize the parameters of the laser cavity. In the experiment, the pulse width can be tuned in a wide range from 13.5 to 119.5 ns without wave-breaking while the peak power remains almost constant. The maximum single-pulse energy is up to 65.58 nJ at a pump power of 508 mW. Numerical results are in good agreement with the experimental results. Numerical results also reveal the role of cavity length and nonlinearity in generating a square pulse without pulse breakup.
In this Letter, we demonstrate a diode-pumped electro-optical cavity-dumped Tm:YAP laser for the first time to our knowledge. A pulse width of 7.1 ns is achieved at a wavelength of 1996.9 nm. A maximum output power of 3.02 W is obtained with a pump power of 58.8 W at a repetition rate of 100 kHz and a high-voltage time of 1000 ns, corresponding to an overall optical-to-optical conversion efficiency of 5.2%. In addition, we study the effect of repetition rate and high-voltage time on the output power characteristics of a cavity-dumped Tm:YAP laser.
A symmetrical heterodyne grating interferometer with both a short period and high signal-to-noise ratio is proposed. It possesses good immunity to environmental disturbances and can simultaneously achieve high resolution and stability. The experimental results show that the standard deviation of 24.67 nm can be realized for the long range of 10 mm. The measurement resolution of better than 2 nm is achieved with the theoretical resolution of 12 pm. Additionally, system stability at less than ±1.5 nm is obtained in just over 10 min. The measurement errors, including cosine error, nonlinear error and non-common path error, are discussed as well.
We propose and demonstrate free-space optical data links based on coaxial sidelobe-modified optical vortices (CSMOVs). In contrast to the optical communication systems based on amplitude, frequency, or phase detection, the proposed scheme uses the radii ratio between the principle ring and the first sidelobe of the CSMOV. Therefore, the demand of stringent alignment and/or accurate phase matching is released. We design and optimize a composite computer-generated hologram to generate a CSMOV with four topological charges (TCs). Extracted from the images captured by a CCD camera, the radii ratio between the principle ring and the first sidelobe of different TCs are consistent with the theoretical values.
In this Letter, a sensor consisting of a fiber Bragg grating (FBG) and a fiber Fabry–Perot interferometer (FFPI) sensor is developed to measure the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and the thermo-optical coefficient (TOC) of a silica-based optical fiber at cryogenic temperatures. The FFPI is fabricated by welding together two acid-etched fibers. The temperature performance of the FFPI-FBG hybrid sensor is studied in the temperature range of 30–273 K. The CTE and TOC of the optical fiber at cryogenic temperatures are derived analytically and verified by experiments.
We propose a two-cascaded, constant-resistance, symmetrical bridged-T amplitude equalizer for a high-speed visible light communication (VLC) system. With the pre-equalization circuit, the 3 dB bandwidth of the VLC system can be extended from 12 to 235 MHz using a commercially available phosphorescent white light-emitting diode (LED), a blue filter, and a low-cost PIN photodiode. The data rate is 1.20 Gbit/s, exploiting 16-quadrature amplitude modulation-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing with a 300 MHz modulation bandwidth over 50 cm of free-space transmission under the pre-forward error correction limit of 3.8×10 3. To our knowledge, this is the highest 3 dB bandwidth and the highest data rate ever achieved by using a pre-equalization circuit and white LED in a VLC system.
A novel distributed passive vehicle tracking technology is proposed and demonstrated. This technology is based on a phase-sensitive optical time domain reflectometer (Φ-OTDR) that can sense and locate vibrations. Two algorithms, dynamic frequency-space image and 2D digital sliding filtering, are proposed to distinguish a car’s moving signals from severe environmental noises and disturbances. This technology is proved effective by field experiments for tracking a single car and multiple cars. This work provides a new distributed passive way for real-time vehicle tracking and this technology will be extremely important for traffic controlling and public safety in modern society.
In this Letter, we develop the Stokes space-based method for modulation format identification by combing power spectral density and a cluster analysis to identify quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) and phase-shift keying (PSK) signals. Fuzzy c-means and hierarchical clustering algorithms are used for the cluster analysis. Simulations are conducted for binary PSK, quadrature PSK, 8PSK, 16-QAM, and 32-QAM signals. The results demonstrate that the proposed technique can effectively classify all these modulation formats, and that the method is superior in lowering the threshold of the optical signal-to-noise ratio. Meanwhile, the proposed method is insensitive to phase offset and laser phase noise.
Photoacoustic imaging with a synthetic aperture focusing technique (SAFT) is an effective method to improve the lateral resolution for out-of-focus regions in scanning microscopy systems, which commonly require a decent motorized scanning stage for a lateral scan of a transducer to obtain a cross-sectional image. In this study, we propose and test a photoacoustic imaging system with a scanning mirror-based SAFT (SM-SAFT) for simple and fast data acquisition, without the need for a physical scan of the transducer. Photoacoustic images of hair phantoms acquired by SM-SAFT are demonstrated, serving as a proof-of-concept experiment to show the feasibility and potential of the proposed approach.
In this Letter, we discuss Raman–Nath acousto-optic diffraction, and a new model of Raman–Nath acousto-optic diffraction is presented. The model is based on the individual and simultaneous occurrences of phase-grating diffraction and the Doppler effect and optical phase modulation and photon–phonon scattering. We find that the optical phase modulation can cause temporal and spatial fluctuations of the diffracted light power escaping from the acoustic field.
A polarization-insensitive, square split-ring resonator (SSRR) is simulated and experimented. By investigating the influence of the asymmetrical arm width in typical SSRRs, we find that the variation of the arm width enables a blue shift of the resonance frequency for the 0° polarized wave and a red shift of the resonance frequency for the 90° polarized wave. Thus, the resonance frequency for the 0° polarized wave and the resonance frequency for the 90° polarized wave will be identical by asymmetrically adjusting the arm width of the SSRR. Two modified, split-ring resonators (MSRRs) that are insensitive to the polarization with asymmetrical arm widths are designed, fabricated, and tested. Excellent agreement between the simulations and experiments for the MSRRs demonstrates the polarization insensitivity with asymmetrical arm widths. This work opens new opportunities for the investigation of polarization-insensitive, split-ring resonator metamaterials and will broaden the applications of split-ring resonators in various terahertz devices.
Zinc strontium phosphate glasses doped with different trivalent praseodymium ion (Pr3+) concentrations are presented and their photoluminescence properties are investigated upon 442 nm excitation. With the Pr3+ concentration decreasing, the orange emission of Pr3+ (D21 HJ3) is enhanced steadily at the cost of its blue emission (P1,03 H43). Monochromic orange emission of Pr3+ ions is obtained when the Pr3+ doping is reduced to 0.05 mol.%. The mechanism controlling the monochromatic characteristic of Pr3+ emissions is supposed to be associated with the phonon-aided nonradiative relaxation process of Pr3+: Pj3→</mml:mo
A number of zinc oxide (ZnO) films are deposited on silicon substrates using the magnetron sputtering method. After undergoing thermal treatment under different conditions, those films exhibit hexagonal wurtzite structures and different photoluminescent characteristics. Besides the notable ultraviolet emission, which is related to the free exciton effect, a distinct blue fluorescence around 475 nm is found in some special samples. The blue photoluminescence emission of the ZnO film is believed to be caused by oxygen vacancies.
We demonstrate a large-mode-volume transverse-electric-polarized λ/4 shifted distributed feedback (DFB) cavity on silicon-on-insulator (SOI). A 2.86 mm-long DFB cavity with sidewall corrugation on the ridge is fabricated on a silicon rib waveguide. The cavity structure is designed to enlarge both the longitudinal and transversal mode profiles of the cavity to enclose more luminescent media. Design strategies are verified by both finite difference time domain simulation and experiments. A linewidth of 69 pm and an extinction ratio of 15 dB is obtained, indicating not only the well confinement of the longitudinal mode, but also its well stretching to the cavity ends. The mode volume is 75.39 μm3.
In this Letter, silver (Ag) hierarchical nanostructures grown on black silicon (BS) are used as the catalyst and a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) detector integrated in a microfluid. The BS is fabricated via femtosecond laser ablation in an atmosphere of sulfur hexafluoride, and then hydrogenated with hydrofluoric acid. As formed, the BS substrate directly acts as a reducing template to grow silver hierarchical nano-structures. Particularly, Ag-BS composite micro/nano-structures can be in-situ constructed in silicon-based microchannels. These structures simultaneously serve as integrated catalytic reactors and a SERS substrate for sensing. The sensitivity is tested to be as low as 10 8 mol/L using Rhodamine 6G.
Using the first-principles method based on the density functional theory (DFT), the work function of seven different GaN (0001) (1×1) surface models is calculated. The calculation results show that the optimal ratio of Cs to O for activation is between 3∶1 and 4∶1. Then, Cs/O activation and stability testing experiments on reflection-mode negative electron affinity GaN photocathodes are performed. The surface model [GaN (Mg): Cs] Cs-O after being activated with cesium and oxygen is used. The experiment results illustrate that the adsorption of O contained in the residual gas increases the surface potential barrier and the reduction of the effective dipole quantity is the basic cause of the quantum efficiency decay.
The far-zone scattered spectral density of a light wave on the scattering from a collection of particles is investigated, and the relationship between the character of the collection and the distribution of the scattered spectral density is discussed. It is shown that both the number of particles and their locations in the collection play roles in the distribution of the far-zone scattered spectral density. This phenomenon may provide a potential method to reconstruct the structure character of a collection of particles from measurements of the far-zone scattered spectral density.