 View fulltext
View fulltext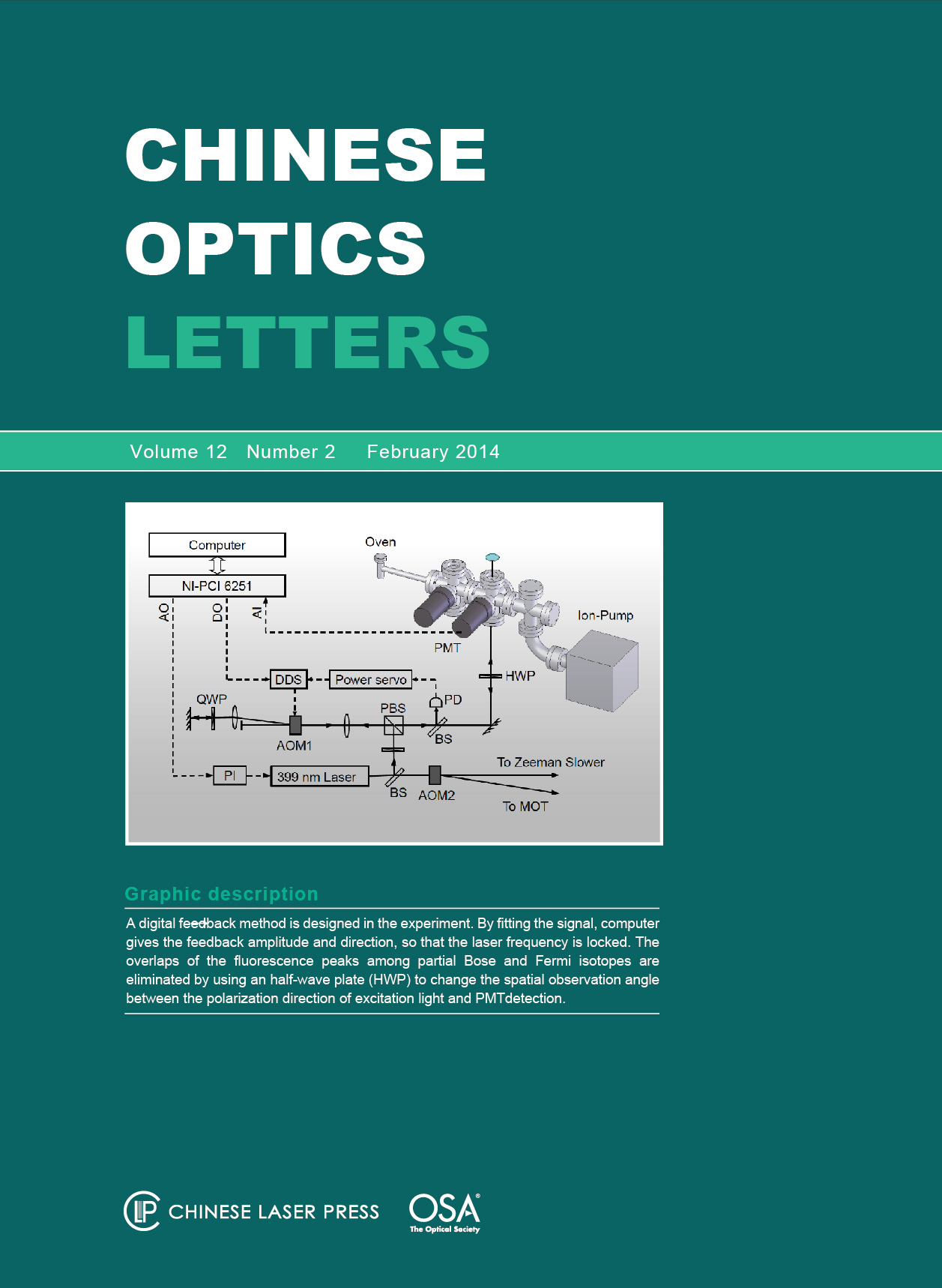
We design two types of reflectors by using subwavelength high-index contrast gratings, which exhibit similar high focusing capabilities at normal incidence with a TE-polarized plane wave. One type has bars of different heights, whereas the other has bars of different depths. Both grating reflectors are designed to be approximately 22 \mu m in structural length and 10 \mu m in focal length, at an operating wavelength of 1.55 \mu m. Both achieve a full-width-half-maximum of 0.9 \mu m at the focal plane, which is fairly close to the diffraction limit. Their reflectance reach as high as 94% and 91%.
We propose a polarization-insensitive and broadband subwavelength grating reflector based on a multilayer structure. The reflector has an overlapped high reflectivity (>99.5%) bandwidth of 248 nm between the TE and the TM polarizations, which is much higher than the previously reported results. We believe this subwavelength grating reflector can be applied to unpolarized devices.
The laser source is an important element whose properties have influence on the output performance of single sideband (SSB) optical comb based on recirculating frequency shifter (RFS). The theoretical and experimental results show that the tone-to-noise ratio (TNR), flatness, and stability of optical comb improve using laser source with narrower linewidth. In order to obtain the optical comb with TNR larger than 42 dB and degree of stability (DOS) smaller than -6.7 dB, external cavity laser (ECL) with linewidth from 100 kHz to 1 MHz is a trade-off choice.
A photonic generation of multi-frequency source based on the heterodyne of two phase-locked optical frequency combs (OFCs) is proposed and demonstrated. By applying an optical phase-locked loop, the phase noise induced by optical links is decreased by approximately 70, 66, and 35 dB at 0.01, 0.1, and 1.0 Hz offset frequencies, respectively. The proposed scheme provides 8 radio frequency signals, the frequencies of which span from 540 to 4040 MHz, with a 500-MHz interval. The number of generated signals can be readily scaled by using OFCs with broader bands, whereas the frequencies can be scaled by tuning the repetition rates of OFCs.
We construct a dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)-based photonic crystal fiber (PCF) temperature sensor with enhanced sensitivity. A solid-core PCF with large mode area is employed to supply the in-line Mach-Zehnder interference between the fundamental and cladding modes. Thus, temperature sensing can be realized because of the shift of interference spectrum at different temperatures.The DMSO solvent is infiltrated between the main sensor and a silica tube to increase the temperature sensitivity of the sensor. The obtained sensitivity (0.315 nm/oC) is one or two orders of magnitude higher than that of previously published results. The proposed sensor is adapted for high-temperature sensing.
A simple optical fiber cantilever vibration sensor consisting of two opposite aligned bare optical fibers sealed in a quartz capillary is presented.The fiber with the longer bare section is suspended in air and acts as a cantilever. By detecting the transmission power of the sensor directly, the environmental vibrational frequencies and amplitudes may be obtained. By adjusting the cantilever's natural deflection angle, the sensor can achieve high sensitivity, good response linearity, and a wide dynamic range. Coupling conditions are optimized to minimize temperature effects by simply setting an appropriate air gap between the bare fibers.
A simple configuration for the generation of a switchable dual-wavelength fiber ring laser is presented. The proposed configuration employs a short twin-core photonic crystal fiber acting as a Mach–Zehnder interferometer at room temperature. A polarization controller is further utilized to enable switchable dualwavelength operation.
The laser cooling of ytterbium (Yb) atoms needs a 399-nm laser which operates on the strong 1S0 -1P1 transition and can be locked at the desired frequencies for different Yb isotopes. We demonstrate a frequency locking method using the fluorescence spectrum of an Yb atomic beam as a frequency reference. For unresolved fluorescence peaks, we make the spectrum of the even isotopes vanish by using the strong angular-dependence of the fluorescence radiations; the remained closely-spaced peaks are thus clearly resolved and able to serve as accurate frequency references. A computer-controlled servo system is used to lock the laser frequency to a single fluorescence peak of interest, and a frequency stability of 304 kHz is achieved. This frequency-locked laser enables us to realize stable blue magneto-optic-traps (MOT) for all abundant Yb isotopes.
We present a high-precision optical phase-locking based on wideband acousto-optical frequency shifting. Increasing the modulating bandwidth stabilizes the loop at a high loop gain, thus improving phase correction capability. An optical phase-locked loop with a wide control bandwidth is constructed. The closed-loop residual phase error is only 0.26o or smaller than \lambda/1000. The loop exhibits excellent correction capability for high-frequency noises. The correctable frequency range reaches 35 kHz when the noise amplitude is +(-)\lambda/2, and becomes even wider for smaller noise amplitudes.
A non-adiabatic microfiber coupler is fabricated by flame brushing technique and then theoretically and experimentally analyzed. The effective length of the microfiber coupler is determined by simulation, and a low-noise laser is demonstrated using various lengths of erbium-doped fiber (EDF) when incorporated in a laser setup. At 18.6-mW input pump power, the maximum output power of 20 \mu W and the lowest lasing threshold of 3.8 mW are obtained with a 90-cm-long EDF.
A compact monolithic Nd:YAG non-planar ring laser with diffusion-bonded Cr4+:YAG is demonstrated, and high stable pulsed single-frequency laser at 1.06 \mu m is realized. Theoretical analysis and simulation results of pulsed laser parameters are illustrated. 14.96-kW maximum peak power, pulse-width of 4.8 ns is achieved for single-frequency operation.
A passively Q-switched tunable Yb-doped double-clad fiber laser is demonstrated with graphene epitaxially grown on SiC. The spectral tuning of the Q-switched fiber laser is implemented by rotating a quartz plate filter inside the cavity. The central wavelength of the fiber laser can be continuously tuned from 1038.54 to 1056.22 nm. The maximum pulse energy of 0.65 \mu J is obtained at the pump power of 4.08 W, and the corresponding pulse duration and average output power are 1.60 \mu s and 35 mW, respectively.
Mid-infrared (MIR) emissions of 2.4 and 3.5 m from Tm3+:LiYF4 single crystals attributed to 3H4->3H5 and 3H5->3F4 transitions as well as MIR emissions of 4.2, 4.3, and 4.5 \mu m from Nd3+: LiYF4 lasers attributed to 4I15/2->4I13/2,4I13/2->4I11/2, and 4I11/2->4I9/2 transitions, respectively, are observed. LiYF4 single crystals possess high transmittance of over 85% in the 2.5-6 \mu m range. The large emission crosssections of Tm-doped crystals at 2.4 \mu m (1.9\times 10-20 cm2) and Nd-doped crystals at 4.2 \mu m (0.84\times 10-20cm2) as well as the high rare-earth doping concentrations, excellent optical transmission, and chemicalphysical properties of the resultant samples indicate that Nd3+ and Tm3+ singly doped crystals may be promising materials for application in MIR lasers.
We theoretically study the light outcoupling efficiency of top-emitting organic light-emitting diode (OLED) with inverted structure and thin-film encapsulation. Thin-film optics is used to optimize the layer thickness to obtain high transmittance. Dipole mode is used to analyze the light outcoupling efficiency of the top-emitting OLED. Through this process, we can optimize the thin-film thickness with high transmittance and optimize the outcoupling efficiency of OLED. Compared with previous research, the current design method is a novel process.
A numerical simulation is performed to study the far-field diffraction properties of planar diamond waveguides. The far-field intensity distributions of a planar air waveguide and a diamond waveguide with different distances are given by numerical calculations. In the experiment, the diffraction patterns on the screen with different distances are recorded using a He-Ne laser as the light source, wherein the laser beam is coupled with and propagates in the diamond waveguide. The simulation results are found to be consistent with the experimental ones.
A new method based on Maxwell's equations, ABCD ray matrices, and total internal reflection is proposed to theoretically analyze the characteristics of eigenmodes confined in nano-width rectangle resonators. Using this method, mode wavelengths and indices of transverse and longitudinal modes are obtained. Another method based on the finite difference time domain technique and Pad′e approximation is used to numerically calculate resonant wavelengths, mode field distributions and quality factors. The results of two methods show that the resonant wavelengths obtained from both methods are very close, and the maximum relative error is less than 2%. The mode indices of transverse and longitudinal modes obtained agree well with mode field distribution patterns calculated by finite difference time domain techniques.
A phase retrieval method for dual-wavelength in-line digital holography is presented with double axially displaced holograms. A synthetic wavelength is used during iterative propagations to retrieve wrap-free phase distributions with a much extended measurement range. The simulation and experimental results demonstrate a better elimination of the twin image, a faster rate of convergence of the iterative routine and less number of wavelengths are compared with previously reported multiple-wavelength in-line holography.
A psychophysical experiment under constant stimuli is conducted on a CRT display to measure the visual suprathreshold color differences for five color centers recommended by CIE under the same five background colors. The performances of four CIELAB-based, three CIECAM02-based, and two OSA-UCS-based formulas are tested. Detailed analysis results indicate the existence of chromatic crispening effect. CIEDE2000 performs best for the gray center and gray background, whereas CAM02-LCD and CAM02-UCS have the best performance for non-neutral backgrounds. CAM02-LCD significantly outperforms all other formulas for all color centers under all background colors.
Traditional integral colorimeters use tungsten–halogen or xenon lamps for illumination, as well as correcting filters to make the instrument's spectral response meet the Luther condition. This structure causes the instruments to have relatively higher error and poor repeatability. Thus, this letter proposes a new measurement design that uses compound LEDs as the instrument's measurement light source. The new design adjusts the instrument's spectral response by modifying the spectra of the compound LEDs. A compound LED light source is designed for integral colorimeters, and an experiment is conducted to evaluate the performance of the integral colorimeter. Experiments show that the design effectively reduces the error of integral colorimeters.
The computed tomography imaging of a local region inside a sample with a size larger than the field of view is particularly important for synchrotron X-ray imaging. In this letter, an improved algorithm is proposed to reconstruct the local structure inside a sample using almost completely local data. The algorithm significantly reduces the X-ray radiation dose and improves computational efficiency. Simulation results show that the new algorithm works well and has a higher reconstruction precision than previous methods, as confirmed by experimental results carried out at the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility.










