 View fulltext
View fulltext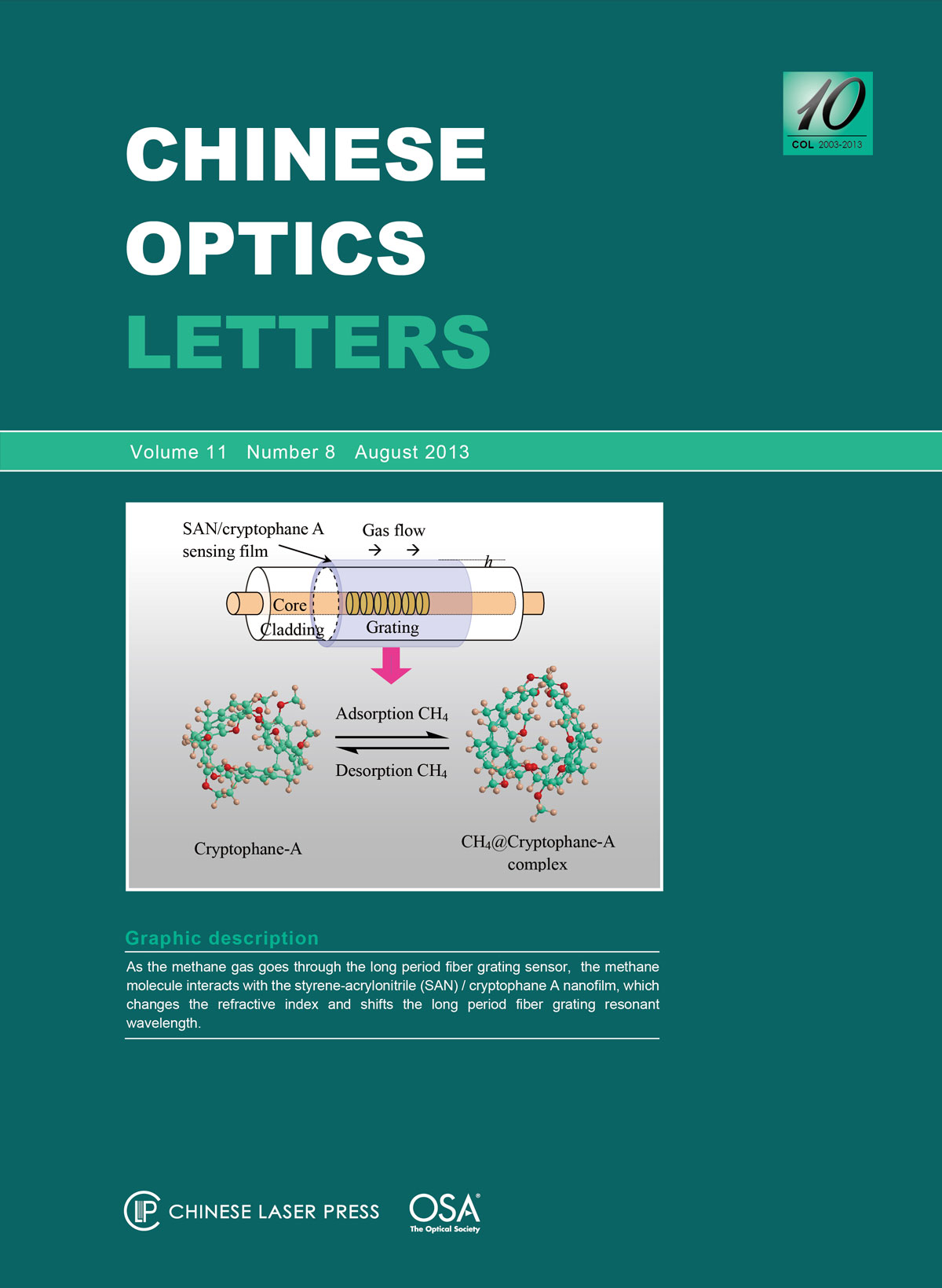
We present a grating imaging scanning lithography system for the fabrication of large-sized gratings. In this technology, +(-)1-order diffractive beams are generated by a phase grating and selected by a spatial filter. Meanwhile, a 4f system enables the +(-)1-order diffractive beams to form a grating image with a clear jagged-edge boundary on the substrate. A high-precision two-dimensional (2D) mobile stage is used for complementary cyclical scanning, thereby effectively eliminating image stitching errors. The absence of such errors results in a seamless and uniform large-sized grating. Characterized by a simple structure, high energy use, and good stability, this lithography system is highly relevant to the high-speed and cost-effective production of large-sized gratings.
A high-sensitivity long-period fiber grating (LPFG) methane sensor that contains a compact and uniform styrene-acrylonitrile (SAN)/cryptophane A nanofilm is presented. The sensor is prepared by using an automatic dip-coater in a solution of cryptophane A, SAN resin dissolved in ortho-dichlorobenzene, a low-volatile solvent. The effect of film thickness on the LPFG's resonant wavelength is thoroughly investigated. The optimum sensor among the three LPFGs with different film thicknesses is directly used to detect the methane concentration in a coal mine gas sample. The results indicate that the sensors with film thicknesses of 484 to 564 nm exhibit a redshifted resonant wavelength when the methane concentration is increased from 0% to 3.5% (vol). The data demonstrates that the sensor with a film thickness of 484 nm has remarkable sensitivity (~0.633 nm%-1), and its detection limit can reach 0.2%. The methane concentrations determined by our sensor are consistent with those obtained by gas chromatography.
The single sideband (SSB) modulation is assessed as a means to mitigate the dispersion-induced power fading on the distribution of ortogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) ultra wideband (UWB) radio signals along long-reach passive optical networks (LR-PONs). Particularly, two different SSB architectures, namely, Sieben's architecture and four phase modulator (FPM) architecture are optimized to provide maximum sideband suppression. The minimum optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) required to simultaneously distribute all the 14 OFDM-UWB sub-bands along the LR-PON distances ranging between 80 and 100 km is also evaluated through numerical simulation. FPM architecture is preferable over Sieben's architecture because the latter SSB architecture generates carriers-carriers beat term at the photodetector output with high power, thereby causing significant degradation in the OFDM-UWB sub-bands with lower central frequencies. The simultaneous distribution of the 14 SSB OFDM-UWB sub-bands in the LR-PON using the FPM architecture shows a minimum OSNR penalty of 3 dB compared with the centralized dispersion compensation technique.
We propose a third-order intermodulation distortion (IMD3) compensation scheme based on the bidirectional modulation of 2-Ch phase modulator (PM). We realize the destructive combination of IMD3 by using different modulation efficiencies and appropriately adjusting the input optical power ratio to satisfy a fixed relationship with modulation efficiency. The primary advantage of this scheme is that out-of-phase IMD3 is introduced using only one 2-Ch PM, thereby resulting in the cancellation of IMD3. Up to 27-dB suppression in IMD3 is experimentally demonstrated—a feature that will be useful in low-distortion analog optical transmission.
We propose a novel in-band optical signal-to-noise ratio (OSNR) monitoring method based on polarization interference. The method realizes a monitoring accuracy of ±0.5 dB within the range of 9–34 dB. Our results indicate that the proposed method is transparent to bitrate and modulation format, as well as independent of polarization mode dispersion and chromatic dispersion.
We propose a configuration of a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM)-visible light communication (VLC) system using orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation and an adaptive Nyquist windowing of the OFDM signal in the receiver. Based on this configuration, we demonstrate a 750-Mb/s WDM-VLC transmission based on RGB light-emitting diode (LED) with a distance of 70 cm. The measured bit error rate (BER) for all channels are under the pre-forward error correction limit of 3.8 \times 10-3. The BER performances of all the channels of the proposed WDM-VLC system show considerable improvement compared with those of the system without Nyquist windowing.
We design custom-shaped modes for a sixfold symmetric photonic quasi-crystal fiber (PQF), an optical fiber with a sixfold symmetric quasi-periodic array of air holes in the cladding region. The supermodes of the PQF are calculated by the finite element method, and the coupling of an in-phase supermode for the quasi-periodic optical fiber is numerically optimized to obtain identical values. The optimization is guaranteed by the selection of appropriate PQF design parameters. The eigenvalue equation associated with a seven-core PQF is derived from a coupled mode equation. We realize mode shaping and provide the far-field distribution mode of PQFs. The results are beneficial for the structural design and uniform distribution of the in-phase supermodes of PQFs.
A stable self-starting mode-locked Nd:YVO4 laser with a Herriott-type multiple-pass cavity (MPC) operating at 1 064 nm is demonstrated. An in-band 880-nm laser diode is used as an end-pump and a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) is used for passive mode locking (ML) and providing pulse durations of 14 ps. At a pump power of 26.4 W, the maximum average output power is as high as 10.5 W at a repetition rate of 22 MHz, which corresponds to a single pulse energy of 0.48 \mu J. Optical-tooptical conversion efficiency is as high as 39.8% at the maximum output power with a slope efficiency of 55.2%.
A compact passively Q-switched Yb:YAG microchip laser is demonstrated. Featuring a semiconductor saturable-absorber mirror (SESAM), the laser yields pulses of 219 ps when the length of the microchip Yb:YAG crystal is 100 μm and the beam quality is M2<1.3. To the best of our knowledge, pulses from the proposed laser are the shortest Q-switching pulses obtained from Yb:YAG microchip lasers currently available.
We demonstrate a high-energy, low-repetition-rate, all-fiber, 1 064-nm Yb-doped fiber laser based on the master oscillator power amplifier structure. Pulse-pumping technology is used to suppress amplified spontaneous emission. A maximum output pulse energy of 5.97 mJ is obtained at 16-ns pulses with an M2 of 2.9.
The experimental performance of beam smoothing by combined one-dimensional (1D) spectral dispersion and lens array (LA) technology is presented, as applied in the ninth beam of SG-II. Using 3\omega spectral dispersion with a bandwidth of 270 GHz and a line dispersion that is 24.9 times the beam's diffraction-limited width decreases the focal spot non-uniformity of 80% energy concentration from 46% to 17%. The multiple-beam interference properties of the LA are theoretically and experimentally validated by spatial power spectral density analysis. Peak–spectra suppression ratios of 20 and 10 dB are achieved in the dispersion and orthogonal directions, respectively.
We demonstrate a high-efficiency, high-power-nanosecond fiber laser-pumped broadband mid-infrared output based on a linearly chirped PPMgLN crystal. By using a linearly polarized pulsed Yb-doped fiber laser as the pump, we experimentally obtain a 1.22-W broadband mid-infrared laser output under pump power of 10.15 W. The 3-dB bandwidths of the idler and signal output are approxiwately 150 and 13 nm, centering at 3.60 and 1.51 μm, respectively. The measured idler spectrum shows a smooth spectral profile.
A resolution-improvement scheme of a phase-shifted analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is presented and experimentally demonstrated. To improve resolution via the scheme, the optical output of each quantization channel is quantized by an electrical ADC with multiple thresholds instead of a comparator. A 9.9-GHz sinusoidal analog signal is sampled and quantized using the proposed enhancement scheme. The effective number of bits of 4.31 and the spur-free dynamic range of 40.89 dB are obtained, thus indicating an improvement of 0.66 bits and 7.47 dB, respectively.
We propose and demonstrate a tunable optical filter based on a tapered silica microcylinder, whose diameter is gradually varied along its longitudinal axis. The tapered microcylinder comprises a slowly varying transition zone fabricated through the fiber drawing technique. Given the tapered diameter of the microcylinder, the resonant wavelengths can be tuned by displacing the tapered microcylinder. This tunable filter exhibits a high Q-factor (~106) and a large tuning range (>1 free spectral range (FSR)).
Taking into account anisotropy, nonparabolicity of the conduction band, and geometrical confinement, we discuss the heavy-hole excitonic states in a strained GaxIn1-xAs/GaAs quantum dot for various Ga alloy contents. The strained quantum dot is considered as a spherical InAs dot surrounded by a GaAs barrier material. The dependence of the effective excitonic g-factor as a function of dot radius and Ga ion content is numerically measured. Interband optical energy with and without the parabolic effect is computed using structural confinement. The interband matrix element for different Ga concentrations is also calculated. The oscillator strength of interband transitions on the dot radius is studied at different Ga concentrations in the GaxIn1-xAs/GaAs quantum dot. Heavy-hole excitonic absorption spectra are recorded for various Ga alloy contents in the GaxIn1-xAs/GaAs quantum dot. Results show that oscillator strength diminishes when dot size decreases because of the dominance of the quantum size effect. Furthermore, exchange enhancement and exchange splitting increase as exciton confinement increases.
AlPO4-SiO2 films doped with Rhodamine 6G (Rh6G) are prepared using the sol-gel dip-coating method. The surface morphology is characterized by atomic force microscopy. The results indicate that the surface morphology of the films is not significantly affected by the amount of dyes loaded. The absorption and excitation spectra indicate low aggregation even at a Rh6G doping concentration of 1.0 \times 10-3 mol/L. Efficient fluorescence with a band centered at 553 nm is observed.
To suppress the fluctuation effect due to laser power instability and terahertz radiation fluctuation, a homomorphic filtering method is proposed to process the terahertz images obtained from a pulsed terahertz raster scanning imaging system. The physical model of homomorphic filtering for terahertz imaging is established. The mathematical expressions are given with the specific physical meaning in accordance with the imaging principle. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the method, a homomorphic filtering experiment based on two raw terahertz images selected from the literature using a continuous-wave (CW) terahertz source is also performed. The effect of the method is compared with those described in the literature, and the advantages of homomorphic filtering are discussed. The pulsed- and CW-terahertz image processing results both show that in addition to suppressing the fluctuation effect, the method can also enhance target imaging.
Commercial iris biometric systems exhibit good performance for near-infrared (NIR) images but poor performance for visible wavelength (VW) data. To address this problem, we propose an iris biometric system for VW data. The system includes localizing iris boundaries that use bimodal thresholding, Euclidean distance transform (EDT), and a circular pixel counting scheme (CPCS). Eyelids are localized using a parabolic pixel counting scheme (PPCS), and eyelashes, light reflections, and skin parts are adaptively detected using image intensity. Features are extracted using the log Gabor filter, and finally, matching is performed using Hamming distance (HD). The experimental results on UBIRIS and CASIA show that the proposed technique outperforms contemporary approaches.
A new sub-aperture overlapping area fusion algorithm based on wavelet transformation is proposed to retain high-frequency components as much as the measurements in the sub-aperture overlapping areas. The principles of sub-aperture stitching are briefly introduced, and the fusion algorithm based on wavelet transformation is demonstrated. The results of the experiment indicate that the new algorithm improves the retention of high-frequency measurement components.
Global change in the dispersive behavior of terahertz (THz) plasmons on metal wires with wide radii ranging from 5 nm to 0.5 mm is systematically investigated. Through rigorous numerical calculations, we find that the dispersion of a metal wire with a radius of 5 nm increases by about 4-6 orders of magnitude compared with the case of a metallic wire with a radius of 0.5 mm. Zero-dispersion points appear when the frequency is lower than 3 THz, and the positions of the zero-dispersion points can shift with the frequency. Finally, we provide an explicit expression that agrees very well with the numerical calculations.
The capability of the parameters derived from waveform data in discriminating objects is assessed and the effect of the relative calibration of full-waveform data in discriminating land-cover classes is evaluated. Firstly, a non-linear least-squares method with the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm is used to fit the return waveforms by a Gaussian function. Gaussian amplitude, standard deviation, and energy are extracted. Secondly, a relative calibration method using the range between the sensor and the target based on a radar equation is applied to calibrate amplitude and energy. The change in transmit pulse energy is also considered in this process. A support vector machine classifier is used to distinguish the study area into non-vegetated area (including roads, buildings, and vacant lots), grassland, needle-leaf forests, and broad-leaf forests. The overall classification accuracy ranges from 79.33% to 87.6%, with the combination of the two groups of the three studied parameters. Calibrated data classification accuracy is improved from 1.20% to 6.44%, thus resulting in better forest type discrimination. The result demonstrates that the parameters extracted from the waveforms can be applied effectively in identifying objects and that relative calibrated data can improve overall classification accuracy.
An in-line Fabry-Perot (FP) refractive index (RI) sensor based on an intrinsic FP cavity and fabricated by the etching and fusion splicing method is proposed. The experimental results demonstrate that the sensor possesses a high resolution of 1508 nm/RIU for the measurement of acetylene gas RI. The temperatureresponse measurement shows that the sensor is insensitive to room temperature variations. The FP RI sensor is suitable for applications in biosensing and environmental monitoring because of its high sensitivity and structural simplicity, thereby making it suitable for low-cost mass production.
Graphene oxide (GO)/Ag nanoparticle (NP) hybrids are obtained by in situ reduction of Ag NPs on GO sheets. In this letter, the influence of the conformation of GO sheets on the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) effect of GO/Ag NPs is investigated by covalently grafting folic acid (FA) molecules onto graphite sheets. SERS measurements are conducted in aqueous solutions with different pH values. Data show that the SERS signals of FA are pH dependent, consistent with the morphological changes of GO sheets.
Orthogonal polynomials over the interior of a unit circle are widely used in aberration theory and in describing ocular wavefront in ophthalmic applications. In optics, Zernike polynomials (ZPs) are commonly applied for the same purpose, and scaling their expansion coefficients to arbitrary aperture sizes is a useful technique to analyze systems with different pupil sizes. By employing the orthogonal Fourier–Mellin polynomials and their properties, a new formula is established based on the same techniques used to develop the scaled pupil sizes. The description by the orthogonal Fourier–Mellin polynomials for the aberration functions is better than that by the ZPs in terms of the wavefront reconstruction errors.
A method on amplitude-weighted array technology is proposed based on an analytical formula in which the radiation amplitudes of array elements are evaluated analytically by a random symmetrical far-field radiation pattern. Using this formula, any desired spatial radiation pattern in the far field could be built by applying the analytical solutions of radiation amplitudes of array elements. To check the validity of this formula as well as the proposed technique, an annular intensity distribution as target far-field pattern is designed, and the respective radiation amplitude of array elements are determined by solving the formula analytically. The available far-field pattern is calculated by applying these solutions and then compared with the target far-field pattern. The theoretical results show the capabilities of the analytical derivation as well as the proposed technique in forming specific radiation patterns.










