 View fulltext
View fulltext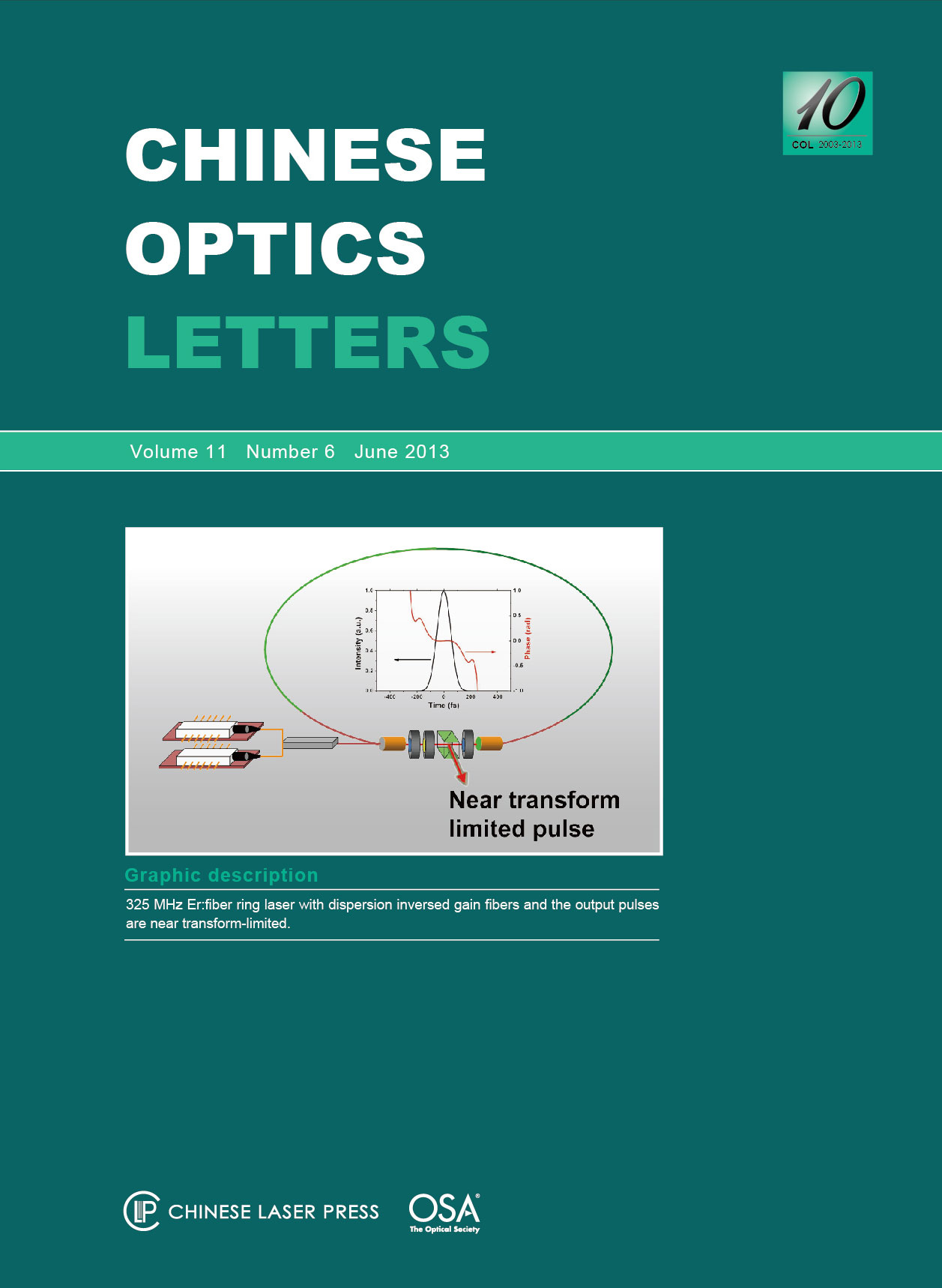
This letter presents a polarimetric interferometer (PI) that can measure the ellipsometric parameter \theta with an accuracy of 0.01o leading to a potential accuracy of 17 pm. The PI is constructed and compared with a commercial heterodyne interferometer (HI). Given its low nonlinearity, the PI is used to measure the residual nonlinearity of a heterodyne interferometric displacement system. A rotating half-wave plate is used to compensate for a part of the nonlinearity error caused by the misalignment of the axis between input polarizing states and beamsplitter.
A conceptual dispersion imaging spectrometer (DIS) is proposed. It consists of a telescope, four prisms, an imaging lens, and a detector. The first prism allows only the first set of wavelengths along the first direction to pass and disperse. The second prism allows only the second set of wavelengths along the second direction, which is perpendicular to the first. The third and fourth prisms are used to compensate for the angular deviations from the optical axes of the first and second prisms, respectively. The proposed DIS disperses the spectra of a target to form an L-shaped dispersion pattern (LDP). The theoretical calculation and numerical simulation of the LDP are presented. The DIS can locate multiple targets based only on data obtained from a single frame. It is suitable for detecting and locating energetic targets in real time.
We investigate InAs/GaAs quantum dot (QD) lasers grown by gas source molecular beam epitaxy with different growth temperatures for InAs dot layers. The same laser structures are grown, but the growth temperatures of InAs dot layers are set as 425 and 500 oC, respectively. Ridge waveguide laser diodes are fabricated, and the characteristics of the QD lasers are systematically studied. The laser diodes with QDs grown at 425 oC show better performance, such as threshold current density, output power, internal quantum efficiency, and characteristic temperature, than those with QDs grown at 500 oC. This finding is ascribed to the higher QD density and more uniform size distribution of QDs achieved at 425 oC.
A compact Er:fiber ring laser operated at a fundamental repetition rate of 325 MHz is reported. Two gain fibers with opposite dispersion are employed to shorten the fiber laser cavity for high repetition rate and soliton-like pulse generation without losing gain and compactness. The spectral bandwidth of the output pulse is 24 nm and the direct pulse duration is 123 fs without extra-cavity compression, which are values near the transform-limited range.
A simplified modal method to explain the resonance phenomenon in guided mode resonance (GMR) gratings with asymmetric coatings is presented. The resonance observed is due to the interaction of two propagation modes inside the grating. The reflectivity spectra and electric field distributions calculated from the simplified modal method are compared using rigorous coupled-wave analysis (RCWA). The influences of high-order evanescent modes on the resonance peak are analyzed. A matrix Fabry-Perot (FP) resonance condition is developed to evaluate the resonance wavelength. An explanation for the resonance phenomenon observed based on the FP resonance phase condition is also proposed and demonstrated. The simplified method provides clear physical insights into GMR gratings that are useful for the analysis of a variety of other resonance gratings.
The design of a two-dimensional (2D) microscanner actuated electrostatically is presented, and a silicon-oninsulator (SOI) micromachining process is utilized to fabricate the sample. The microscanner can oscillate at inherent frequencies of 1146 and 360 Hz around two rotational axes, generating maximum twisting angles of ±10o and ±5.3o under two 10-V square waves, respectively. A monochromatic laser projection system based on Lissajous pattern is demonstrated using the developed microscanner, revealing an image resolution of 168 \times 56 at 20 frames per second.
We demonstrate by finite-difference time-domain simulations that a one-dimensional (1D) photonic crystal (PC) structure between glass substrate and indium tin oxide layer can improve the light extraction efficiency of organic light-emitting diodes. The extraction efficiency depends on the emitters' positions varying laterally in a unit cell of PC. The highest efficiency is obtained when the emitters are under higher refractive index strips. Efficiency decreases when the emitters shift to lower refractive index strips. Simulations for both transverse magnetic and transverse electric modes indicate that when emitters are close to the middle of the higher refractive index strips, the guided wave transmits with less divergence and inhibited reflection because of the guiding effect of higher refractive index strips. A modified method that considers the position effects is proposed to calculate the extraction efficiency more precisely.
We propose a joint nonlinear electrical equalization approach in coherent optical discrete-Fourier-transform spread orthogonal-frequency-division-multiplexing (DFT-spread-OFDM) systems with polarization division multiplexing (PDM). This method is based on an adaptive Volterra series expansion for nonlinear distortions of two orthogonal polarizations. The nonlinear electrical equalization is validated through numerical simulation of 100-Gb/s quadrature phase shift keying and 200-Gb/s 16 quadrature amplitude modulation PDM DFT-spread-OFDM systems.
The optical orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) signal is affected by impairments introduced by electrical filters and optical chromatic dispersion. An enhanced fourth-power algorithm for phase estimation with frequency separation is used to estimate and compensate the phase rotation of OFDM subcarriers. The performance of the proposed phase estimation algorithm is evaluated on a 4-Gb/s OFDM signal at different frequencies. Experimental results using the proposed algorithm show a 1.8-dB received power sensitivity improvement at a bit error rate of 1×10-4 after a 100-km standard single-mode fiber transmission, compared with the conventional technique.
A room division multiplexing (RDM)-based hybrid visible light communication (VLC) network for realizing indoor broadband communication within a multi-room house is presented. The downlink information is transmitted by light-emitting diode lamps, whereas the uplink information is transmitted through WiFi. RDM is introduced to improve the VLC network throughput; in addition, the associated signaling localization and active handoff mechanisms are designed for implementation. The experimental platform demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed hybrid architecture, along with the RDM and active handoff mechanisms.
A crosstalk-free integral imaging display consisting of a display panel and double plano-convex micro-lens array is proposed. The double plano-convex micro-lens array includes two micro-lens arrays, A and B. Micro-lens array A is used to eliminate crosstalk by completely reflecting crosstalk lights. Micro-lens array B, located near micro-lens array A, is used to display three-dimensional images. Computer simulations based on ray-tracing are conducted. Crosstalk-free reconstruction images may be clearly observed from the simulation results.
Silica-based Yb3+-doped glass is prepared by non-chemical vapor deposition. The drawn photonic crystal fiber (PCF) has a strong absorption at 976 nm and emission wavelength of approximately 1 037 nm. The intensity and spectral lineshape of the near infrared (NIR) luminescence of the Yb3+-doped PCF are recorded and discussed in terms of excitation power, excitation wavelength, fiber length, and Yb3+ ion concentration. The emission intensifies as the excitation power and Yb3+ ion concentration increase. The intensity of the shorter wavelength side of the luminescence spectrum decreases as the length of the PCF increases.
We present a theoretical study of surface Tamm states localized at an interface that separates a semi-infinite isotropic left-handed metamaterial (LHM) and one-dimensional photonic crystal made of anisotropic indefinite metamaterial (IMM) (always-cutoff material). We discuss the dispersion properties of the Tamm states in different bandgaps and demonstrate that the cap layer, angular frequency, and arrangement of photonic crystal can provide flexible control for the dispersive properties of the Tamm states.
A Dy3+-doped LiYF4 single crystal capable of generating white light by simultaneous blue and yellow light emission of phosphorescent centers is produced. Chromaticity coordinates and photoluminescence intensity vary with excitation wavelength. Under 350, 365, and 388 nm excitation, the crystal shows excellent white light emission. The most efficient wavelength for white light is 388 nm. The CIE coordinates are x=0.316 and y =0.321, and the color temperature (Tc) is 6 368 K. These results indicate that the studied crystal is a potential candidate for ultraviolet light-excited white light-emitting diodes.
YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb phosphors with a triple-doped system are prepared by conventional solid-state reaction method. The fluorescence emission and excitation spectra are measured and analyzed. The influences of Yb3+ doping concentration on the emission of Yb3+ and Nd3+ in YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb are studied. The fluorescence decay spectra, lifetime, and energy transfer efficiency of Ce3+ in different host materials of YAG-Ce and Yb, and YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb are also compared. Furthermore, the trends of fluorescence decay spectra and the lifetimes of Nd3+ and Yb3+ in YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb with the increase of Yb3+concentration are discussed. Results indicate that YAG-Ce, Nd, and Yb are good candidates for downconverting phosphor, with energy transfer efficiency reaching as high as 82.8%.
Sm3+/Yb3+ co-doped tellurite glasses are prepared by melt-quenching technique. The density of the glasses varies between 4.65 and 4.84 g/cm3. The optical absorption spectra consist of eight bands in the wavelength range of 350–2 000 nm, which correspond to the transitions from ground level 6H5/2 to the various excited states of the Sm3+ ion. Energy band gaps vary in the range of 2.73–2.91 eV, and the Urbach energy ranges from 0.21 to 0.27. Emission spectra exhibit four peaks originating from the 4G5/2 energy level centered at 576, 613, 657, and 718 nm. Quenches in emission bands may be due to the energy transfer from the Sm3+ to Yb3+ ions.
We propose AND, NOR, and XNOR logic gates realized simultaneously for 40-Gb/s networks, in which the realization of NOR and XNOR logic gates using only MgO-doped periodically poled lithium niobate (MgO: PPLN) is reported. In our configuration, we exploit broadband quasi-phase matching (QPM) cascaded second harmonic and difference-frequency generation (cSHG/DFG), cascaded sum-frequency and difference-frequency generation (cSFG/DFG) in one MgO:PPLN, and the narrow band QPM sum-frequency generation (SFG) in another MgO:PPLN. The performance, including the quality-factor (Q-factor) and extinction ratio (ER), of the proposed multifunctional logic device is also simulated.
A rigorous supermode solution method in a strong absorption slab multilayer waveguide is performed. The method is directed toward finding solutions for a sophisticated complex determinant in a complex plane. The rigorous results are applied to design a waveguide photodetector that has a configuration of a vertical directional coupler. Absorption lengths of the supermodes and coupling length of the coupler are calculated based on an effective index approach by using the rigorous results of the strong absorption slab multilayer waveguide to optimize the directional coupling waveguide photodetector.
We describe the application of incoherent broadband cavity-enhanced absorption spectroscopy (IBBCEAS) for in situ measurements of atmospheric NO2 using a blue light-emitting diode. The mirror reflectivity is determined by the transmitted intensity variation through the cavity caused by Rayleigh scattering. Concentrations of atmospheric NO2 (1 to 35 ppbv) during the seven-day period are retrieved from the absorption spectra. The IBBCEAS measurement data are compared with those of a commercial long path differential optical absorption spectroscopy. The linear regression has a correlation coefficient and a slope of 0.983 and 0.975, respectively.
We report a ring cavity passively harmonic mode-locked fiber laser using a newly developed thuliumbismuth co-doped fiber (TBF) as a gain medium in conjunction with a carbon nanotube (CNT)-based saturable absorber. The TBF laser generates a third harmonic mode-locked soliton pulse train with a high repetition rate of 50 MHz and a pulse duration of 1.86 ps. The laser operates at 1 901.6 nm with an average power of 6.6 mW, corresponding to a pulse energy of 0.132 nJ, at a 1 552 nm pump power of 723.3 mW.
The ionization current generated by two-color laser interaction with different gas atoms can produce strong terahertz (THz) emissions. The ionization potential of atoms determines the ionization rate. Thus, THz emission from different atoms varies. Particle-in-cell simulations are conducted to investigate the THz emission from He, Ne, Ar, and N. The THz emissions as a function of the laser field are different because the ionization rate and electron speed depend on the laser field and ionization potential.










