 View fulltext
View fulltext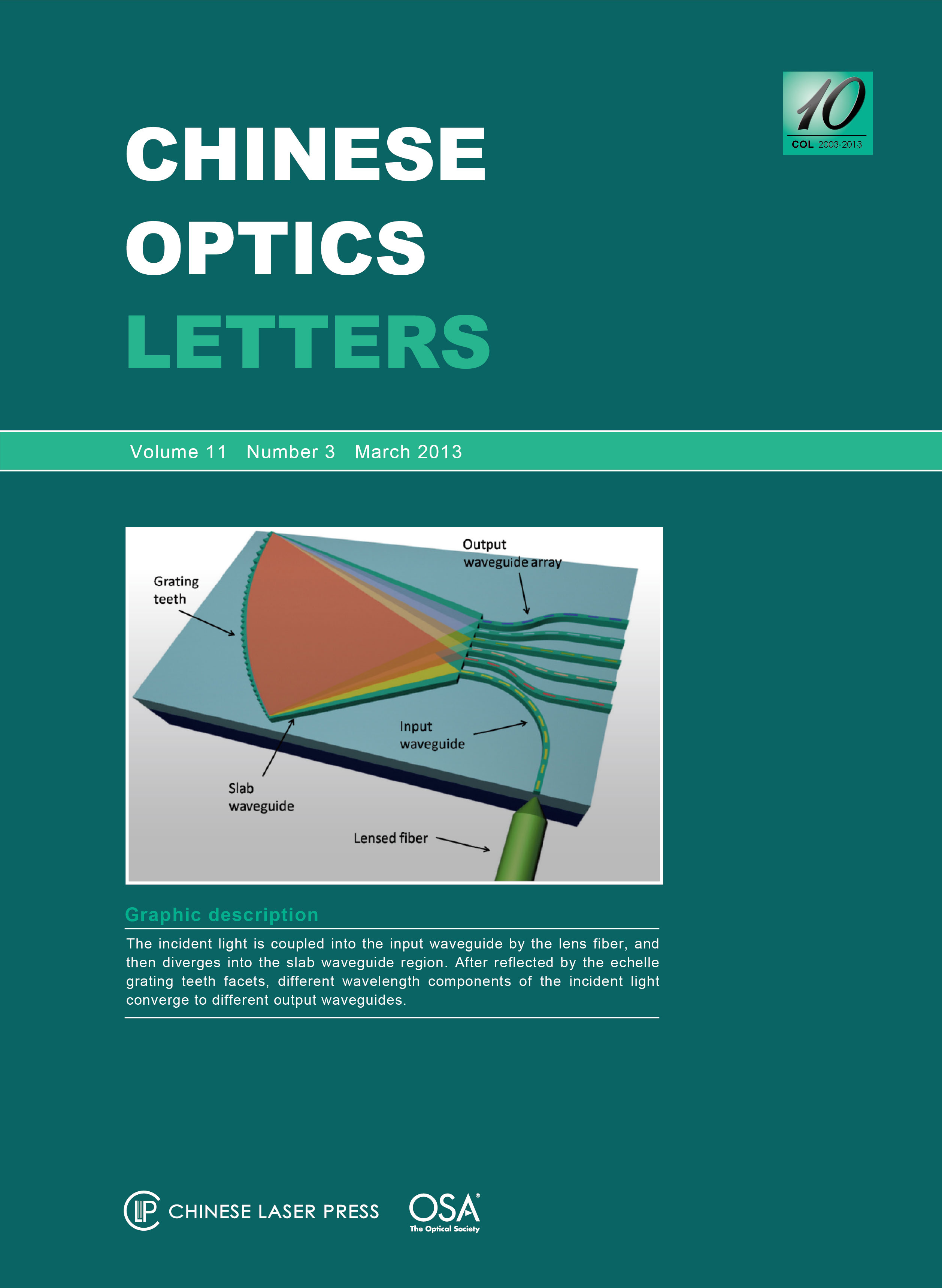
We investigate the multilevel modulation for red-green-blue light emitting diode (RGB LED). A simple approach for extracting soft values from the modulation is proposed. The mapping way from bits to the modulated symbols for the multilevel modulation is also investigated. The modified modulation is obtained through the brute force. Based on the Monte Carlo simulations, the proposed approach and modified modulation are confirmed and better bit error rate (BER) performances are obtained.
We investigate the on-line writing identical fiber Bragg grating (FBG) arrays using the phase mask technique. Given the limitation of laser power, the energy density uniformity and the horizontal width of the writing spot cannot be further optimized. The results show that the FBG arrays obtained in the optimal process (drawing speed of 12 +(-) 0.15 m/min and average tension of 38.2 g) have a central wavelength bandwidth of less than 0.1 nm and an average reflectivity of 0.26%. Thus, the phase mask method is a promising alternative for on-line writing identical FBG arrays.
We propose a new phase-modulation-combination system for the generation of arbitrarily shaped repetition rate pulses. In this system, the pulses from two electro-optic switches are modulated and interferentially combined, thereby improving the shaping resolution and narrowing the pulse width. This method allows the arbitrary tuning of pulse width, repetition rate, and temporal profile in an all-fiber configuration. The system is compatible with and can be easily embedded in other systems to achieve higher pulse energy and higher pulse repetition rate.
This letter proposes a scheme for the format conversion of on-off keying (OOK) signal to quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) and 16-ary quadrature amplitude modulation (16QAM) signals via cross-phase modulation (XPM) in a semiconductor optical amplifier (SOA). Theoretical and experimental analyses of the format conversion scheme are conducted to validate its feasibility. The phase changing is obtained because of the XPM in the SOA. The QPSK and 16QAM signals are converted from the OOK signal. The performance of the 10 Gb/s format conversion system is evaluated and discussed. The receiver sensitivities of the converted QPSK and 16QAM signals after detection are -27.25 and -23.5 dBm, respectively, at a bit error rate (BER) of 10-9.
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a photonic approach to estimate the time-difference-of-arrival (TDOA) and the angle-of-arrival (AOA) of a microwave signal. TDOA and AOA are estimated from the carrier power difference of the two outputs of the Mach-Zehnder modulator (MZM) using only one dual-drive 1 \times 2 MZM. Experimentally, the TDOA of a microwave signal at 3 GHz from 27.78 to 166.67 ps is measured with maximum measurement errors of +(-) 2.24 ps; correspondingly, the AOA from 60o to 85.2o is measured with maximum measurement errors of +(-)0.4o.
The provision of quintuple-play services along wavelength division multiplexed (WDM) long-reach passive optical networks (LR-PONs) employing an ultra-bendable fiber in last-mile distribution is demonstrated experimentally. Particularly, the simultaneous transmission of three 100-GHz-spaced optical channels for the provision of double sideband orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) wireless and wired quintuple-play services to the premises of users located at 75, 85, and 100 km away from the central office is demonstrated. The OFDM-WDM LR-PON is tested considering the last-mile fiber distribution suffering from severe bending conditions without optical dispersion compensation. The experiments are performed for a worst last-mile fiber bending case emulated by considering a Corningr ClearCurver fiber experiencing 20 bends and a bend radius of 7.5 mm. All the OFDM signals received at the premises of users present error vector magnitude (EVM) levels compliant with the EVM thresholds of the corresponding standards. An EVM degradation in the OFDM signals received by each user not exceeding 0.8 dB due to the last-mile distribution fiber is achieved.
An ultra-compact variable optical attenuator based on slow light photonic crystal waveguide with thermooptic effect is demonstrated. Along with power consumption of as low as 30.7 mW, a variable attenuation range of 10 dB is experimentally achieved by shifting the transmission spectrum at about 4.6 nm. The length of the proposed device is only 20 \mu m.
An improved method for stabilizing a frequency-quadrupled 214.5-nm tunable diode laser system is reported. Improvements to the method include a homemade logic circuit and the use of a Fabry-Perot optical spectrum analyzer as a transfer cavity. Lasers locked with this method exhibit megahertz-level frequency stability measured with an optical frequency comb referenced to a cesium atomic standard. The laser can be locked for hours to days, depending on experiment requirements. Being relatively inexpensive, stable, and robust, the control method can be applied to stabilizing essentially all lasers of deep ultraviolet wavelengths.
We study nanometer copper thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering and treated with laser shock processing (LSP). We observe the formation of firstborn twin crystals and some complete twin crystals in the copper thin films. After LSP, scanning electron microscope (SEM) images show obvious plastic deformation of the copper grain on the film surface, dramatically increased grain size, and the appearance of a large number of twin crystals. Moreover, the width of the crystals is a few dozen nanometers, and the cross angle is more than or close to 90o. Many vacancy defects appear during the sliding of atomic plane, which leads to a faulty structure; however, no obvious dislocation is observed. These substructures play a significant role in improving the mechanical performance of nanometer copper thin films.
A wireless terahertz digital transmission link is demonstrated, in which a quantum-cascade laser and a spectrally-matched quantum-well photodetector serve as the emitter and receiver, respectively. An on-off modulation scheme is used. By directly amplitude modulating the laser emitting at 4.13 THz, a 1.0-Mbps pseudorandom signal is transmitted over a distance of 2.2 m.
High-strained InGaAs/InGaAsP multiple quantum wells (MQWs) distributed feedback (DFB) lasers, fabricated using metal organic chemical vapor deposition, are presented at 1.82 \mu m with a high side-mode-suppression ratio of 49.53 dB. The current- and temperature-tuning rates of the DFB mode wavelength are 0.01 nm/mA and 0.13 nm/\circ, respectively. A characteristic temperature of 51 K is also confirmed. The DFB laser demonstrates good performance and can be applied to H2O concentration sensing.
We describe a Q-switched Er:GdVO4 laser resonantly pumped by a MgO-doped periodically poled LiNbO3 optical parametric oscillator (MgO: PPLN OPO) at 1 536 nm. In continuous-wave lasing, the maximum output power is 1.14 Wwith an incident pump power of 4.7 Wand a slope efficiency of 27%. In Q-switched operation, 1.1 mJ of output pulse energy is achieved at 200 Hz. The upper-state lifetime at different pulse repetition frequencies is also calculated.
The domain wall regions in periodically poled MgO-doped LiNbO3 (PPMgLN) crystal are examined by using second harmonic generation (SHG). The results show that the average domain walls that separate the individual domains have a width in the order of about 1 μm, and the walls are neither completely smooth nor uniform along the walls from the imaging of the SHG. It is proposed that the origin of the second harmonic signal in the regions around domain wall is attributed to the non-180o domain walls in the ferroelectric domains.
Stripe motion artifacts caused by phase fluctuation in phase-resolved optical coherence tomography (OCT) result in the quality degradation of the image ofin vivo blood flow of human eye. In order to suppress the stripe motion artifacts, we design a kind of frequency rejection filter aimed at the frequency spectrum characteristics of the image. Blood flow images of human eye acquired by our research group and another group are filtered to show the performance of the proposed method. Experimental results indicate that the stripe motion artifacts in the projection images are rejected significantly with minimal loss of signal information. The proposed filter can also be used in other imaging systems with similar stripe noise.
This letter shows that the human eye fundus tissue has higher reflectivity at the near-infrared (NIR) wavelength, and that some aberrations exist at the pre-optical system from cornea to vitreous. We design a NIR fundus camera with inner focusing, which can be applied to the –10 D to 10 D range of vision and has the advantage of ensuring the stability of image when is focused. Considered as Liou’s eye aberration model, we correct the integrated aberration to ensure a 100 lp/mm resolution when we complete the assembly and calibration of the fundus camera. Kohler illumination is also applied to obtain uniform fundus illumination. Moreover, we put forward a novel method for stray light elimination based on polarization switch, which inhibits ghost image formation near the focal plane when the illumination beam is reflected by the eyepiece surface. The result shows that this method is effective in ensuring an illumination uniformity of 80%, with the advantage of simple structure and easy assembly.
A unified theory to construct exact optical rogue wave solutions of (1+1)-dimensional nonlinear Schrodinger equation with varying coefficients is proposed. The dynamics of the first-order optical rogue waves in nonlinear graded-index waveguide amplifiers exhibiting self-focusing or self-defocusing Kerr nonlinearity are also investigated. Moreover, under the suitable parameter condition, the propagation characteristics of the rogue waves in the nonlinear optical media are discussed. The properties of the optical rogue waves, such as width, amplitude, and position, can be controlled in the nonlinear optical media.
An echelle diffraction grating based high-resolution spectrometer-on-chip on silicon oxynitride (SiON) waveguide platform operated at a wavelength range of 850 nm is demonstrated. The chip comprises 120 output waveguides with 0.25-nm wavelength channel spacing and has a size of only 11 \times 6 (mm). The experimental results show that the insertion loss is –14 dB, the measured adjacent channel crosstalk is less than –25 dB, the 3 dB channel bandwidth is < 0.1 nm, and the channel non-uniformity is 3 dB for 56 channels with a wavelength ranging from 838 to 852 nm.
A systematic series of silicon (Si) wafer with microstructured anti-reflection film is prepared by femtosecond laser pulse. The dependence of the morphology and optical properties of the microstructured Si on the experimental parameters is thoroughly investigated. With the laser pulse duration of 40 fs, central wavelength of 800 nm, repetition rate of 250 kHz, laser pulse power of 300 mW, 250 \mu m/s scanning speed, and 2 \mu m of displacement between the parallel scans in the air, the quasiordered arrays of grain microstructures on the Si wafer up to 800-nm tall and 800-nm diameter at the bottom offered near-unity transmission in the mid-infrared wavelength. An anti-reflection film of approximately 3 \times 3 (mm) is developed on the (211) Si substrate with the optimized parameters, Moreover, up to 30% improvement of the response performance is demonstrated.
High contrast transparent Ramsey fringes are observed using double microwave pulses interaction with the prepared atomic coherent state in a warm 87Rb vapor with mixture buffer gases in a closed cell. The Ramsey fringes are generated by the pulsed technique, a strong coupling light pulse and a weak signal light pulse are applied to prepare the atomic coherent state, followed by the application of double microwave pulses to interact with the atomic coherent state. Afterwards, the light pulses are applied again with weaker intensity and detecting the signal transmission is delected. The central line of the transparent Ramsey fringes has narrow linewidth of 125 Hz and high contrast of 21%. The light shift is dramatically reduced since the interrogating process is not involved the light field, and the cavity pulling effect is negligible due to the low Q requirement, which is promising for building small, compact, and stable atomic clocks.
Accommodation and convergence play critical roles in the natural viewing of three-dimensional (3D) scenes, and these must be accurately matched to avoid visual fatigue. However, conventional stereoscopic head-mounted displays lack the ability to adjust accommodation cues. This is because they only have a single, fixed image plane, but the 3D virtual objects generated by a pair of stereoscopic images are displayed at different depths, either in front or behind the focal plane. Therefore, in order to view objects clearly, the eyes are forced to converge on those objects while maintaining accommodation fixed on the image plane. By employing freeform optical surfaces, we design a lightweight and wearable spatial-multiplexed dual focal-plane head-mounted display. This display can adjust the accommodation cue in accordance with the convergence cue as well as generate the retinal blur cue. The system has great potential applications in both scientific research and commercial market.
Freeform optical surfaces (FOSs) will be the best elements in the design of compact optical systems in the future. However, it is extremely difficult to measure freeform surface with sufficient accuracy, which impedes the development of the freeform surface. The design and fabrication of computer-generated hologram (CGH), which has been successfully applied to the tests for aspheric surfaces, cannot be directly adopted to test FOSs due to their non-rotational asymmetry. A novel ray tracing planning method combined with successively optimizing even and odd power coefficients of phase polynomials in turn is proposed, which can successfully design a non-rotational asymmetry CGH for the tests of FOSs with an F-\theta lens. A new eight-step fabrication process is also presented aiming to solve the problem that the linewidth on the same circle of the CGH for testing freeform surface is not uniform. This problem cannot be solved in the original procedure of CGH fabrication. The test results of the step profiler show that the CGH fabricated in the new procedure meets the requirements.
K-shell X-ray emission from a Cu nanowire target irradiated by an ultraintense femtosecond laser pulse is studied using an elliptically bent quartz crystal and imaging plate. The designed bent crystal spectrometer has better spectral resolution, which is higher than 1 000. The absolute K radiation photon yields are obtained from the experimental results and the Monte-Carlo model. The conversion efficiency of the Cu K line is estimated to be 0.019% from the interaction of 4 J, 50-fs laser pulse irradiated on a Cu nanowire target. The high yield of K shell X-ray has important applications in X-ray emission source.
We experimentally demonstrate the generation of an array of optical bottle beams by employing multiple self-accelerating Airy beams. This kind of optical bottle array is created by superimposing eight Airy beams along a circle, all with inward acceleration directed towards the center. In addition, we demonstrate stable trapping of multiple absorbing glassy carbon particles using the proposedoptical bottle array.










